Biology- Lifestyle, health and risk
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topic 1 of A-Level Biology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Explain diffusion
Movement of particles with the concentration gradient (high to low)
Requires no energy
Explain osmosis
Movement of water from a low to high concentration
Across a semi-permeable membrane
Requires no energy
Explain active transport
Movement acros the concentration gradient
Requires energy
Transport in small unicellular organisms
Substances can be moved by diffusion
Across short distances
Diffusion is fast enough to meet the organism’s requirements
Transport in complex multicellular organisms
Rely on mass transport systems
Over long distances
MASS FLOW
Explain open circulatory systems
Blood circulates in large open spaces
Heart pumps blood into cavities surrounding the animal’s organs
Substances diffuse between the blood and cells
When the heart muscle relaxes, blood is drawn from the cavity, back into the heart through small, valved openings along it’s length
Explain closed circulatory systems
Blood is enclosed within tubes (blood vessels)
Generates a higher blood pressure a the blood is being forced along narrow channels instead of flowing into cavities
Blood travels faster and more efficiently
Show the dipole nature of a water molecule
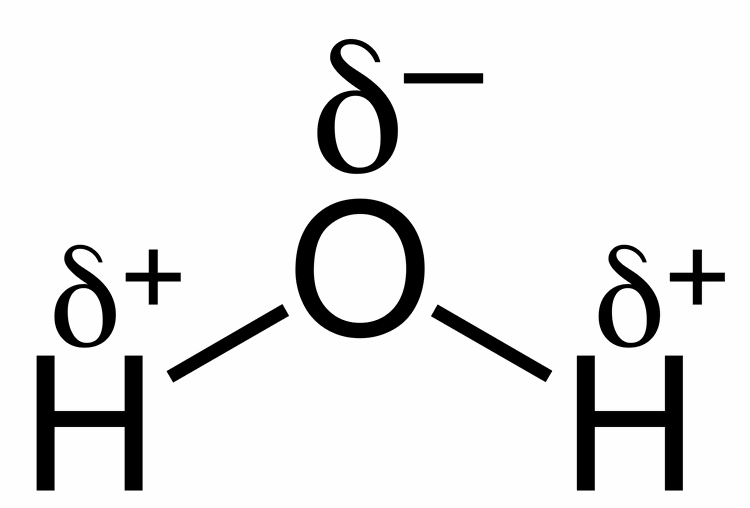
Explain hydrogen bonds
Formed due to the dipole nature
Weak attractions
To evaporate water, they have to break which requires lot of energy because there are lots of them.
Why is water a good habitat?
Takes a lot of energy to change the temperature of the water (due to hydrogen bonds and high shc) so the water temp doesn’t fluctuate much
Explain why water is a good transport medium
A liquid= flows
The molecules form bonds with each other (cohesion) so water flows in a masss flow system
Water form bonds with other molecules (adhesion)
What are the functions of each part of the heart?
Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava.
Right Ventricle: Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries for oxygenation.
Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.
Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body through the aorta.
Differences between dicuspid and tricuspid valves
Dicupid: has two cusps, located on the left side
Tricupid: has three cusps, located on right side
What is the order of which blood travels?
Arteries → arterioles → capillaries → venules → veins
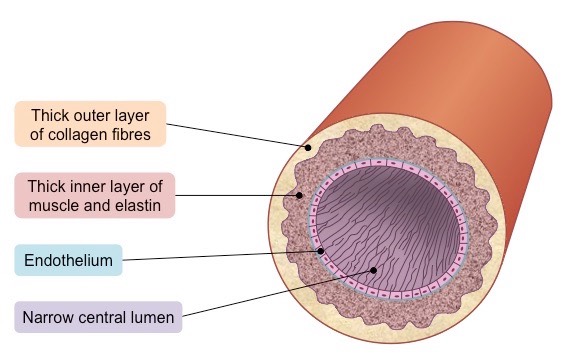
Explain the structure of an artery
Thick walls with more collagen, smooth muscle and elastic fibres
No valves (minus the aorta and pulmonary artery)
High pressure of blood
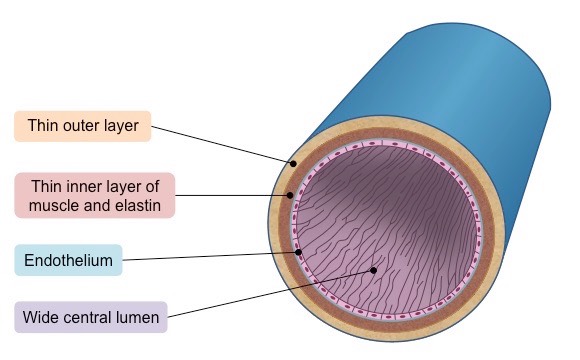
Explain the structure of veins
Thin walls with less collagen and smooth muscle, fewer elastic fibres
Has valves
Low pressure of blood - back to the heart
Explain the structure of capillaries
Walls are one cell thick for diffusion
Low pressure arterioles and venules
Explain what happens during diastole
The heart is relaxed
Elastic recoil causes a low presure in the heart, helping to refill all the chambers with blood
Explain what happens during atrial systole
The atria contrsct, forcing blood into the ventricles
Pressure from the atria force the atrioventricular valves open and blood through.
Explain what happen during ventricular systole
Contraction of the ventricles pushes blood up into the pulmonary artery and aorta
High blood pressure forces the semilunar valves open
Explain the proces of the formation of atherosclerosis
Damage to the endothelium (inner lining of blood vessels)
Cholesterol penetrates the damaged endothelium and accumulates in the arterial wall.
The body responds to the accumulation by sending white blood cells (macrophages) to engulf the LDL, leading to inflammation.
Dead cells, cholesterol, and other substances form a fatty streak, which evolves into a fibrous plaque.
The plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow.
What are the four things needed for blood clotting?
Platelet, Clotting factors, Fibrin, Other cells
What is the process of how your body forms a clot?
Damaged blood vessel → platelets trapped → thromboplastin → prothrombin → thrombin → fibrogen → fibrin → mesh → platelets trapped → clot is formed
What is the process of the whole formation of atheroclerosis to a blood clot forming?
Artery wall damaged → inflammatory response → large white blood cells enter the wall → cholestrol accumulates → atheroma forms → calcium salts and fibrous tissue accumulate → hard plaque forms → wall elasticity reduced → artery narrows → raising blood pressure → atherosclerosis → platerlets in contact with damaged artery wall → platelets become sticky → platelet plug forms → thromboplasitin released from platelets/damaged tissues → cascade of chemical changes → prothrombin → thrombin → fibrogen → fibrin → mesh → platelets trapped → clot is formed
Define Risk
The probability of occurence of some unwanted effect or outcome.
Define Hazard
Anything that can potentially cause harm
Define Probablility
A precise mathmatical meaning and can be calculated to give a numerical value for the risk.
Whats the difference between causation and correlation
Causation refers to a relationship where one event directly affects another, while correlation is when one variable changes, the other variable tends to change as well, but without a direct cause-and-effect relationship.
Whats the Spearmans rank calculation
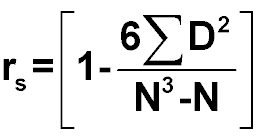
Explain a cohort risk study
A cohort risk study is a type of observational study where a group of individuals with shared characteristics is followed over time to assess their health outcomes and the effects of specific risk factors. Takes a very long time and can be expensive.
Explain case-control studies
A case-control study is a type of observational study that compares individuals with a specific condition or outcome (cases) to those without it (controls) to identify potential risk factors or causes.
What makes a good study?
A representative sample, valid results, reliable results, sample size and controlling variables
Standard deviation equation
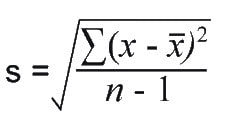
What does a large or small standard deviation tell us?
A large standard deviation= values are far from the mean, low reliability
A small standard devaition= value are close to the mean, high reliability.
Ethical issues that arise using organisms in experiments
Against= animals cant give verbal or informed consent
For= animals can make their decisions by physically resisting what they’re being tested for
Define blood pressure
the measure of hydrostatic force of the blood against the walls of the blood vessel
High blood pressure can be affected by…
tissue fluid and oedema
high salt diet
loss of elasticity in capillary walls
high adrenaline levels
large surface area of blood vessels
Explain how oedema forms/what it is
More excess fluid builds up in tissues which caues swelling. It can be a sign of high blood pressure. Tissue fluid is formed at the arterial end of a capillary where the blood is under pressure. This forces fluid and small molecules into the gaps in the cells of the capillary wall into the inetermolecular pace, forming tissue fluid.
What is a monosaccharide and what does it look like?
A single sugar unit
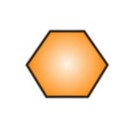
What is a disaccaride and what does it look like?
Two single sugar units combined
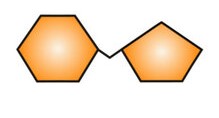
What is a polysaccharide and what does it look like?
A long straight or branched chain of sugar units
What does alpha glucose look like?
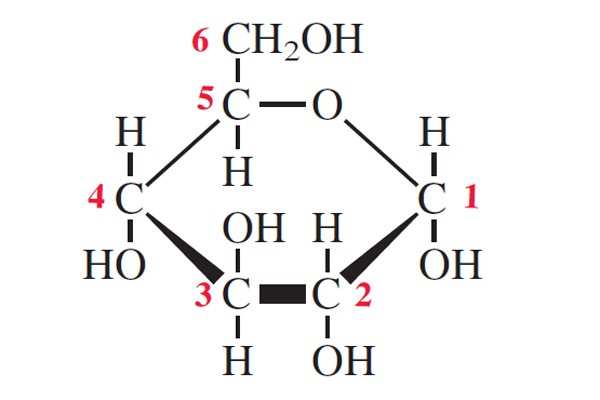
What is starch made of?
Amylose and Amylopectin which are both polymer of alpha glucose
Explain Amylose
Its an unbranched chain with 1,4 glycosidic bonds and is a polymer of alpha glucose.
Explain Amylopectin
Its a branched chain with 1,6 and 1,4 bonds. Its a polymer of alpha glucose.
Explain Glycogen
glucose chain joined by 1,6 and 1,4 glycosidic bonds which allows it to have branches
its stored in the liver and mucus
Whys are glycogen and starch goofd for storage?
the glycosidic bonds can be hydrolised to release glucose molecules
the glucose can be used for respiration to release enegry
glycogen and starch are branched so there lots of terminal end to releae glucose.
Explain saturated fats
said to contain the max amount of hydrogen atoms
the hydrogen chian is long and straight
there are no carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chains
they can pack together closely
the intermolecular bonds between triglycerides result in fats that are solid at room temperature
Explain unsaturated fats
they have one double bond between two carbon atoms in each fatty acid chain
larger number of double bonds that cause a kink in the hydrocarbeon chain, preventing them from packing too close
can be made solid at room temp by adding hydrogen
Give a brief overview of blood cholesterol
25% form food and 75% from the liver
vital component of cell membranes
make up some growth hormones and steroid sex hormones
used to make bile salts
Explain what LDLs (low-density lipoproteins) are
Transport cholesterol through the bloodstream.
Known as "bad cholesterol" because high levels can lead to artery-clogging plaques.
LDLs deliver cholesterol to cells for essential functions like building cell membranes.
Excess LDL result in high blood cholesterol and may be deposited in artery walls forming atheromas
Explain what HDLs (high-density lipoproteins) are
They have a higher level of protein and less cholesterol, reulting in higher density
Made when triglycerides combine with cholesterol and protein
They transport cholesterol
When broken down they lower blood cholesterol
How does smoking increase risk of CHD
Carbon monoxide binds to haemoglobin instead of oxygen resulting in an increased heart rate
Nicotine stimulate adrenaline and cause arteries to restrict, raiing blood pressure
Numerous chemical damage the artery walls and trigger atherosclerosis
How does high blood pressure increase risk of CHD
Increases the risk of athersclerosis which increase the risk of CHD
How does inactivity increase risk of CHD
Raises blood pressure and lowers HDL
Higher chance of developing type 2 diabetes
Lower chance of surviving a heart attack or stroke
How does salt increase risk of CHD
High levels cause the kidney to retain water
High fluid levels in blood causes elevated blood pressure and cardiovascular disease risks
How does stress increase risk of CHD
Sometimes linked to poor stress management
High stress raises adreanaline which causes arteries and arteriole to constict and lead to high blood pressure
How does alcohol increase risk of CHD
Heavy drinking raises blood pressure, contributes to obesity and can cause irregular heartbeats
Excess alcohol can result in tissue damage, damage to the liver, brain and heart
How does obesity increase risk of CHD
Increases risk of coronary heart disease and strokes
Raises blood pressure, accelerates blood lipids
More excess fat causes greater risk of CHD