Exercise Physiology
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Name the 3 Macronutrients:
__________
__________
__________
CHO, FFA, CHON
1 kcal: amount of ______ needed to raise 1kg of ___ at __ degrees
Energy, H20, 15
1g CHO _kcal
4
These energy systems and nutrients are used for _____, ______ & ________.
Growth, repair, mobility
Energy sources are stored in form of ____.
ATP
___ & _____ - energy at rest; _____ - building blocks
CHO, FFA, CHON
Exercise - >___ than FFA
CHO
Formation of ___ provides ____ with a means of storing and conserving energy in a ____-energy compound.
ATP, cells, high
Name the 3 elements that form your nutrients:
_________
________
________
Carbon dioxide, nitrogen
Carbohydrates are converted into _______ and taken up by _____ & _____-glycogen
Glucose, muscles, liver
_______ is limited to ______kcal (32km run), and stored in cell _______.
Carbohydrates, 2000, cytoplasm
True or False: There are more stores of fat than carbs.
True
Name 2 types of Fats:
________
________
Glycerol, FFA
1g of C16H18O2 is equivalent to _kcal energy.
9
_______ of _______ _______ must be at a controlled rate, and is determined by the choice of fuel.
Rate of Energy release
__% to __% of human energy is degreaded to ____.
60, 70, heat
ATP Production:
ADP Biphosphate, 7.6
____-__ system is the simplest energy system made through ___________, and _______ _____
ATP-PCr, phosphocreatine, creatine kinase
ATP system during a sprint can only supply you for a maximum of __ seconds
15
_________ system is the breakdown (lysis) of glucose converted to ________-6-________
Glycolytic, glucose-6-phosphate
_ moles of ATP for glycogen, _ moles of ATP for glucose
2, 3
True or False: The Anaerobic system produces large amounts of ATP.
False
_________ allow the muscle to generate
_______ ______ involves cellular respiration and occurs in the _________.
Oxidative Phosphorylation, Mitochondria
________ ______ process by which the body __________ fuels with the aid of oxygen to generate energy
Cellular respiration, disassembles
What are the 3 Processes of the Aerobic system
___________
___________
___________
Glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle, Electron Transport chain
The Electron Transport Chain:
- __ combine with _ coenzymes
- ___ and ___ [Missing Info]
__________ of ___ contributes to muscle’s energy reserve…
Oxidation of Fat
_________ are the main energy sources
Triglycerides
Lipolysis = _______ + ____
Glycerol, FFA
____ diffuses to blood vessels & enter skeletal muscles.
FFA
______ ___________ wherein FFA cleaved into halbes the converted into acetyl CoA.
Beta oxidation
ATP produced from 1 moleculr of palmitic acid:
Fatty acid activaiton
B oxidation
Krebs cycle
Total = ______
-2, 35, 88, 129
The Aerobic system can supply a minimum of __ minutes of physical actiivty
20
____________ is when amino acids is converted into glucose
Gluconeogenesis
_______ __________ is changed to either _______ or ______ ___
Protein metabolism, pyruvate, acetyl CoA
Combustion calorie amounts:
Lab combustion - _______ kcal per gram
Body combustion - _______ kcal per gram
5.65, 5.20
True or False: Urince collection lasts for 12-24 hour period
True
____ a measure of the muscle’s maximal capacity to use oxygen…
VO2
_______ is the rate in which the body uses energy
Metabolic rate
The minimum amount of energy required to sustain essential physiological functions is called ________.
Basal Metabolic Rate
The primary criterion for measuring VO₂ max is the ________ or peaking of VO₂ despite increasing workload.
Leveling off
If no leveling off occurs, ________ VO₂ is used instead.
Peak
A lactate level of ________ mmol or ________ mg/100 mL of blood or higher indicates VO₂ max attainment.
8-10, 70-80
VO₂ max is considered reached when an individual attains more than ________% of their age-predicted maximum heart rate.
85
A respiratory exchange ratio (RER) greater than ________ is a criterion for VO₂ max measurement.
1.10
_______ activity indicates its ________ ______.
Enzyme, oxidative potential
True or False: The SDH enzyme is directly proportional to its O2 content
True
_____ ____ determines oxidative capacity.
Fiber type
_____ ______ have greater oxidative properties
Slow twitch
______ _____ are better for glycolytic energies
Fast twitch
_________ training enchances oxidative _____.
Endurance, power
Fiber rely heavily on ___ for ___ production
fat, ATP
True or False: Type 1 muscles fibers can become Type 2 while the vice verse CANNOT happen.
True
_________ happens in an insulated airtight chamber where body heat warm the water in which the ______ is recorded.
Direct Calorimetry, temperature
_________ ______ measured using respiratory gases where in gas exchange happens (CO2 and 02)
Indirect Calorimetry
______ amount of O2 used depend on the type of fuel oxidized, measures the amount of __ released (VCO2) & __ (VO2) consumed.
Respiratory Exchange Ration, CO2, O2
______ is the oxygen debt mechanism since O2 is required for work
Post-Exercise Oxygen consumption
In th Excess Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption:
Fast component of the curve (Immediate Drop): __ required to rebuild ___ and __
Slow component of the curve: _________ tissues
02, ATP, PCR
New Theory:
__ borrowed [Missing INFO]
________ point at which blood lactate begins to accumulate [Missing INFO]
Lactate treshold
Add the graphs | Before LT (Aerobic) After LT (Anaerobic)
1.5m/s Anaerboic | Oxygen Blood Lactae 4ml moles
Range of thr Activities of Daily Living: _______- ________kcal
1800-3000
True or False: The younger the person the higher BMR this person has
True
A.K.A as the maximal oxygen uptake in the body
VO2 max
True or False: Intensity = O2 consumption unless VO2 max is achieved, oxygen consumption is no longer efficient and body switches to anaerobic respiration.
True
Give 3 causes of Fatigue:
__________
__________
__________
Energy system, accumulation of metabolic by products, fiber contractile mechanisms
Neuromuscular causes of fatigue…
Reduced synthesis of ___
Hyperactive/hypoactive ________
Competitive _______
More __+ leakage
Ach, cholinesterase, inhibition, K
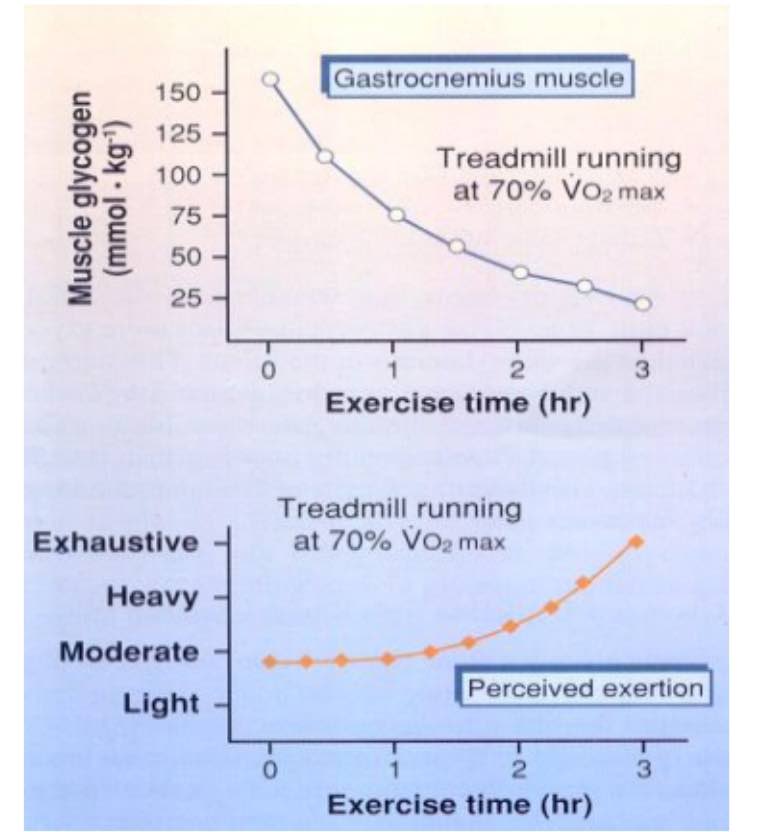
Muscle glycogen levels, exercise time, Borg’s rate of perceived exertion (Type 1)
1
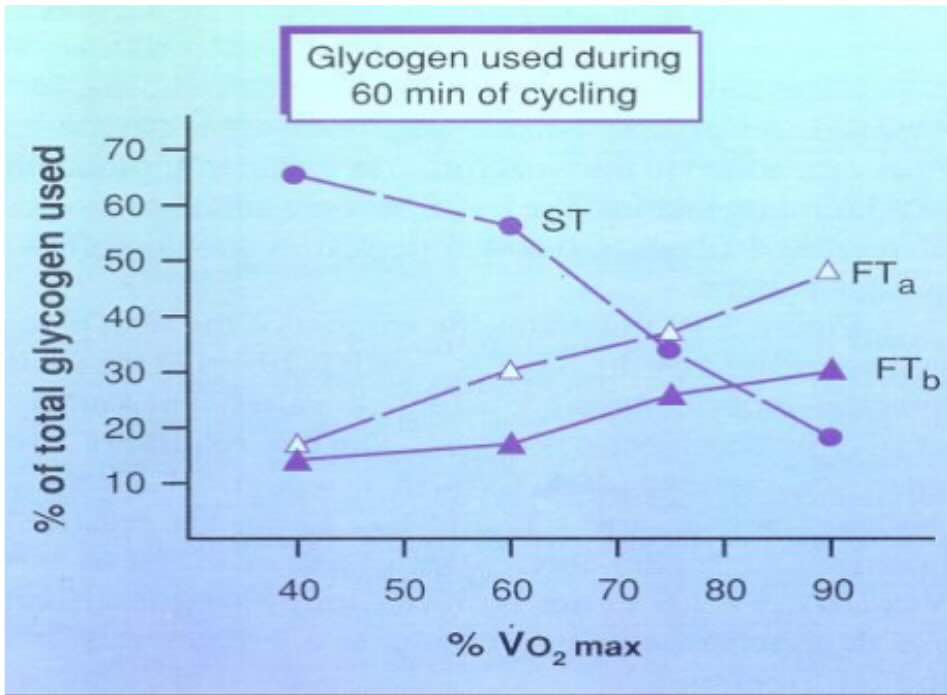
True or False: Submaximal exercises uses slow twitch muscle fibers and anaerobic respiration
False
True or False: When you are running uphill you are utilizing fast-twitch muscles while running downhill you use slow-twitch muscles.
True
The amount of fatigue is directly proportional to its __ _______.
pH levels
_______ adaptations: Increased _______ content….
Shuttles __ to the _______
Gives __ fibers their red color
Increases 75-80%
Aerobic, Myoglobin, O2, mitochondria, ST
________ adaptations: ST grows 7-22%
Fibers vary according to the sport
Critical in events of great power and strength
______ supply increases during endurance training as much as 15%
Muscle, Capillary
______ allow athletes to better tolerate subsuquent demands.
Carbohydrates
__ are close to the mitochondria and have increased ______ for B oxidation
Fats, enzymes