Adaptive Immunity
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Define adaptive immunity
The response of antigen-specific lymphocytes (B & T cells) to antigen, including the development of immunological memory
What are characteristics of adaptive immunity?
Acquired (not innate)
Highly specific - efficient
Increase recognition of pathogens by the innate immune system
Gradual response (generated over 3-4 days)
What are three advantages of the adaptive immune system?
Precise
Memory
Adapts
What are the 2 branches of the adaptive immune system?
Humoral (HI) and Cell Mediated (CMI)
What does the Humoral immune system target? What is it mediated by? Is it transferable?
Targets extracellular pathogens (bacteria), mediated by antibodies, transferable
What does the cell mediated immune system target? What is it mediated by? Is it transferable?
Targets intracellular pathogens (virus), mediated by cytotoxic T cells, not transferable
What cell is like a “keystone” that connect the innate and adaptive immune response?
CD4T cell
Define antigen. What is the most common type?
Any molecule, macromolecule, virus, particle, or cell that contains a structure recognized and bound by an Ig or TCR. Majority are proteins.
Define antigenic determinant (Epitope)
Portion of antigen recognized by antibody
How do B & T cells each recognize antigens? And do they bind specifically?
B cells recognize by BCR or immunoglobulin (soluble form = Ab)
T cells recognize by TCR (no soluble form)
Both bind specifically (lock & key)
Describe the structure of immunoglobulins and BCR
2 heavy and 2 light chains
Constant and variable region on each chain
Some soluble, some with transmembrane region on B cells
Antigen bind to variable region
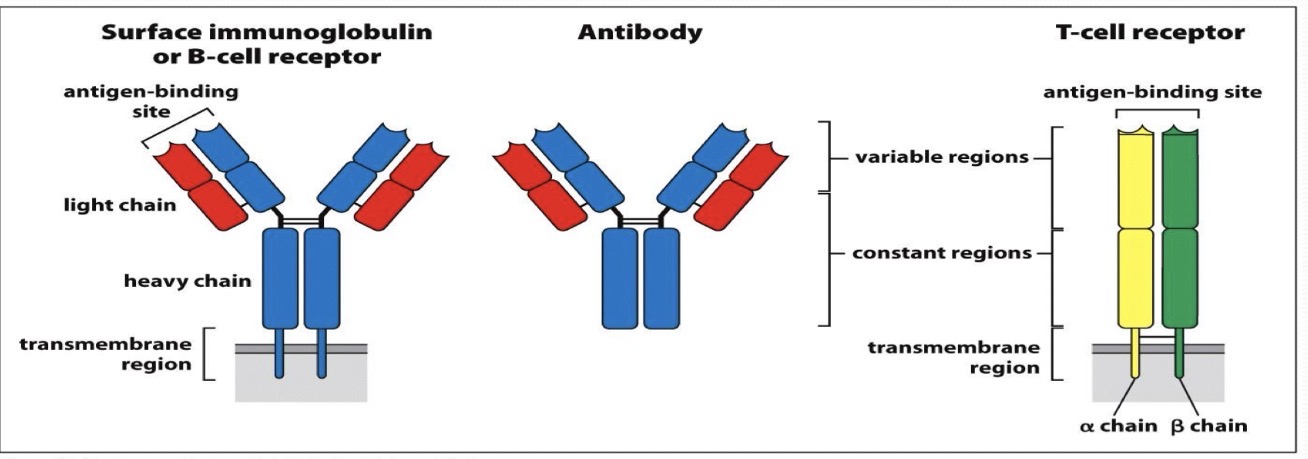
Describe the structure of T-cell receptors
Alpha and beta chain
Constant and variable region on each chain
Transmembrane region
Antigen bind to variable region
Are antibodies specific?
Very
Define antibody repertoire
Total number of antibody specificities to an individual
Increased diversity of antibody specificities is due to what processes?
Gene rearrangement (Somatic recombination)
Junctional diversification
Define gene rearrangement (somatic recombination)
Enzyme catalyzed process of recombination
Define junctional diversification and the types of junctions in each chain
Junctional diversification: Gene arrangement with nucleotide insertions at the joint to produce a functional gene
Heavy & beta chain: V, D, & J
Light & alpha chain: V & J
What are the 4 simplified postulates of clonal selection?
Each cells has 1 receptor for 1 antigen (specificity)
Cell binds tightly to antigen = activation
Differentiated effector cells are exact copies (clonal expansion)
Cells that bind tightly to “self” are destroyed early on (clonal deletion)
What cells link innate and adaptive immunity? Why?
Dendritic cells carry antigen to lymphoid tissue and activate T-cells
Describe the steps of antigenic processing and presentation
Dendritic cell takes up pathogen for degradation
Pathogen is taken apart in dendritic cell
Pathogen proteins are unfolded and cut into small pieces
Peptides bind to MHC molecules and the complexes go to the cell surface
T-cell receptors bind to peptide:MHC complexes go to the cell surface
What does MHC stand for?
Major histocompatibility complex
What the two classes of MHC? What type of antigen do they present? On what cell types are they present?
MHC Class I
Presents peptides from intracellular pathogen
Present on all nucleated cells
MHC Class II
Presents peptides from extracellular pathogens
Present only on professional Antigen Presenting Cells (pAPCs)
T cells antigen recognition is assisted by internal and external co-receptors. What type of cell does each type of receptor activate? And what class of MHC receptor presents antigen to it?
Intracellular infection: TCR on CD8 (Cytotoxic T cell) binds to APC MHC I
Extracellular infection: TCR on CD4 (Helper T cell) binds to APC MHC II
Describe the differences in B and T cell antigen recognition
B-cell recognition
Free antigen (Native)
BCR - membrane bound antibody
No antigen processing required
TCR recognition
Processed antigen (Peptide fragment)
TCR - T cell receptor
Must be presented on MHC molecule
CD8 → MHC I (Intracellular)
CD4 → MHC II (Extracellular)
Name the 3 pAPCs
Macrophages
Dendritic cells
B-cells
Describe the steps of basic activation of B cells
B cells bind bacteria, cells engulf and degrade them, producing peptides
Peptides bound by MHC II in endocytic vesicle
Bound peptide MHC II complex is transported to cell surface
Helper T cell recognizes complex and activates B cell
What are the 2 major functions of antibodies?
Neutralization: Prevents pathogen growth, replication or interaction with host cells
Opsonization: Aid in engulfment and destruction by phagocytosis
What are the isotypes of antibodies?
IgA
IgD
IgE
IgG
IgM
Describe the benefits of somatic recombination, junctional diversification, isotype switching, and somatic hyper mutation
Somatic recombination: increases variety of antibodies
Junctional diversification: increases variety of antibodies
Isotype switching: improves specialization of function and ability to recruit effectors
Somatic hypermutation: improves antigen binding by the antibody