What are compounds?
2 or more separate elements that combine together
What is the state symbol for solid out of the 4?
1
What is the state symbol for gas?
3
What is the state symbol for soluble in water?
4
What is the state symbol for liquid?
2
What are ions?
particles that lose, share or gain electrons
Why are hazard symbols used?
to indicate the dangers associated with the contents to inform people about safe-working precautions
What are some safety precautions that one should take when dealing with harmful substances?
Use protective clothing such as a lab coat and goggles
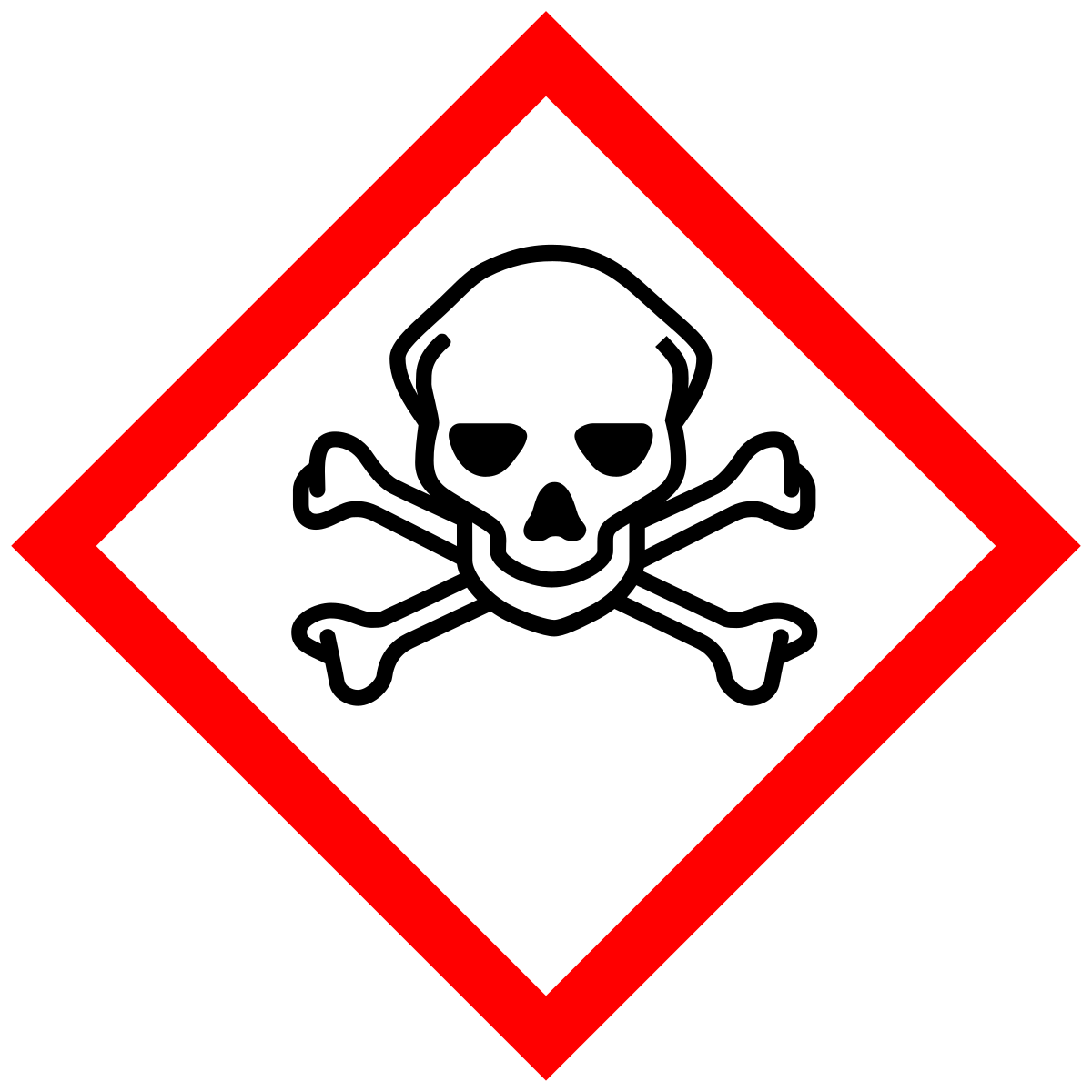 What does this symbol mean?
What does this symbol mean?
Toxic
How has the John Dalton model of an atom changed?
it changed overtime because of the discovery of subatomic particles
Describe the structure of an atom
A nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in a shell
What is the relative charge of a neutron?
0
What is the relative mass of an electron?
1/1836
What is the relative mass of a proton?
1
what is the relative mass of a neutron?
1
What is the relative charge of an electron?
-1
What is the relative charge of a proton?
+1
Describe the nucleus of an atom
The nucleus of an atom is very small in comparison to the overall size of the atom
Where is most of the mass concentrated in an atom?
the nucleus
Explain why atoms contain equal number of protons and electrons
Atoms are neutral and the charges of a proton is +1 and the charge of an electron is -1 so the charge cancels each other out.
What is meant by the term “atom mass”?
the total number of protons and neutrons
What are isotopes?
different atoms of the same element containing the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in their nuclei
What is the formula for finding the relative atomic mass of an element?
(isotope 1 x abundance)+(isotope 2 x abundance)
100
How did Mendeleev arrange the table of elements?
by using properties of these elements and their compounds
Describe electronic configuration
How many electrons are in the outermost shell
What is a cation?
A positively charged ion
What is an anion?
A negatively charged ion
What is an ion?
an group of atoms that have a positive or negative charge
Explain the formation of ions in group 1 elements
ions produced in group 1 elements lose 1 electron to form a charge of +1
Explain the formation of ions in group 2 elements
group 2 metals will lose to electrons to make a charge of +2
Explain what formation of ions group 6 elements will have
group 6 non-metals will gain 2 electrons and form a charge of -2
Explain what formation of ions group 7 elements will have
Group 7 non-metals will gain 1 electrons and will have an overall charge of -1
What does the ending “-ide” at the end of a compound name mean?
it means that the compound contains 2 elements (one non-metal)
What does the ending “-ate” at the end of a compound name mean?
It means that the compound contains at least 3 elements (one of which is oxygen)
Give the chemical formula for Oxides
O2
Give the chemical formula for hydroxides
OH¯
Give the chemical formula for halides
-1 ion
Give the chemical formula for nitrate
NO3-
What is the chemical formula for carbonate
CO₃²⁻
What is the chemical formula for sulfate
SO-2 4
What is the structure of an ionic compound?
lattice structure consisting of a regular arrangement of ions held together by an electrostatic force of attraction
How is covalent bonding formed?
when atoms share electrons they create very strong bonds that occur in most non-metallic elements
What does covalent bonding result in?
The formation of molecules
What is the typical size (in magnitude) of atoms and small molecules
atoms are smaller than small molecules such as oxygen molecules
Demonstration of the dot and cross diagram used for hydrogen
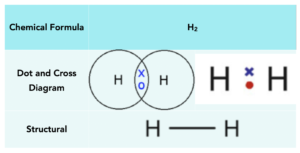
Demonstration of the dot and cross diagram used for hydrogen chloride
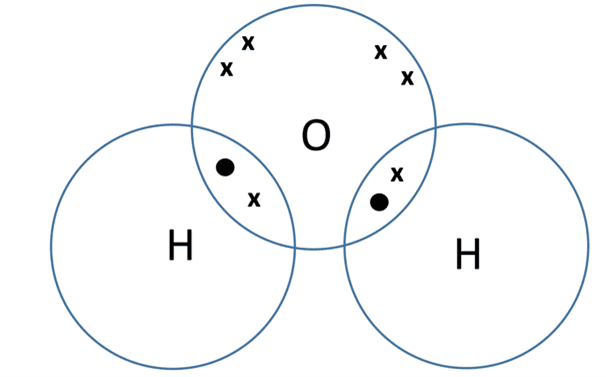
Demonstration of the dot and cross diagram used for water
Demonstration of the dot and cross diagram used for methane
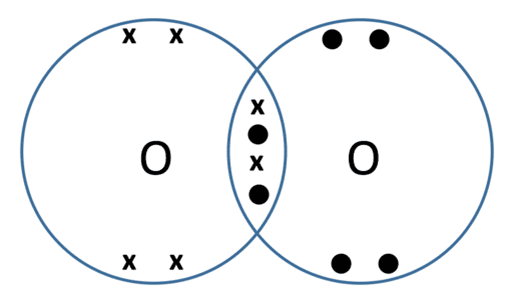
Demonstration of the dot and cross diagram used for oxygen
Demonstration of the dot and cross diagram used for carbon dioxide
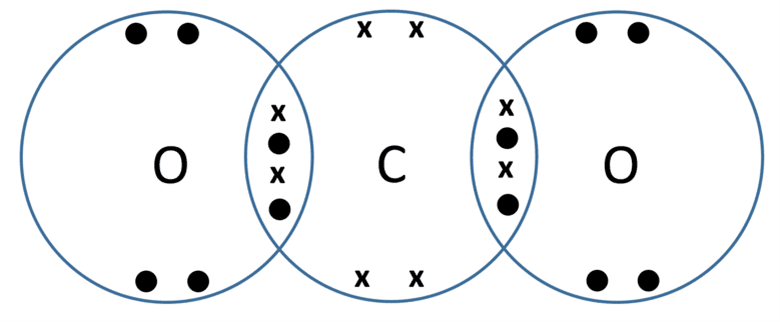
What are properties of ionic compound?
made out of metals and non-metals
have regular structures and are held together by a strong force of attraction
have high melting and boiling points
when melted or dissolved in water, the compounds conduct electricity
What are some properties of simple molecular compounds?
substances that consist of small molecules an have a low boiling and melting point
made up of non-metals
the small molecules have a weak inter-molecular force
they do not conduct electricity
many are insoluble but some are soluble
What are some properties of giant covalent structures?
made up of non-metals
very high melting points
all the atoms are connected by a strong covalent bond
some giant covalent structures conduct electricity but others don’t
What are some properties of metallic (metal) structures?
they are arranged in a regular pattern
always made out of metallic elements
electrons in the outer shell are delocalised so they can move around the structure
Metals have very strong metallic bonding
have a high melting point and boiling point
conduct heat and electricity
Explain properties of ionic compounds
high melting point and boiling point
strong electrostatic force of attraction
do not conduct electricity when solid
Explain properties of covalent and molecular compounds
-low melting and boiling points
-poor conductivity
What are diamond and graphite ?
different forms of giant covalent substances
Describe the structure of graphite
one carbon bond is attached to 3 other carbon bonds
weak inter-molecular forces
graphite is soft and slippery
one electron from each atom is delocalised
it can conduct electricity
Describe the structure of diamond
joined to 4 other carbon molecules covalently
very high melting point
does not conduct electricity
Why is graphite used to make electrodes and used as a lubricant?
graphite conducts electricity
it has weak inter-molecular forces and no covalent bonds between layers so it is soft and slippery
Why are diamonds are used in cutting tools?
diamonds are very hard and rigid
What is graphene used for?
electronics and composites
made out of a single layer of graphite
Properties of the fullerene Carbon
hollow shape
based on hexagonal rings of carbon with 5 or 7 carbon atoms
first fullerene to be discovered was Buckminsterfullerene(C60)
What are carbon nanotubes?
cylindrical fullerenes with high length to diameter rations
useful for nanotechnology, electronics and materials
Describe the chain of molecules for poly(ethene)
polymers are large molecules
atoms in polymers are linked to other strong covalent bonds
inter-molecular forces are relatively strong and are solid at room temperature
What does the term malleable mean?
the layers of atoms slide over each other