Animal Classification
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Movement
All organisms move, with some movements invisible to the human eye, such as flowers moving toward the sun.
Respiration
Organisms exchange gases with the environment, using specialized structures like lungs or the cell membrane.
Sensation
Organisms sense their surroundings and respond, receiving messages through receptors like the eye.
Growth
All organisms grow bigger until they achieve a size and stop growing.
Reproduction
All organisms must reproduce for the species to survive, with some needing two individuals and others just one.
Excretion
All organisms need to remove waste products from their bodies.
Nutrition
Organisms need nutrients from the environment to survive, with plants using photosynthesis and animals requiring an external source of energy.
Dichotomous key
A tool for classifying objects based on physical attributes, providing two contrasting choices that lead to subsequent pairs of choices or directly to the object.
Circular Key
A classification tool read from the inside to the outside to classify animals, with examples provided for clarity.
Tabular Key
A tool used for finding names of things by reading each point and selecting the one that fits the characteristic.
Binomial Nomenclature
The method of naming animals and writing their scientific names correctly.
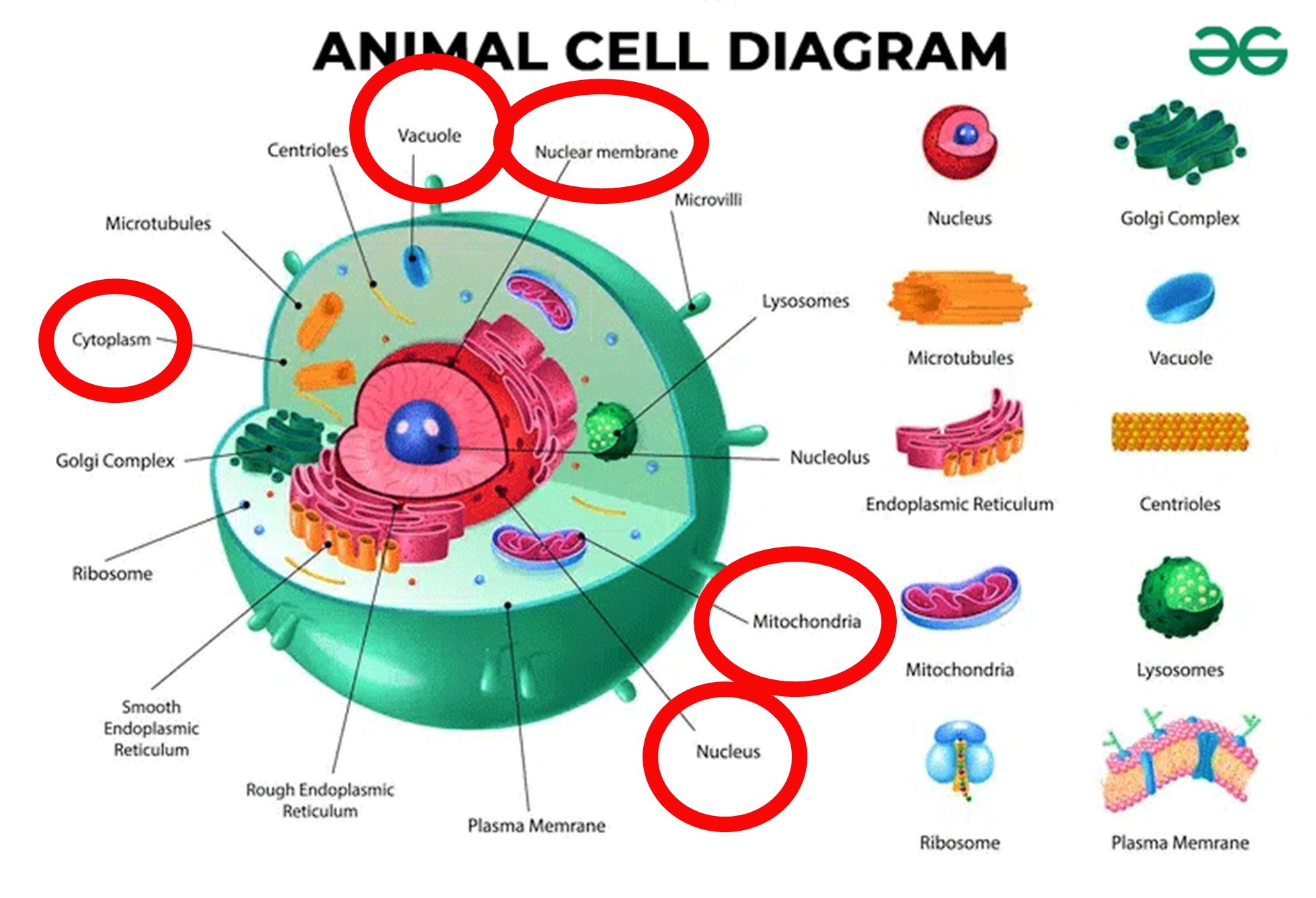
Animal Cell
The basic structure includes a vacuole, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, and nucleus.
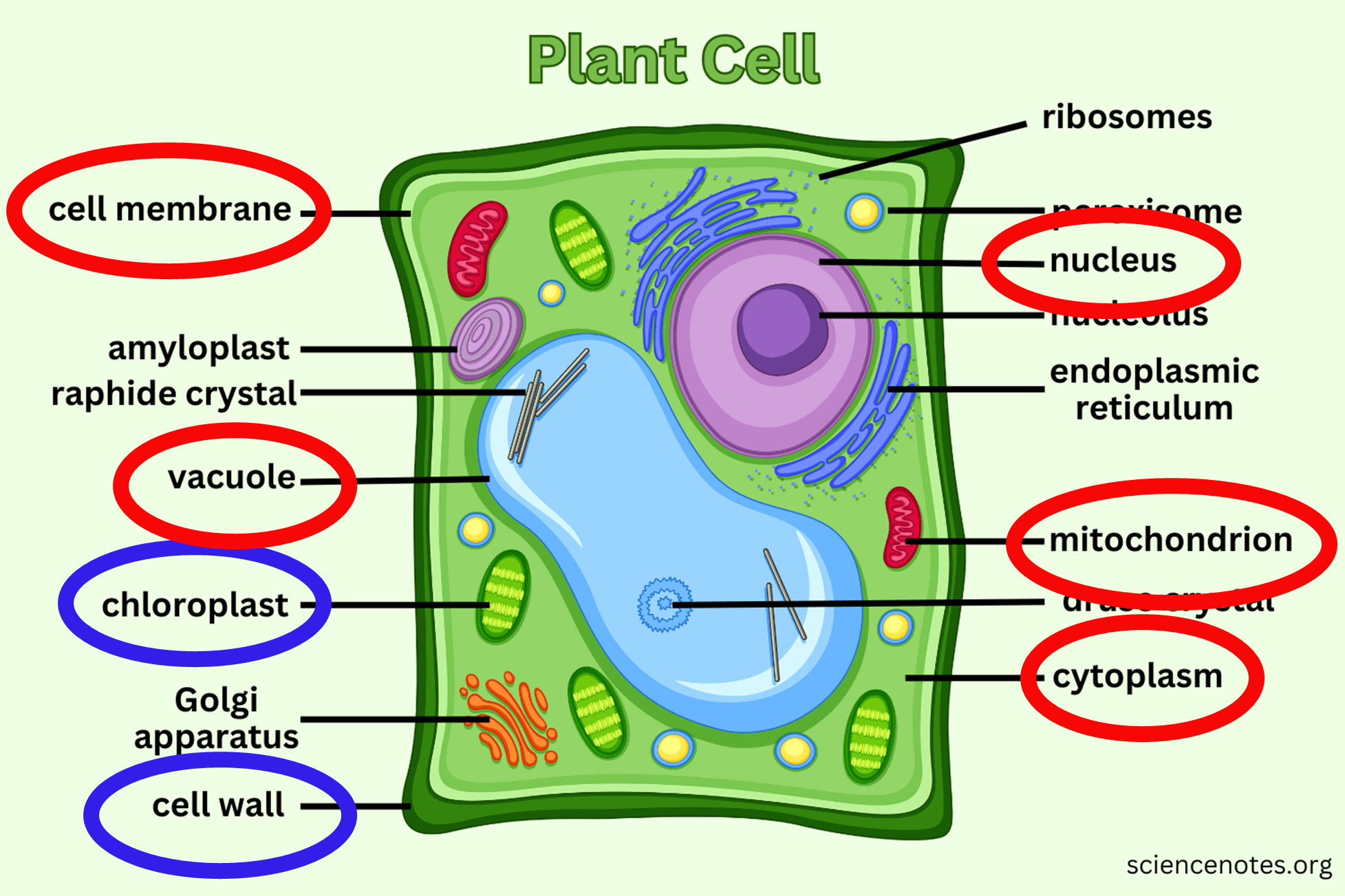
Plant Cell
Contains a chloroplast for photosynthesis and a cell wall for strength and protection, distinguishing it from animal cells.
Vertebrates vs. Invertebrates
Invertebrates lack a backbone, while vertebrates have a spinal column, with differences in skeletal structure and complexity of organ systems.
Phyla of Vertebrates
The main groups are fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals, each with distinct characteristics and examples provided.
Reptiles
Examples - snakes, lizard, tortoise, crocodile. Characteristics include skin with scales, changing body temperature, lungs for breathing, and eggs with membranous or leathery shells laid on land.
Birds
Examples - kookaburra, emu, penguin, cockatoo, parrot. Characteristics include skin with feathers, eggs with hard shell, beak for feeding, and constant body temperature.
Mammals
Examples - wallaby, possum, dog, cat, human. Characteristics include skin with hair or fur, females with mammary glands that secrete milk, and constant body temperature.
Amphibians
Examples - Frog, toad, salamander. Characteristics include soft moist skin without scales, changing body temperature, eggs laid in water without shells, and larvae usually living in water.
Arthropods
Phylum of invertebrate animals with joint limbs, shell, and periodic shedding of the shell. They are scavengers and likely belong to insects, arachnids, or crustaceans.
Classes of Mammals
Placental, monotremes, and marsupials. Mammals are warm-blooded vertebrates that feed milk to their young, have hair or fur, and possess a more complex brain than most animals.
Endotherms
Old term: warm-blooded animals. Endotherms can maintain a constant body temperature without external help, using metabolism to regulate heat production and loss.
Ectotherms
depend on external sources for body heat regulation.
MRS GREN
Movement
Resperation
Sensation
Growth
Reproduction
Excretion
Nutrition
Vacuole
A space or vesicle within the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosed by a membrane and typically containing fluid.
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm: is the gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell. It is composed of water, salts, and various organic molecules.
Cell Membrane
Is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment
Mitchondria
generates most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions.
Nucleus
contains the chromosomes (DNA) and is the brain of the cell
Animal Cell Diagram
Chloroplast
A chloroplast is an organelle within the cells of plants and certain algae that is the site of photosynthesis
Cell wall of plant cell
The cell wall surrounds the plasma membrane of plant cells and provides tensile strength and protection
Diff between animal and plant cell
Plant cell have chloroplast and cell wall, animal cell does not have it.
Plant Cell
Classifying organisims
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Eukaryote
Multiple celled
5 Kingdoms
Animali, Protista, Monera, Plants, Fungi
Prokaryote
Single Celled
Animalia
Eukaryote (Multi celled)
Fungi
A fungus is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the traditional eukaryotic kingdoms
Plants
Eukaryotes, predominantly photosynthetic. Obtain energy from sunlight using chloroplasts
Monera
Prokaryotes. Lack a nucleus
Protista
Mostly single cellled. Have a nuclei