Kinesthetic Sense, Proprioception, Olfaction
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Smell
occurs when volatile molecules from an object evaporate into the air and reach your nose. at the top of your nasal passages, special neurons with cilia detect odor molecules in the air triggering the perception of smell
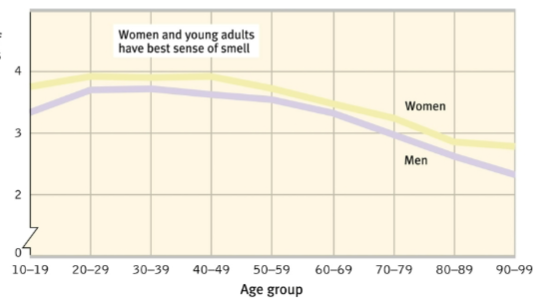
Age + Gender Related to Smelling
ability to identify smell peaks during early adulthood, but steadily declines after that. Women are better detecting odors than men
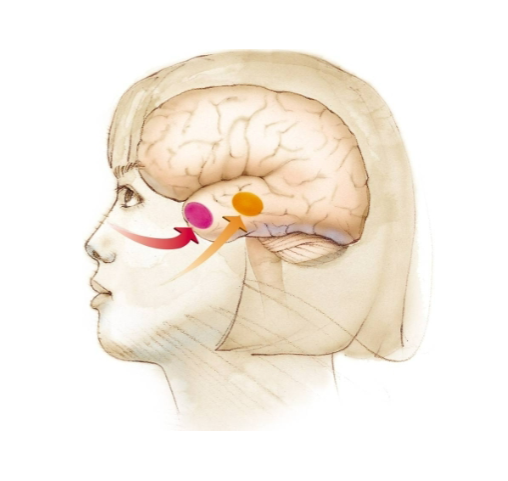
Smell Related to Memories
The brain region for smell (in red) is hard wired into brain regions involved with memory (the limbic system). Strong memories can be related to the sense of smell
Anosmia
Complete loss of the ability to smell
Pheromones
Animals use pheromones for communication, conveying genetic identity and sexual receptivity; these chemical signals are detected by the vomeronasal organ (VNO), which sends information to a specific part of the olfactory bulb for processing
Taste
taste buds located on papillae on the tongue detect flavors. this drives appetite and protects us from harm by making us crave essential nutrients and causing us to avoid bitter + sour taste often linked to poisons
The Four Basic Tastes
Sweet, Salty, Sour, Bitter
Proprioception
the sense of the relative position of neighboring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement (how yk where your nose is) (mainly concerned with postion)
Balance
result of a number of body systems working together (eyes, ears, and proprioception)
Kinetheisa
the sense which helps us detect weight, body position, or relationship between movements in our body parts (mainly concerned with movements)
Audition (sense of hearing) Outer Ear
outer ear captures and concentrates the sounds we hear and channels them into the middle ear. made up of two parts called the pina and the outer ear canal
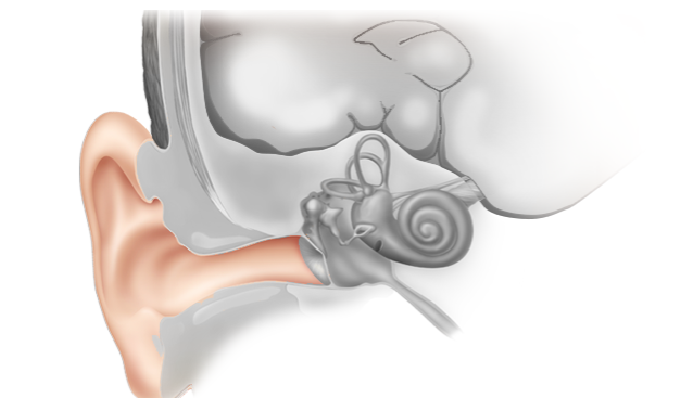
Middle Ear
starts with tympanic membrane (ear drum) which vibrates due to differences in pressure caused by soundwaves. the eardrum is connected to three small interconnected bones called the auditory ossicles that vibrate with the eardrum
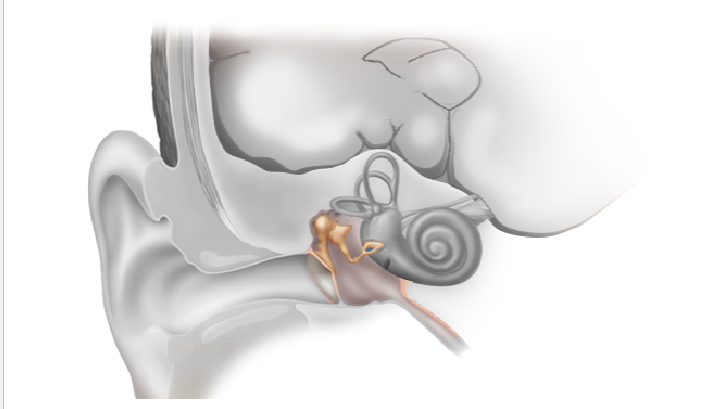
Inner Ear
contains the organs that create our sense of hearing and balance
Epidermis (Sense of Touch)
made of dead skin cells, serves as a protective + waterproof wrap for the underlying skin layers and the rest of the body. contains melanin.
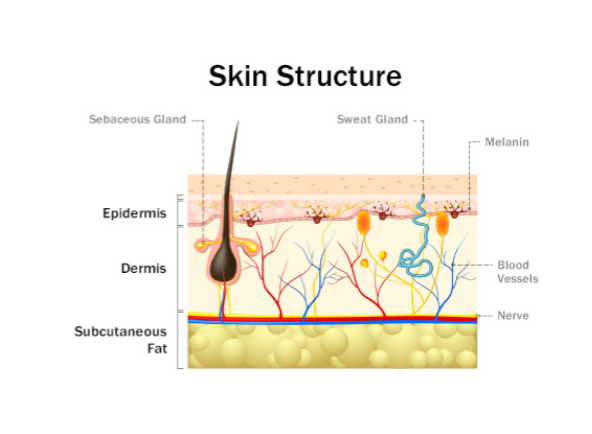
Dermis (Sense of Touch)
contains hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous (oil) glands, blood vessels, nerve endings, and a variety of touch receptors
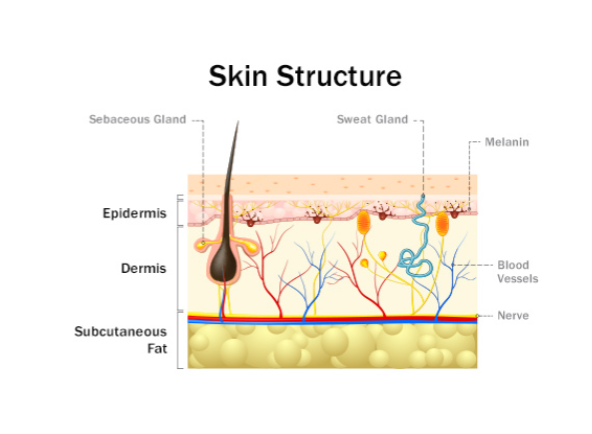
Subcutaneous Tissue
fat acts as an insulator and helps regulate body temp. also acts as a cushion.
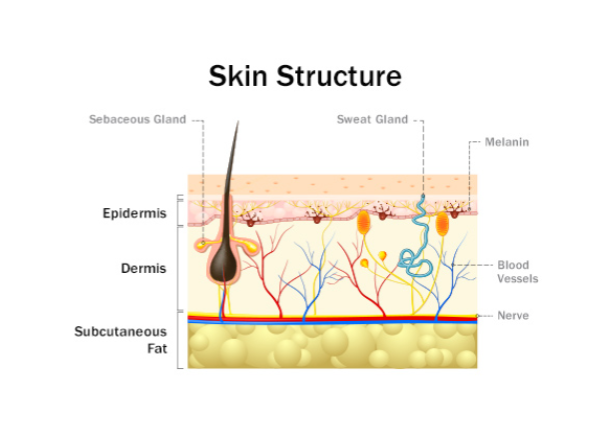
Somatosensory System
made up of nerve endings and touch receptors in the skin, controls our sense of touch and includes four main receptor types: mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, pain receptors, and proprioceptors
Mechanoreceptors
perceive sensations such as pressure, vibrations, and texture
Thermoreceptors
perceive sensations related to the temperature of objects the skin feels. Cold receptors are stimulated from 41° F - 95° F. Heat receptors are stimulated from 86° F - 113°F
Pain Receptors (Nocireceptor)
detect pain that is caused by mechanical stimuli, thermal stimuli, or chemical stimuli. over 3 million through the body
Proprioceptors
sense the position of the different parts of the body in relation to each other and the surrounding environment
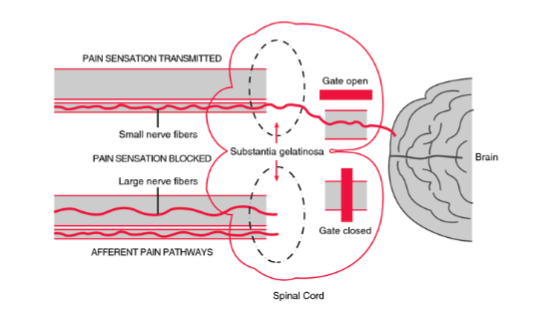
Gate-Control Theory
neurological gateways in our brains decide which brain signals get to come through and which are kept out
Synesthesia
stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to automatic, involuntary experiences in a second sensory or cognitive pathway