particle model, density, and changes of state
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
particles of solids
strong forces hold the particles together in a fixed, regular arrangement
they dont have a lot of energy so they can only vibrate around their fixed positions
their density is the highest in this state as the particles are the closest together
particles of liquids
there are weaker forces of attraction between the particles
they are close together, but can move past each other, forming irregular arrangements
they have more energy than particles in the solid state
they move in random directions at low speeds
they are less dense that solids
particles of gases
almost no forces of attraction between the particles
they have more energy than solid or liquid particles
they are free to move and travel in random directions at high speeds
they have low densities
what is density
a measure of the compactness of a substance. a less dense material has its particles more spread out whilst a denser material has its particles more packed together.
what is the formula for density?
density (kg/m³) = mass (kg) ÷ volume (cm³)
how do you find the density of a solid object?
measure the mass of the object on a scale
to find its volume, submerge it in a eureka can filled with water. put a measuring beaker at the bottom of the spout
the water displaced in the measuring beaker is the volume of the object
divide the mass by the volume to get the density
how do you find the density of a liquid
place a measuring cylinder on a scale and zero the balance
add 10ml of the liquid into the beaker and record the mass
add another 10ml of the liquid into the beaker and record the total volume and mass again
repeat this until all of the liquid is gone
for each measurement, work out the density
find an average with the calculated densities
what is internal energy
internal energy is stored by the particles that make up a system. the particles in a system vibrate or move around. they have energy in their kinetic energy stores. the internal energy of an object is the total energy that its particles have in their kinetic and potential energy stores
what happens when you heat a system
the system transfers energy to its particles, which increases the internal energy. this leads to either a change in temperate or a change in state. the size of the temperature depends on the mass of the substance, the specific heat capacity, and the energy input.
what happens in a change in state and what is it?
a change of state is a physical change instead of a chemical change. he particles have enough energy in their kinetic energy stores to break the bonds holing it together. mass is always conserved in a change of state
what happens when you cool a substance?
the particles loose energy and form bonds, changing the state
what are the changes of state
solid → liquid : melting
liquid → solid : freezing
liquid → gas : boiling/evaporating
gas → liquid : condensing
solid → gas : sublimating
what is specific latent heat
the specific latent heat of a substance is the energy needed to change 1kg of it from 1 state to another without changing its temperature. for cooling, specific latent heat is the energy released by a change in state. it is different for different materials, and for changing between different states
what is the specific latent heat for changing between a solid and a liquid called?
specific latent heat of fusion
what is the specific latent heat for changing between a liquid and a gas called?
specific latent heat of vaporisation
what is the formula for specific latent heat?
energy (J) = mass (kg) × specific latent heat (J/kg)
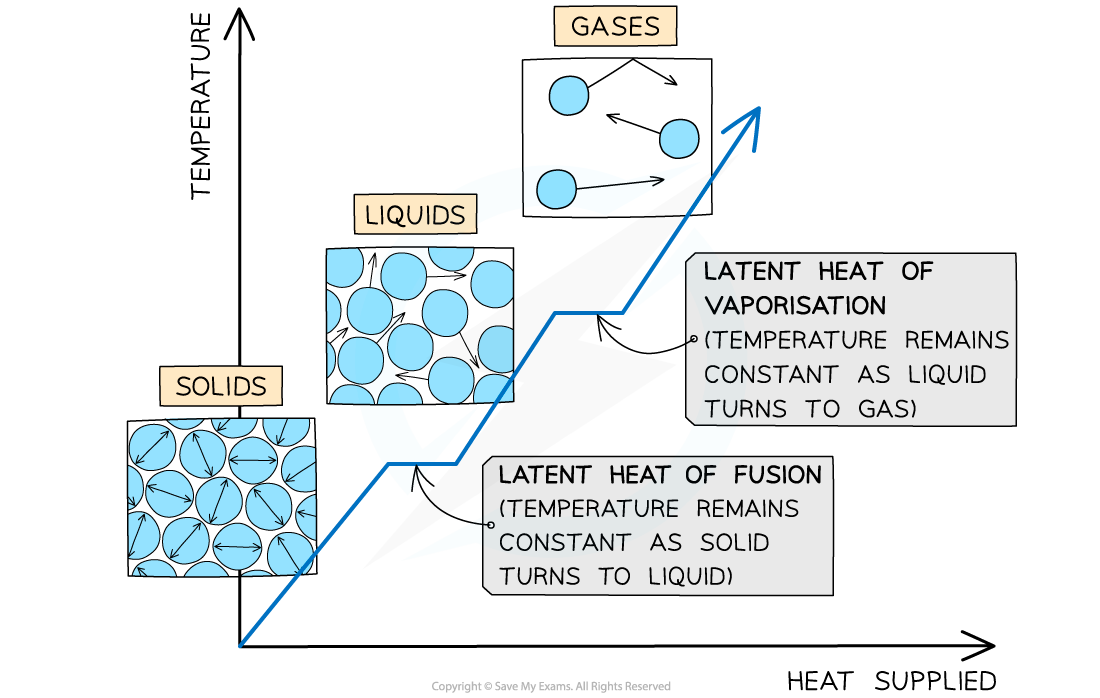
what does the straight line mean?
change in state
how can you measure the specific heat capacity of an object?
using a metal block:
measure the mass of the metal block in kilograms
put the thermometer and immersion heaters into the holes in the block
connect the immersion heater, joulemeter and power supply together
measure the temperature of the metal block and switch on the power supply
wait until the temperature pf the block has gone up by about 10C.
write down the reading on the joulemeter - this is the amount of energy transferred to the immersion heater
keep looking at the thermometer and write down the highest temperature shown by it
calculate the increase of temperature of the block. use this to work out the specific heat capacity of the block