HDFS 2100 Exam 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:07 PM on 11/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
1
New cards
Benefits of Marriage
Healthier lifestyle
Longer life expectancy
More satisfying sex life
More wealth/economic assets
Happier/safer environment for children
Longer life expectancy
More satisfying sex life
More wealth/economic assets
Happier/safer environment for children
2
New cards
Trends in Black Marriage
Higher income
More conflict
Men benefit more than women
More conflict
Men benefit more than women
3
New cards
Components of Successful Marriage
Independent and mature
Love each other and selves
Enjoy being together and apart
Know selves
Established in occupations
Assertiveness
Foundation in friendship
Enlightened self-interest
Love each other and selves
Enjoy being together and apart
Know selves
Established in occupations
Assertiveness
Foundation in friendship
Enlightened self-interest
4
New cards
Assertiveness
Expressing oneself in a direct and positive manner, component of successful marriage.
5
New cards
Law of Enlightened Self-Interest
When you focus on your partner's needs, they tend to focus on yours; component of successful marriage.
6
New cards
Marriage Encounter
Largest marriage education program (1970s).
7
New cards
The Healthy Marriage
Marriage education initiative funded at the federal level (2006).
8
New cards
Stages of Premarital Education
Premarital inventory
Training
Discussion group
Continued enrichment
Training
Discussion group
Continued enrichment
9
New cards
Premarital Inventory
Couples should assess and receive feedback from a trusted source about it.
10
New cards
Driver's 3 Types of Marriage
Validating
Volatile
Conflict-avoiding
Volatile
Conflict-avoiding
11
New cards
Gottman's Divorce Predictors
Emotional disengagement
Four Horsemen
Flooding
Bad memories
Four Horsemen
Flooding
Bad memories
12
New cards
Four Horsemen
Developed by the Gottman Institute; criticism, contempt, defensiveness, and stonewalling.
13
New cards
Family of Origin
Family in which an individual was raised throughout childhood.
14
New cards
Vitalized Couples
Strength in communication, conflict resolution, sexual relationship, and finances.
15
New cards
Harmonious Couples
Strength in roles and the ability to resolve conflicts.
16
New cards
Conventional Couples
Strength in spiritual beliefs, roles, and support networks.
17
New cards
Conflicted Couples
Limited strengths, require growth.
18
New cards
Devitalized Couples
Strength in seeking marital therapy.
19
New cards
Role of Self-Forgiveness
Leads to compassion towards self when mistakes are made and provides more marital satisfaction.
20
New cards
Role of Sacrifice
Expresses overall commitment and leads to mutual trust.
21
New cards
Role of Prayer
Forgiveness and a relationship/communication with God lead to satisfaction (amen).
22
New cards
Federal Healthy Marriage Initiative
Attempt to promote healthy marriage throughout a more diverse population, focusing on minority couples specifically.
23
New cards
Wilcox
Said that married/cohabiting parents have a higher degree of happiness than single parents.
24
New cards
Factors of High Marital/Parenting Quality
More education
More financial resources
Sharing responsibilities
Support from family/friends
Faith
Shared beliefs
Sexual satisfaction
Generosity
More financial resources
Sharing responsibilities
Support from family/friends
Faith
Shared beliefs
Sexual satisfaction
Generosity
25
New cards
Characteristics of Successful Adoption
Exploring: Open/healthy expectations
Demonstrating: Stability, quality, flexibility
Creating: Openly acknowledging/communicating situation
Understanding: Intensity of commitment/possible issues
Demonstrating: Stability, quality, flexibility
Creating: Openly acknowledging/communicating situation
Understanding: Intensity of commitment/possible issues
26
New cards
Child-Free Alternative
Growing in popularity due to raised costs, wage gaps, and expectations placed on women.
27
New cards
Accelerated-Consensus Trajectory
Same political/personal reproduction beliefs.
28
New cards
Mutual-Negotiation Trajectory
No prior discussion of reproductive beliefs, therefore, the decision is being made together.
29
New cards
Unilateral-Persuasion Trajectory
One partner with stronger reproductive beliefs influences the other who does not have an opinion.
30
New cards
Bilateral-Persuasion Trajectory
Both partners have strong, opposing reproductive beliefs.
31
New cards
Parental Support
Amount of affection a parent exhibits.
32
New cards
Parental Control
Amount of flexibility a parent uses in disciplining child.
33
New cards
Democratic Parenting
Clear rules and expectations; self-reliant, cheerful, and high-achieving child.
34
New cards
Authoritarian Parenting
Rigid rules and strict expectations; conflicted, irritable, unstable, and unhappy child.
35
New cards
Permissive Parenting
Allows child's preferences to take over; impulsive, rebellious, and under-achieving child.
36
New cards
Rejecting Style Parenting
Pay little attention to child's needs; immature and psychologically challenged child.
37
New cards
Uninvolved Parenting
Allow child's preferences to prevail as long as parent is uninterrupted; solitary, withdrawn, and under-achieving child.
38
New cards
Behaviorist Theory
Operate from learning theory/reinforcement perspective.
39
New cards
Bidirectional Effects
Both the parents effect the child and the child effects the parents.
40
New cards
Psychodynamic Theory
Places importance on a positive emotional environment.
41
New cards
Organismic Theory
Strongly encourages developmentally appropriate toys and activities.
42
New cards
TLC Discipline Approach
Time; must be spent with child
Limits; if set higher, expectations should be higher too
Care; must be expressed
Limits; if set higher, expectations should be higher too
Care; must be expressed
43
New cards
Positive Discipline
Focuses on teaching responsible behavior; shows honor and love to the child.
44
New cards
Corporal Punishment
Use of physical force as behavioral control; is ineffective and leads to further behavioral problems.
45
New cards
Cascading Circumstance
Stress builds to a point where parents use harsh punishment.
46
New cards
NICHD Study of Early Childcare
Higher quality leads to better outcome
Time spent in childcare matters
Different impacts depending on age
Parents/family are more influential than childcare
Time spent in childcare matters
Different impacts depending on age
Parents/family are more influential than childcare
47
New cards
Coparenting
How parents coordinate and support each other.
48
New cards
Single Mothers
Higher levels of stress, lower income.
49
New cards
Absent Father Phenomenon
Limited initiative of father figure to act as a provider, protector, and caregiver. Leads to poor outcomes.
50
New cards
Middle Age
Age 35-65; between early and late adulthood, overcoming old challenges and facing new ones.
51
New cards
Baby Boom Generation
Post WWII sudden rise in birth and population increase.
52
New cards
Midlife Crisis/Correction
Not necessarily bad but more of a transitional stage, reevaluation of goals, no research to support.
53
New cards
Menopause
Cessation of reproductive ability and menstrual periods for women. Many uncomfortable physiological and emotional symptoms.
54
New cards
Andropause
Male menopause, emotional/physical changes due to a decline in hormone production.
55
New cards
Empty-Nest Syndrome
Feelings of depression when children move out of the house. Can be a positive experience with more free room, time, and finances.
56
New cards
Boomerang Kids
Adult children who return home.
57
New cards
Cluttered Nest
When adult children return home post-grad in order to establish self and save money.
58
New cards
Sandwich Generation
Caretaking of children and aging parents at the same time.
59
New cards
Crisp Retirement
Making a clean break from employment and stopping work entirely.
60
New cards
Blurred Retirement
Repeatedly leaving and returning to work.
61
New cards
Young-Old
65-74 years; retired, in good health, and capable of following new interests.
62
New cards
Old-Old
75-84 years; begin to show age and have more age related issues.
63
New cards
Oldest-Old
85+; commonly characterized by frailty, loneliness, and poverty.
64
New cards
Centenarians
100-109 years old.
65
New cards
Supercentenarians
110+ years old.
66
New cards
Psychological Phenomenon
Mental attitude one has of their past achievements and possibilities of the future.
67
New cards
Biological Reality
Variation among older adults capabilities due to genetics.
68
New cards
Social Phenomenon
How one's social class and standing effects their life expectancy/health.
69
New cards
Family Process
How family members' attitudes lead one to define themselves as they age.
70
New cards
Ageism
Prejudging an older person negatively solely due to their age.
71
New cards
Stress
Daily pressure that is encountered by everyone and how we react to it.
72
New cards
Coping
Actions taken when something is identified as stressful.
73
New cards
Homes & Rahe Social Readjustment Rating
Physical and emotional issues that present throughout major and minor life changes; links stress and physical illness.
74
New cards
Ambiguous Loss
When part of someone becomes absent, but they haven't actually died.
75
New cards
"A" in Family Crisis Model
Stressor event
76
New cards
"B" in Family Crisis Model
Crisis-meeting resources
77
New cards
"C" in Family Crisis Model
Definition given to the event
78
New cards
"X" in Family Crisis Model
Crisis
79
New cards
Family Crisis Model
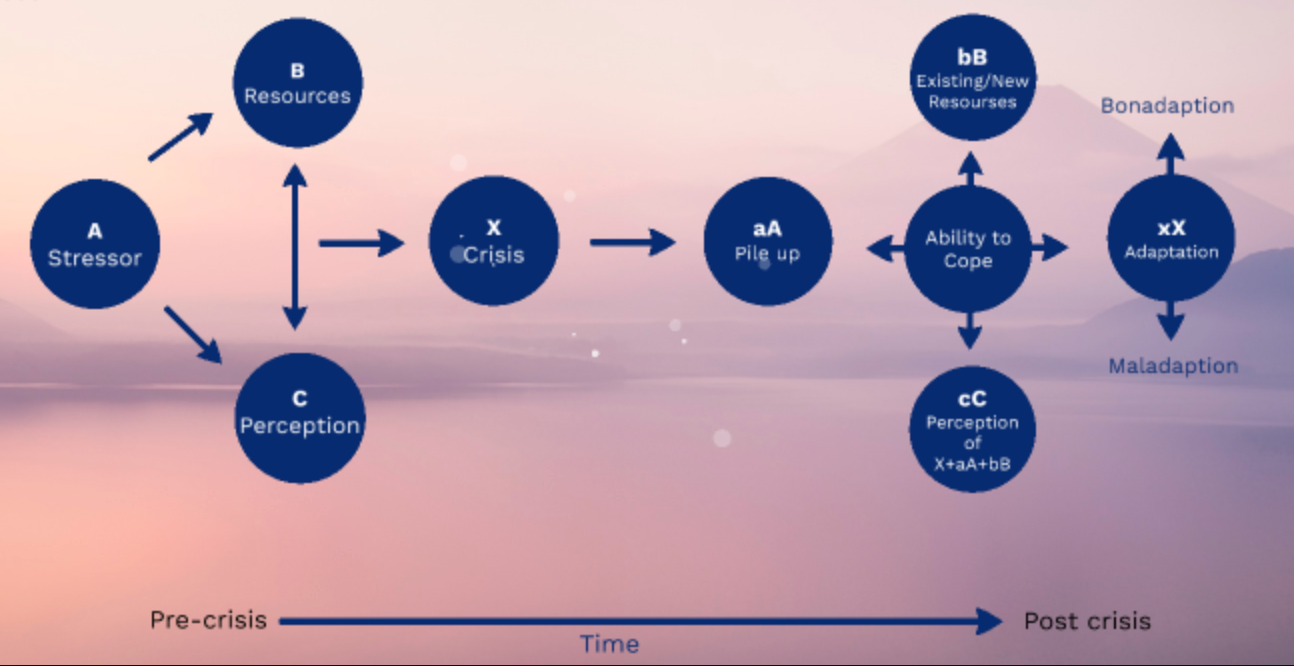
80
New cards
Deployment
Military personnel leaves the family and engages in training/combat.
81
New cards
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Results from traumatic event, disrupts relationships, and is treated with a combination of drugs, therapy, and social networks.
82
New cards
Chinese View of Crisis
That it is dangerous, yet provides opportunity.
83
New cards
Intimate Terrorism
Violence enacted as one partner takes control over another.
84
New cards
Violence Resistance
Response to a partner's abuse.
85
New cards
Situational Couple Violence
When there is a contentious situation within the relationship.
86
New cards
Family Systems Perspective of Abuse
Child from an abusive home has learned how to be a victim and victimize others.
87
New cards
Learned Helplessness Perspective of Abuse
Those who are battered tend to lose sense of confidence.
88
New cards
Catharsis Conflict
Process of venting anger verbally; can lead to physical abuse or loss of control.
89
New cards
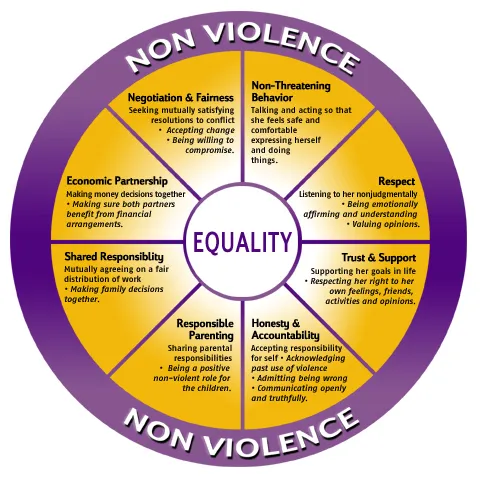
Equality Wheel