Serology Exam 1
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
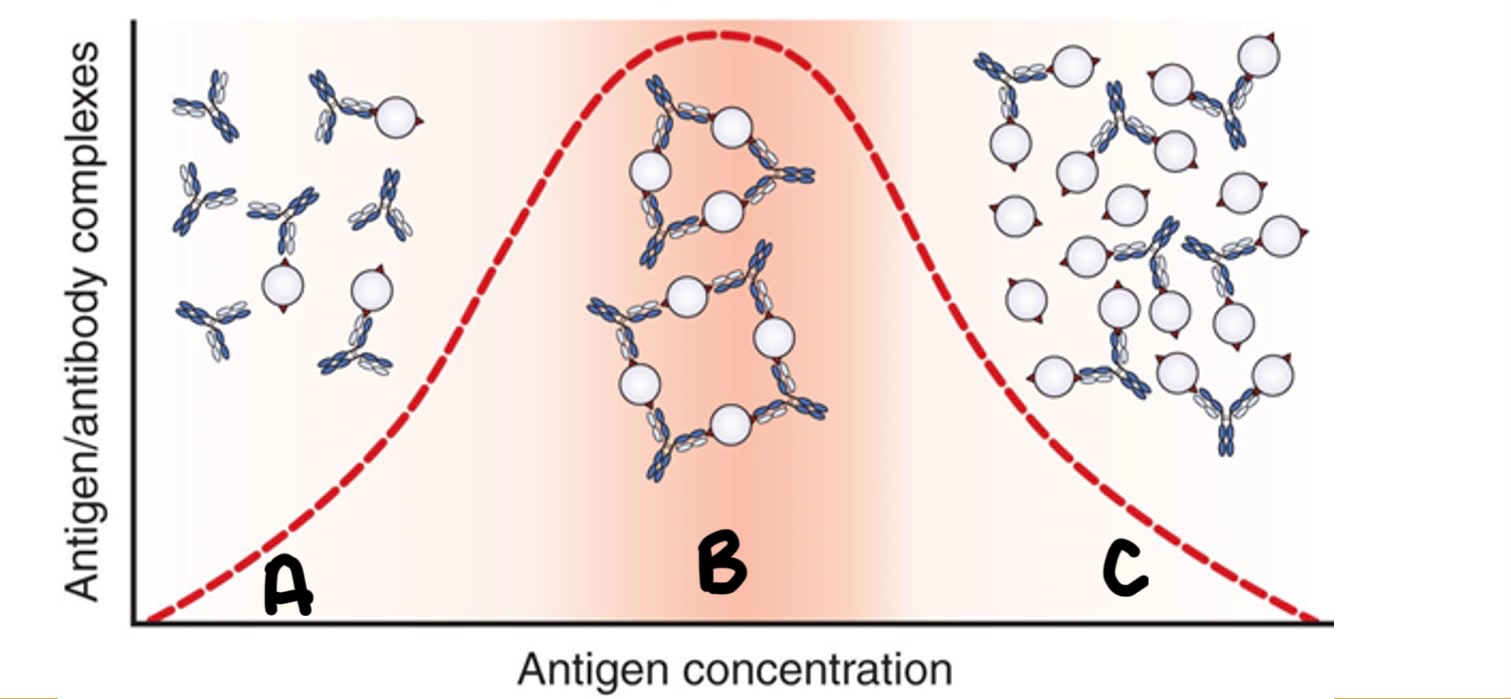
Label the immune response curve
A-Prozone B-Zone of Equivalence C-Postzone
Zone of equivalence
Lattice formation: Ag-Ab together in approximately equal proportions
Prozone
Antibody excess. It appears false-negative
Postpone
Antigen excess
Lag phase
Time period between the encounter with the antigen and the production of a detectable antibody
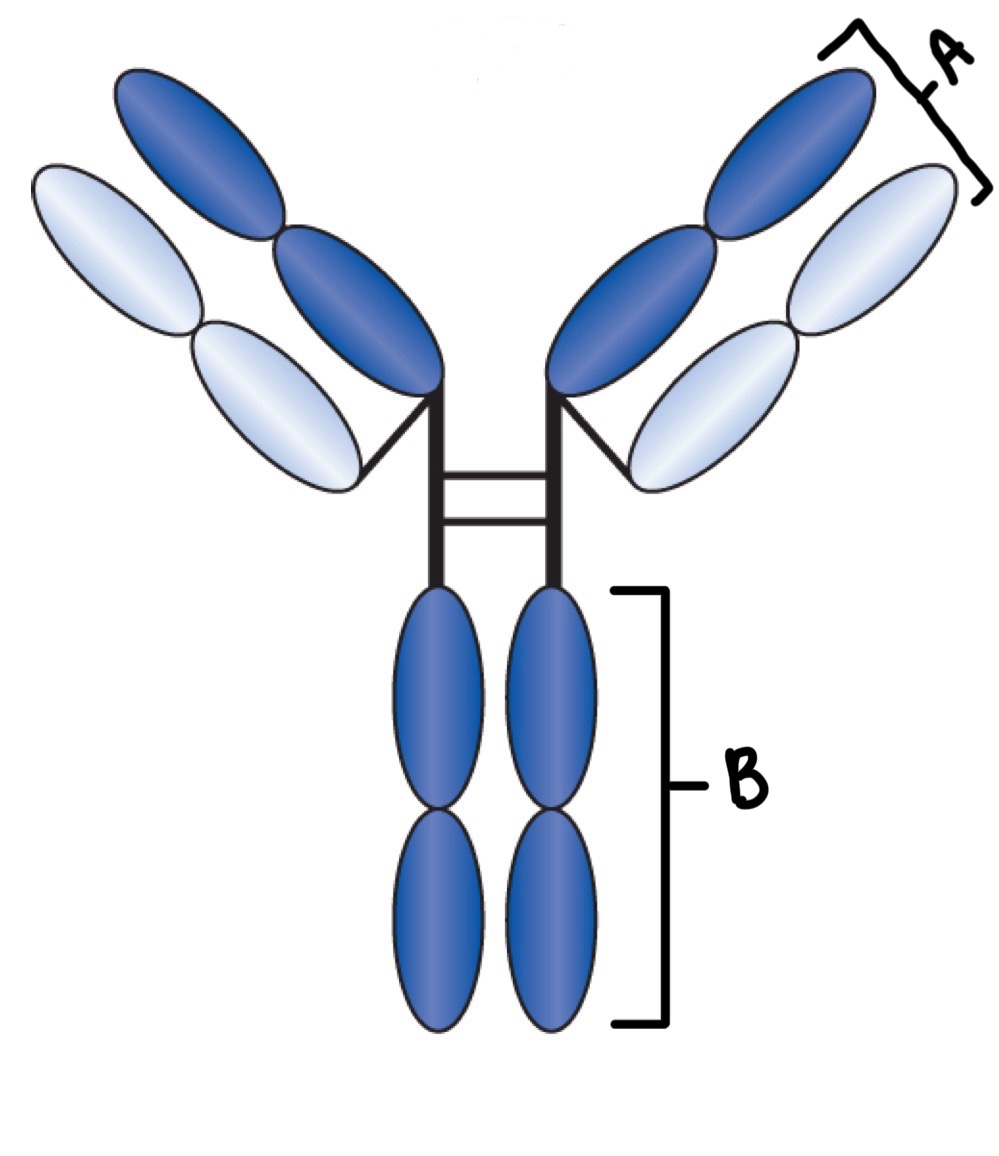
Label
A- Fab Region
B- Fc Region
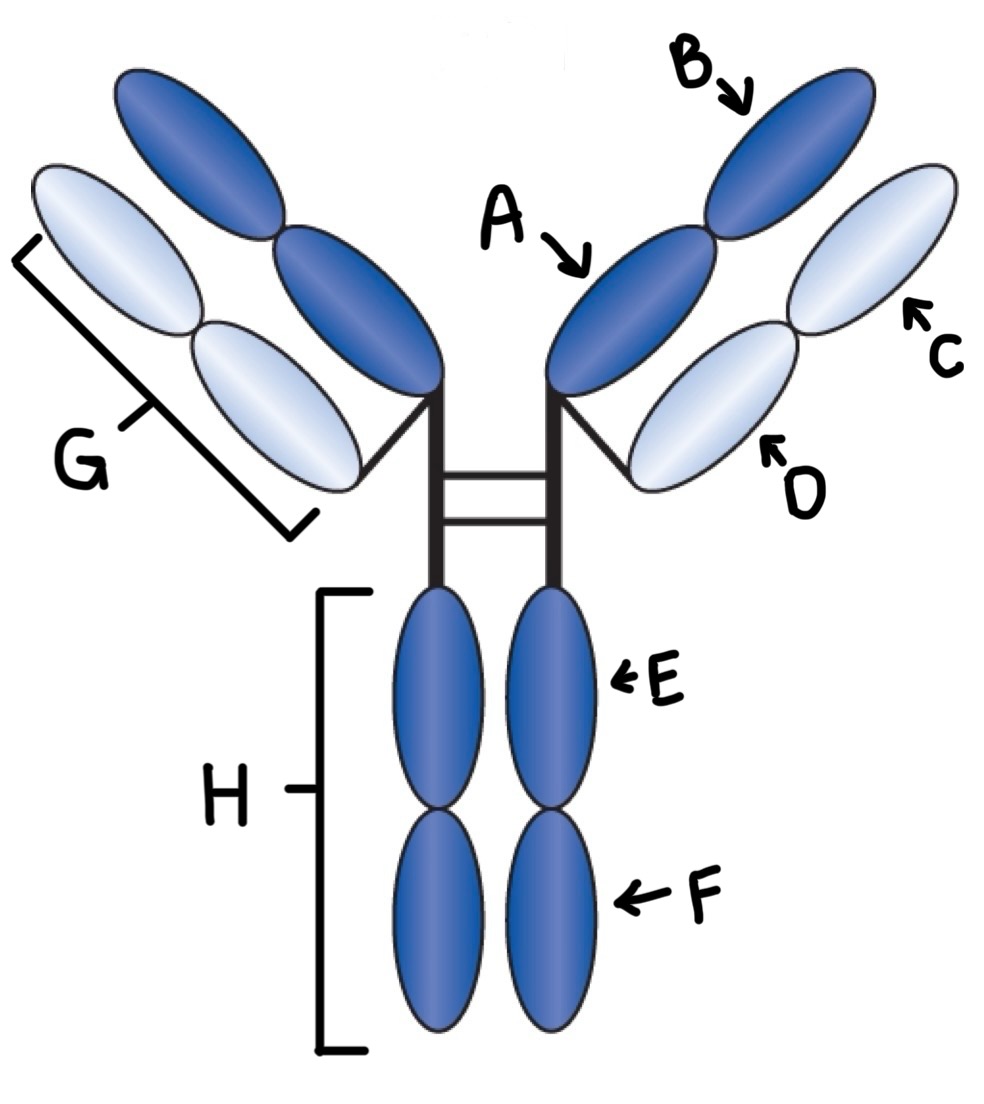
Label
A- CH1
B- VH
C- VL
D- CL
E- CH2
F-CH3
G- Light chain
H- Heavy chain
How do primary and secondary response differ?
Primary response has a longer lag phase, secondary response has a shorter lag phase
Which immunoglobulin is produced first in an immune response?
IgM
What is the predominant antibody in a secondary response?
IgG
Where does complement attach to the immunoglobulin molecule?
Fc region
What role does complement play in the immune response?
Enhance phagocytosis by opsonization and lyses certain bacteria and other cell types
Last steps in complement activation result in the formation of _
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC)
How is complement on a patient’s sample inactivated?
Heat
What is the monoclonal antibody, why are they important, how are they made?
Contain a single antibody that recognizes only 1 epitope on a multivalent antigen and cannot cross react.
Delivery of therapeutic agents in diseases (Continuos source)
Developed based on knowledge that B cells are genetically preprogrammed to synthesize very specific antibody.
What is an antibody titer?
Indication of antibody strength
What is considered a diagnostic increase in titer?
A four fold rise in a titer
What is seroconversion?
Change of a serological test result from antibody negative to antibody positive from samples obtained during the course of an immune response
When should the convalescent specimen be drawn for serological testing?
2 weeks after presentation of symptoms
In serological testing what is meant by the “window period”?
The time between infection and the detection of antibodies in the blood, during which tests may yield false negatives.
When an antibody is present in the blood of a newborn, how can one determine if it is passively acquired maternal antibody or antibody produced by the baby?
Testing for specific immunoglobulin types, such as IgG or IgM, can help distinguish between maternal antibodies and those produced by the infant.
Which antibody class may require the use of an enhancement technique to visualize the reaction in the lab?
IgG
What is a hapten?
A simple chemical group that can bind to antibody once it is formed but that cannot stimulate antibody formation unless bound to a larger carrier molecule
Active vs passive immunity
Active- Individual produces antibodies
Passive- Antibodies transferred to individual
What is the difference between quality control and quality assurance?
Quality control is a system that helps us detect/prevent errors that would impact the accuracy and precision of tests results; Quality assurance establishes standards and documentation to ensure quality requirement is met
List and give examples of the three phases of quality assurance. Pre-Analytical
Orders test, patient preparation, sample drawn, sample transported, sample delivered, sample processed
List and give examples of the three phases of quality assurance. Analytical
Sample analyzed for accuracy and precision, ensuring that test results are reliable before being reported.
List and give examples of the three phases of quality assurance. Post-Analytical
Results verified, results reported, and physician sees patient
In which phase of testing do most errors occur?
Pre-analytical
Positive predictive value
The percentage of all positives in a serological test that are TRUE positives
Negative predictive value
The probability that a person with a negative screening test does not have the disease being tested for
Analytical sensitivity
The lowest measurable amount of analyte that can be reliably detected by a test.
Clinical/diagnostic sensitivity
The proportion of people who have a specific disease or condition and who have a positive result
Analytical specificity
An assay’s ability to generate a negative result when the analyte is not present
Clinical/diagnostic specificity
The proportion of people who do not have a specific disease or condition and who have a negative result
Accuracy
The ability of a test to measure what it claims to measures
Precision
The ability to consistently reproduce the same result upon repeated testing of the same sample
Solute, solvent, solution
A solute is a substance that is dissolved in a solvent to create a solution, which is a homogeneous mixture of the two.
Cross reactivity
When the antibody combines with an antigen that is structurally similar to the immunogen that stimulated the antibody reaction
According to CAP, how often must quality control statistics be calculated?
At least once every 24 hours or at the beginning of each shift
What is the name of a sample that is chemically and physically similar to the unknown and can be tested in the same manner as the unknown to monitor the precision of the test system?
Control or standard
Who should run controls?
Laboratory personnel or technicians responsible for testing.
When should results of control be verified for acceptability?
Before patient’s results are reported
Which part of a quality management program involves the use of external controls?
Quality assurance
What is an antigen?
Macromolecule that is capable of eliciting formation of immunoglobulins or sensitized lymphocytes in an immunocompetent host
What is an epitope?
The key portion of the immunogen against which the immune response is directed
What is an antibody?
Glycoprotein produced by B lymphocytes and plasma cells in response to foreign substance exposure
Define affinity
The initial attraction force between a single antibody binding site and a single epitope
Define avidity
The sum of the attractive fore’s between a multivalent antigen and an antibody that keeeps the molecule together
Direct agglutination
A clumping of cells that occurs when antiibodies react with antigens that are naturally found on the surface of the cells
Hemagglutination
An antigen-antibody reaction that results in the clumping of RBC (direct)
Passive agglutination
A reaction in which particles coated with antigens not normally found on their surfaces clump together because of their combination with antibody
Agglutination inhibition
Based on competition between antigen-coated particles and soluble patient antigens for a limited number of antibody-combining sites. Lack of agglutination = positive reaction
Reverse passive agglutination
Antibody is attached to carrier particle. Agglutination occurs if antigen is present in patient’s sample.
Hemagglutination inhibition
A test for detecting antibodies to certain viruses, based on lack of agglutination that results from antibody neutralizing the virus
Compare precipitation vs agglutination
Both are immunological reactions used to detect and quantify antigens or antibodies, but precipitation involves soluble antigens and antibodies to produce visible insoluble complexes, whereas agglutination involves specific antigens.
Compare nephelometry and turbidimetry
Nephelmetry measures light scattered, turbidimetry measures light absorbed
Compare Ouchterlony vs Radial immunodiffusion
Ouchterlony is a double diffusion technique with both Ag and Ab diffusing in two dimensions. Radial immunodiffusion is a single-diffusion technique where only Ag migrates. Both are end-point reactions
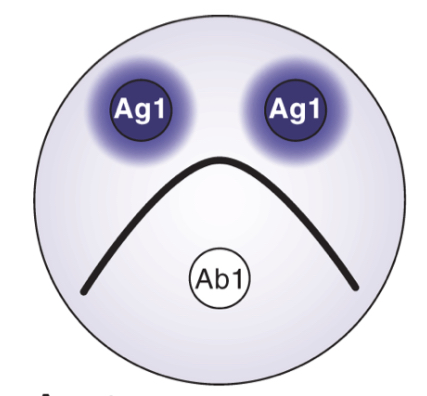
Determine result
Serological Identity
Serological identity
If antigens are identical, they will react with the same anti-body and precipitate to form a continuous arch
Determine result
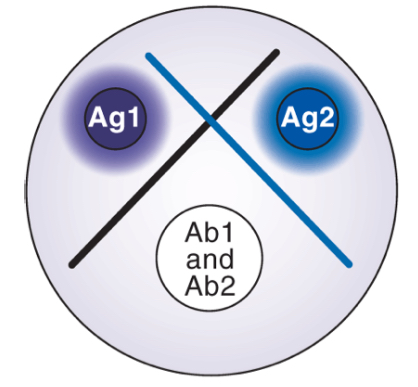
Non-identity
Non-identity
If antigen share no identical determinants, they will react least with different antibodies and two cross lines are form
Determine result
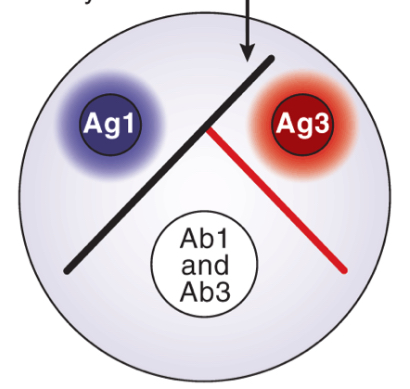
Partial identity
Partial identity
Antibodies react with two similar antigens, forming two line and a spur that point to the simpler antigen (react least with antibody)
What are some sources of error in the ouchterlony/radial immunodiffusion technique?
Improper dilutions, overfilling wells, nicking the side of the well when filling, contaminating samples, and inconsistent agarose thickness.
Know how to determine concentration of unknown from Radial immunodiffusion
Measuring the diameter of the precipitin ring formed in the agarose and comparing it to a standard curve created using known concentrations.
What type of antibodies can cause false positive reactions in hemagglutination tests?
Cold agglutins
What must be present in the serum for tests based on hemolysis of RBCs?
Antibodies
Which is more sensitive precipitation or agglutination?
Agglutination is more sensitive than precipitation.
What happens if you rotate your agglutination card for more than the recommended time?
False-positive
Rank the following methods in order of lowest to highest sensitivity (Agglutination, Precipitation, Immunoassay)
Precipitation, agglutination, immunoassay
Compare labeled and unlabeled immunoassays
Labeled immunoassays utilize conjugated markers, enhancing sensitivity and enabling detection of lower analyte concentrations, whereas unlabeled assays depend on visual methods that may require higher concentrations for effective analysis.
Compare competitive vs non-competitive, which is most sensitive?
Competitive immunoassays are generally more sensitive than non-competitive immunoassays, as they consist of limited antibody and labeled antigen.
Compare homogeneous v heterogeneous, which is most sensitive?
Heterogenous immunoassays require physical separation of bound from free analyte, making them generally more sensitive than homogeneous assays that do not require this step.
In a competitive immunoassay the amount of signal is inversely or directly proportional to the amount of patient's antibody?
Inversely
In a non-competitive immunoassay the amount of signal is inversely or directly proportional to the amount of patient's antibody?
Directly
What step is required in a heterogeneous immunoassay that is not required in a homogeneous immunoassay?
Centrifugation, binding solid-phase material or magnetic separation
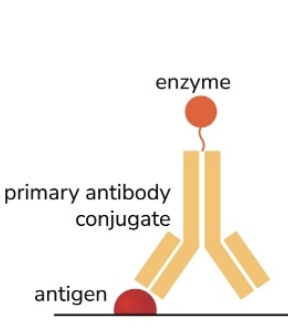
ELISA
Direct
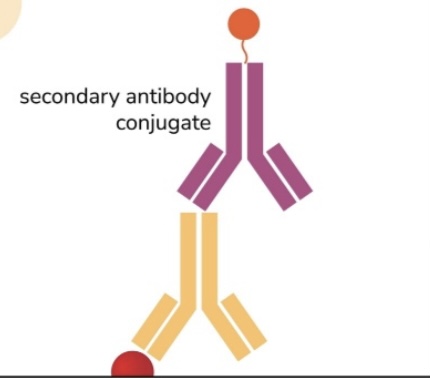
ELISA
Indirect
ELISA
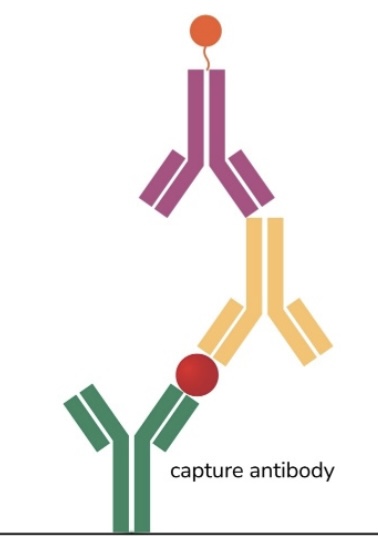
Sandwhich
ELISA
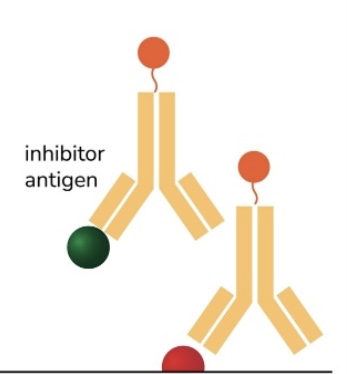
Competitive
Fluorescent immunoassay
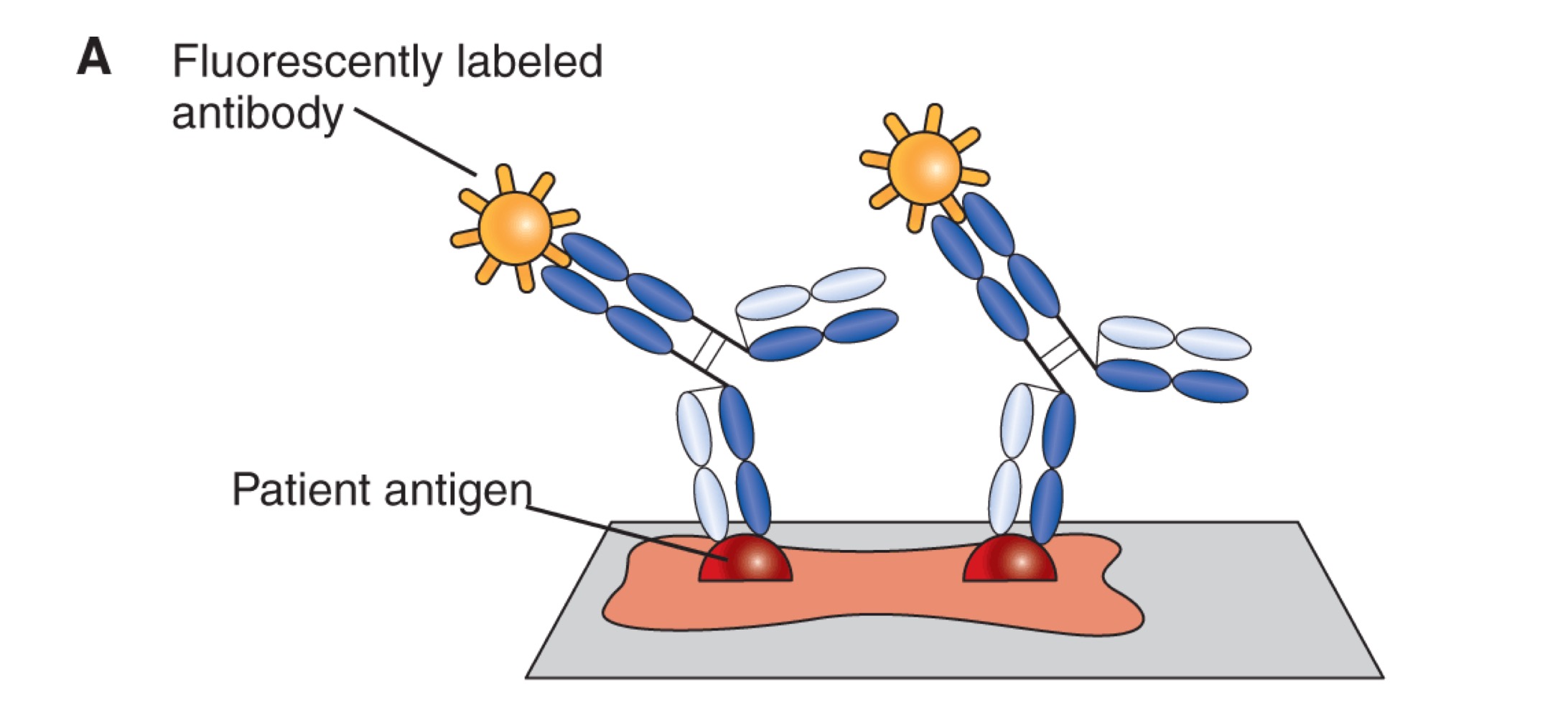
Direct
Fluorescent immunoassay
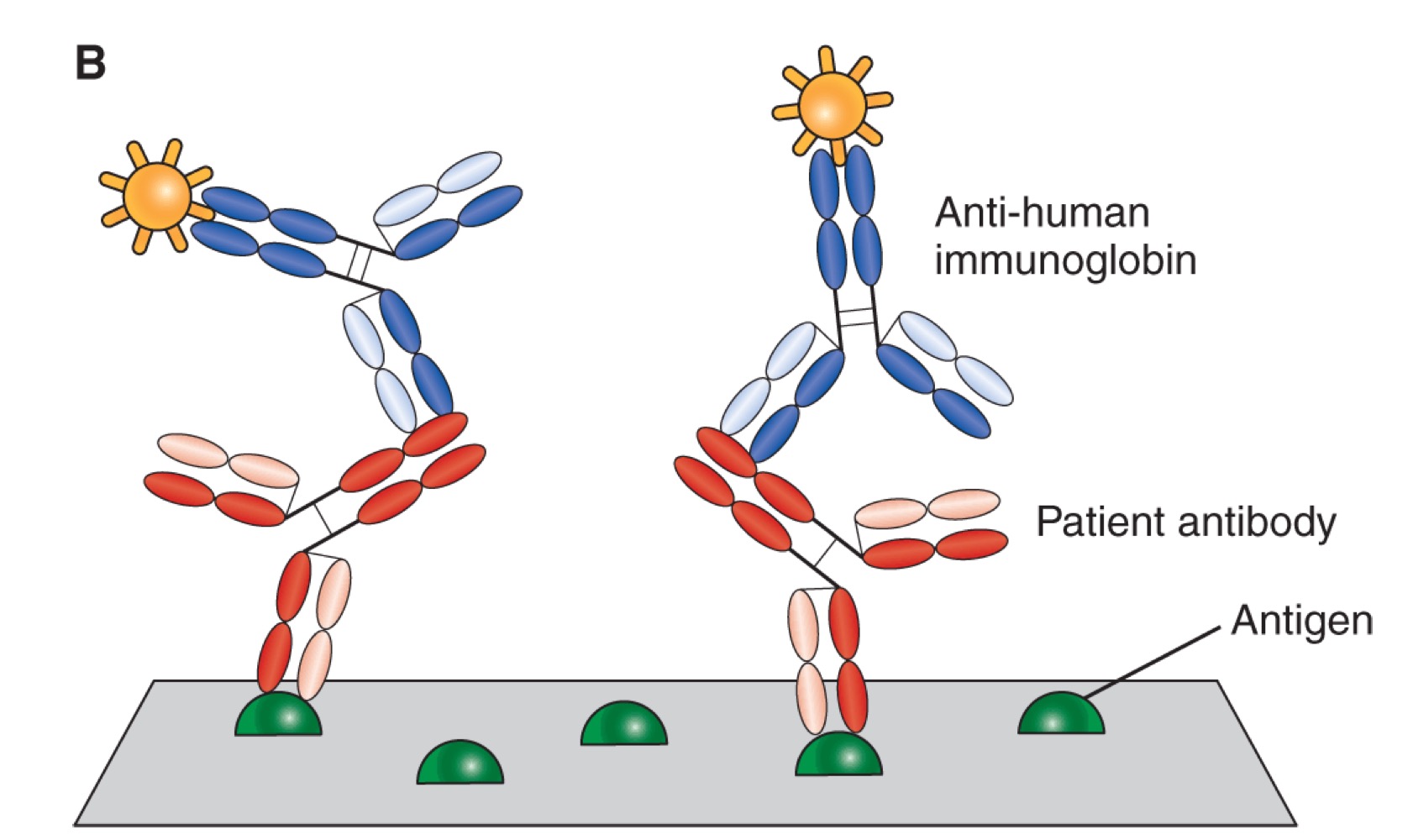
Indirect
Sources of error in ELISA testing
Contamination, pipetting errors, reagents, and improper incubation.
First types of immunoassays used what label?
Radioisotope
Why are enzyme immunoassays (EIA) replacing most radioimmunoassays?
Due to their safety, stability, ease of use, and the absence of hazardous radioactive materials, which makes them more suitable for routine diagnostic testing.
What enzyme labels are commonly used in EIA procedures?
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), B-D-galactosidase, and G6PDH
What is measured in enzyme immunoassays?
Visible light, UV light, fluorescent light and luminescence
What can cause a false positive result in enzyme immunoassays?
Heterophiles, anti-animal Ab, auto-antibodies (RF), and biotin
Bands in serum protein electrophoresis, which band travels farthest toward the anode?
Albumin
What band do antibodies migrate to in serum protein electrophoresis?
Gamma globulin band
Explain immunofixation electrophoresis (IFE), what is it useful for
A qualitative technique that can be used to visualize increases or decreases in immunoglobulin production ant to differentiate monoclonal from polyclonal immunoglobulins
Compare monoclonal vs polyclonal gammopathy
Monoclonal gammopathy is a disorder in which a clone of lymphoid cell causes overproduction of a single immunoglobulin component towards a same epitope. Polyclonal gammopathy is a disorder in which a clone of lymphoid cell causes over production of multiple immunoglobulin components towards different episodes.
Waldenström's primary macroglobulinemia vs Multiple Myeloma including types of immunoglobulins commonly seen.
Both are monoclonal gammopathy. Multiple myeloma causes an overproduction of IgAs and IgGs, while Waldenström cause overproduction of IgMs
Explain “flow-through” membrane-bound EIA
A type of enzyme immunoassay where the sample flows through a membrane impregnated with capture antibodies, allowing for the detection of specific antigens or antibodies in a continuous manner.
What type of immunoassay would be best used for point of care?
A lateral flow immunoassay is best used for point of care due to its simplicity, rapid results, and ease of use.
What additional quality control is required for tests with built-in controls?
Running positive and negative controls
Which methods are most often used on automated immunoassay analyzers?
Turbidimentry and nephelometry are commonly used methods on automated immunoassay analyzers.
What is chemiluminescence?
The production of light energy by a chemical reaction
Name a disease that can cause false positive results in latex agglutination tests because of an antibody in the serum that reacts with IgG?
Rheumatoid arthritis