cell the unit of life class 11 NEET (not finished in the making)
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
what is cell
Is the fundamental structural and functional unit of life
Robert Hook
1st person to discover a cell. He observed a dead cell - cells of cork tissue (oak tree) through a hand made microscope.
He wrote and illustrated The Micrographia, published in 1665
the first major work to share a scientist's observations made through a microscope.
Anton on Leeuwonhoek
Discovered the first LIVING cell that are capable of moving, such as bacteria, protozoa, spermatozoa and Erythrocytes (RBCS) under his own designed microscope.
Robert Brown
Discovered the nucleus
Purkinje
In 1839, he coined the term "protoplasma" for the fluid substance of a cell.
Thomas Huxley
protoplasm is the physical basis of life
Cell theory
Explains common characteristics and features in all living cells of organisms
introduced by Mathias Schleiden Theodore Schwann
completed by Rudolf Virchow
Mathias Schleiden (1838)
German BOTANIST, widely studied all plants (anatomy)
all plants are made up of different kinds of plant cells
Theodore Schwann (1839)
British ZOOLOGIST studied different types of animal and animal tissues
discovered cell wall and plasma membrane
Rudolf Virchow
Studied cell division
“omnis-cellula e-cellula”
new cells arise from pre existing cells through cell division
3 Points of cell theory
Cell is the structural and functional unit of all living organisms, they are made up of cells, and their product
New cells come form from pre-existing cells
Activities of an organism due to interactions and coordination functions between constitutive cells
Exceptions for cell theory
Viruses as they do not have unit membrane
considered as neither living or non-living
as they live inside a host but do not live outside host
Porter
Discovered ER
Camille Golgi
Discovered Golgi body
Christian de Duve
Discovered lysosomes
Palace
Discovered ribosomes
Smallest living cells
Mycoplasma (PPLOS)
0.1-0.3um in diameter
do not have a cell wall unlike almost every bacteria
thus antibodies do not effect them
Ostrich egg
largest isolated single cell
14cm
Nerve cell
Longest single cell
0.1-1m in length
RBC (erythrocytes)
immature rbc - round and oval shaped, contains cell organelles
mature rbc - e-nucleated cell, biconcave - gets thinner to be able to move through the bloodstream easier
they do not have any cell organelles to accommodate space for hemoglobin for the binding of oxygen
Leukocytes (WBC)
Amoeboid shape /irregular shaped
different types of wbc in my life processes flashcards
Epithelial cells
columna - long and narrow
increases surface area for absorption
Mesophyll cells
round and oval shape - to accommodate more chloroplast
are chief cells of leaf to perform photosynthesis
Tracheids
Thin and elongated narrow cells
at maturity they loose protoplast
transports water and minerals
Vibrio
bacteria that are comma , shaped
Bacillus
rod shaped
Spirillum
spiral shaped
Which kingdom doesn’t have unicellular organisms
Animalia also known metazoa (according to 5k classification)
Prokaryotic cell
‘Pro’ meaning before and “karyon” meaning nucleus
have simple body organisation (cellular level)
but have great varitaion in size and shape
have great metabollic diversity
show all types of nutrition and behavior
ex) parasites, autotrophs, saprophytes
Cell envelope
3 layers
glycocalyx
cell wall
cell/plasma membrane
Glycocalyx
Outermost layer of the cell envelope in a bacterial cell, also known as biofilm.
viscious and gelatinous
does not depend on whether the bacteria is gram + or gram -
further divided into two types
Slime layer and capsule layer
Slime layer
Loose sheath, unorganized and non uniform in density and thickness
provides protection from loss of water and nutrients
helps to attach bacterial cell to another bacterial cell
Capsule layer
Thickand tough layer made up of polysaccharides (sugar)
hides bacteria from host immune system
ex) Streptococcus pneumonia
R-strain has no capsule, cannot cause pneumonia
S-strain, capsule present, can cause pneumonia that can lead to death
Cell wall
Tough rigid layer, protects the bacteria from bursting/collapsing
made of peptidoglycan/murien layers
non-living permeable layer
Permits entry/exit of water, gases, small molecules and ions
impermeable for large molecules (macromolecules) and undesirable molecules
peptidoglycan layer
polymers of NAM-NAG
NAM - n-acetyl muramic acid
NAG - n-acetyl glucosamine
connected by Beta-1,4 glycosidic bonds - lysosomes break this bond to kill bacteria
Peptidoglycan layers are connected by peptide cross bridges
Peptide cross bridges / peptidoglycan strands of the cell wall
responsible for stitching together layers of peptidoglycan to make the crosslinked meshwork of the cell wall.
these cross-bridges are also further connected with pentaglycin
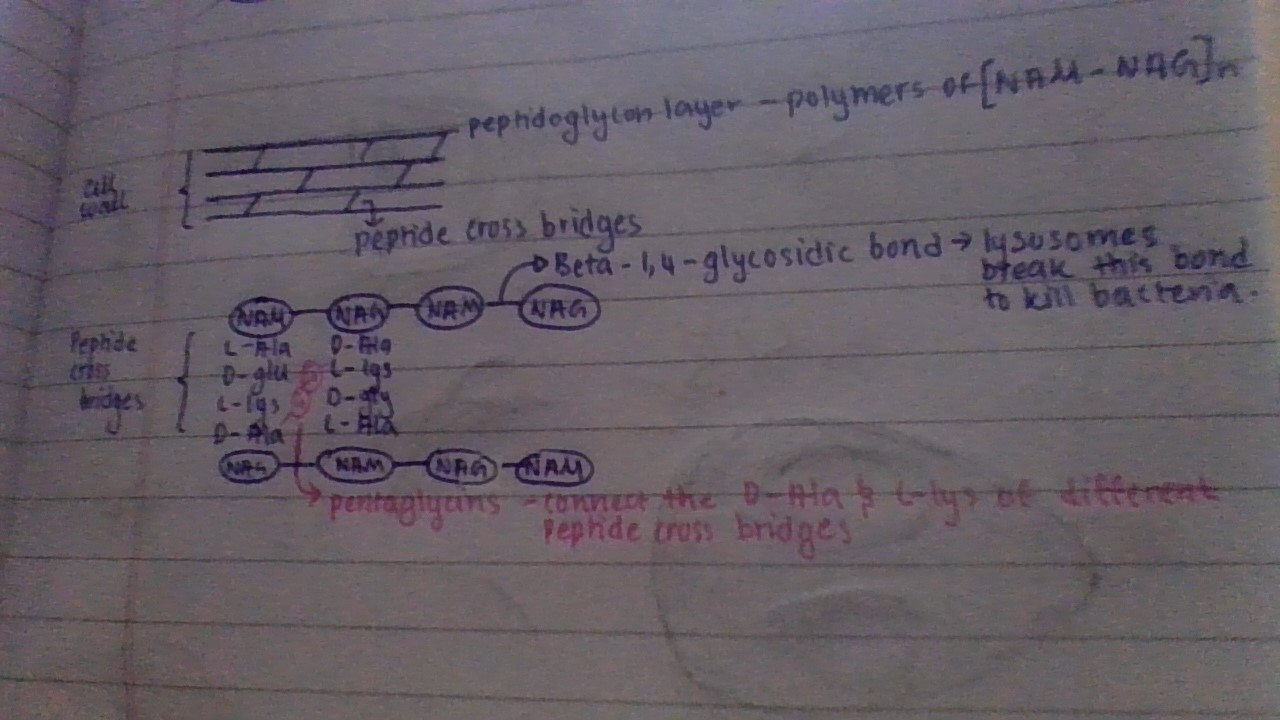
Pentaglycine
connect the D-Ala and L-lys of different cross bridges
antibiotics
inhibits linking of peptidoglycan strands - cell undergoes lysis in the presence of antibiotics.
Lysis
breakdown of a cell caused by damage to its outer membrane
Gram staining
technique which is used to classify bacteria into two groups
gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
developed the gram staining process
Christian Gram
Gram staining process
Fixation of bacteria to glass slide by heating and drying
staining by crystal violet
add iodine - binds to the crystal violets and helps it attach to the bacteria
add alcohol - dissolves lipids, the glycocalyx of both the gram-negative and positive bacteria dissolve, and the outer lipoprotein layer of gram-negative bacteria dissolves.
wash with H2O - gram-positive bacteria are stained purple.
Stain with counter stain safranin (pink in colour) - binds with phospholipid bilayer (cell membrane) of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
End result : Gram-positive bacteria are stained purple and gram-negative bacteria are stained pink
Gram positive bacteria
Get stained crystal violet
the cell wall of gram positive bacteria is thicker (20-80nm) and is made up of peptidoglycan
more easily treated with antibiotics
Since safranin also attaches to the cell membrane in gram-positive bacteria, why doesn't gram-positive bacteria appear pink as well?
Becuase the pink colour of safranin is overshadowed by the deep colour of crystal violet, thus the pink is not shown.
Gram negative bacteria
Get stained pink by safranin
The cell wall of gram positive consists of two layers, a lipoprotein layer and a peptidoglycan layer which is about <10nm
harder to treat with antibiotics
Why does crystal violet dye not attach to gram negative bacteria?
Because the cell wall layer of gram negative bacteria is too thin, thus the violet crystal molecules get washed away.
Plasma membrane
Thin, flexible LIVING layer
phospholipid bilayer
selectively permeable layer
Prokaryotic plasma membrane consists of hopanoids instead of cholesterol
Flagella
Tail like motile structure - gives mobility, allows the bacterium to move towards a favorable environment or move away from a hostile environment.
made with flagellin proteins
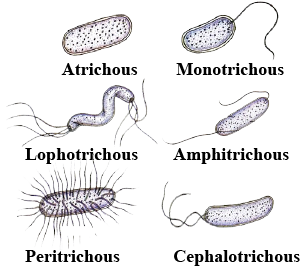
Atrichous bacteria
bacteria that does not have flagellum
Monotrichous bacteria
Has one flagella typically at one pole
Amphitrichous bacteria
Have 2 flagella typically at the poles
Peritrichous bacteria
flagella throughout the bacteria
Lophotrichous bacteria
Many flagella at 2 points of the cell
Cephalotrichous bacteria
Many flagella at 1 point of the cell
images of bacteria with flagellas
Structure of the flagellum of bacteria
Basal body, hook, filament
basal body
The structure of the basal body depends on whether it is a gram positive or gram negative bacteria.
Basal body in gram negative bacteria
consists of the L-ring, P-ring, S-ring, and M-ring all in order from the hook
L-ring is in the lipoprotein layer of the cell wall
P-ring is in the peptidoglycan layer of the cell wall
S-ring and M-ring is in the plasma membrane
all these rings are connected by a rod protein
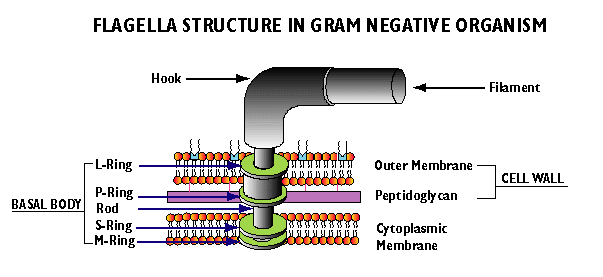
Distal set
consists of the L and P-ring
Proximal set
consists of the S and M-ring
Basal body in gram postive bacteria
They only have one pair of rings , the proximal set consisting of the S and M-ring that are attached to the cell membrane
chemotaxis
Chemical stimuli
Phototaxis
Light stimuli
Pili/Pilus
Elongated tube like structure made up of Pilin protiens
helpfull for conjugation
creates a long hollow tube called a conjugation pilus
helps to exchange plasmids between bacteria
can help in movement (only with specific type of pili)
true pili have only been reported in gram negative bacteria
Conjugation
False sexual reproduction
F+ bacteria
have pili
F stands for fertility factor
F- bacteria
dont have pili
Fimbriae
Filamentous bristle like fibers present on the surface of some bacteria
made up of pilin protein
helps to attach bacteria to rocks in streams or host tissue
No role in motility.
Mesosome
It is a membranous structure formed by the invagination of the plasma membrane - These extensions are in a form of vesicles, tubules and lamellae.
helps in cell wall formation
DNA replication and distribution to daughter cells
aerobic respiration
secretion process
synthesis of the cell membrane
increases surface area of plasma membrane and enzymatic content.
mesosomes are more prominent in gram positive bacteria than gram negative bacteria
Chromatophores (form of mesosomes)
referred to as pigment-containing cells or groups of cells that produce colour.
In some photosynthetic prokaryotes like cyanobacteria the chromatophores are the site of photosynthesis, its a plasma membrane infolding and contains chloroplast.
Ribosomes
Small, think granular structures present freely in the cytoplasm
made of ribonucleo proteins
S stands for svedbergh unit
unit depends on surface area and mass
Mg2+ ions hold the two subunits of a ribosome together
Two types : 70-S and 80-S
Ribozyme
Catalyically active RNA molecule - forms peptide bond between 2 amino acids
all enzymes are proteins except ribozyme
70-S Ribosomes
Made up of 60 different types of proteins, 15-20 nm
Large subunit : 50-S contains 23-S rRNA & 5-S rRNA
Small subunit : 30-S contains 16-S rRNA
*23-S rRNA is the ribozyme
**prokaryotes only have 70-S ribosomes

Polysomes
Only in prokaryotes, made up of many 70-S ribosomes and a mRNA
80-S ribosomes
present in eukaryotic cells only
Contains -
Large sub unit : 60-S containing 28-S rRNA , 5.8-S rRNA & 5-S rRNA
Small sub unit : 40-S containing 18-S rRNA
made up of 80 different types of proteins
Monosome
One 80-S ribosome and a mRNA
Inclusion bodies
Small thick granular structures present in cytoplasm
ribosomes
Storage food granules (consists of two types)
non membranous
Non unit membranous
Non-membranous storage granules
not covered with any membrane
ex) phosphate granules, cynaophycean granules
Non unit membranous storage granules
Covered with a non-unit membrane - protein layer (2-4nm thick)
Ex) sulphur granules, poly-b-hydrooxybutyrate, gas vacuoles
*a unit membrane is a lipid bilayer membrane like cell membrane