Unit 2: Animals: Achieve
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
The hypothalamus functions as a:
control center for sending signals to other parts of the body to change body temperature
All of the above
temperature sensor for sensing changes in body temperature
site for integrating information from temperature sensors in other parts of the body
Option 2:
All of the above
The hypothalamus is an example of a system under negative feedback control that _______ change when an imbalance is detected and _______ change when signals indicate balance has been restored.
Inhibits; inhibits
Initiates; continues initiating
Inhibits; stimulates
Initiates; stop initiating
Option 4:
Initiates; stops initiating
If the body's temperature drops below normal,
shivering will increase the body's temperature towards its set point.
commands from the hypothalamus will stimulate sweating.
shivering will reset the body's set point to a lower temperature.
commands from the hypothalamus will stimulate blood vessels in the skin to dilate.
Option 1:
shivering will increase the body's temperature towards its set point.
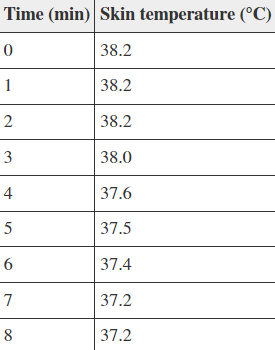
Refer to the table below.
A student runs on a treadmill for 10 minutes. She stops running and begins to measure the temperature of skin on her arm at one-minute intervals for a total of 8 minutes following her run. She records the values in the table shown. What can be inferred from these data?
The student's set point for body temperature is equal to or near 38.2°C.
The student's hypothalamus continued sending the same signals at 7 minutes that it sent at 0 minutes
The student's set point for body temperature is equal to or near 37.2°C.
Both 1 and 3
Option 3:
The student's set point for body temperature is equal to or near 37.2°C.
What did the experiment with homing pigeons in the animation reveal about the cues used by birds to determine direction?
The birds only use cues from Earth’s magnetic field
The birds only use cues from their own internal biological clock
The birds only use cues from the sun’s position in the sky
The birds only use a combination of cues including the sun’s position and cues from an internal clock
Option 4:
The birds only use a combination of cues including the sun’s position and cues from an internal clock
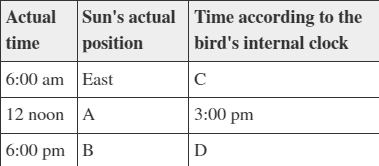
Refer to the table.
Suppose a bird is entrained on a light/dark cycle that is shifted ahead of the normal cycle by 3 hours. Which set of data correctly fills in the blanks in the table?
A=North; B=West; C=9:00 PM; D=9:00 AM
A=South; B=West; C=9:00 AM; D=9:00 PM
A=South; B=North; C=9:00 AM; D=12:00 AM
A=West; B=North; C=9:00 AM; D=12:00 PM
Option 2:
A=South; B=West; C=9:00 AM; D=9:00 PM
A bird trained to seek food at the south food bin of a circular test cage is phase-delayed by 6 hours. The bird is then tested in the cage at 12 noon normal time. What time is it according to the bird’s internal clock, and in which direction will the bird assume the sun is located based on its internal clock?
6:00 PM; east
6:00 AM; west
6:00 AM; east
6:00 PM; west
Option 3:
6:00 AM; east
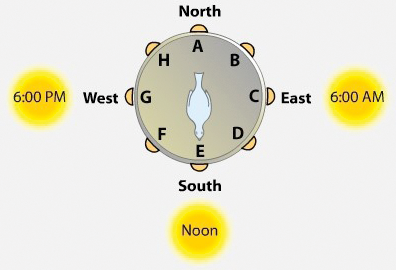
Refer to the figure.
A bird trained to seek food at the south food bin of a circular test cage is phase-delayed by 6 hours. The bird is then tested in the cage at 12 noon. If the bird is using a time-compensated solar compass, from what bin will it seek food?
A
G
C
E
Option 2: G
Which sequence describes the order of structures through which air travels in the bird respiratory system?
Trachea, posterior air sacs, anterior air sacs, bronchus, lung, trachea
Trachea, lung, anterior air sacs, bronchus, posterior air sacs, trachea
Trachea, bronchus, posterior air sacs, lung, anterior air sacs, trachea
Trachea, bronchus, anterior air sacs, lung, posterior air sacs, trachea
Option 3:
Trachea, bronchus, posterior air sacs, lung, anterior air sacs, trachea
How does the respiratory system in birds differ from the mammalian respiratory system?
The respiratory system in birds is unidirectional, whereas the mammalian respiratory system is bidirectional.
The respiratory system in birds allows exchange of fresh air and stale air in one breath, whereas the mammalian system requires two breaths for one exchange
The respiratory system in birds is less efficient than the mammalian respiratory system
The respiratory system in birds uses air sacs in place of the lungs found in the mammalian respiratory system
Option 1:
The respiratory system in birds is unidirectional, whereas the mammalian respiratory system is bidirectional.
What is the function of the air sacs in the respiratory system of birds?
To provide a site for gas exchange between the blood and the surrounding air
To allow mixing of fresh and stale air so that the oxygen/carbon dioxide ratio is optimal
To hold air before and after it passes through the lungs so that it moves in one direction
To provide a storage site for holding fresh air that can be drawn from during periods of high metabolic demand
Option 3:
To hold air before and after it passes through the lungs so that it moves in one direction
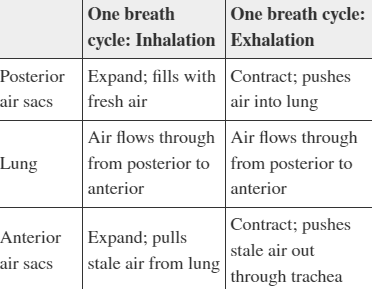
A student creates the table above as a study guide. Evaluate the accuracy of the information shown.
The information is not accurate because air does not flow through the lungs during exhalation
The information is not accurate because air sacs expand during exhalation and contract during inhalation
The information shown is accurate
The information is not accurate because the anterior air sacs push air when they expand and pull air when they contract
Option 3:
The information shown is accurate
The cardiac cycle refers to the rhythmic relaxation (known as _______) and contraction (known as _______) of the _______.
diastole; systole; ventricles
diastole; systole; atria
systole; diastole; ventricles
systole; diastole; atria
Option 1:
diastole; systole; ventricles
During the systole phase of the cardiac cycle, high blood pressure in the ventricles forces the
aortic valve to open
atrioventricular valves to open
atria to contract
pulmonary valve to close
Option 1:
aortic valve to open
How does blood pressure in the aorta change as the heart goes through a cardiac cycle, and why?
Blood pressure in the aorta increases during diastole as the result of muscle contraction in the ventricles
Blood pressure in the aorta increases during systole as the result of increased blood volume in the ventricles
Blood pressure in the aorta increases during diastole as the result of increased blood volume in the ventricles
Blood pressure in the aorta increases during systole as the result of muscle contraction in the ventricles.
Option 4:
Blood pressure in the aorta increases during systole as the result of muscle contraction in the ventricles.
With age, the tissues making up a heart valve can lose flexibility and become stiff and narrowed while retaining their one-way closure properties. Suppose a man's aortic valve is affected by this condition but his ventricles do not change their force of contraction. Which of the following will likely happen?
1. Volume of blood flowing out of the left ventricle during a contraction will increase.
2. Pressure within the left ventricle will increase during the systole phase.
3. Blood will flow more rapidly than normal through the atria and right ventricle.
4. The body's total blood volume will drop.
Option 2:
Pressure within the left ventricle will increase during the systole phase.
Which is the molecular structure that absorbs light in a rod cell?
Transducin
Phosphodiesterase
Retinal
Opsin
Option 3: Retinal
One photon of light can result in thousands of sodium channel closing events within rod cell because
a single photon of light can bounce around many times within a cell to initiate many sodium channel openings
rhodopsin can undergo many cycles of conformational change following one activation event by a single photon
sodium channels are inherently very sensitive structures that can respond to a fraction of the energy of a single photon
each step in the signal transduction pathway activates a much greater number of molecules than the previous step
Option 4:
Each step in the signal transduction pathway activates a much greater number of molecules than the previous step
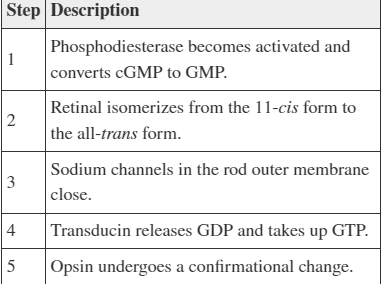
Refer to the table. Place the steps in order of their sequence during signal transduction in a rod cell.
2, 1, 4, 5, 3
2, 5, 4, 1, 3
5, 4, 3, 2, 1
3, 2, 4, 1, 5
Option 2: 2, 5, 4, 1, 3
A study created this study guide. Evaluate the accuracy of the info shown.
The middle column shows information that does not fit with the other two columns
The information is accurate as shown
The left-hand column shows information that does not fit with the other two columns
The right-hand column shows information that does not fit with the other two columns
Option 4:
The right-hand column shows information that does not fit with the other two columns
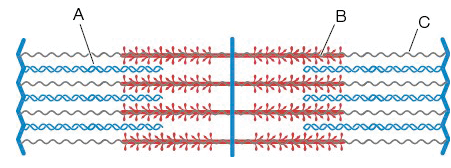
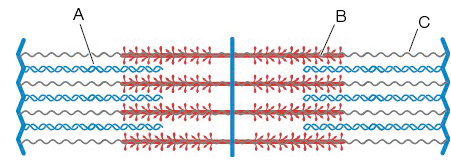
Identify the structures labeled A, B, and C:
A= Myosin filament; B= Actin filament; C= Titin
A=Actin filament; B= Titin; C= Myosin filament
A=Titin; B=Myosin filament; C= Actin filament
A= Actin filament; B=Myosin filament; C= Titin
Option 4:
A= Actin filament; B=Myosin filament; C= Titin
The sliding filament theory states that during muscle contraction
actin and myosin filaments shorten and then lengthen
troponin and tropomyosin slide past each other
actin and myosin filaments change positions relative to each other
filaments in muscle fibers contract, causing sliding motion
Option 3:
actin and myosin filaments change positions relative to each other
Muscle contraction is an energy-dependent process, requiring the hydrolysis of ATP to supply the necessary energy. At what point during a muscle contraction does ATP hydrolysis occur?
Immediately following dissociation of the actin-myosin complex (cross bridge)
During binding of tropomyosin to actin
Immediately following release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
During formation of actin-myosin complex (cross bridge)
Option 1:
Immediately following dissociation of the actin-myosin complex (cross bridge)
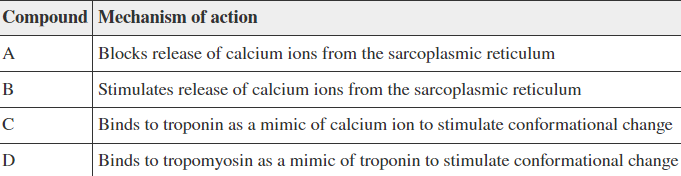
A pharmaceutical company is interested in a drug that can act as a muscle relaxant. Preliminary research has led to the development of four compounds, each have a different mechanism of action in muscle tissue as described in this table. Which compound has potential to be developed as a muscle relaxant?
A
B
C
D
Option 1: A
In women, ovulation occurs at approximately in which day of the 28-day ovarian cycle?
21
1
28
5
14
Option 5: 14
At the end of the ovarian cycle, if a woman is not pregnant, the corpus luteum
grows into a new follicle
attaches to the uterine lining
begins producing progesterone and estrogen
disintegrates
Option 4: disintegrates
What regulates the ovarian and uterine cycles?
Changes in hormone levels
Changes in the uterine lining
External signals from the environment
Primary oocyte development
Option 1:
Changes in hormone levels
A class of pharmaceutical agents taken by women act as contraceptives- agents that prevent pregnancy. Which agent would act as a contraceptive.
An agent that inhibits secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) by the anterior pituitary
An agent that speeds up the menstrual cycle so that events taking place in the first five days are compressed into one day
An agent that slows the release of progesterone by the corpus luteum, causing the menstrual cycle to extend an extra day or two
An agent that increases the amount of proliferation of the uterine lining during the uterine cycle
Option 1:
An agent that inhibits secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) by the anterior pituitary