Paleo 200
1/138
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
Paleontology
The study of all prehistoric life
Fossil
Any preserved evidence left behind by pre historic organism
Adaptations
Traits that have evolved because they serve specific functions
Vertebrates
Animals that have two special kinds of skeletal adaptations: skulls & vertebrae
Vertebrae
Structures made primarily made of bone and/or cartilage that surrounds a portion of the spinal cord
Vertebral column
A bunch of vertebrae interlocked in a series
Invertebrates
Animals that lack vertebrae
Nares
The pair of openings for the nostrils
Orbits
The pair of openings for the eyes
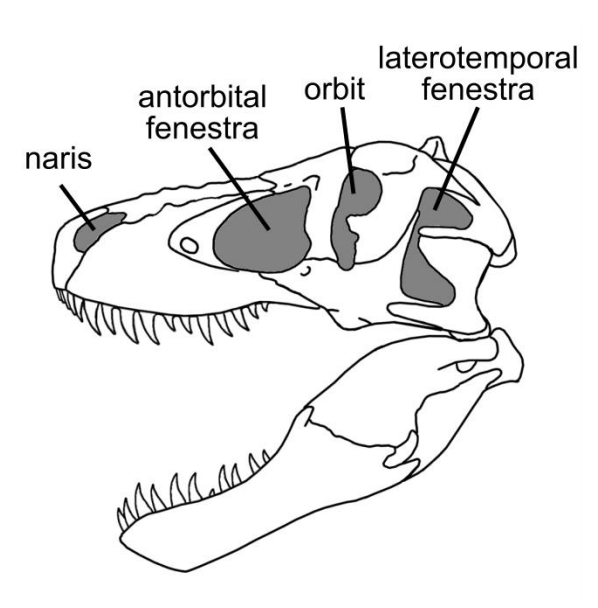
Fevestrae
Additional openings in the skull, behind each orbit, dinosaurs have two of these on each side of the skull
Laterotemporal fenestrae
The fenestrae on the lateral sides of the skull
Antorbital fenestrae
The third pair of fenestrae located between the orbit and the naris
Centrum
A vertebra has a spool or disk shaped body called the ___
Neural canal
The opening in each vertebra through which the spinal nerves run
Vertebral processes
Provides attachment surfaces for muscles and sometimesprovide articulation surfaces for ribs
Transverse processes
Extend down the lateral sides of the vertebrae
Spinous processes
Extend upwards from the neural arch
Cervical vertebrae
Vertebrae in the neck they have extra large openings for blood and nerve channels and are adapted to support the weight of the head
Dorsal vertebrae
The vertebrae in the back, there are typically extra long spinous processes and rib articulation surfaces
Sacral vertebrae
Vertebrae in the hips, the pelvic bones are fused to these vertebrae , so that the powerful leg muscles have a strong anchor
Sacrum
For further strength in the hips, the sacral vertebrae are fused with one another and form a single solid bone
Caudal vertebrae
Vertebrae in the tail
Chevrons
Located under the caudal vertebrae, they protect the large blood and nerve channel and provides support for the tail muscles
Gastralia
Small ribs positioned across a dinosaurs underbelly-under the rib cage
Tetrapod
An animal that evolved from an ancestor with four feet and four limbs
Limb girdles
The limbs are connected to the rest of the skeleton by
Pectoral girdle / shoulder girdle
The forelimbs are connected via the
Scapula/ shoulder blade
The largest bone inside of the pectoral girdle
Pelvic girdle
The hind limbs are connected to the skeleton via the __
Ilium
The upper hip bone
Pubis
Bone positioned in front of the ischium nearer the belly
Ischium
Is positioned behind the pubis, nearer the tail
Acetabulum
The depression or the hole (in dinosaurs) in the pelvic girdle into which the hind limb articulates
Humerus
Located between the shoulder and elbow, is the largest bone in the forelimb
Radius
Between the elbow and the wrist are two parallel bones __ and ulna. Is thinner of the two
Ulna
Thicker of the two wrist bones, radius and ___
carpals
The bones in the wrist
Metacarpals
The bones between the wrist and fingers
Phalanges (hands)
The finger bones
Metatarsals
The bones between the ankle and toes
Phalanges (feet)
Bones in the toes
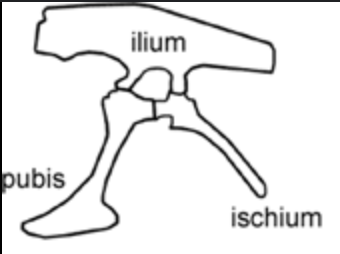
Saurischian
Dinosaurs that share an evolutionary ancestor that had a pubis that extended downward and forward, toward the ribcage -"lizard hipped”
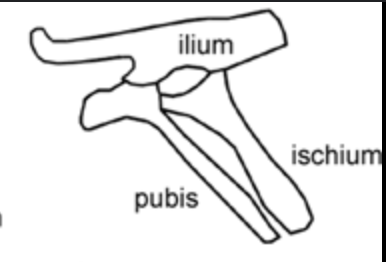
Ornithischian
Dinosaurs that share an evolutionary ancestor that had both a special beak-forming bone in the upper jaw and a pubis that extended downwards and backwards towards the tail, "bird hipped” - birds are not bird hipped
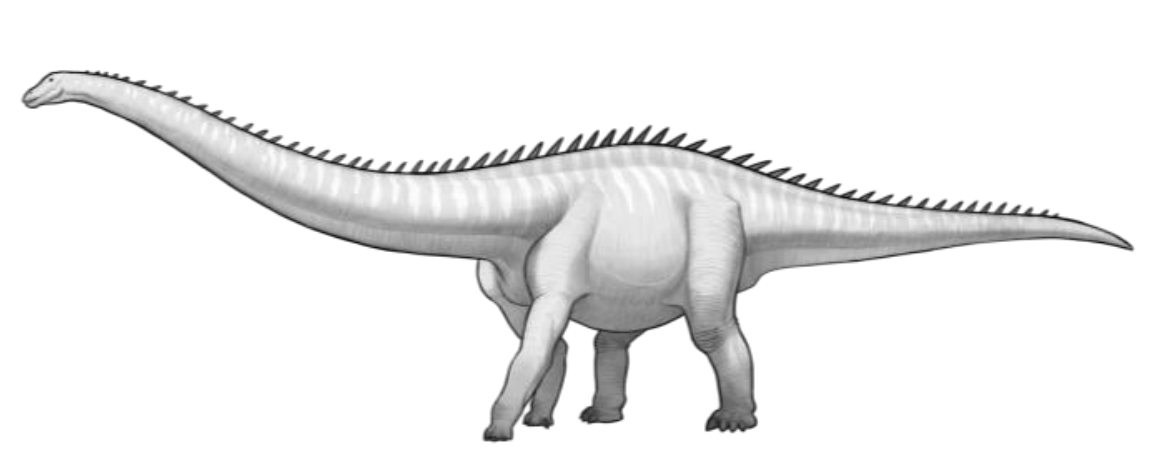
Sauropomorphs
Large herbivores with elongated necks and relatively small heads
Prosauropods
Were an early group of sauropodomorphs and were the first group of large-bodied herbivorous dinosaurs to evolve
Sauropods
Later group of sauropodomorphs, were truly a gigantic size, a group of animals that were the largest to walk the earth
Theropods
Were bipedal saurischian dinosaurs that shared a carnivorous ancestor. Many had serrated blade-like teeth and sharp hooked claws, but some were herbivorous and few lack teeth altogether
Ornithopods
Include a wide range of dinosaurs that lack armour and that either walked bipedally all the time or a bipedal stance while running - about the size of small antelopes
Iguanodonts
Large ornithopods with a spike-shaped claw on each hand
Hadrosaurs
"Duckbilled dinosaurs“ - evolved late in the history of dinosaurs, but were highly successful. Some have elaborate boney crests, and have strikingly large beaks and dense, tightly packed rows of small teeth in the rear of their mouth
Dental batteries
Small densely packed teeth form a large chewing surfaces
Pachycephalosaurs
Bipedal with short arms, unusually stout and strong tails and armoured skulls, some have thick domed skull roofs and backwards pointing horns
Ceratopsians
A group of late evolved dinosaurs in history, have a large parrot-like beaks and skulls that are greatly expanded in the rear

Stegosaurs
A group of quadrupedal dinosaurs with rows of projecting osteoderm plates down their backs and long osteoderm spikes on their tails
Osteoderms
Bones that develop within the skin and are a common component of animal armour
Ankylosaurs
Are heavily armoured, are quadrupedal with short legs and wide ribcages, are covered with spikes protective osteoderms, tail club
Integument
The covering of a dinosaurs body, skin, feathers, scales, fur, etc
Keratin
A tough but flexible material that covers the skin, also hair, feathers, fingernails, outside of claws, beaks, and horns
Melanosomes
The pigment cells within a feather, having different arrangements for different colours
Scipionyx
A small theropod dinosaur, found in Italy. found preserved mineralized remains of the trachea and the intestines. An additional red smudge was found in the belly region, which could represent the decayed remains of the heart, liver or spleen. Some muscles were also preserved and the keratinous swaths over the claws
Taphonomy
The study of natural processes that involve an organism after it dies, decay, being scavenged by other organisms, becoming fossilized and erosion
Bloat-and-float
Shortly after death, decay causes a body to swell with putrid gasses and can cause the carcass of large animals to float easily and be transported by shallow, weakly floating water
Disarticulate
A skeleton that is separated into its various components, could be carried by water, scavengers, etc
Plastic deformation
Occurs when pressure causes the shape of a buried fossil to be changed, so that if the pressure is removed the fossil doesn't go back to its original shape
Fluvial deposits
Ancient river and stream deposits
Lacustrine deposits
Ancient lake deposits, have a better chance of preserving soft tissues like hair or feathers in these fossils
Costal environments
Although there were no marine dinosaurs, they can still be found in these environments and sometimes (rarely) deeper-water environments if the dinosaur was washed out to sea during a storm or tsunami
Aeolian or wind-based deposits
Dinosaur fossils are rarely found in sediments representing ancient deserts, because there isn't enough sediments to cover the skeleton
Sedimentary rocks
Are rocks that form when mineral and organic particles accumulate and become either cemented or compacted together.
Metamorphic rocks
Rock that forms when sedimentary or igneous rocks are changed by heat and pressure
Sedimentology
The science of how sedimentary rock forms, different types of sedimentary rocks form indifferent environments understanding the conditions that the rocks were formed in helps us learn important clues about the habitat of The organism
Mudstone and shale
Sedimentary rocks that form from mud and silt
Sandstone
Sedimentary rocks made from sand, coming from a former beach, river channel, or ocean floor environment
Coal
Type of sedimentary rock that forms from the compressed remains of plants, and indicates a swampy environment.
Limestone
Rock formed from the accumulation of shells and exoskeletons of small marine invertebrates almost always indicates a shallow marine environment
Preservation styles
The different ways that fossils are formed
Permineralization
Occurs when the empty internal spaces of a bone are filled with minerals
Replacement
Occurs when the original bone gradually decays and minerals fill the space that the bone once occupied
Badlands
Are avid environments where vegetation is sparse, where erosion rates are high, and where large expanses of ancient sedimentary rocks are exposed
Overburden
The rock that covers a fossil specimen that must be removed before the the full extent of the specimen can be judged, need large indelicate tools like shovels, pickaxes, and sometimes jackhammers and bulldozers
Orientation
This is very important in a bone bed, the position of the fossils is important I long bones that are aligned in the same direction indicate that the bones were transported by water and can tell us the direction that the water was flowing
Abrasion
Scraping or wearing down of something
Tooth marks
Scratches on the bones could be ____, which indicate that a carnivore fed on the carcass, not necessarily meaning killed by a carnivore
Herbivores
Tend to have thin, ridged or “leaf-shaped" teeth for shearing and broad, flat teeth for grinding
Carnivores
Tend to have sharp pointed teeth for piercing, and sharp hooked claws for holding struggling prey
Serrations
Small sharp bumps on a tooth that are arranged in a line that usually runs from the tip to the base of the tooth
Frugivores
Eats primarily fruit, the beak is sharp and hooked to take off the peals and protective husks
Piscivores
Specialized carnivores that primarily eat fish, tend to have tall, sharp, conical teeth that usually lack serrations
Insectivores
Are specialized carnivores that primarily eat insects, some have sharp piercing teeth for puncturing the exoskeletons
Durophagy
Some carnivores have sharp teeth for puncturing and ripping flesh but also have strong rounded teeth that enable them to crack bones, also have extremely powerful jaws
Omnivores
Are animals that eat significant amounts of both meat and plants, humans are a good example, tend to have unspecialized teeth or beaks
Resorption
The chemical process by which a dinosaur breaks down its own teeth and bones so that the minerals and nutrients that compose them to be reused
Cellulose
The walls of plant cells are made of a compound it is tough and it is difficult to breakdown as a food source animals cannot digest it on their own. Animals need from bacteria that live within their stomach and intestines. Dental batteries for the help breakdown the plant matter
Gastroliths
Small little stones in the ribcage of herbivorous dinosaurs, commonly in animals that lack teeth
Dromaeosaurs
A group of theropod dinosaurs with thin tails supported by special rod-like projections of their caudal vertebrae and chevrons, a velociraptor is a famous example
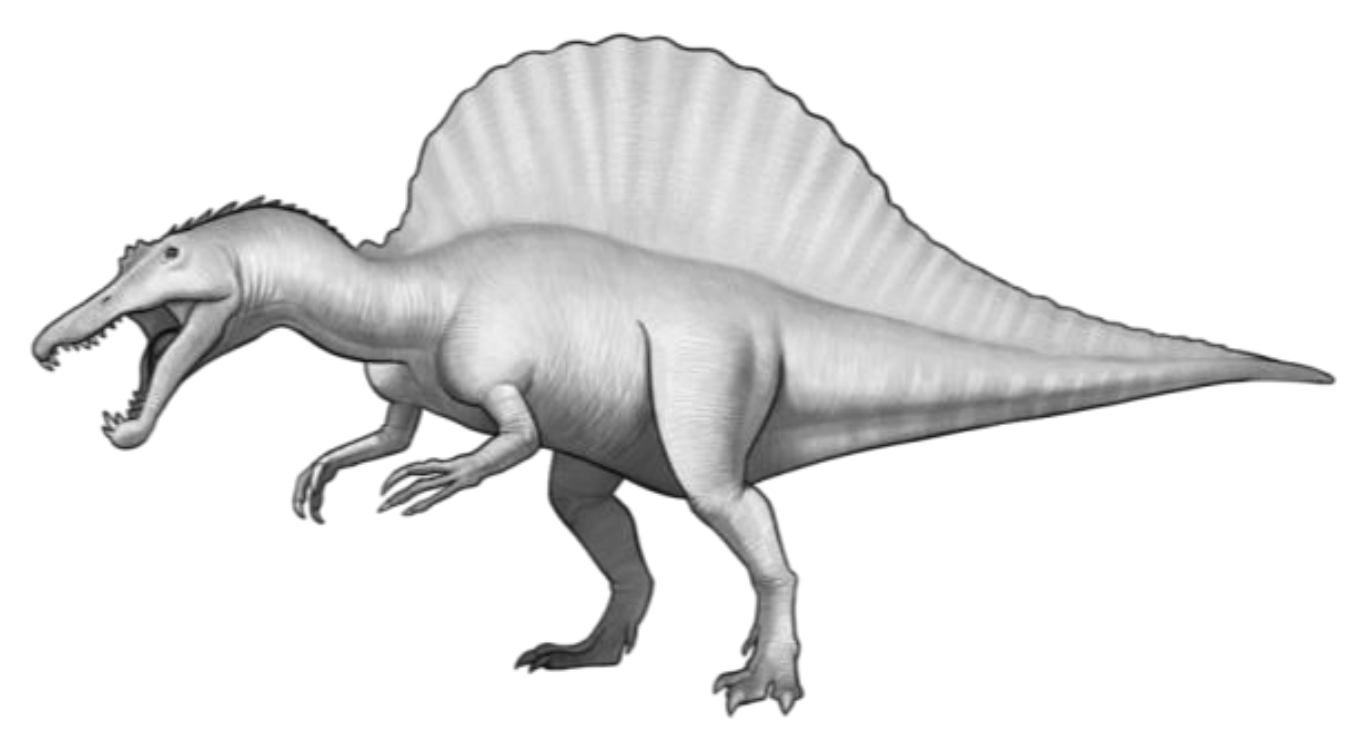
Spinosaur
A group of theropods with skulls that strongly resemble those of crocodiles, were likely piscivores, teeth are comical, have sharp tips and have little to no serrations
Alvarezsaurs
A group of small theropods with short front limbs and compact hands, were likely insectivores, have reduced teeth and short but strong front limbs
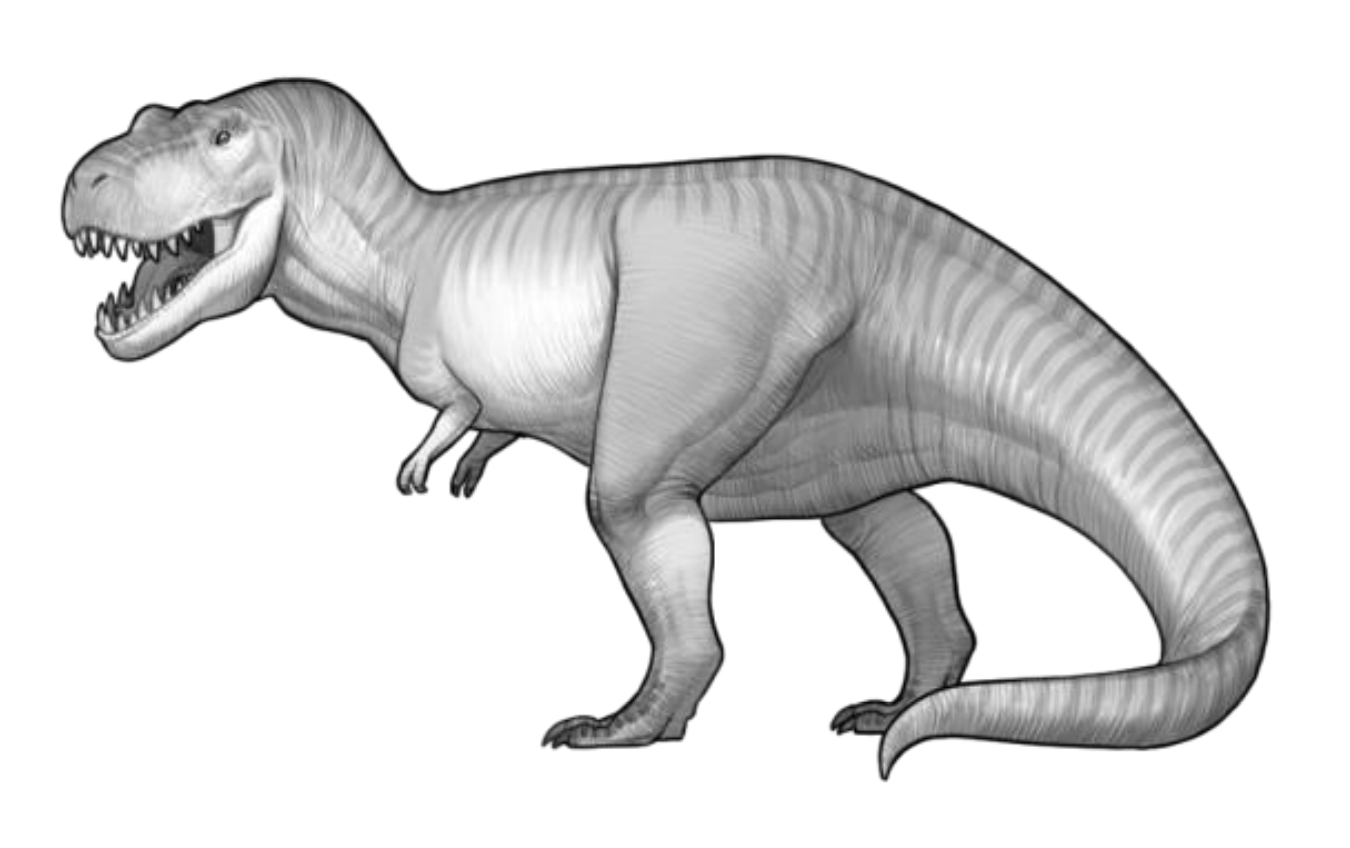
Tyrannosaur
A group of the theropods that evolved late in the history of dinosaurs and have reduced front limbs and robust skulls, teeth have serrated edges and are well adapted for puncturing and cutting flesh, have a tremendous biting force
Scavenging
Refers to the consumption of an already dead animal by a carnivore that did not play a part in killing it
Cololites
The fossilized gut contents, can help give info about diet