16) Foliated and Non-foliated rocks
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what gives indication of the pressure and temperature the rock was subjected to?
mineral assemblage
definition of metamorphic facies
characterized by particular mineral associations, indicative of pres and temp conditions of the rock in the formation process
mineral characteristics that describe the formation of a meta rock
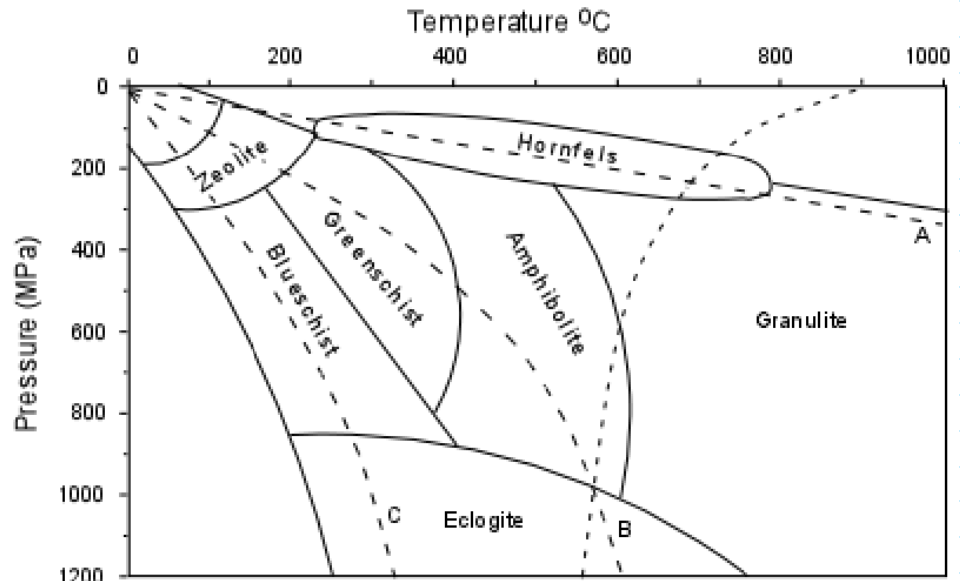
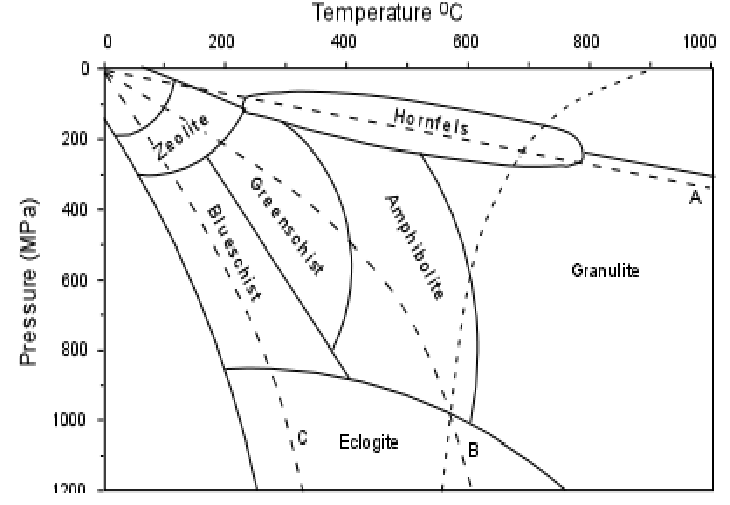
what are the 4 dotted lines on this diagram
geothermal gradients, first is wet partial melting of granite
A: high, contact metamorphism, low P, high T, large change in temp without getting too deep
B: normal, regional/burial meta, high P, high T, compressional tectonics, pushed deep into the earth and heated up
C: low, subduction, high P, low T, not much change in temp, big change in pres, ocean crust is cold and dense, sinking down and cold
explain geothermal gradient
going on the line, you;ll have a certain assemblage of mineral, then as the pres and temp change, the minerals change to be a more stable version at those pres and temp conditions (all in solid state)
fill in the blank
.
characteristics of foliated rocks
platy or elongate and oriented parallel or sub-parallel to each other to make a planar fabric
compressive stress in one direction
metamorphic grade order for shale pelite protolith
slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss, migmatite
slate
protolith: shale
elongated and platy minerals aligned and compressed
breaks smoothy along foliation planes
very fine grained

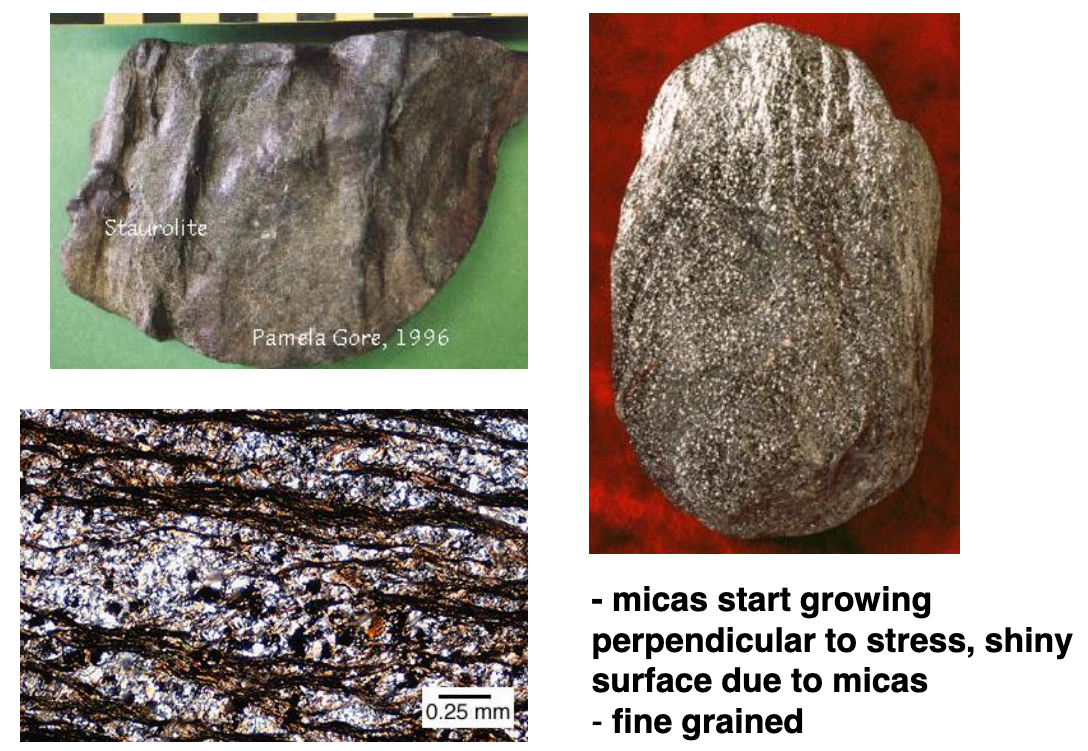
phyllite
micas start growing
perpendicular to stress, shiny surface from micas
fine grained

schist
micas growing parallel
coarser than phyllite, will break along cleavage planes
often folded (higher pressure)

gniess
minerals segregated into light and dark bands
can be tightly folded
coarser than schist, won’t break along foliation planes
recrystallized, more angular than expected
unfoliated textures
granoblastic: grains approx equidimensional, platy and elongate minerals subordinate
hornfelsic: grains irregular and intercluded, elongate at random orientation
cataclasic: clastic textures from breaking or grinding, angular/rounded fragments set in a finer grained, sometimes streaked or layered groundmass
quartzite
non-foliated
recrystallized sandstone
almost pure quartz
no pore space or matrix
marble
non-foliated
recrystallized calcite
any fossils will be recrystallized as well
if impure there can be banding