A&P:The General and Special Senses
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Anything that causes a response in a tissue?
Stimulus
Includes smell, taste, sight, hearing, and balance?
Special senses
Includes touch, pressure, pain, temperature, vibration, itch, and proprioception?
General senses
Respond to pain, temperature, and rich?
Free nerve endings
Detect light touch and superficial pressure; located in the epidermis; a capsule surrounding a nerve ending?
Merkel's disease disks
Respond to fine, discriminative touch; located just deep to the epidermis?
Meissner's corpuscles
Monitor continuous touch or pressure in the skin?
Ruffini's end-organs
Detect deep pressure, vibration, and position (proprioception); located in the tendons and joints?
Pacinian corpuscles
There are (2) kinds of pain. Rapidly conducted impulses give rise to sharp __________, pricking pain, whereas slowly propagated impulses give rise to _________, burning, aching pain?
localized; Diffuse
A painful sensation in a region of the body that is not the source of the pain stimulus is called _________?
Referred pain
Specialized cells in the epithelium of the nasal cavity; airborne molecules bind to receptors on these cells, producing action potentials?
Olfactory neurons
Received the olfactory nerves?
Olfactory bulb
Relays action potentials from the olfactory bulb to the brain?
Olfactory tract
Sensory structure that detects taste stimuli?
Taste bud
Enlargements on the surface of the tongue; contains taste buds?
Papillae
Makeup a taste bud; each has taste hairs that extend through a taste pore?
Taste cell
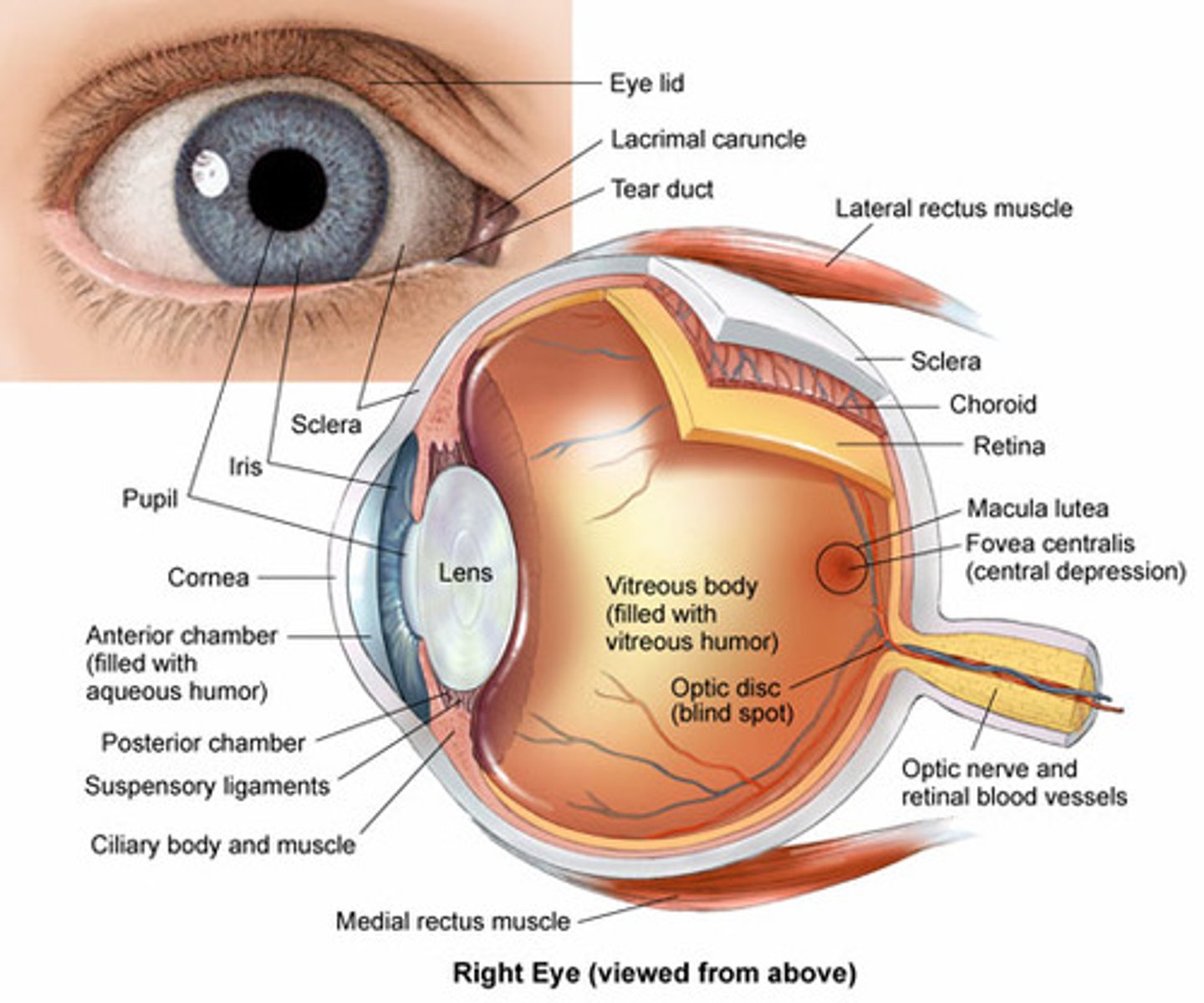
Prevent perspiration from running down the forehead into the eye?
Eyebrows
Protects the eye from foreign objects and lubricate the eye by spreading tears?
Eyelids
Thin, transparent membrane that covers the anterior surface of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids?
Conjunctiva
Produces tears?
Lacrimal gland
Collect excess tears from the medial corner of the eye?
Lacrimal canaliculi
Empties excess tears into the nasal cavity?
Nasolacrimal duct
Moves the eyeball?
Extrinsic eye muscles
Outer layer of the eye, consisting of the sclera and cornea?
Fibrous tunic
Middle layer of the eye, consisting of choroid, ciliary body, and iris?
Vascular tunic
Inner layer of the eye, consisting of the retina?
Nervous tunic
Firm, opaque, white, outer posterior five sixths of the eye; maintains the shape of the eye and provides an attachment site for the extrinsic eye muscles?
Sclera
Avascular, transparent, anterior one sixth of the eye; allows light to enter the eye and also refracts light?
Cornea
Vascular tunic associated with the scleral portion of the eye; prevents light reflection?
Choroid
Contains ciliary muscles (smooth muscles) that attach by suspensory ligaments to the lens?
Ciliary body
Flexible, biconvex, transparent disc?
Lens
Contains smooth muscle that regulates the amount of light entering the eye?
Iris
The opening in the iris through which light passes?
Pupil
Outer part of the retina; its black color prevents light reflection?
Pigmented retina
Inner part of the retina containing rods and cones?
Sensory retina
Photoreceptor cells responsible for color vision?
Cones
Photoreceptor cells that are very sensitive to light and function in dim light?
Rods
Photopigment in rods that breaks down when struck by light; vitamin A is necessary for its manufacture; lack of vitamin A results in night blindness?
Rhodopsin
Small yellow spot near the center of the posterior retina?
Macula lutea
Small pit with the highest concentration of cones and the greatest ability to most clearly detect images; located in the macula lutea?
Fovea centrailis
Blind spot of the eye; place where blood vessels and the optic nerve pass through the wall of the eye?
Optic disc
Fills the anterior compartment of the eye; maintains pressure, refracts light, and provides nutrients to the inner eye surface?
Aqueous humor
Fills the posterior compartment of the eye; helps to maintain pressure within the eye and holds the lens and retina in place?
Vitreous humor
Bending of the light rays as they pass from air into some other, more dense substance?
Refraction
Part of the eye that produces the greatest amount of convergence of light?
Cornea
Part of the eye that accomplishes fine adjustments in focusing by changing shape?
Lens
Process of allowing the lens to assume a more spherical (convex) shape; enables the eye to focus objects that are closer than 20ft?
Accommodation
Condition of the ciliary muscles during accommodation?
Contracted
Condition of the ciliary muscles for distant vision (greater than 20ft)?
Relaxed
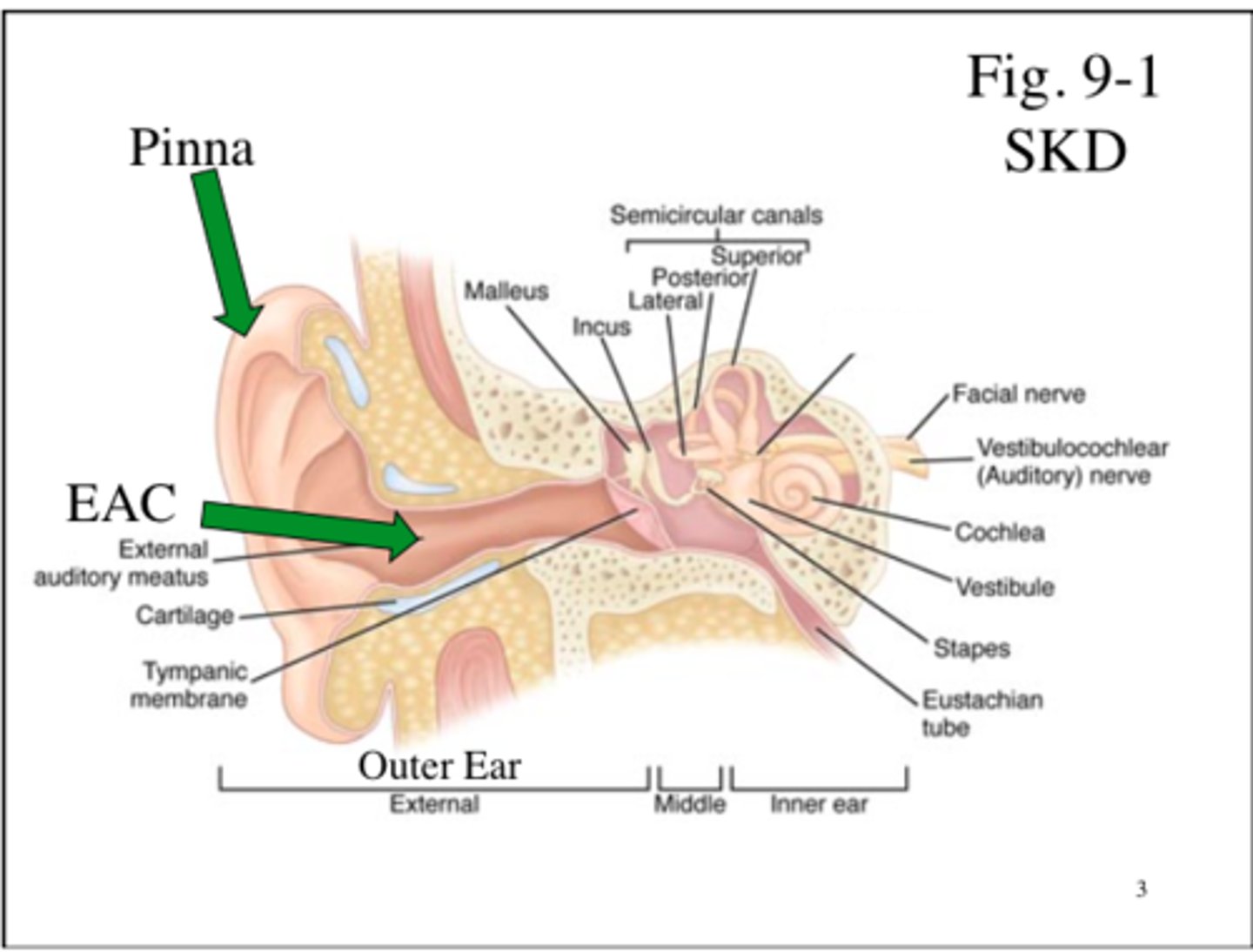
Fleshy part of the external ear on the outside of the head?
Auricle
Passageway that leads to the tympanic membrane?
External auditory meatus
Modified sebum, commonly called earwax, that helps to prevent foreign objects from reaching the tympanic membrane?
Cerumen
Thin membrane that separates the external and middle ear; vibrates in response to sound waves; also called the eardrum?
Tympanic membrane
Opening between the middle and inner ear; contains the stapes?
Oval window
Membrane-covered opening between the middle and inner ear?
Round window
Ear bones that transmit and amplify vibrations of the tympanic membrane to the oval window; the malleus, incus and stapes?
Auditory ossicles
Structure that enables air pressure to be equalized between the outside air and the middle ear; the Eustachian tube?
Auditory tube
Interconnecting tunnels and chambers within the temporal bone?
Osseous labyrinth
Membranes that are found within the osseous labyrinth?
Membranous labyrinth
Fluid within the membranous labyrinth?
Endolymph
Fluid between the osseous and membranous labyrinth?
Perilymph
Part of the inner ear involved with hearing?
Cochlea
Two parts of the inner ear involved with balance?
Semicircular canals & vestibule
Sound waves in the air are collected by the _________ and conducted by the external auditory meatus to the _________. which vibrates?
Auricle; Tympanic membrane
The vibrations are transferred to the auditory ossicles. Vibration of the _______, which is attached to the tympanic membrane, causes vibration of the ________, which is attached to the _________?
Malleus; Incus; Stapes
Movement of the stapes within the _______ produces vibration in the ________ of the scala vestibule?
Oval window; Perilymph
Because the scala vestibule is connected to the scala tympani, perilymph movement causes the membrane of the ______ to move?
Round window
Movement of the stapes within the oval window produces vibrations of the perilymph of the scala vestibule. The vibrations of the perilymph cause the ________ membrane to vibrate?
Vestibular
The vibration of this membrane causes the ______ of the cochlear duct to vibrate, which in turn causes the ______ membrane to vibrate?
Endolymph; Basilar
The spiral organs rests on this membrane, and as the membrane moves it causes the _______ of the spiral organ, which are embedded in the _________ membrane to bend?
Hair cells; Tectorial
The bending of the hair cells results in the production of _______ that are conducted to the brain through the cochlear branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
Action potentials
Sounds with different _________ cause different regions of the basilar membrane to vibrate, whereas sounds with increased ________ cause the basilar membrane to vibrate more intensely?
Pitch; Volume
List the sensations produced through the general senses and the special senses?
General senses: touch, pressure, pain, temperature, vibration, itch, and proprioception (sense of position).
Special senses: smell, taste, sight, hearing & balance (equilibrium)
List the (6) types of receptors associated with the general senses?
Free nerve endings, Merkel's disk, hair follicle receptors, Meissner's corpuscles, Ruffini's end-organs, and Pacinian corpuscles.
List the (4) basic tastes detected by the taste buds?
Sour, Salty, Bitter & Sweet
List the (3) coats or tunics of the eye?
Fibrous, Vascular, and Nervous tunics
Name the (2) major compartments of the eye and the substance that fills each?
Anterior compartment filled with aqueous humor and posterior compartment filled with vitreous humor.
Name the (2) types of photoreceptor cells and state their functions?
Rods: very sensitive to light and function in dim light.
Cones: less sensitive to light (require more light to operate than rods), and are responsible for color vision.
Name the structures that relieve pressure in the middle ear and the inner ear?
Middle ear: auditory tube
Inner ear: round window
The type of receptor associated with pain and itch sensations?
Free nerve endings
Pain sensations
All of the above:
*Are conducted rapidly or slowly.
*Can be blocked by input from the left dorsal columns.
*Can be felt at body locations that are not a source of pain stimulation.
Olfactory neurons
All of the above:
*Have projections called cilia
*Have axons that combine to form the olfactory nerves.
*Connect to the olfactory bulb.
*Have receptors that react with molecules dissolved in fluid.
Taste
Can be divided into (4) basic types: Sour, salty, bitter & sweet
Tears
Lubricate and clean the eye, and protect against eye infections.
Given the following structures:
1. choroid
2. retina
3. sclera
Choose the arrangement that list the structures in the order a pin would pass through them going from the outside of the eye to the inside?
3,2,1
Aqueous humor
Produces pressure that keeps the eye inflated.
Given the following structures:
1. lens
2. aqueous humor
3. vitreous humor
4. cornea
Choose the arrangement that lists the structures in the order that light entering the eye would encounter them?
4,2,1,3
When light strikes rods, a series of chemical events occur that result in production of action potentials.
Given the following events:
1. retinal attaches to opsin; ATP molecules are required
2. retinal changes shape
3. retinal separates from opsin
Choose the order in which the arrangement would occur?
2,3,1
Assume that you are looking at an object that is 20ft away from you. If you suddenly look at an object that is 1ft away, which of the following events would occur?
Ciliary muscles contract and the lens becomes more spherical (rounder)
Which structure is found within or is part of the external ear?
Auricle
Given the following structures:
1. Perilymph
2. Endolymph
3. Vestibular membrane
4. Basilar membrane
Choose the arrangement that lists the structures in the order sound waves coming from the outside would encounter them.
1,3,2,4
Given the following structures:
1. Stapes within the oval window
2. Membrane of the round window
3. Tympanic membrane
Choose the arrangement that lists the structures in the order sound coming from the outside causes them to move?
3,1,2
Labeling the eye
The ear labeled