molecular motors
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what does a motor do?
a motor converts energy into mechanical work or motion
what kind of molecular motors are there in biology + example for each
linear motors → Myosin, cytoskeleton motor proteins
rotational motors → F0F1-ATPase
How can energy be transformed into force per 1 nm?
divide energy by 10-9 m
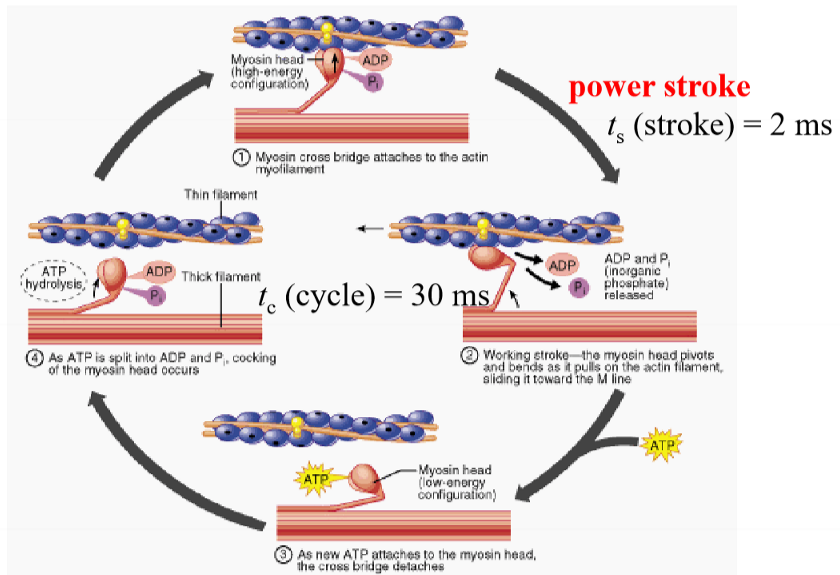
How does ATP hydrolysis lead to motion?
ATP hydrolyse → small conformational change in motor domain → amplified and translated into movement
Why does nature need molecular motors?
transporting vesicles with polymerization of filaments is inefficient
How many filaments would you need to transport a vesicle R = 50 nm, viscousity = 40 pas with a velocity of 1 micrometer/s? Calculation (chemical potential of polymerization ~ 8kT, length per monomer 2.9 nm)

Stoke’s Law

Structure of Myosin II
2 heavy chains
motor domain with ATP binding site
rod-like tail region
2 light chains
wrapped around neck region
similar to calmodium
Steps in mysosin-actin cycle
FRET (definition, and formula for FRET efficiency, Föster radius
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer
if donor and acceptor are close together the energy is transfered and the acceptor releases a fluorophore
the efficiency decreases with the distance r between the acceptor and donor
the föster radius is the radius at which the efficiency = 0.5
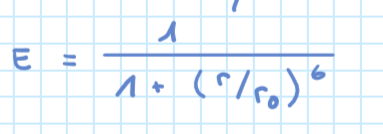
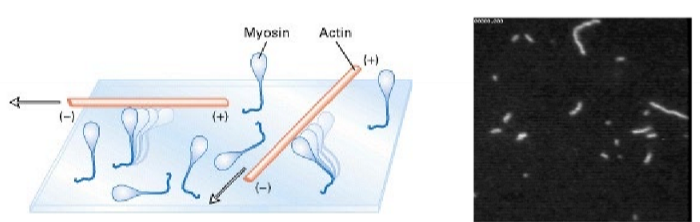
What is another experimental approach to look at the mechanics of actin-myosin?
in vitro motility assay
mysoin is bound to substrate (immobilized) → watch how fluorescence labeled actin filaments are displaced
Processive vs non-processive motors
non-processive motor:
→ motor undergoes only one kick before it detatches (released)
processive motor:
→ motor undergoes many consecutive steps along filament
Formula for processive and non-processive motors

what is an important measure for this? Formula
duty ratio r
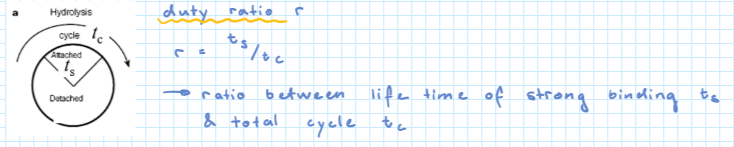
Example for non-processive motor and processive motor
non-processive: myosin II
processive: Kinesin (speed independent from kinesin density)
How does the F0F1-ATPase work?
takes 1/3 rotational steps and converts el.mechanical energy into chemical energy (ATP)
driven by proton gradient
almost 100% energy efficiency