unit 5 study guide bio
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals?
All gametes from a homozygote will carry the same version of the gene, while a heterozygote's gametes will carry different versions.
When constructing a Punnett square, what do the symbols on the outside of the boxes represent? while those inside the boxes represent
_______.
The symbols on the outside of the boxes represent gametes.
while those inside the boxes represent the progeny (offspring)
True or false? The same phenotype can be produced by more than one genotype.
✅ True - For example, both AA and Aa can result in the same dominant phenotype.
True or false? In diploid organisms, a dominant phenotype will only be expressed if the individual is homozygous dominant for that trait.
✅ False - A dominant phenotype is expressed if at least one dominant allele is present (e.g., both AA and Aa express the dominant trait).
If an organism with the genotype AaBb produces gametes, what proportion of the gametes would be Bb?
✅ None - Gametes carry one allele per gene, not combinations like Bb. Possible gametes would be: AB, Ab, aB, ab — all combinations of one allele from each gene.
Two mice are heterozygous for albinism (Aa). What percentage of their offspring would have an albino phenotype?
✅ 25 - The cross Aa × Aa results in a genotypic ratio of 1 AA : 2 Aa : 1 aa, where only aa shows the albino phenotype.
What is the genotype of the plant whose phenotype appeared once out of every 16 offspring in a 9:3:3:1 ratio?
✅ ttpp - In a dihybrid cross (TtPp × TtPp), the 1 in the 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio represents the double recessive genotype — ttpp, which expresses both recessive traits.
What is an
allele?
an alternative version of a gene
Which of the following statements correctly describes the terms monohybrid cross
and dihybrid cross?
A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters that are being studied, and
A monohybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for only one character being studied.
A diploid animal is dihybrid at the Head shape (H) and Tail length (T) loci. Which of the following gamete genotypes can it produce
Ht
Albinism is a recessive trait where an individual does not produce the pigment melanin. A man and woman both produce melanin, but both have one parent with albinism. What is the probability that their first child will have
albinism?
1/4
Consider pea plants with the genotypes GgTt and ggtt How many types of gametes can be produced by each of these two plants?
four, one
In pea plants, the tall phenotype is dominant to the dwarf phenotype. If a heterozygous pea plant is crossed with a homozygous tall pea plant, what is the probability that the offspring will be dwarf in
size?
0
In cattle, roan coat color (mixed red and white hairs) occurs in the heterozygous
(
C
R
C
W
)
offspring of red
(
C
R
C
R
)
and white
(
C
W
C
W
)
homozygotes. Which of the following crosses would produce offspring in the ratio of 1 red:2 roan:1
white?
roan × roan
You cross a true-breeding, red-flowered snapdragon with a true-breeding, white-flowered one. All of the
F
1
are pink. What does this say about the parental
traits?
red shows incomplete dominance over white
Black fur in mice
(
B)
is dominant to brown fur
(
b
).
Short tails
(
S
)
are dominant to long tails
(
s
).
What fraction of the progeny of crosses
BbSs
×
BBss
will be expected to have black fur and long
tails?
1/2
Radish flowers may be red, purple, or white. A cross between a red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant yields all-purple offspring. The flower color trait in radishes is an example of which of the following inheritance
patterns?
incomplete dominance
In human blood types, Rh positive is a trait that shows simple dominance over Rh negative. The Rh phenotype is recorded by stating "positive" or "negative" after the individuals ABO blood type. A woman who has blood type A positive has a daughter who is type O positive and a son who is type B negative. Which of the following phenotypes is possible for the
father?
B positive
Red-green color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait in humans. Two people with normal color vision have a son with colorblindness. Given this information, the genotypes of the parents are
________.

Cinnabar eye color is an X-linked, recessive characteristic in fruit flies. If a female having cinnabar eyes is crossed with a male having wild-type, red eyes, what percent of the
F
1
males will have cinnabar
eyes?
100%
Which of the following individuals will inherit an X-linked allele from a male parent who carries the
allele?
all of his daughters FDD MSR
The two strands of a DNA double helix are held together by _____ between pairs of nitrogenous bases.
hydrogen bonds
In a DNA double helix an adenine of one strand always pairs with a(n) _____ of the complementary strand, and a guanine of one strand always pairs with a(n) _____ of the complementary
strand.
thymine ... cytosine
In analyzing the number of different bases in a
DNA sample, which result would be consistent with the base-pairing
rules?
A+G=C+T
A sample of double-stranded DNA contains 42% cytosine. Approximately what percent of the nucleotides in this sample will be
thymine?
8%
A sample of double-stranded DNA contains 28% thymine. Approximately what percent of the nucleotides in this sample will be
guanine?
22%
Which of the following combinations of base pairs will be found in a molecule of
DNA?
A + C = G + T
Short segments of newly synthesized DNA are joined into a continuous strand by
_____.
ligase
After DNA replication is completed,
_____.
each new DNA double helix consists of one old DNA strand and one new DNA strand
The action of helicase creates
_____.
replication forks and replication bubbles
Why is the new DNA strand complementary to the 3' to 5' strands assembled in short
segments?
DNA polymerase can assemble DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction
An old DNA strand is used as a _____ for the assembly of a new DNA
strand.
template
What catalyzes DNA
synthesis?
DNA polymerase
Which of the following statements about DNA synthesis is
true?
Primers are short sequences that allow the initiation of DNA synthesis.
Which part of a deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) molecule provides the energy for DNA
synthesis?
Phosphate groups
Which of the following enzymes creates a primer for DNA
polymerase?
Primase
Which of the following statements about Okazaki fragments in
E. coli
is
true?
They are formed on the lagging strand of DNA
Which of the following enzymes is important for relieving the tension in a helix as it unwinds during DNA
synthesis?
Topoisomerase
True or false? Single-stranded DNA molecules are said to be antiparallel when they are lined up next to each other but oriented in opposite
directions
True
The elongation of the leading strand during
DNA synthesis
depends on the action of DNA polymerase.
DNA strands are antiparallel. Which of the following statements defines
"antiparallel"?
A 5' to 3' DNA strand is paired with the 3' to 5' DNA strand.
In E. coli, which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a new DNA strand in the 5'
→ 3' direction?
DNA polymerase III
In bacteria, which of the following proteins is responsible for removing nucleotides from the RNA primer that is used for initiation DNA synthesis?
DNA pol I
What is the RNA primer sequence starting at the underlined T? The sequence of nucleotides below is present at a DNA location where the chain opens to form a replication fork:
3' C C T A G G C
T
G C A A T C C 5'
✓ 5' A C G U U A G G 3'
What is the difference between leading and lagging strands?
✓ The leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the opposite direction.
What is a semiconservative replication template?
✓ One strand of the DNA molecule.
What is the function of the enzyme topoisomerase in DNA
replication
relieving strain in the DNA ahead of the replication fork caused by the untwisting of the double helix
What is the role of DNA ligase in the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA
replication?
It joins Okazaki fragments together.
Which of the following types of molecules help to hold the DNA strands apart while they are being
replicated?
single-strand DNA binding proteins
Semiconservative replication involves a template. Which of the following best describes the template molecule?
one strand of the DNA molecule
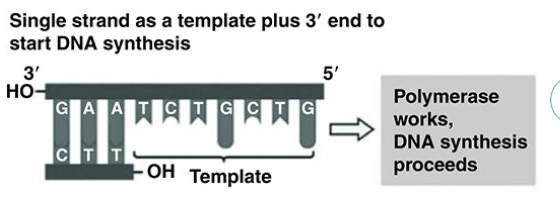
Use the figure to answer the following question.
Referring to the figure, what bases will be added as DNA replication proceeds on the bottom
strand?
5' A, G, A, C, G, A, C 3'
What is the flow of genetic information?
✓ DNA to RNA to protein.
What is the complementary strand of 5'-ATTGCA-3'?
✓ 3'-TAACGT-5'.
What is a codon?
✓ Three nucleotides that correspond to an amino acid.
What is the mRNA codon from the DNA template 5'-AGT-3'?
✓ 3'-UCA-5'.
Identify a
5 Superscript prime Baseline right arrow 3 Superscript prime5′ → 3′
sequence of nucleotides in the
DNADNA
template strand for an
mRNAmRNA
coding for the polypeptide sequence
Phe-Pro-Lys.

What amino acid sequence will be generated based on the following mRNA codon sequence?
5'-AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG-3'
Met-Ser-Ser-Leu-Ser-Leu
Which of the following processes occurs as part of
transcription
RNA is synthesized
What molecule carries DNA information to the ribosome?
✓ mRNA.
What is the pairing of DNA and RNA nucleotides for GTTACG?
✓ GTTACG pairs with CAAUGC.
In which direction does RNA synthesis occur?
✓ 5' → 3'.
What is the function of RNA polymerase?
✓ It unwinds the double helix and adds nucleotides to a growing strand of RNA.
What occurs during the termination of transcription in prokaryotes?
✓ RNA polymerase transcribes through the terminator sequence, causing the polymerase to separate from the DNA and release the transcript.
What is RNA splicing in eukaryotes? After an RNA molecule is transcribed from a eukaryotic gene,
what are removed, and what are spliced together, to produce an mRNA molecule with a continuous coding
sequence?
✓ Introns are removed, and exons are spliced together.
Where does translation occur?
✓ Ribosome.
What nucleic acid is translated to make a protein?
✓ mRNA.
What is an example of post-translational modification?
✓ Phosphorylation.
What is the last step in the initiation of translation?
✓ The large ribosomal subunit joins the complex.
At which site do new aminoacyl tRNAs enter the ribosome during
elongation?
A-site
The initiator tRNA attaches at the ribosome's _____
P-site to start translation.
What are the steps of transcription?
✓ Initiation: RNA polymerase binds to promoter.
✓ Elongation: RNA polymerase adds RNA nucleotides.
✓ Termination: RNA polymerase stops at terminator and releases RNA.
What is the definition of translocation?
✓ The ribosome slides one codon down the mRNA.
True or False: The anticodon on tRNA terminates translation.
✓ False.
What enzyme catalyzes the attachment of an amino acid to
tRNA
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
The tRNA anticodon, GAC, is complementary to the mRNA codon with the sequence
__
CUG
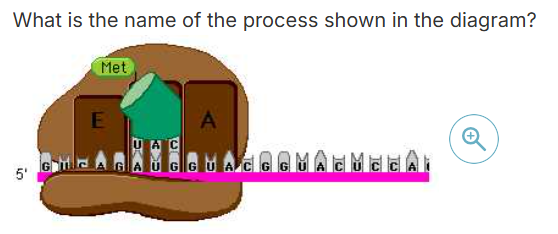
What is the name of the process shown in the
diagram?
initiation (of translation)
Which component is directly involved in
translation?
ribosome
In eukaryotes which of the following is the first step in
translation?
the small subunit of the ribosome recognizes and attaches near the 5' cap of mRNA
What is the function of the release factor during translation in
eukaryotes?
It binds to the stop codon in the A site in place of a tRNA.
What is the tRNA anticodon for the mRNA codon CCG-ACG?
✓ 3'-GGC-5'.
What are the molecules directly involved in translation?
✓ mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA.
What is the first site in the ribosome where codon-anticodon pairing occurs?
✓ A site.
What structure causes translation termination?
✓ A stop codon.
What is the effect of a nonsense mutation?
✓ It introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA.
What is the effect of substituting A for T?
✓ It could cause a silent, missense, or nonsense mutation because those are the types that can be caused by a nucleotide-pair substitution like this one.
Why is frameshift missense more severe than substitution missense?
✓ A substitution missense affects only one codon, but a frameshift missense affects all codons downstream of the frameshift.
Which sequence shows a frameshift mutation?
✓ 5'-AUGCAUACAUCUGGAGUGA-3' (insertion shifts frame).
wild-type | 5'-AUGCAUACAUUGGAGUGA-3' |
mutant | 5'-AUGCAUACAUCUGGAGUGA-3' |
A
missense
Mutation causes a wild-type amino acid to be replaced by a different amino acid.
nonsense
A
mutation causes an early Stop codon to occur.
silent
mutation does not change the wild-type amino acid sequence
What is the effect of deleting AGC from DNA spanning CTA and GCC?
✓ All of the amino acids after the deletion would be altered due to the frameshift.
Suppose that the triplet of nucleotides indicated in bold (AGC) spans two codons, that is, CTA and GCC. If the triplet AGC were deleted from this DNA coding sequence, what effect would it have on the resulting protein?
The two flanking codons would be altered, but the rest of the amino acid sequence would be the same because there would be no frameshift.
What is a frameshift mutation?
✓ A mutation where nucleotides are inserted or deleted, changing the reading frame of codons in mRNA.
Does adding/removing 3 nucleotides cause a frameshift?
✓ No, only if the number of nucleotides inserted or deleted is not a multiple of 3. Substitution only changes one base; frameshift changes the reading frame.