quizlet: jessiebeedmd Reactive Lesions: Physical & Chemical Injuries of Oral Cavity
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
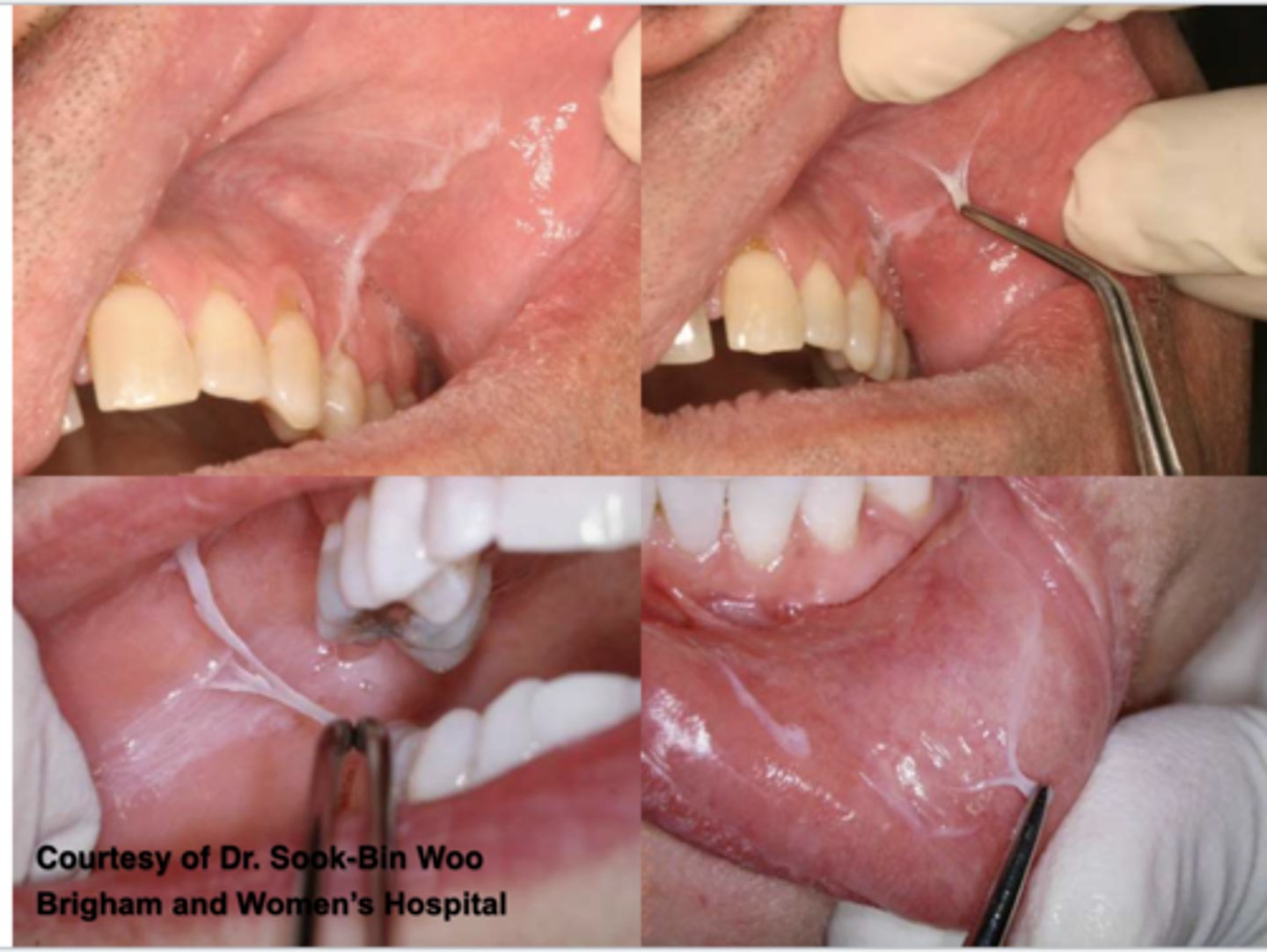
What does the following describe?
-inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia
- tumor-like hyperplasia associated w/ flange of poorly fitting denture
epulis fissuratum
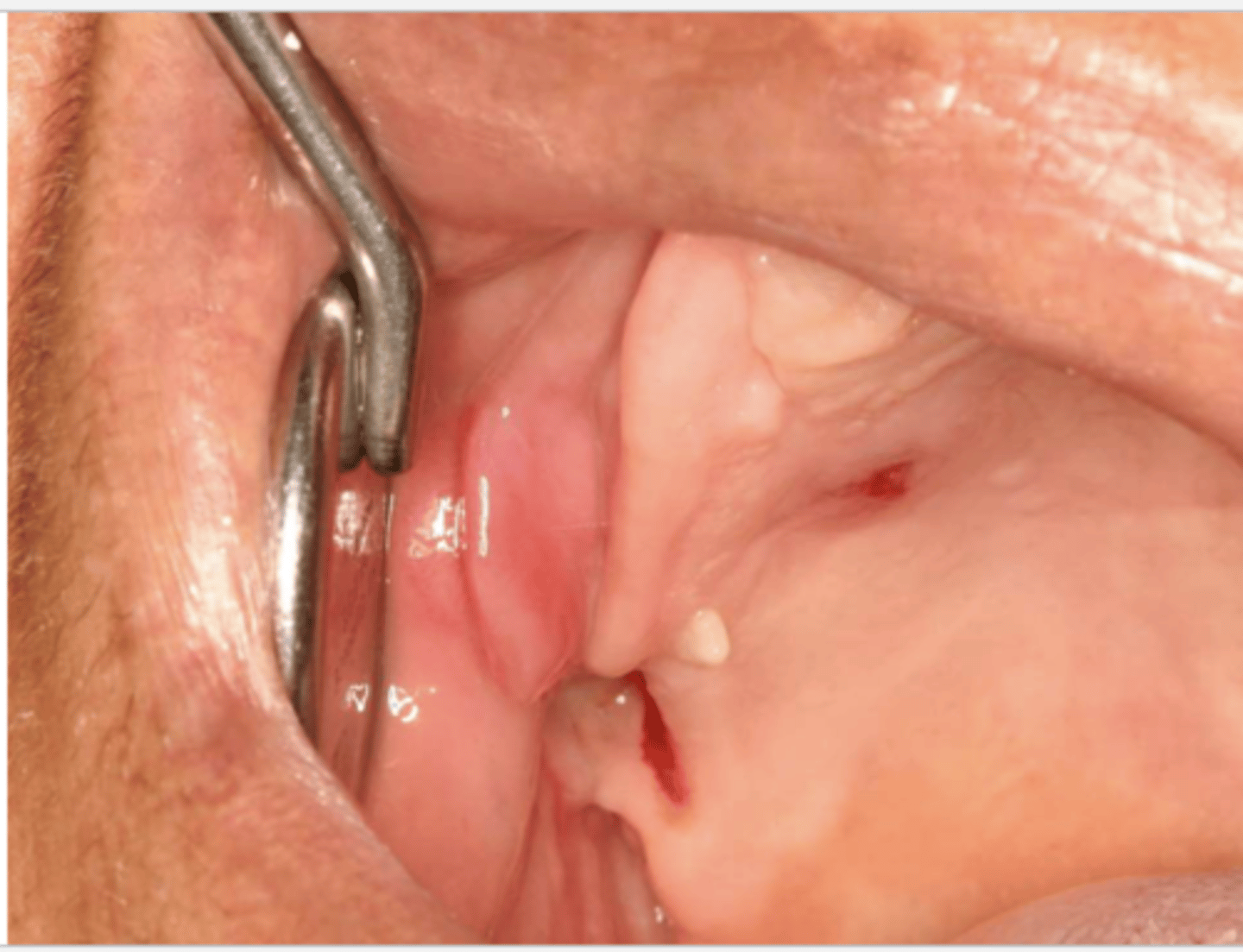
What do the following clinical features describe?
-single or multiple folds of hyperplastic tissue in alveolar vestibule
-fibroepithelial poly/leaf-like denture fibroma may be seen along palatal mucosa
epulis fissuratum
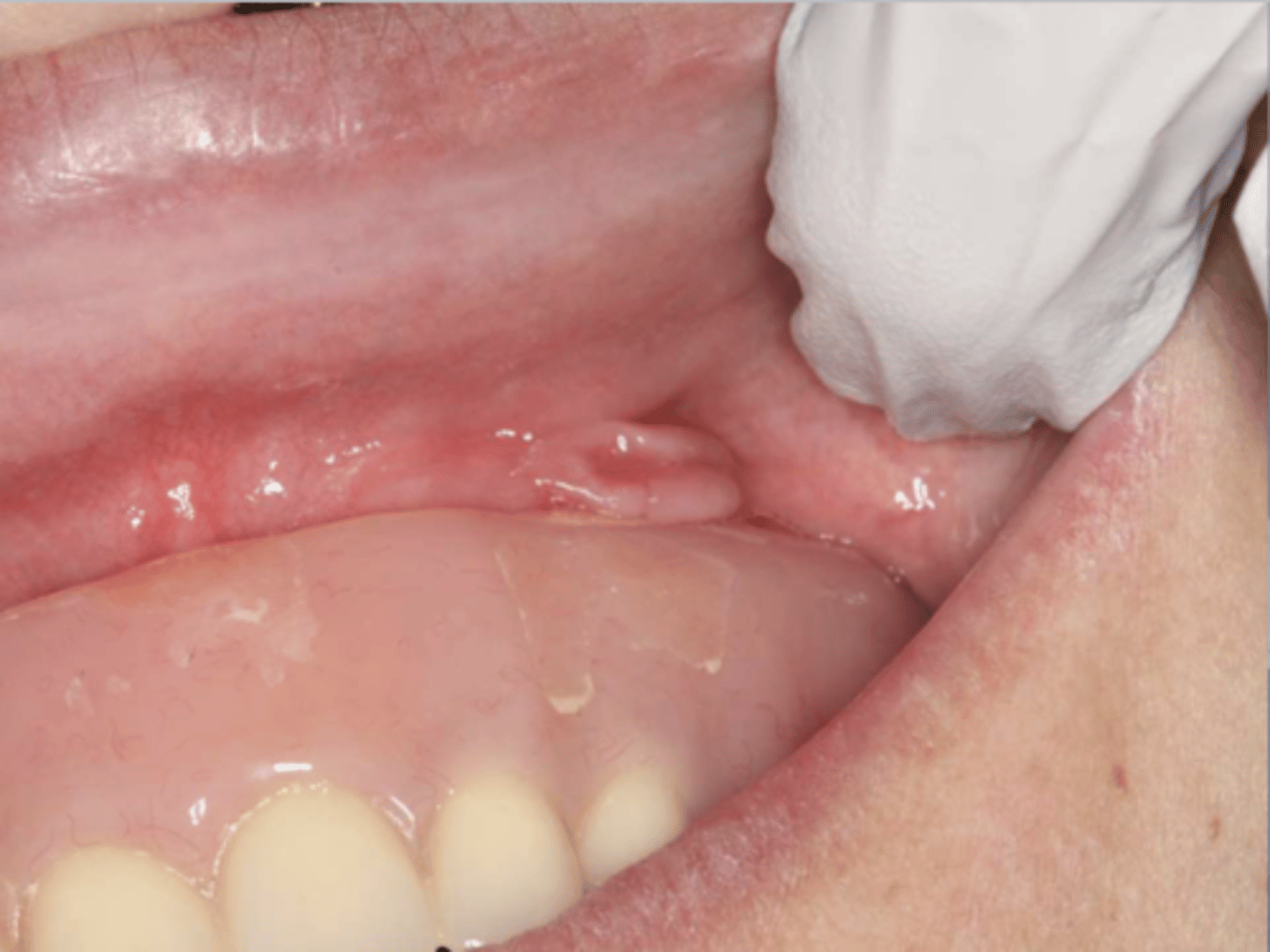
What do you suspect?
epulis fissuratum
what is an epulis?
tumor of gingiva or alveolar mucosa
*not interchangeable w/ epulis fissuratum (this is a type of epulis)
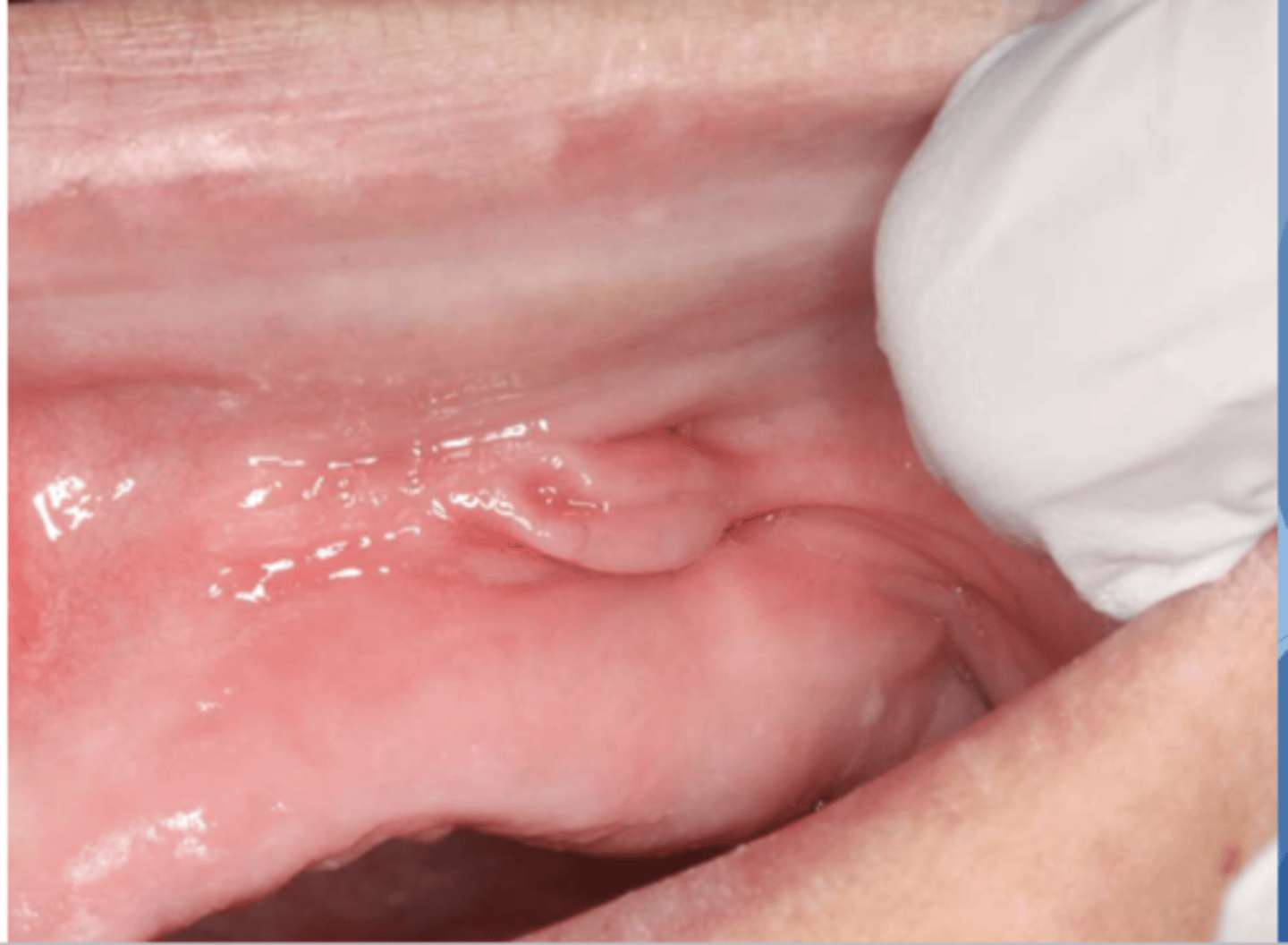
Pt complains that it hurts to wear their denture. What do you suspect?
epulis fissuratum

Patient reported that their lower denture irritates their mouth. What do you suspect?
epulis fissuratum

what do you suspect?
epulis fissuratum
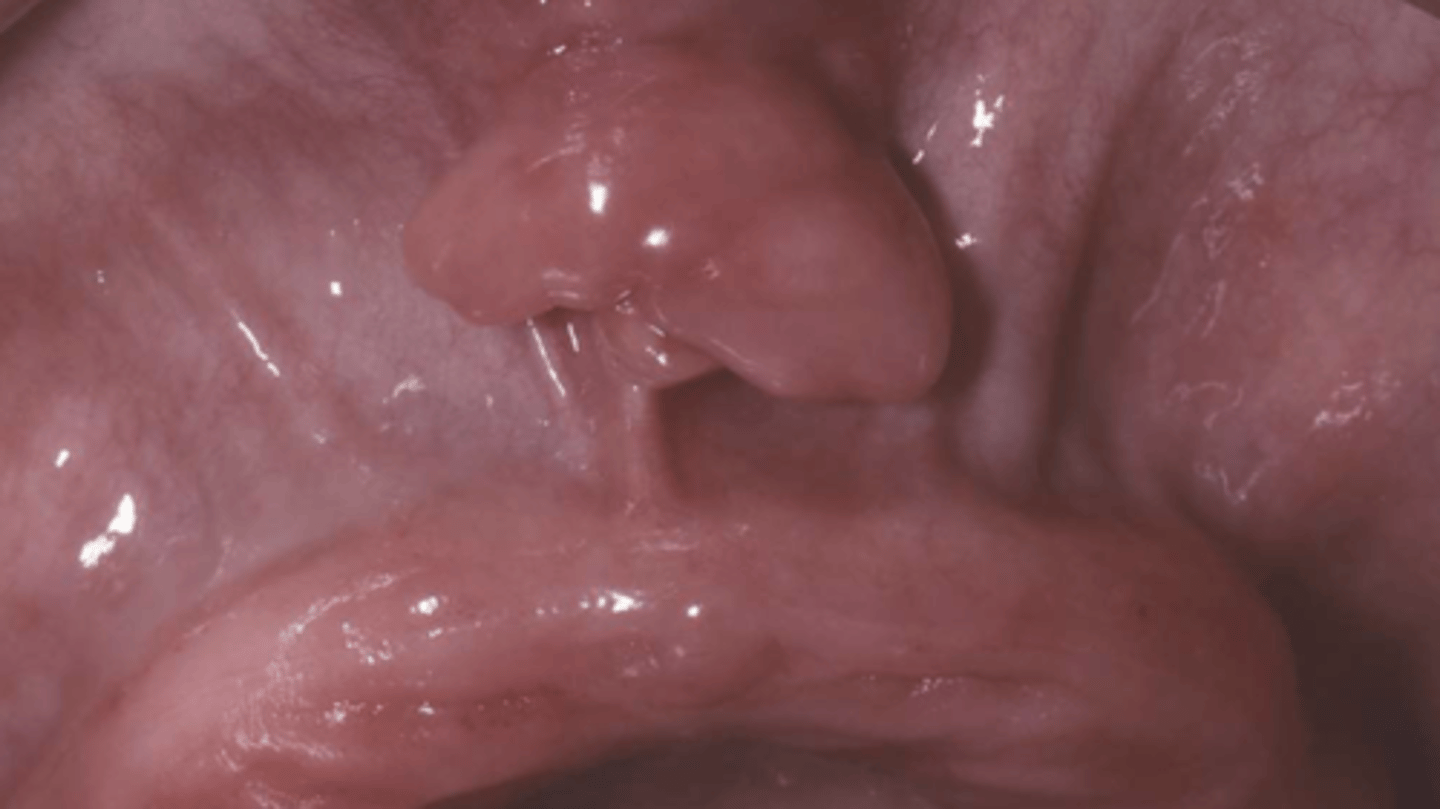
Patient reported that they stopped wearing their dentures because they were painful. What do you suspect?
epulis fissuratum
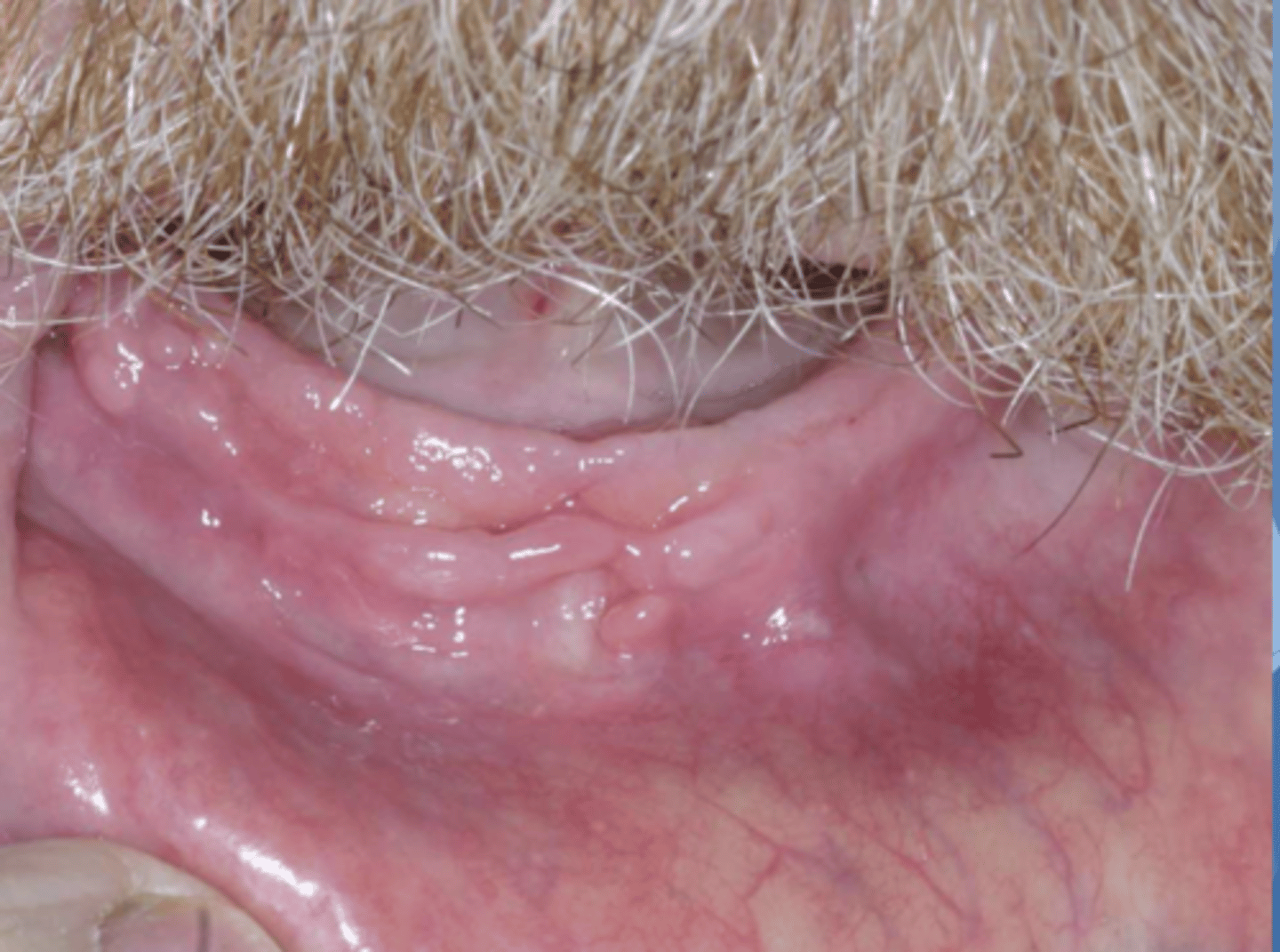
Patient reported that wearing his denture causes pain. What do you suspect?
epulis fissuratum
the following describe the histopathological features of what?
-hyperparakeratosis or hyperorthokeratosis
-papillary hyperplasia &/or pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia
-hyperplasia or connective tissue
epulis fissuratum
how is epulis fissuratum treated? (2)
-surgical removal
-remake denture to prevent recurrence
what does the following describe?
-reactive tissue growth
-associated w/ poorly-fitting dentures, poor denture hygiene, &/or continuous denture wear
inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
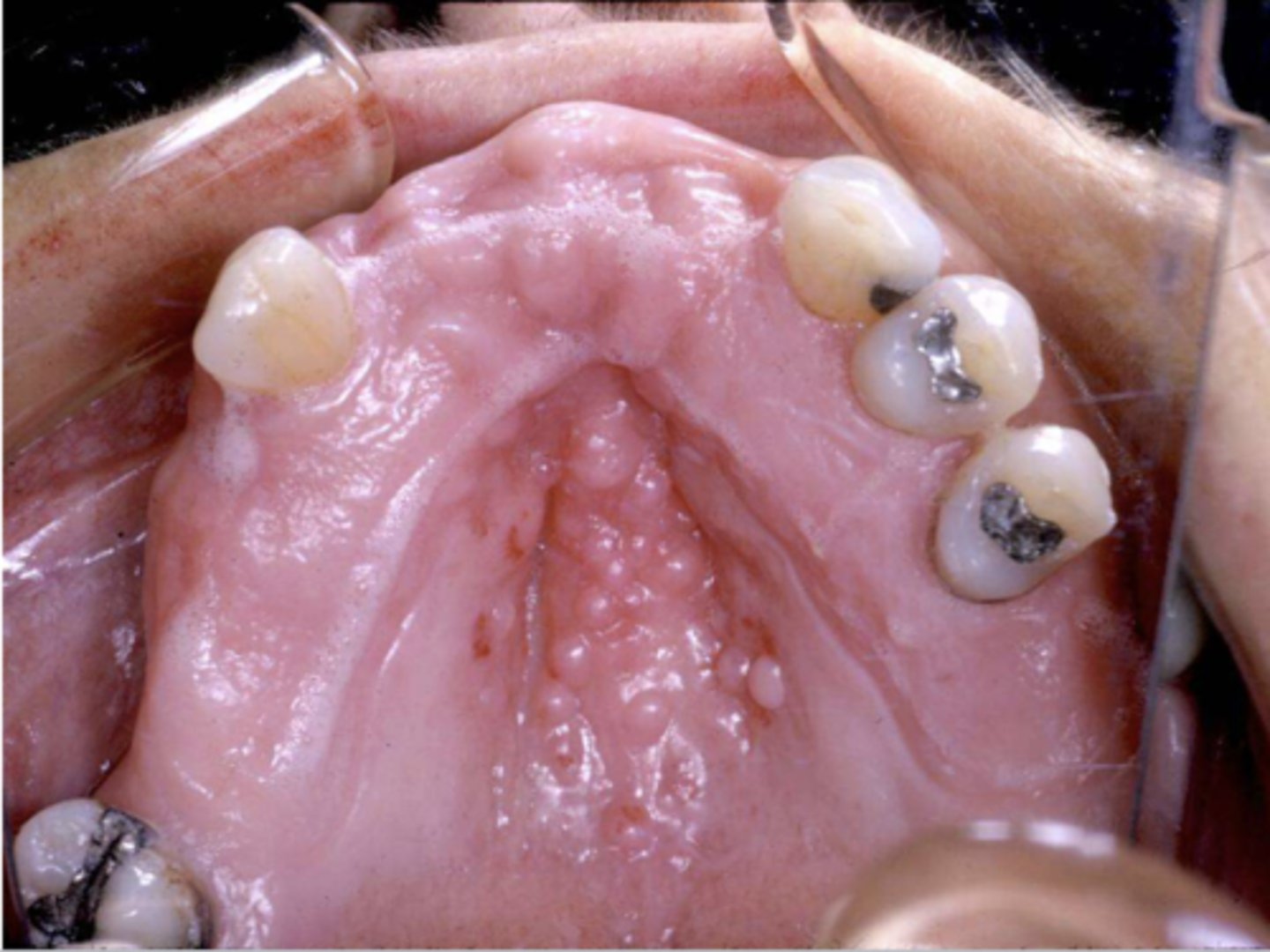
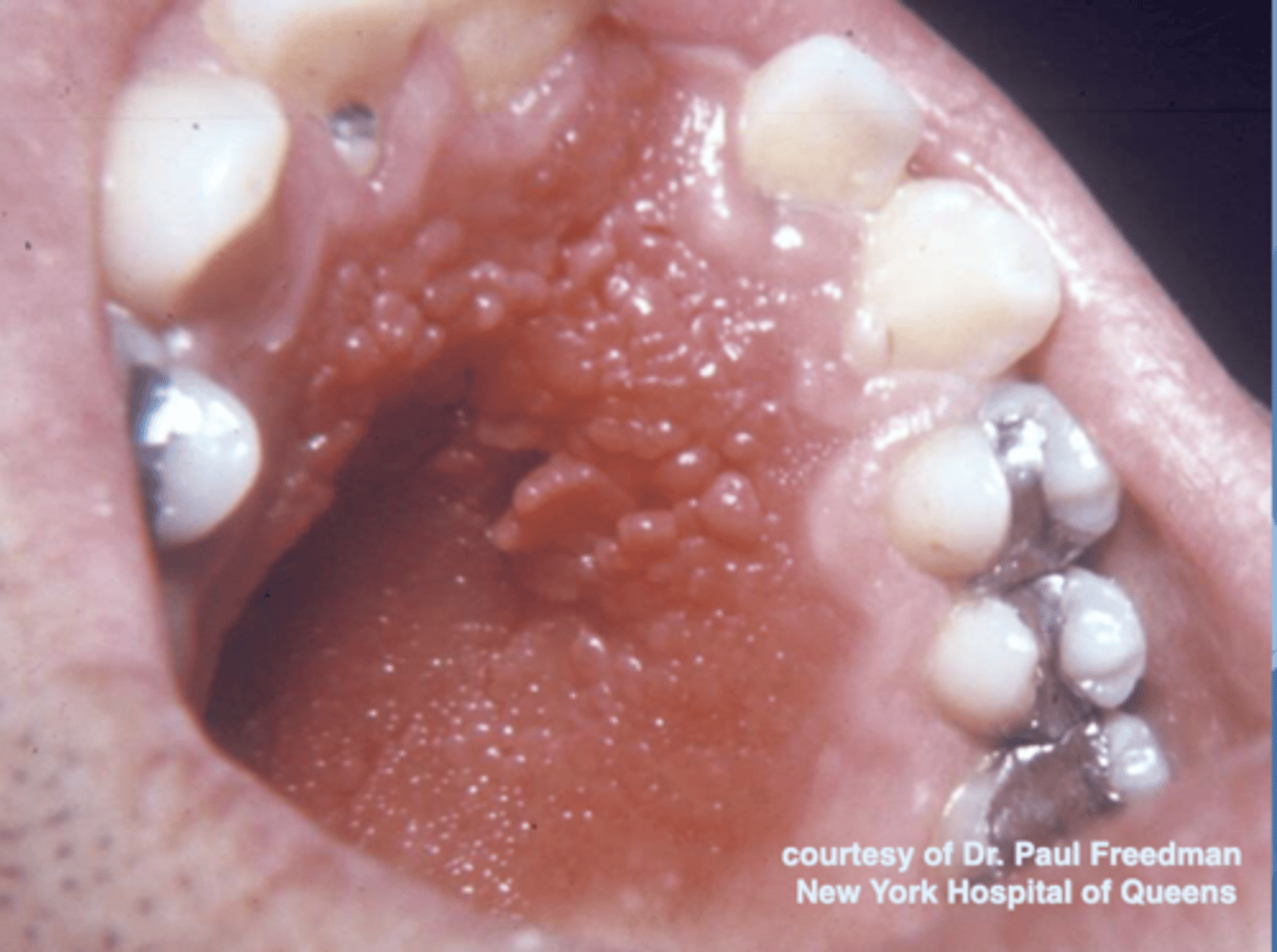
what are these clinical features of?
-hard palate beneath denture base
-pink or pebbly mucosa
-erythema --> suggests secondary candidal infection
inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
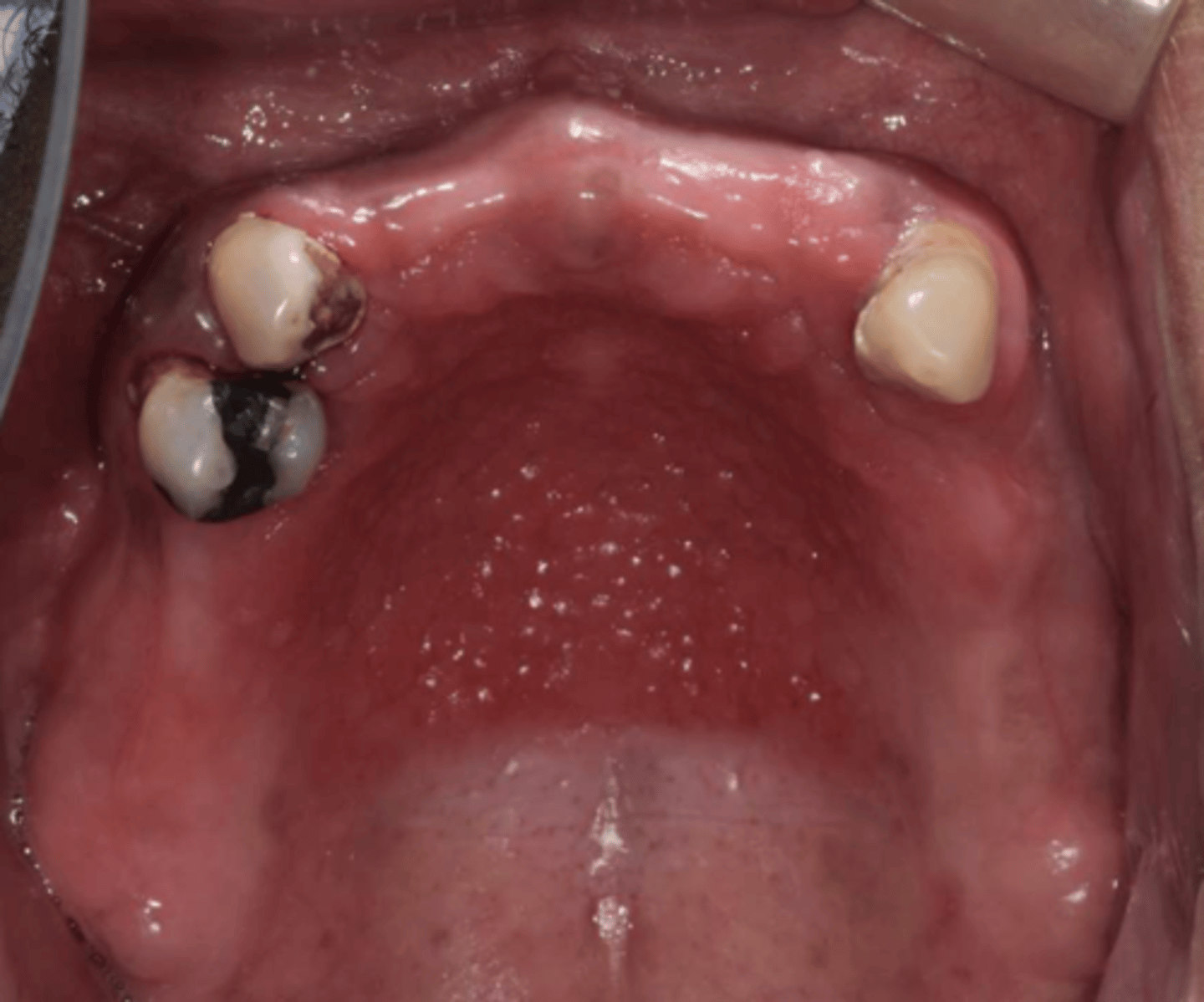
Patient has an RPD. What do you suspect?
inflammatory papillary hyperplasia w/ secondary candidal infection
*can tell pt also has candidiasis b/c of erythema
When the patient removed their complete maxillary denture, you see this. They reported wearing their denture to continuously throughout the day & night. What do you suspect?
inflammatory papillary hyperplasia w/ secondary candidal infection
*can tell pt also has candidiasis b/c of erythema
what do you suspect?
inflammatory papillary hyperplasia w/ secondary candidal infection
*can tell pt also has candidiasis b/c of erythema
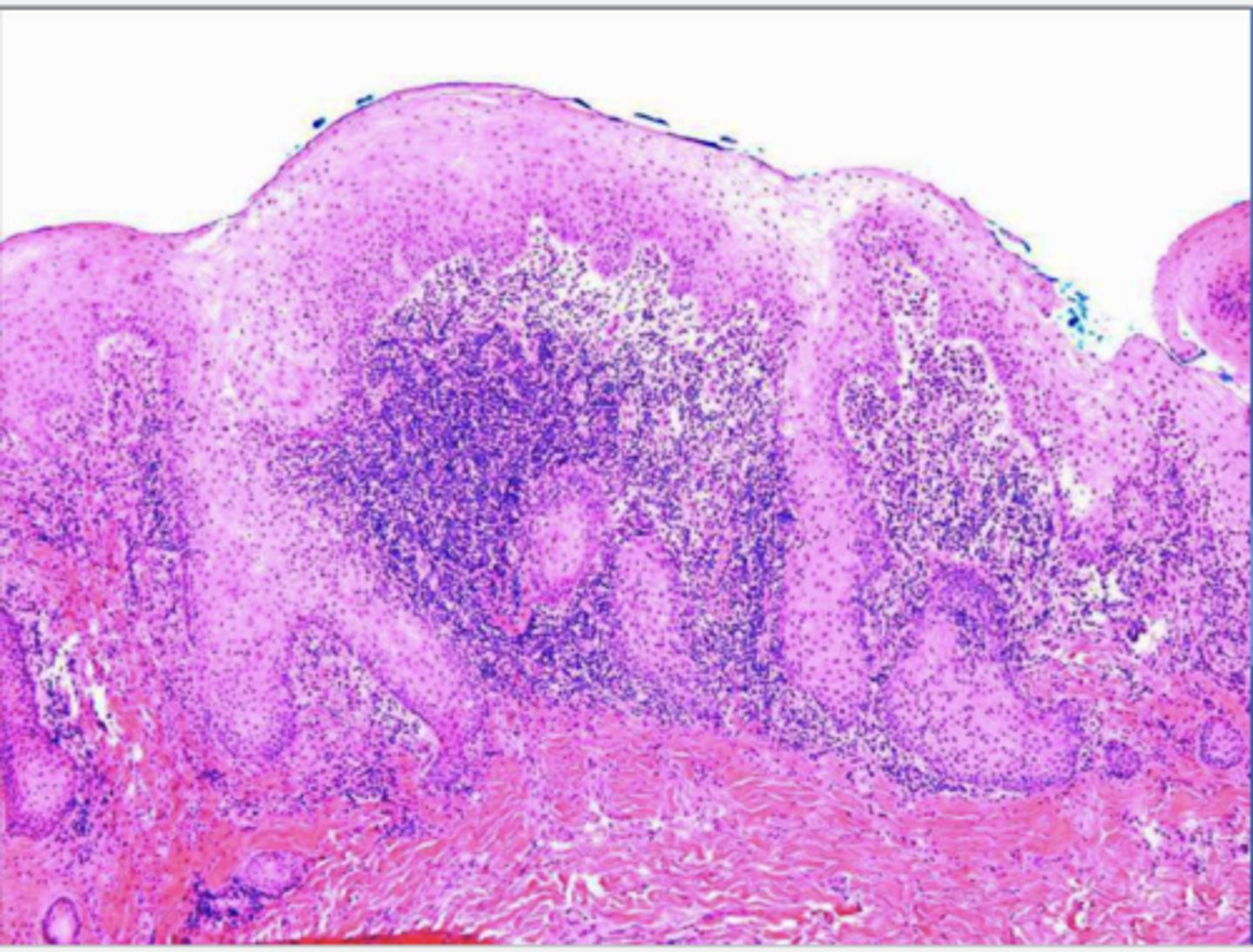
The following describes the histopathological features of what?
-papillary growths on surface
-may show pseudoepithliomatous hyperplasia
-sialadenitis
inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
True or False: Mild cases of inflammatory papillary hyperplasia resolve with removal of denture
True
how is inflammatory papillary hyperplasia treated? (3)
-mild cases --> resolved w/ removal of denture
-established cases --> excision of hyperplastic tissue + relining/refabrication of denture
-antifungal therapy if needed
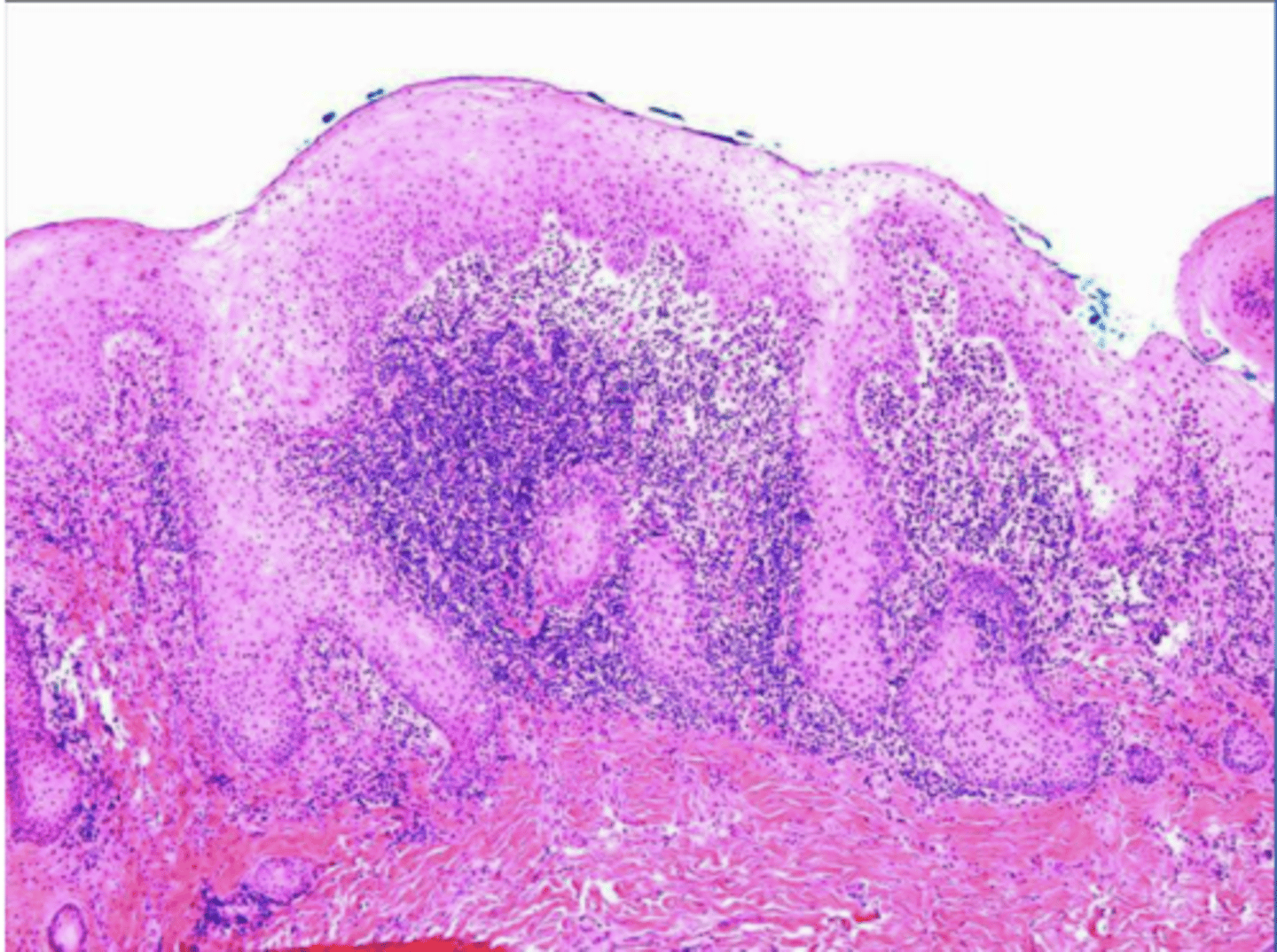
why can an histological image of pseudoepithliomatous hyperplasia be mistakenly diagnosed as squamous cell carcinoma?
histo of epulis fissuratum has pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia that resemble cancer b/c rete pegs running thru the horizontal plane & we may be unable to see connection to surface due to the orientation of the section we're viewing --> so it looks like de novo formation of epithelia w/ CT = suspicion for cancer
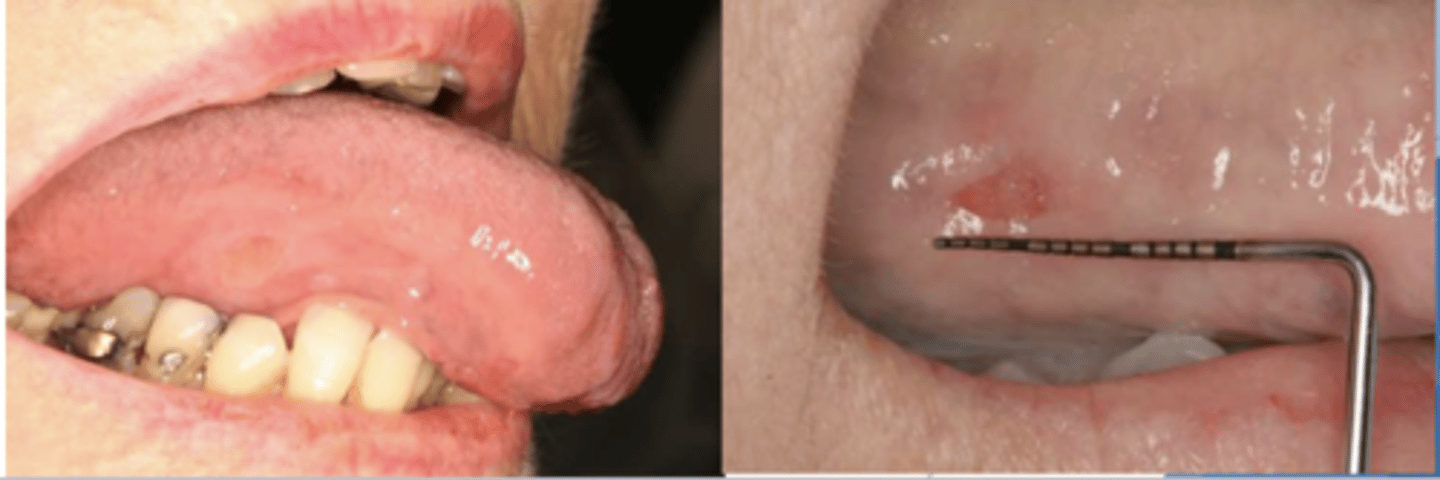
what causes traumatic ulcers?
acute injury
-biting (most common)
-commonly occurs on the tongue, buccal mucosa, & lower lip
the following describes the histopathology of what?
-ulcerated surface w/ fibrin membrane
-granulation tissue
-variable amounts of inflammation
traumatic ulcers
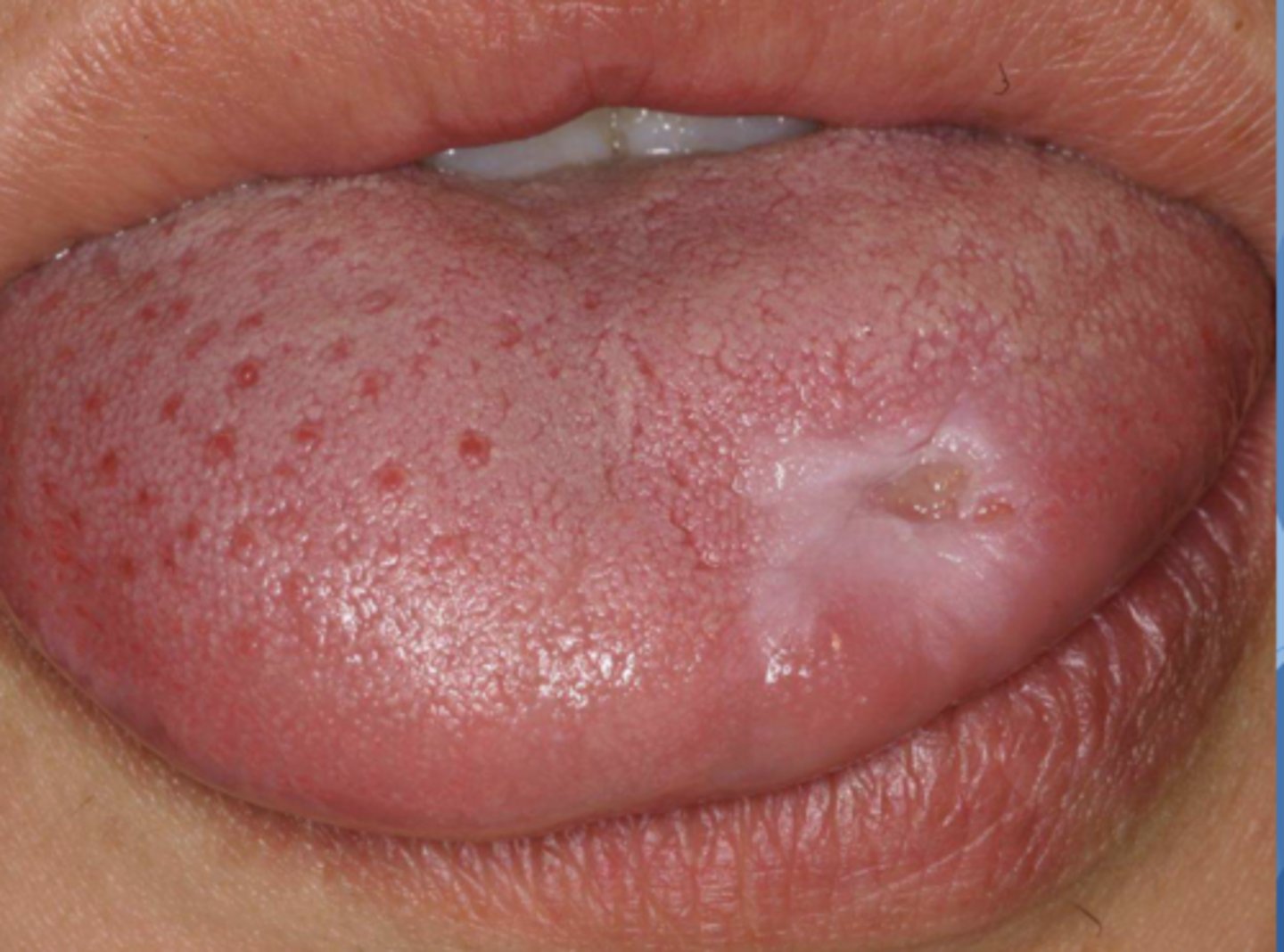
Patient reported that they bit the side of their tongue. What do you suspect?
traumatic ulcer
what does the following describe?
-ulceration
-history of recent dental treatment
-often secondary to inferior alveolar nerve block
anesthetic-associated lip bite
* = type of traumatic ulcer
True or False: Traumatic Ulcerative Granuloma is a granuloma by definition
False ==> not a true granuloma
What does the following describe?
-slow-healing, penetrating ulcer that takes weeks - months to resolve
-may be mistaken for malignancy
traumatic ulcerative granuloma
True or False: Traumatic ulcerative granuloma has a male predilection
True
Where is the most common location for traumatic ulcerative granuloma?
tongue
what can help distinguish traumatic ulcerative granuloma from aphthous ulcers & squamous cell carcinoma?
traumatic ulcerative granuloma often surrounded by white hyperkeratotic rim
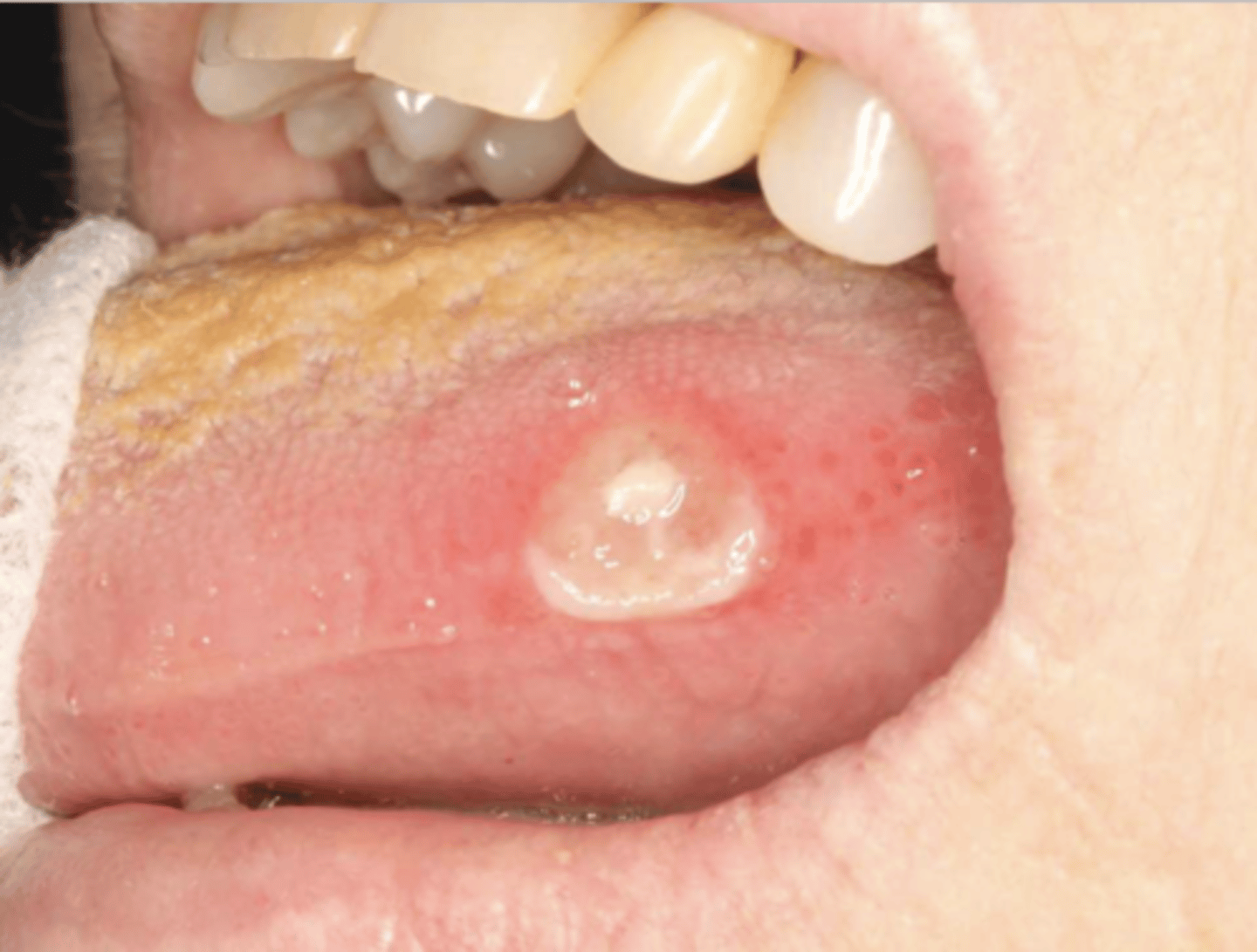
What do you suspect? Patient suspected biting their tongue repeatedly over the past month
traumatic ulcerative granuloma

What do you suspect? Patient suspected biting their tongue repeatedly over the past month
traumatic ulcerative granuloma
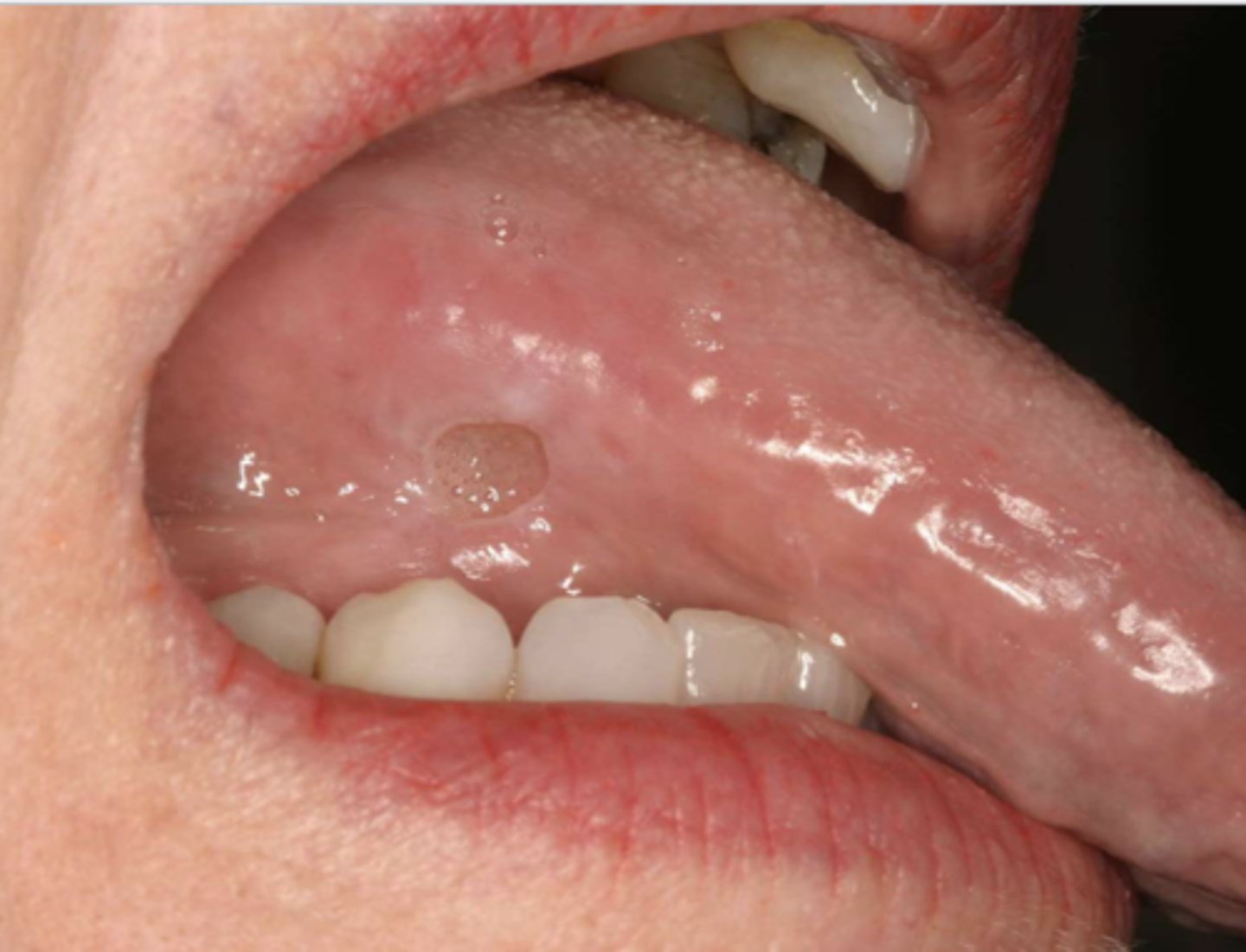
Patient reported that they accidentally burned their tongue on a cigarette and have since been repeatedly accidentally biting on the lesion. What do you suspect?
traumatic ulcerative granuloma
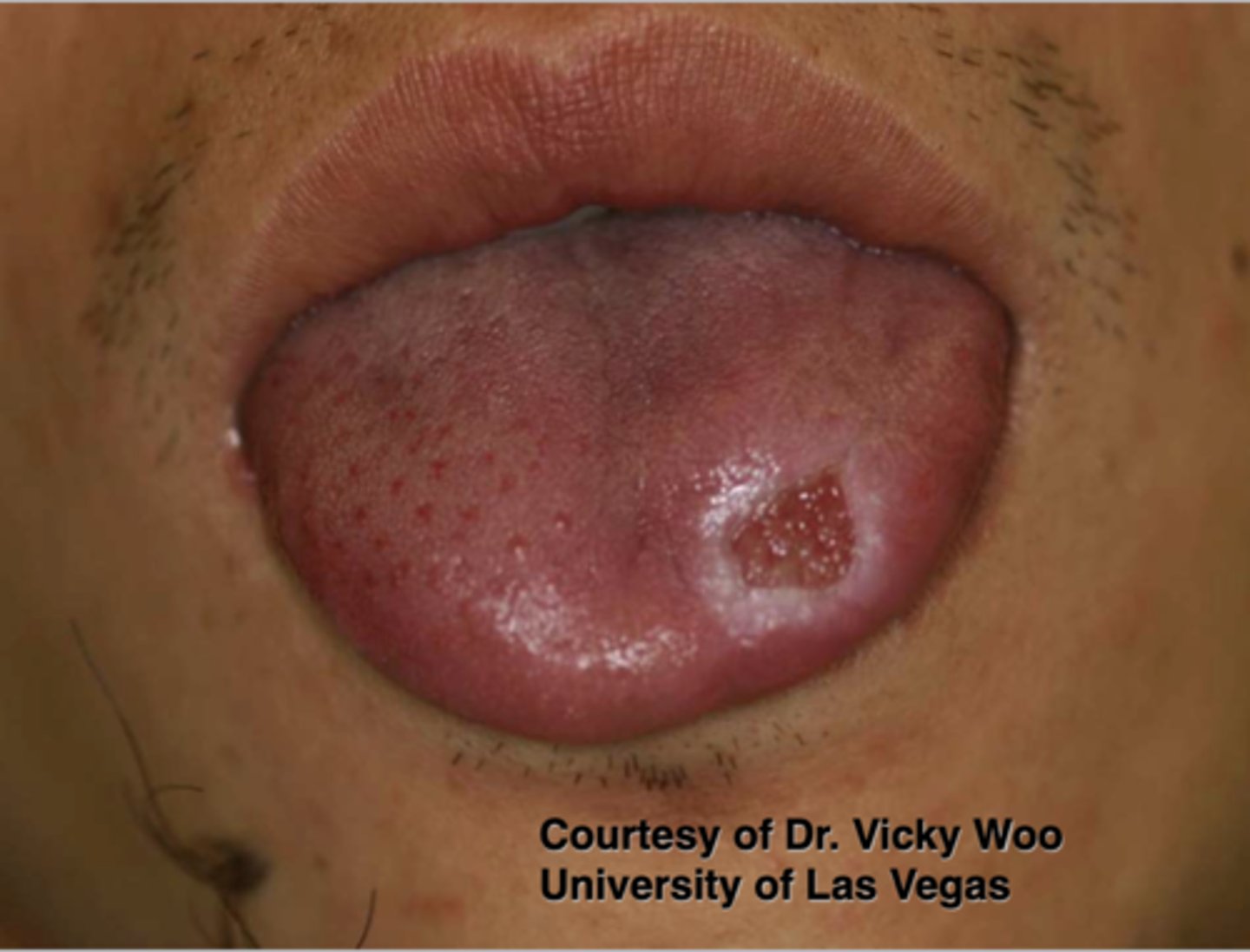
Patient reportedly bites their tongue in the same spot a few times per week. What do you suspect?
traumatice ulcerative granuloma
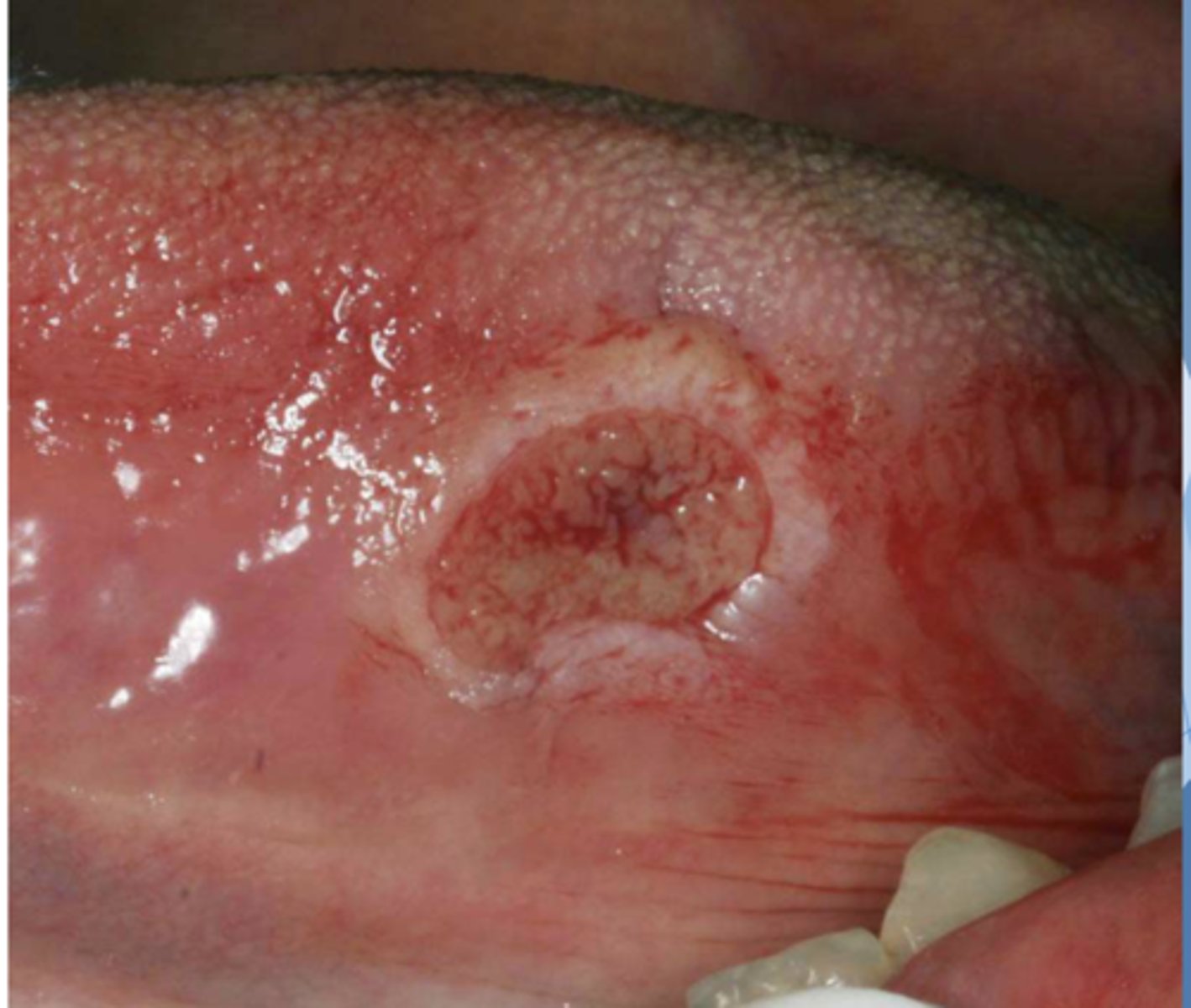
Patient reported biting their tongue for the 5th time this week. What do you suspect?
traumatic ulcerative granuloma
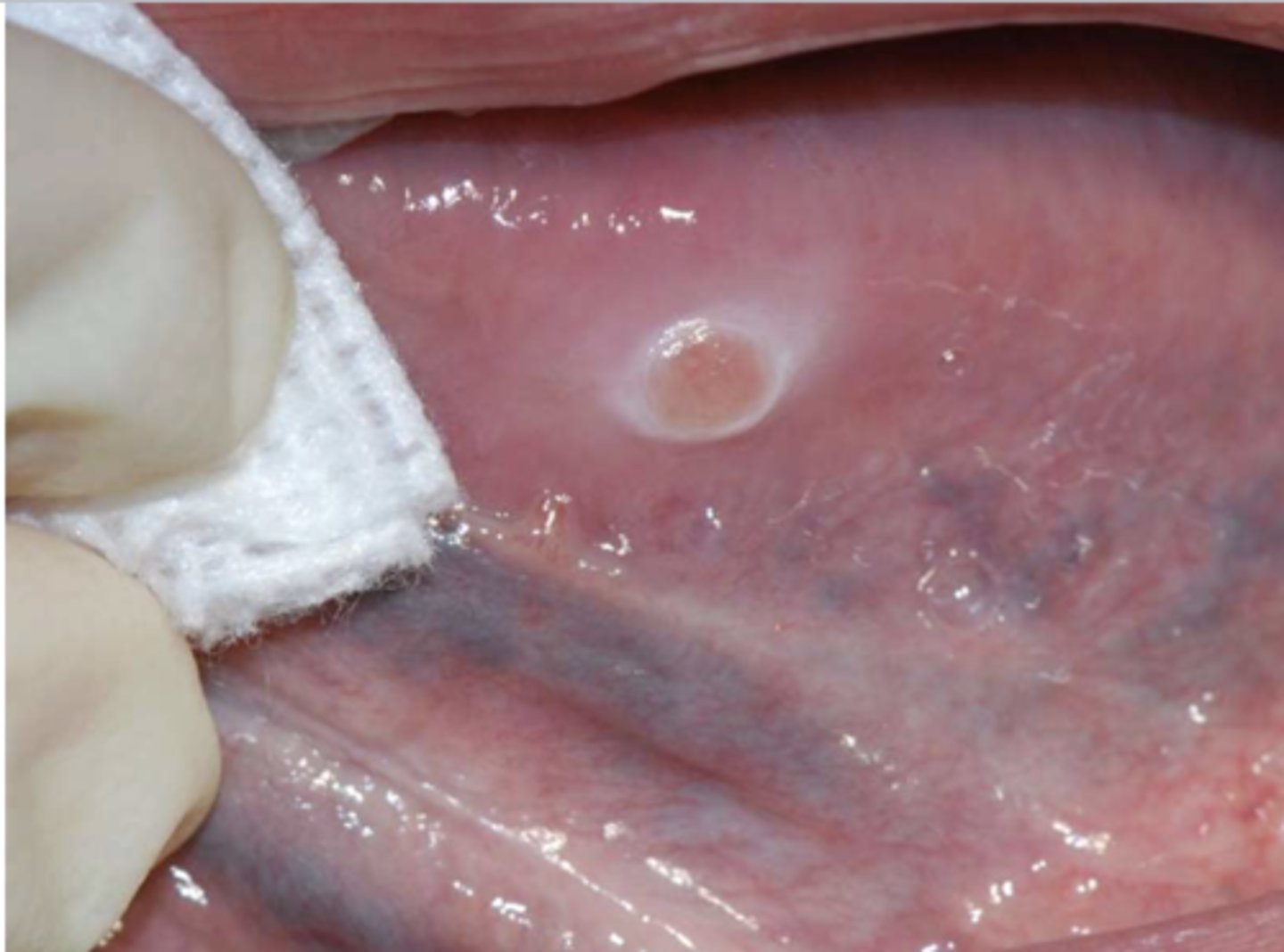
Patient reported that they accidentally burned their tongue a few weeks ago and the sore gets irritated every time they chew. What do you suspect?
traumatic ulcerative granuloma
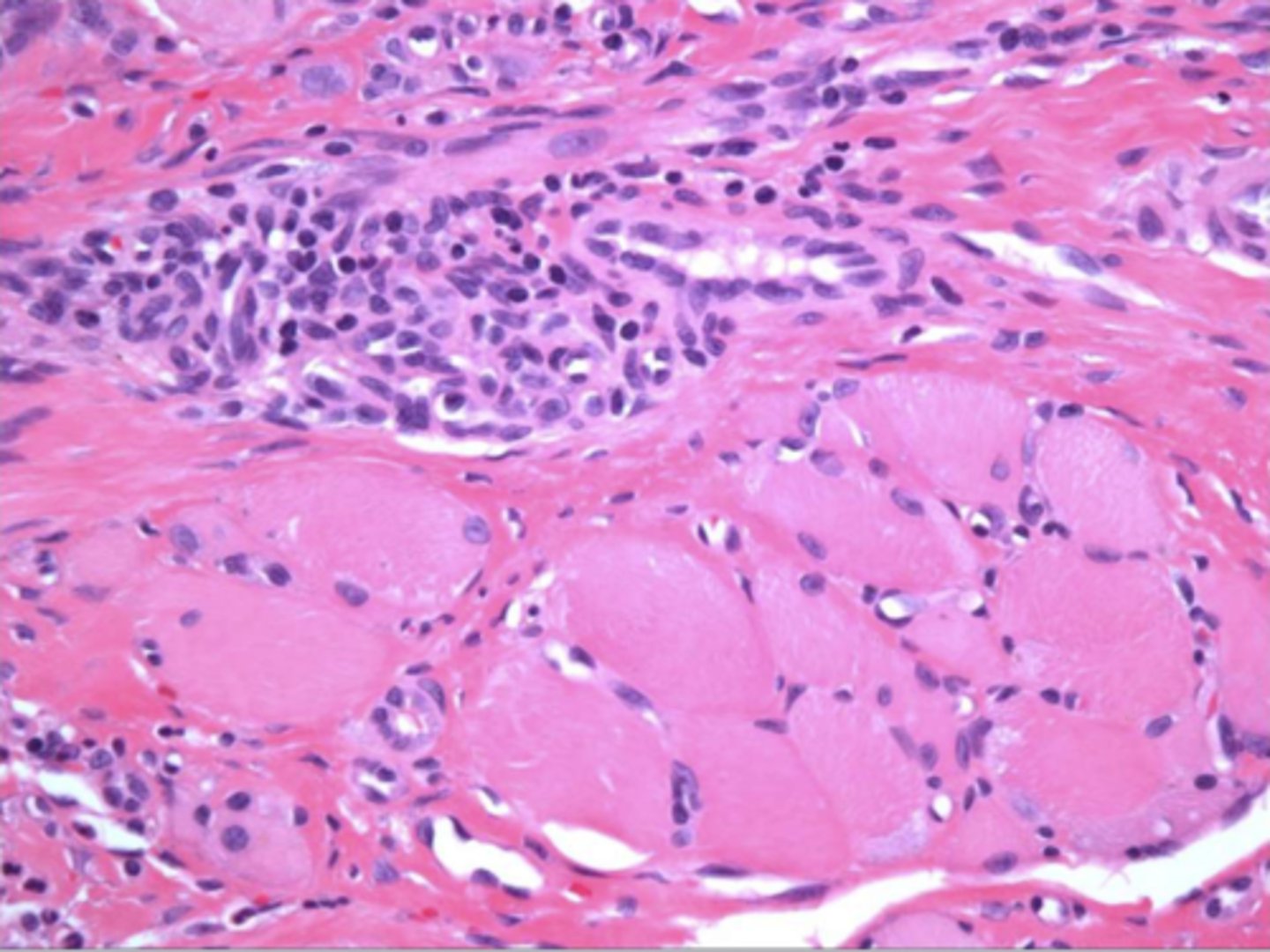
the following describe the histopathological features of what?
-numerous eosinophils
-inflammation of skeletal muscle
-granulation tissue
traumatice ulcerative granuloma
how is traumatic ulcerative granuloma treated? (3)
-remove irritant
-excision of excess tissue if necessary
-topical &/or intra-lesional steroids
what does the following describe?
-hyperplastic epithelium of mouth, skin, & genitalia
-lipid-laden macrophages beneath epithelium
-papillary, not but associated w/ HPV
verruciform xanthoma
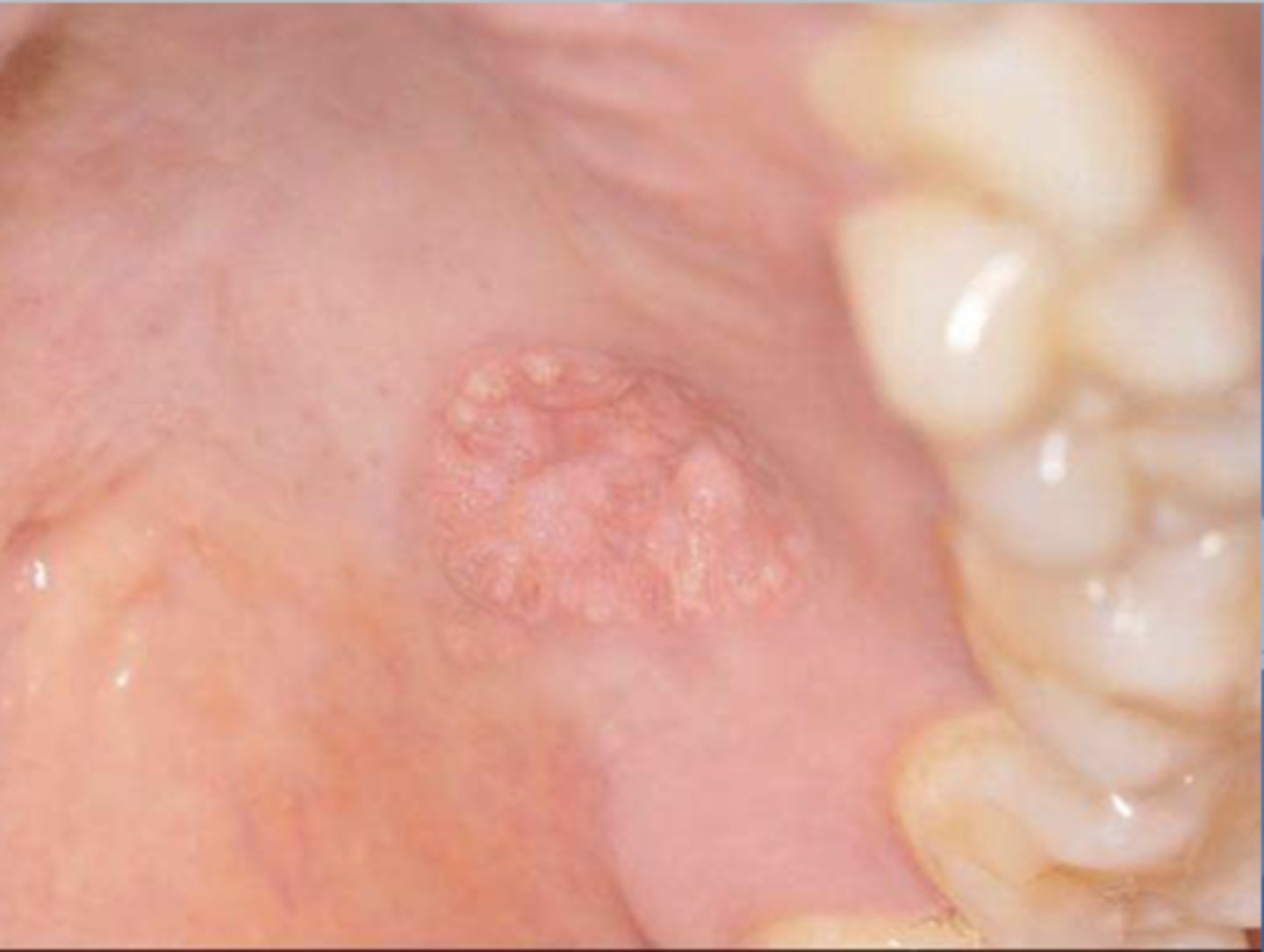
the following are the clinical features of what?
-50% of oral lesions on the gingiva or alveolar mucosa
-may be pink, white, red, yellow, or orange
-well-demarcated verrucous mass
-may resemble squamous papillomas or early carcinomas
verrucifom xanthoma
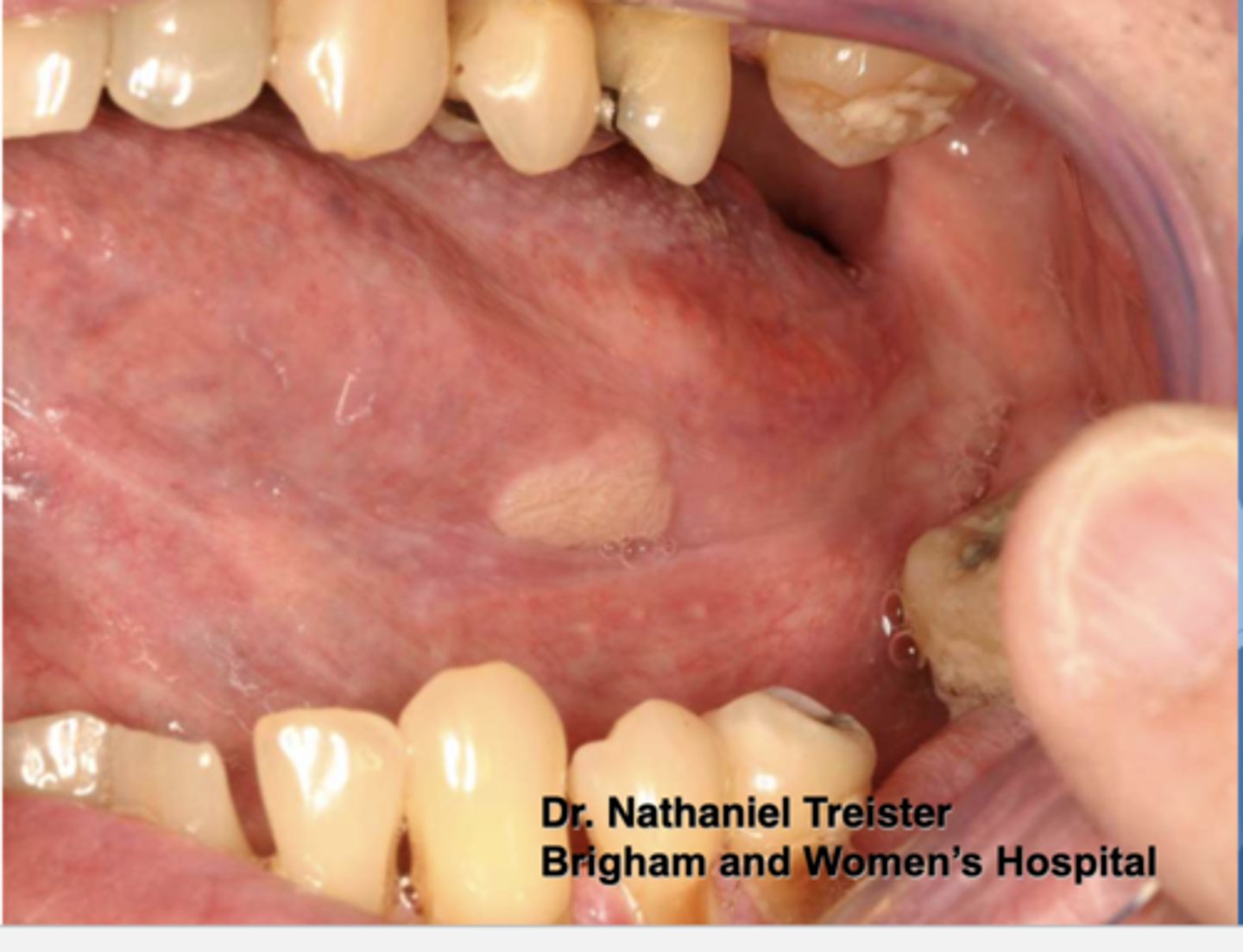
Pt presents with this papillary lesion but is negative for HPV. What do you suspect?
verruciform xanthoma
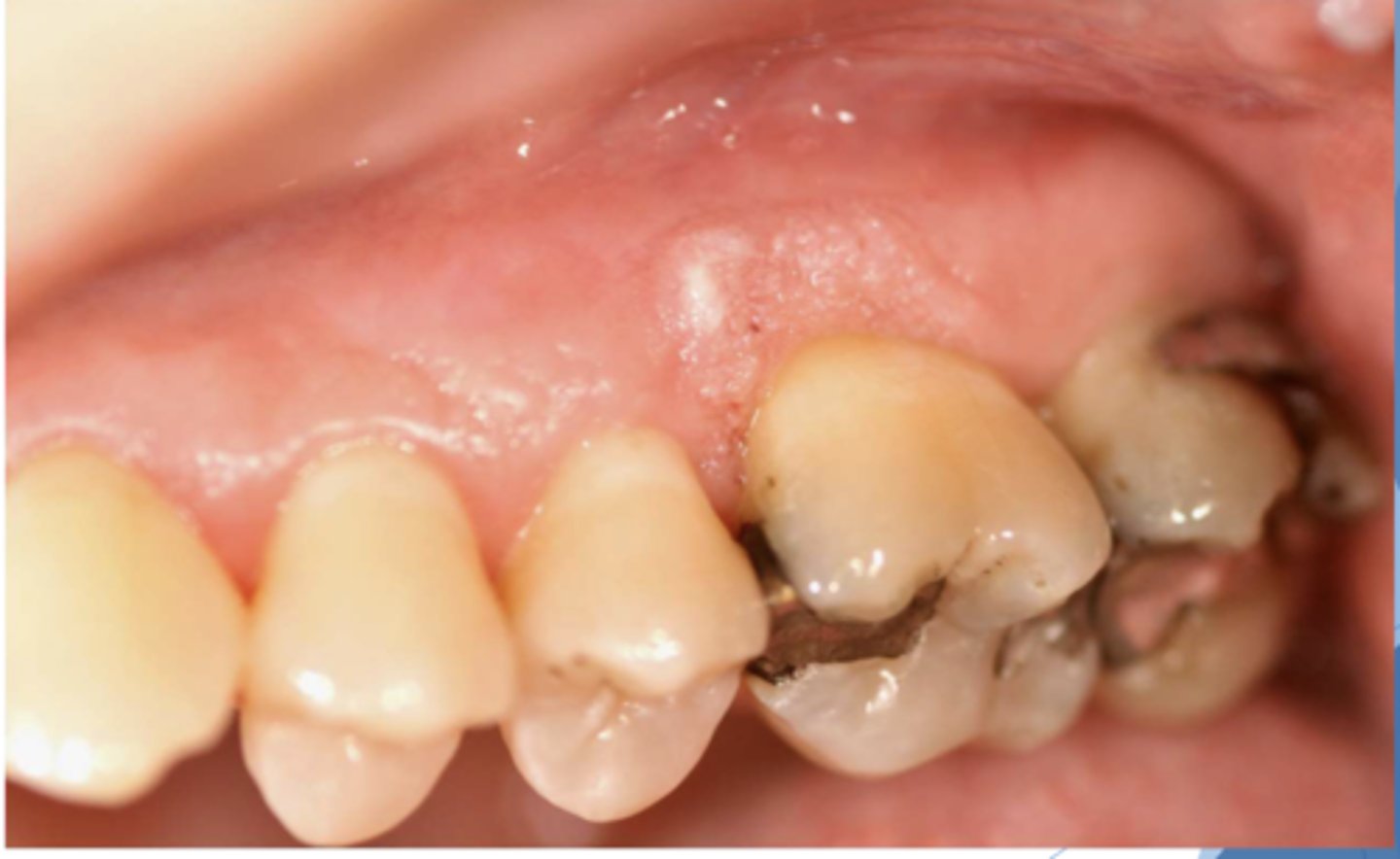
Patient negative for HPV. What do you suspect?
verruciform xanthoma

Patient negative for HPV. What do you suspect?
verruciform xanthoma
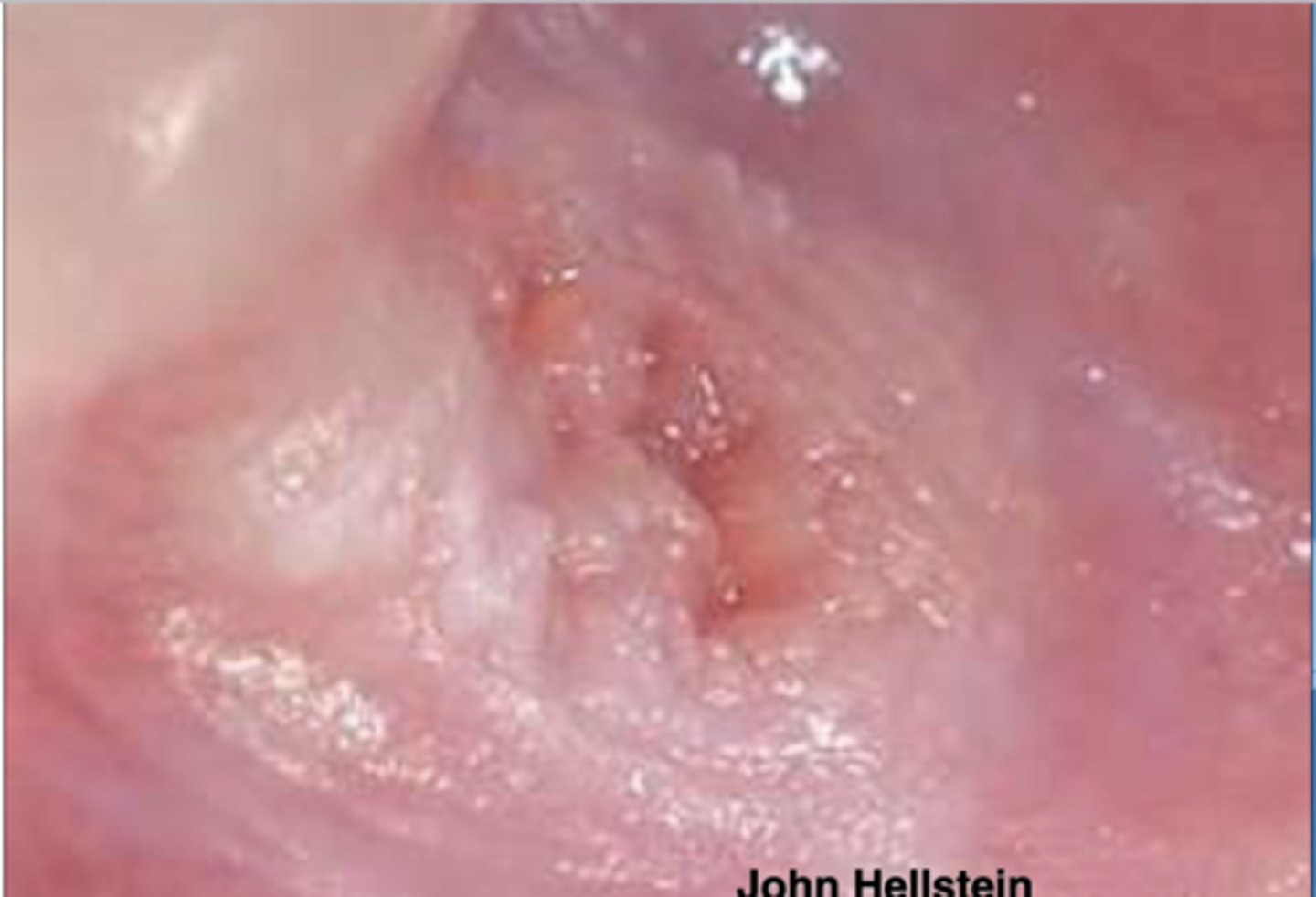
Patient presents with this wart-like lesion on a portion of their oral mucosa. HPV has been ruled out. What do you suspect?
verruciform xanthoma
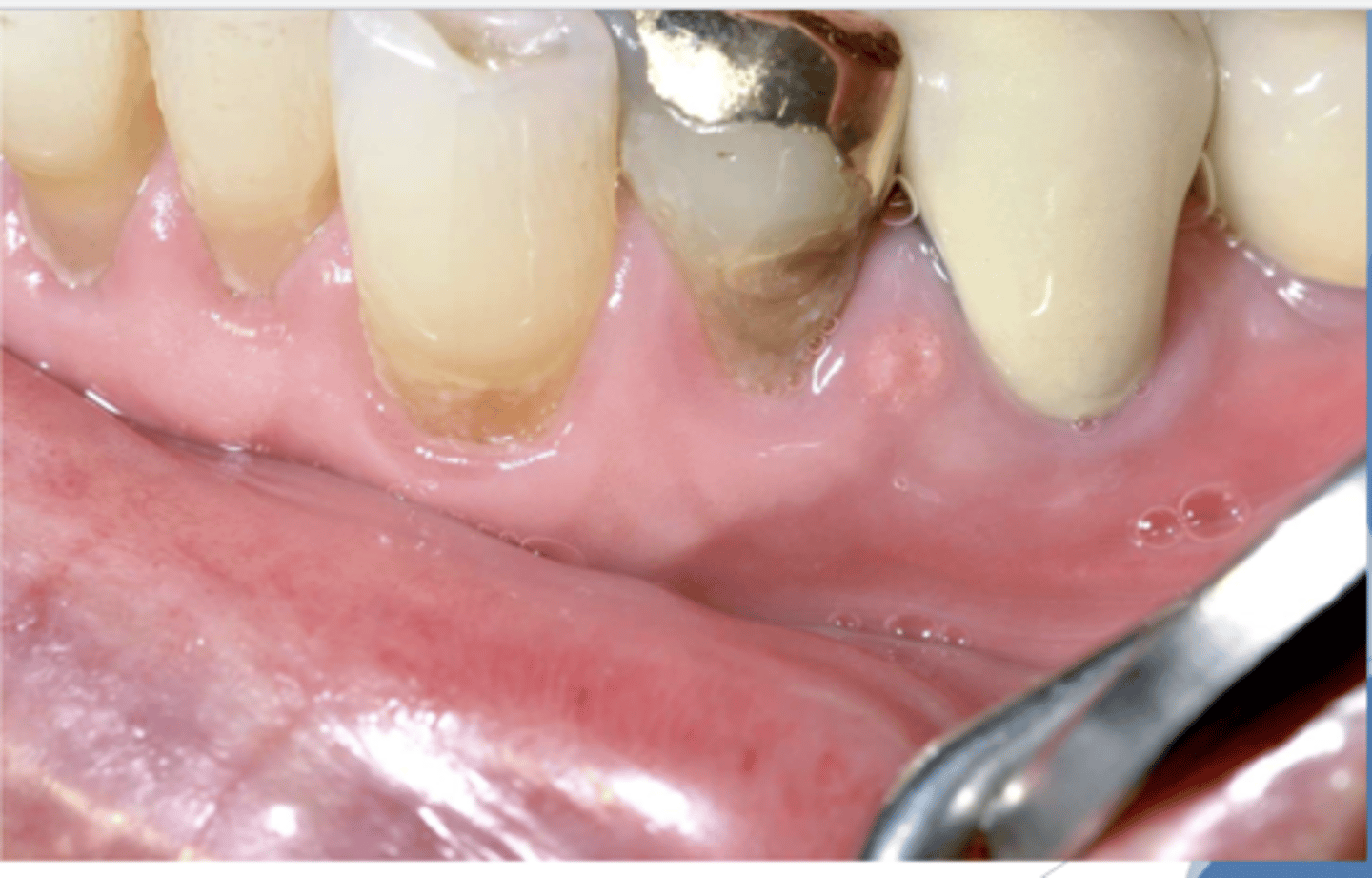
Find the lesion. What diagnosis differential would you consider?
well-demarcated papillary lesion on the buccal dental papillae between #20 & #21; Possible Differential:
-HPV --> papillary, will need to confirm with biopsy, HPV testing
-squamous cell carcinoma
-verruciform xanthoma --> benign lesion that may resemble squamous papillomas or squamous cell carcinoma
*v. xanthoma is what this lesion is but there's no way to differentiate from the differential clinically w/o HPV testing/biopsy
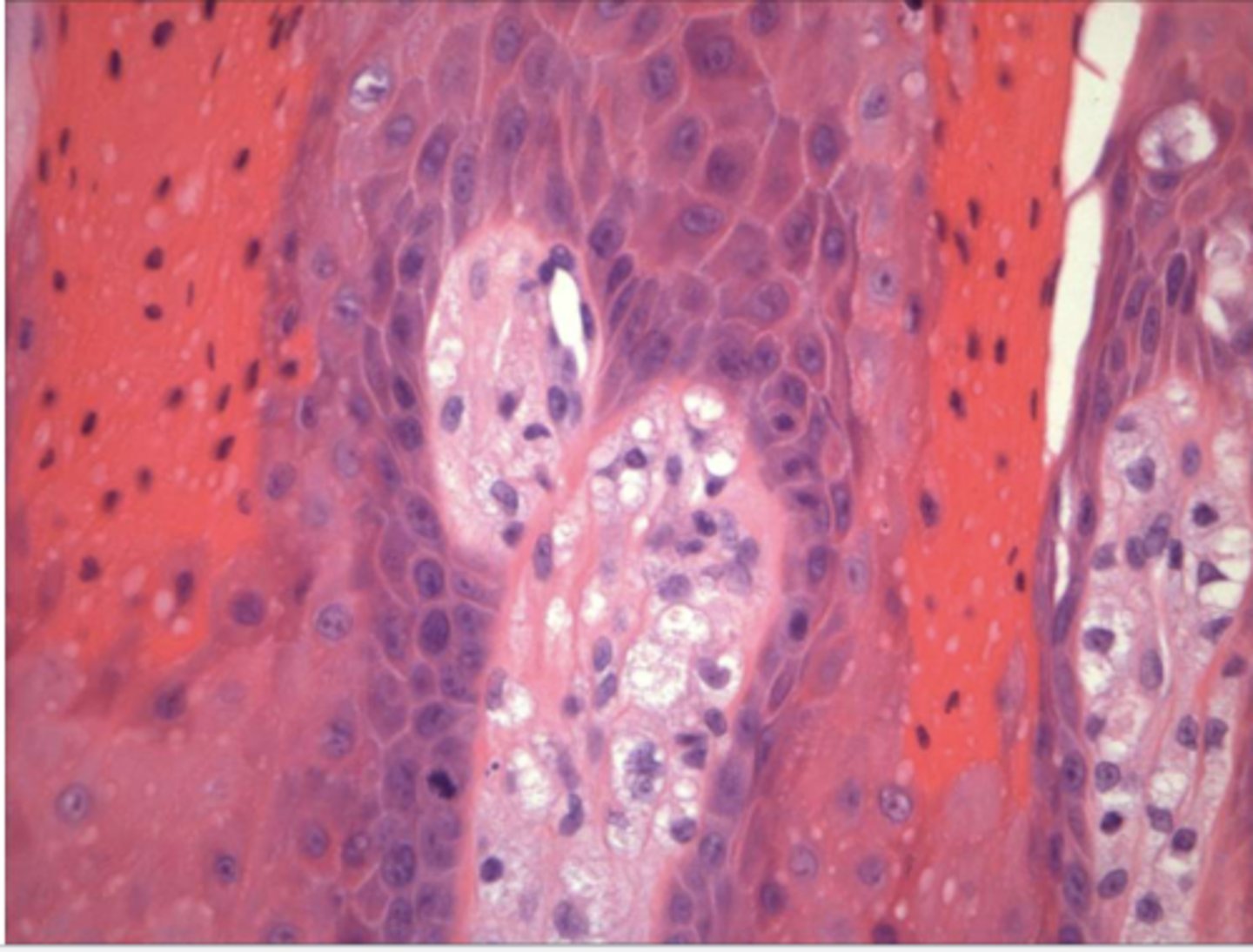
the following describe the histopathological features of what?
-papillary, acanthoic surface covered by parakeratin
-large macrophages w/ foamy cytopalsm
verruciform xanthoma
how is verruciform xanthoma treated?
conservative excision
True or False: Like HPV, there are frequent recurrences of verruciform xanthoma
False ==> recurrences are rare
what are some common factitial medicaments that can cause chemical injury within the oral cavity? (3)
-aspirin
-mouthwashes/hydrogen peroxide
-tooth-whitening products
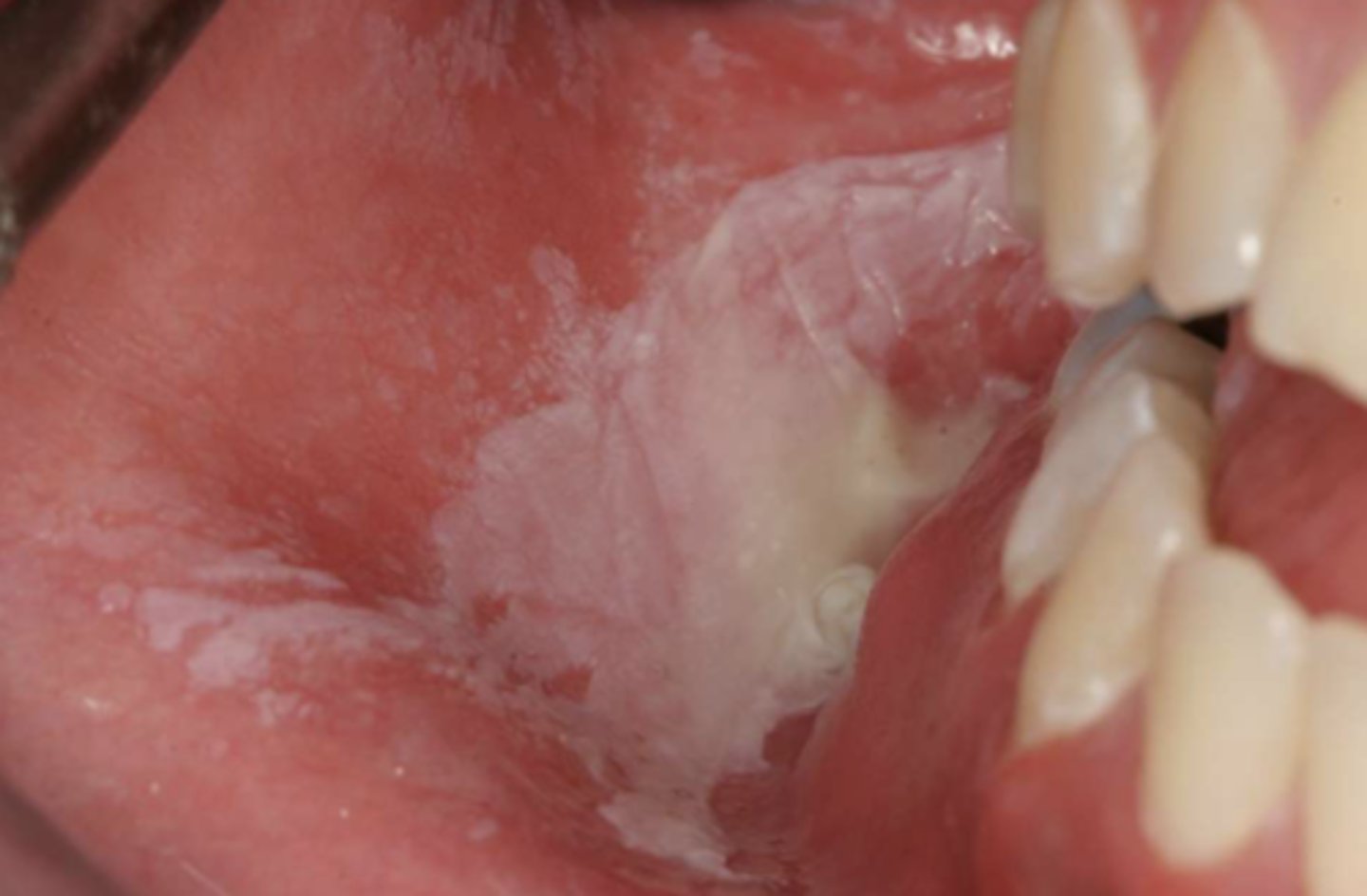
Patient reports that a portion of his inner cheek has turned white over the past month. The lesion is asymptomatic. There are no changes to his medical history, but he noted that he has been trying out a new tooth whitening product. The patient isn't currently taking any medications. The white macule doesn't (*does) slough off upon clinical manipulation. What do you suspect?
chemical injury --> due to new tooth-whitening product
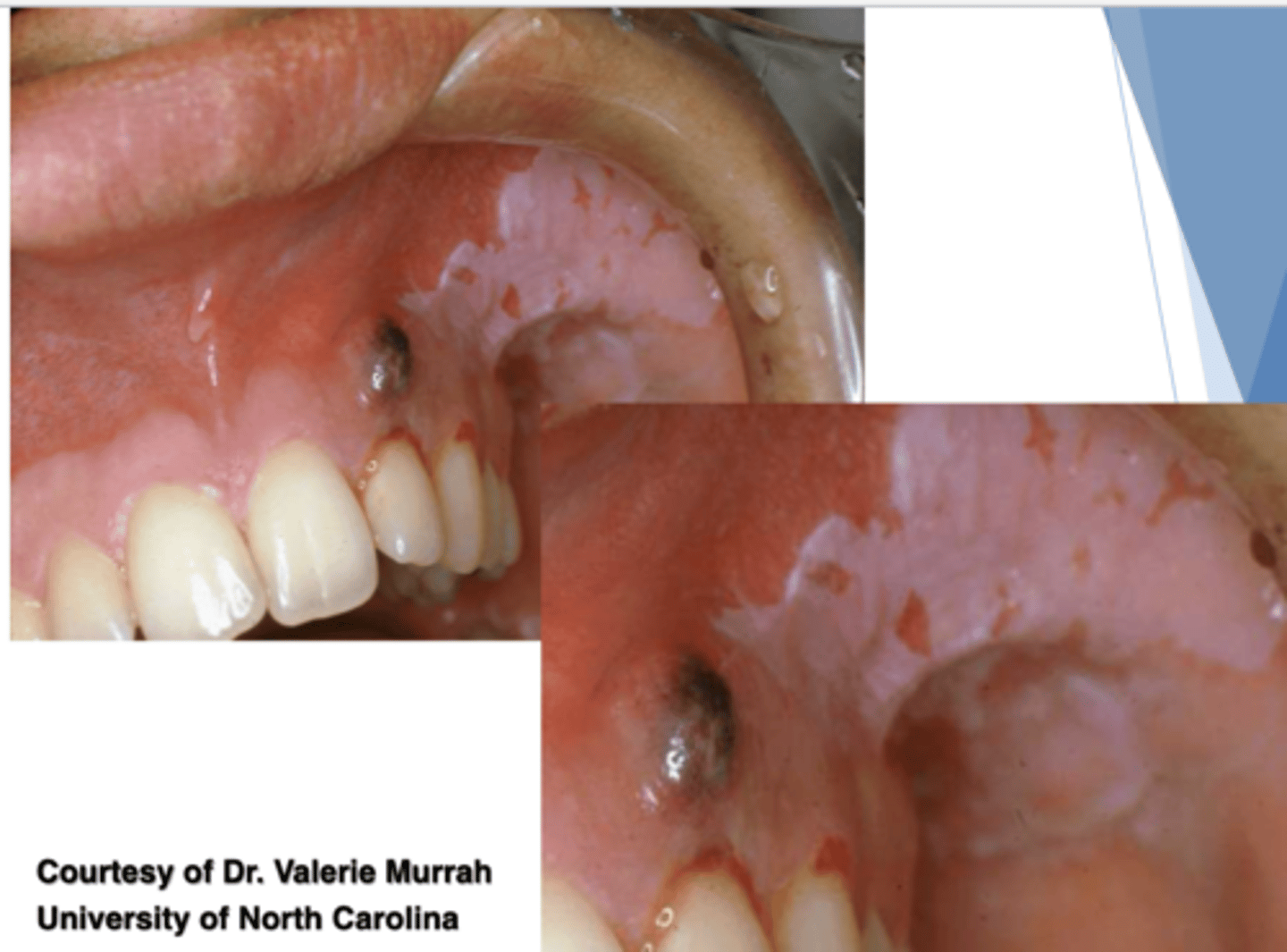
Patient reported that they have multiple minor headaches per week and take a 500mg Aspirin as needed to relieve the pain. Patient reported being unable to swallow pills, so she sucks on the aspirin until it dissolves in her mouth. What do you suspect the white lesion encompassing her buccal mucosa is due to?
chemical injury due to acid burning from aspirin
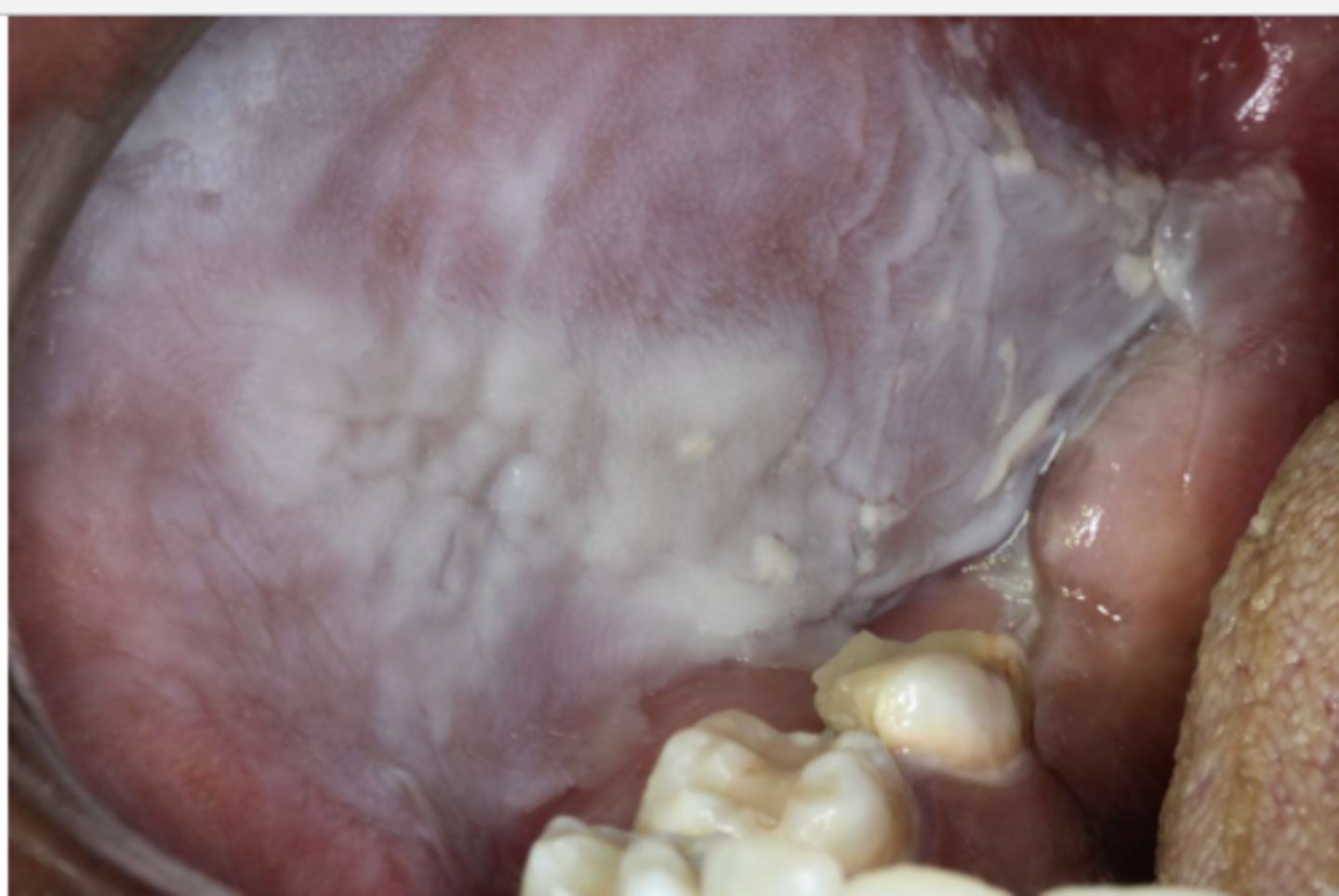
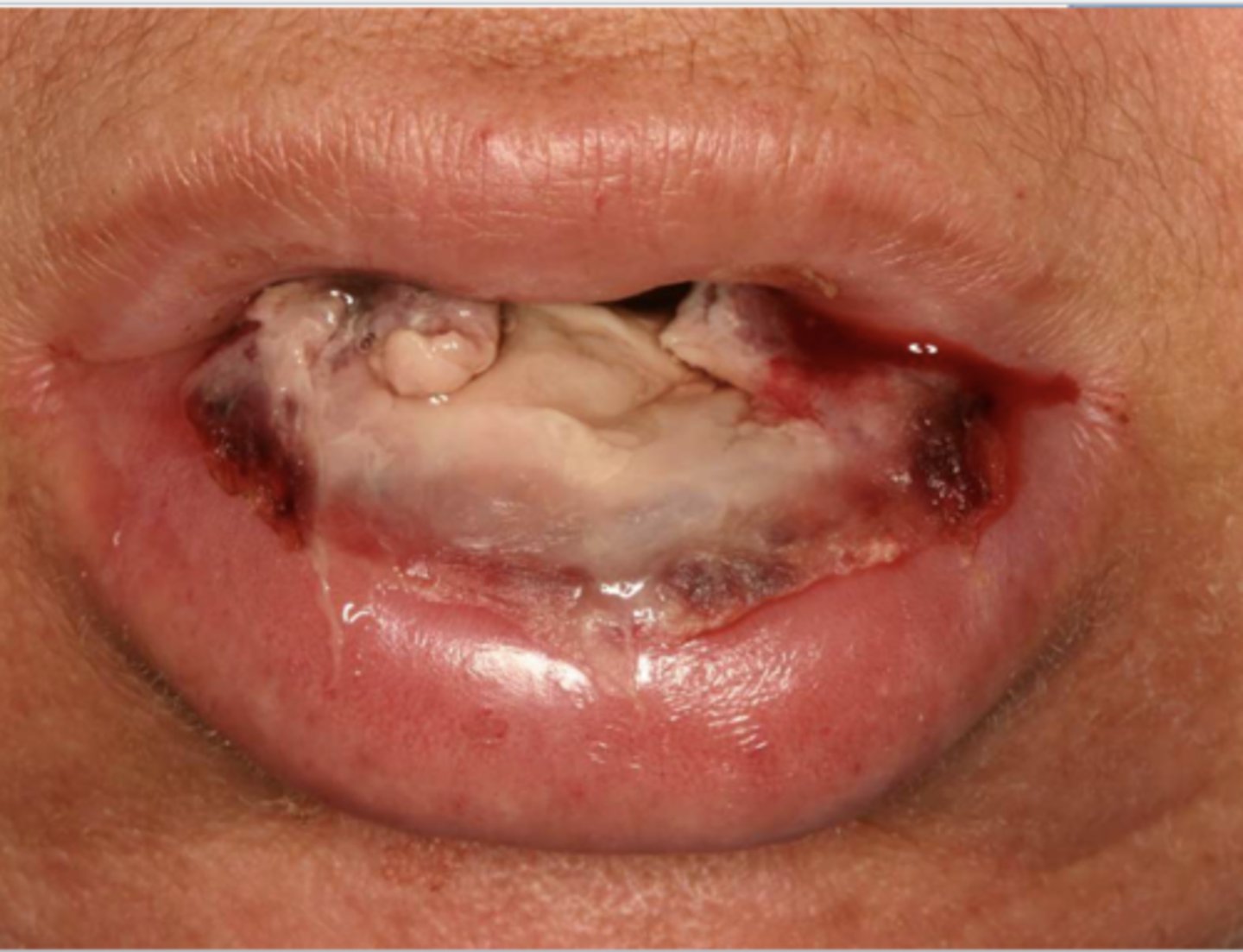
Patient reported rinsing with a new listerine mouthwash 3x/ day. The listerine is not alcohol free. Clinical findings are the sloughing off buccal mucosa as seen above. What do you suspect?
chemical injury due to alcohol mouthwash
What are some common iatrogenic causes of chemical injuries in the oral cavity? (5)
-silver nitrate
-phenol
-endodontic materials
-cotton roll "burn"
-rubber dam application reduces incidence
how can cotton roll burn happen? (2)
-medicament concentrated on cotton roll against the tissue (ex: acid etch)
-removal of cotton roll without first moistening --> strips the mucosa
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy can cause what 2 acute changes within the oral cavity?
-mucositis
-hemorrhage
How soon does mucositis occur due to chemotherapy?
within days
what are the oral complications of chemotherapy? (3)
-mucositis --> occurs w/in days
-bone marrow suppression --> thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis
-opportunistic infections --> herpes simplex, candidiasis
What are the consequences of bone marrow suppression die to chemotherapy? (2)
-thrombocytopenia
-agranulocytosis
what are some opportunistic infections that can occur as a complication of chemotherapy? (2)
-herpes simplex
-candidiasis
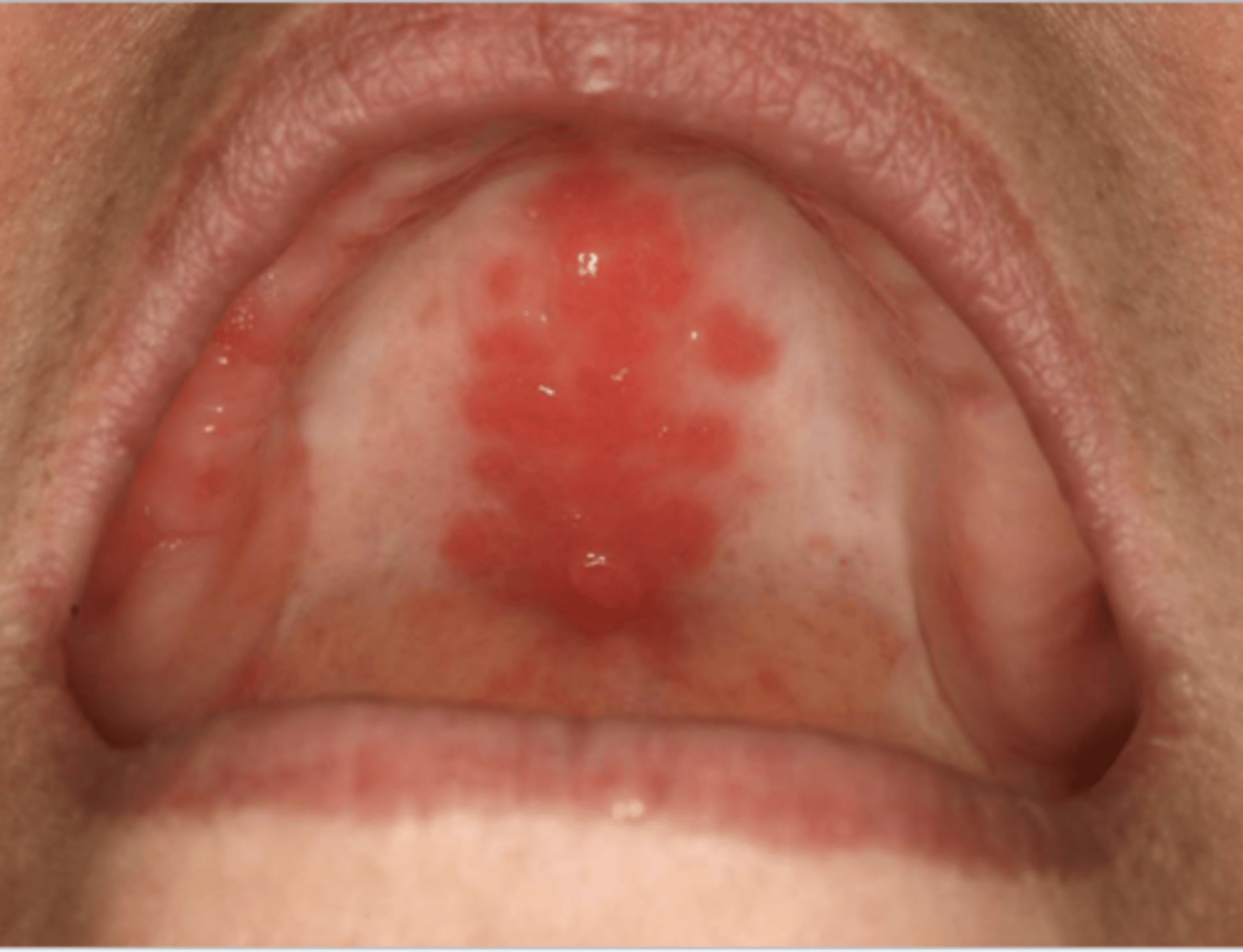
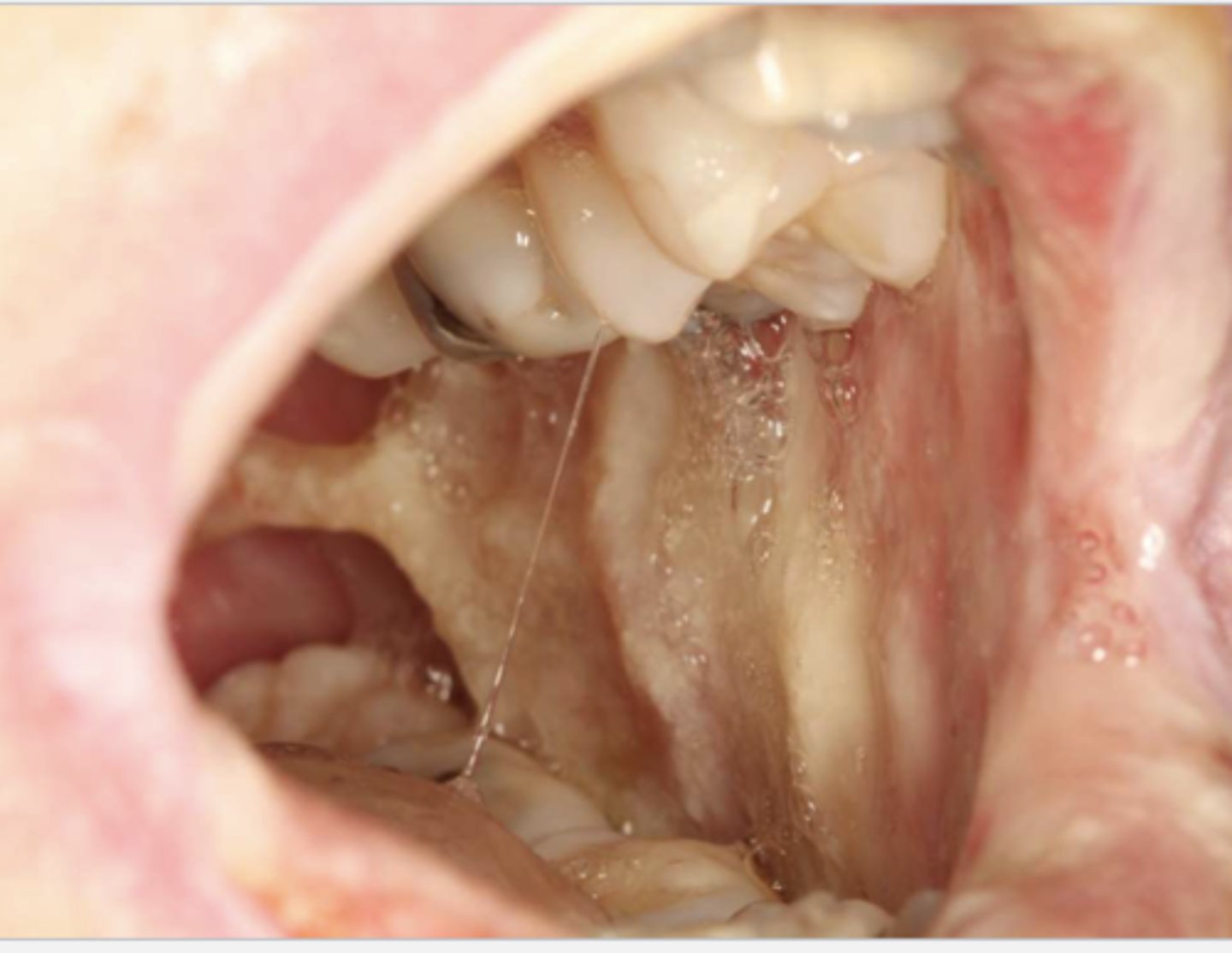
Patient has lung cancer & is currently undergoing chemotherapy. What do you suspect?
severe mucositis due to chemotherapy
*can present w/ ulceration & hemorrhage as depicted
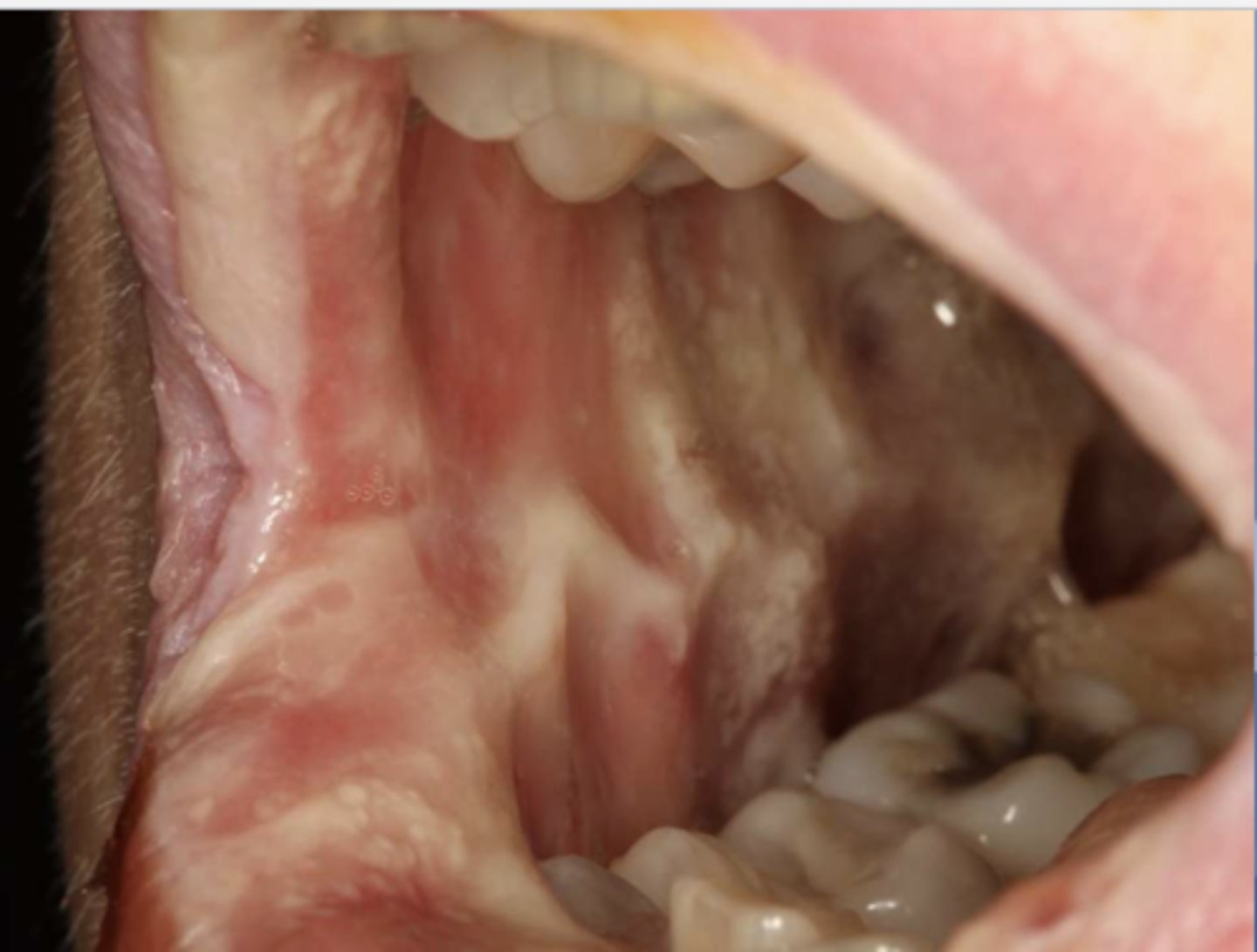
Patient is currently undergoing chemotherapy for colon cancer. What do you suspect?
chemotherapy related mucositis
Patient is has breast cancer and is currently on chemotherapy. What do you suspect?
chemotherapy related mucositis
what are some common causes of osteonecrosis of the jaws? (6)
-medication
-radiation
-infections
-chemicals
-trauma
-idiopathic
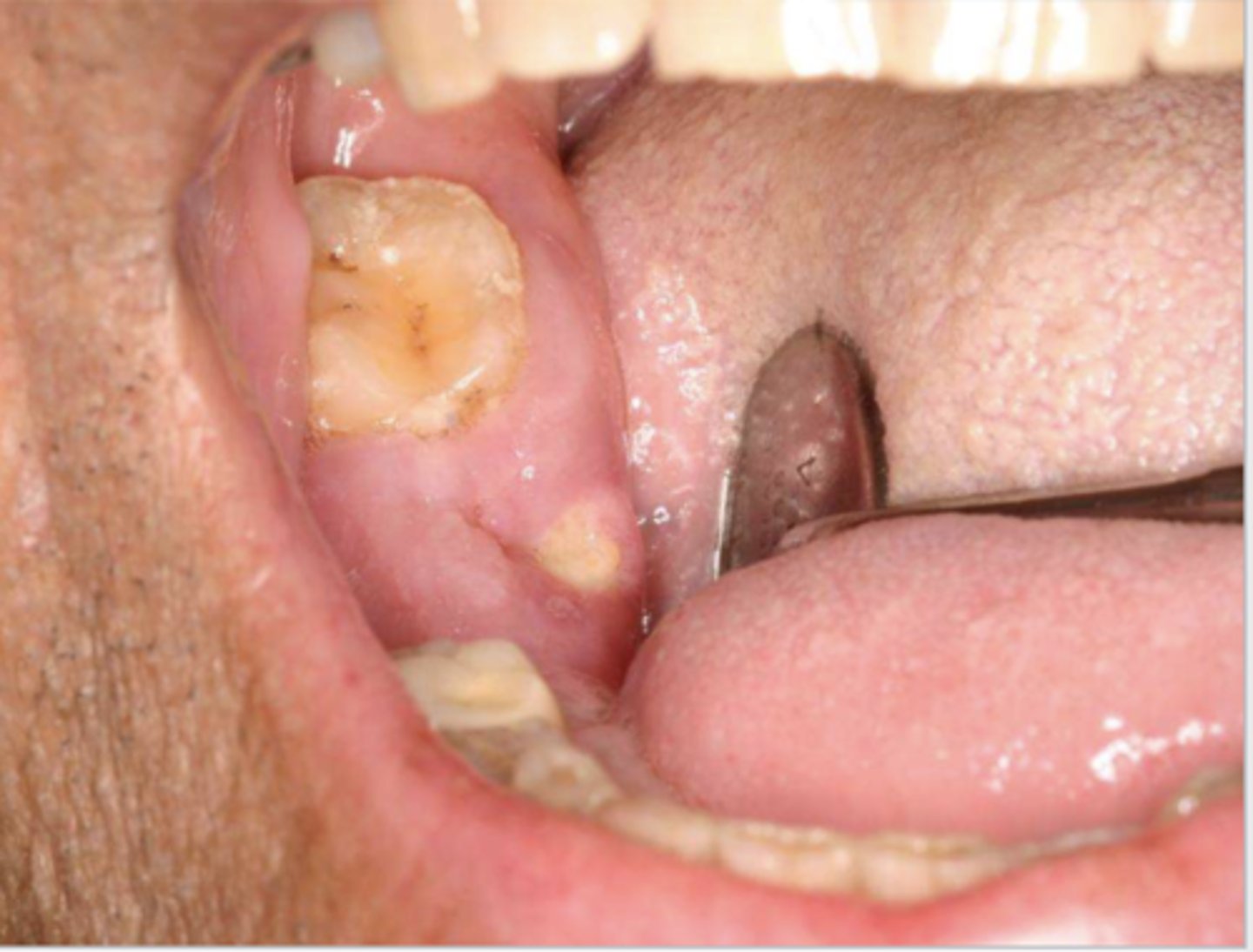
what do you suspect?
osteonecrosis
what anti-resorptive agents can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws? (2) (i think more so help bc they are ANTI-resorptive)
-bisphosphonates
-denosumab --> Prolia, Xgeva
what anti-angiogenic agents can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws?
-Monoclonal antibodies --> bevacizumab
-tyrosine kinase inhibitors --> Sunitinib, Sorafenib
what is a possible oral side effect of prolia?
a denosumab anti-resorptive agent that can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws
what is a possible oral side effect of xgeva?
a denosumab anti-resorptive agent that can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws
what is a possible oral side effect of bevacizumab?
a monoclonal antibody anti-angiogenic agent that can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws
what is a possible oral side effect of sunitinib?
a tyrosine kinase inhibitor anti-angiogenic agent that can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws
what is a possible side effect of sorafenib?
a tyrosine kinase inhibitor anti-angiogenic agent that can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws
what is the general mechanism of action of bisphosphonates?
anti-resorptive via inactivation of osteoclasts
what does the following describe?
-exposed bone or bone that can be probed through a sinus tract persisting > 8 wks.
-current or previous treatment with anti-resorptive or anti-angiogenic agents
-no head & necj radiation or obvious metastasis to the jaws
medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ)
what conditions/disease are within the diagnoses differential for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws? (9)
-alveolar osteitis
-gingivitis/periodontitis
-sinusitis
-caries
-periapical pathology
-fibro-osseous diseases
-cancer
-condensing osteitis
-temporomandibular disorders
what processes/conditions are involved in the pathogenesis of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ)? (5)
-anti-osteoclastic
-anti-angiogenic
-inflammatory/infectious
-immune dysfunction
-soft tissue toxicity
True or False: Nitrogen containing bisphosphinates are more commonly prescribed than non-nitrogen containing bisphosphonates
True ==> nitrogen containing are more potent
Are the following nitrogen or non-nitrogen containing bisphosphonates?
-etidronate (dironel)
-clodronate (Bonefos)
- tiludronate (skelid)
non-nitrogen containing
*not as potent --> decreased likelihood of causing MRONJ (compared to nitrogen containing)
Are the following nitrogen or non-nitrogen containing bisphosphonates?
-pamidronate (aredia)
-alendronate (fosamx)
-ibandronate (boniva)
-risedronate (actonel)
-zoledronic acid (zometa)
(pariz)
nitrogen containing
*more potent --> greater likelihood of causing MRONJ
When is bisphosphinate therapy indicated? (6)
-osteoporosis/osteopenia
-multiple myeloma
-metastatic carcinomas to bone
-paget disease
-osteogenesis imperfecta
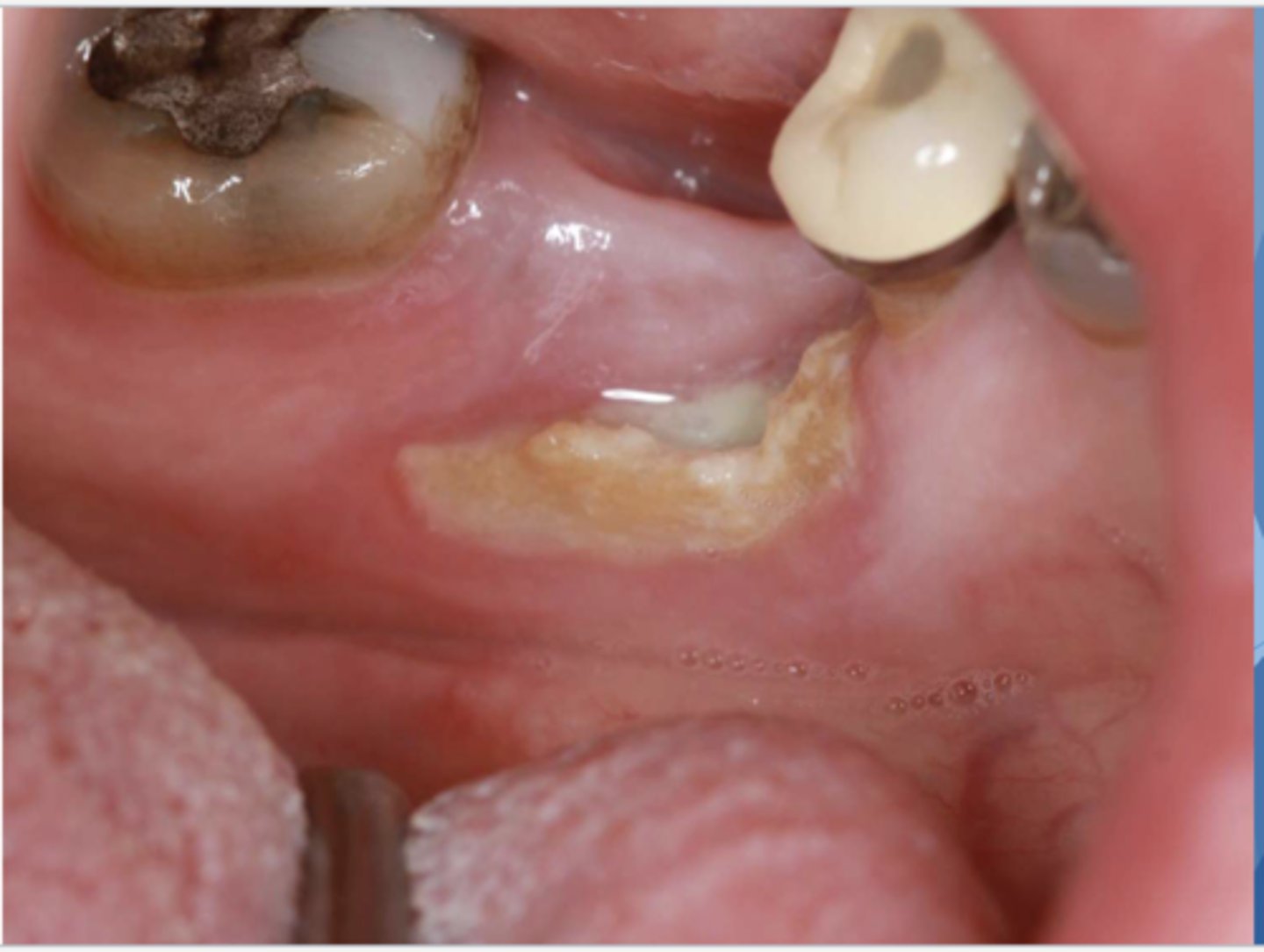
What do you suspect? Hint: Patient is taking Zometa to treat osteoporosis
MRONJ
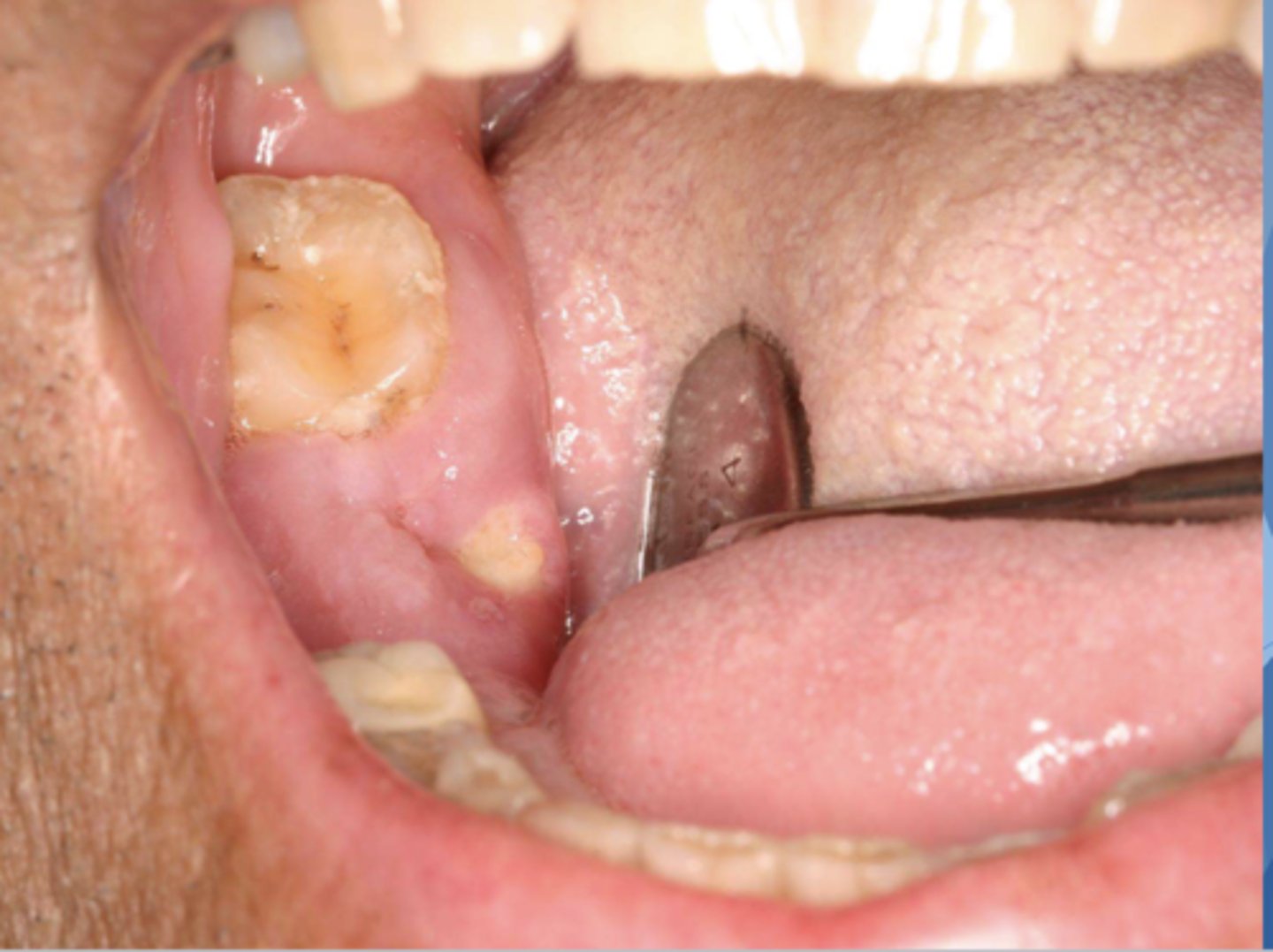
Patient has multiple myeloma and is currently on chemotherapy and taking Flosamax (Alendronate). What do you suspect?
MRONJ
Upon clinical examination, you find a lesion that appears to be necrotic bone showing through the lingual attached gingiva of #31. What do you suspect? Is there anything you should look for in the patient history?
osteonecrosis/osteoradionecrosis/ MRONJ
*should see if patient is currently taking a bisphosphonate, undergoing head/neck radiation therapy, or on any other anti-resorptive or anti-angiogenic therapy
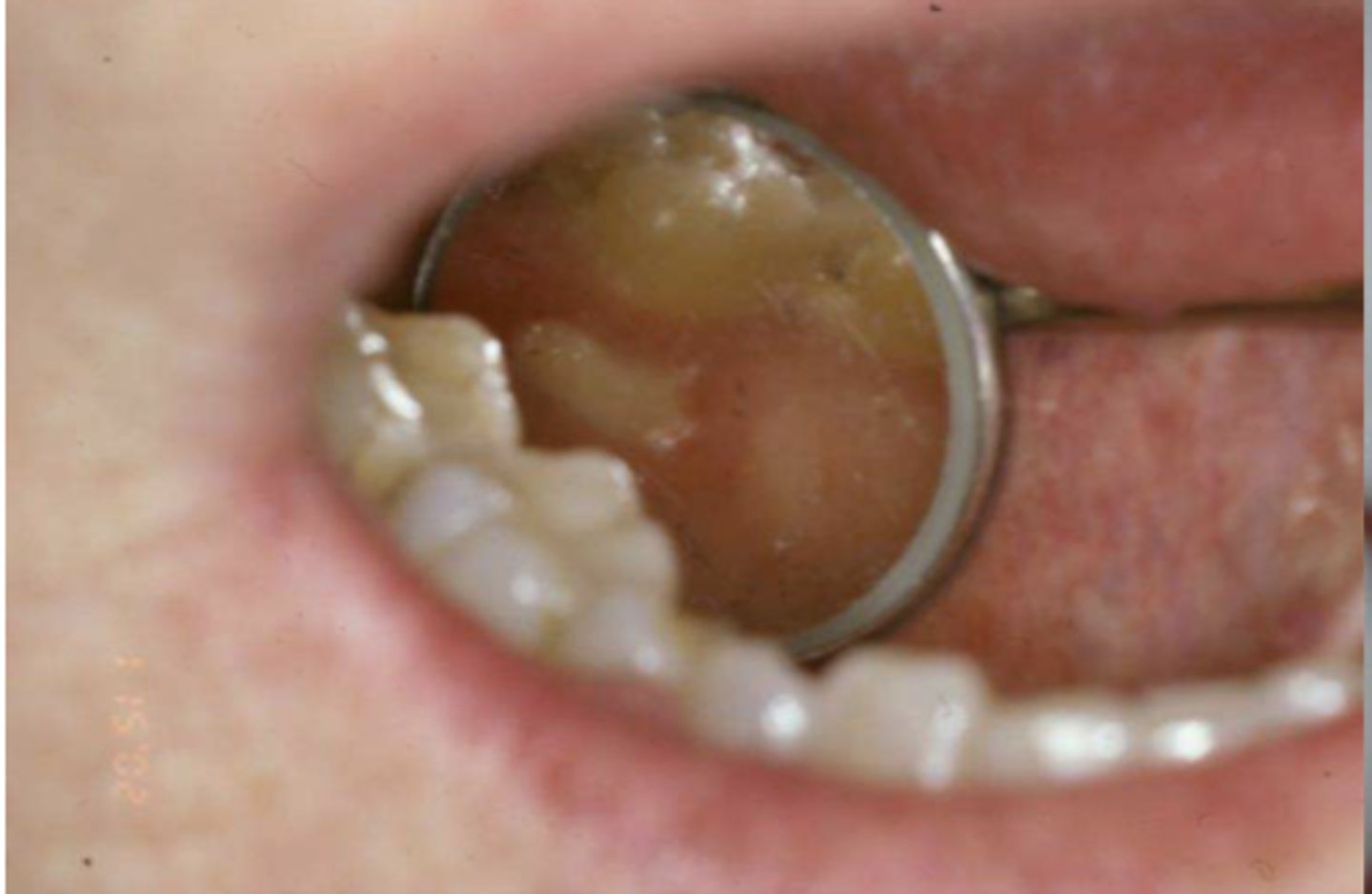
Patient was diagnosed with Paget's disease 6 mo ago and began anti-resorptive therapy upon diagnosis. What do you suspect this lesion is?
MRONJ
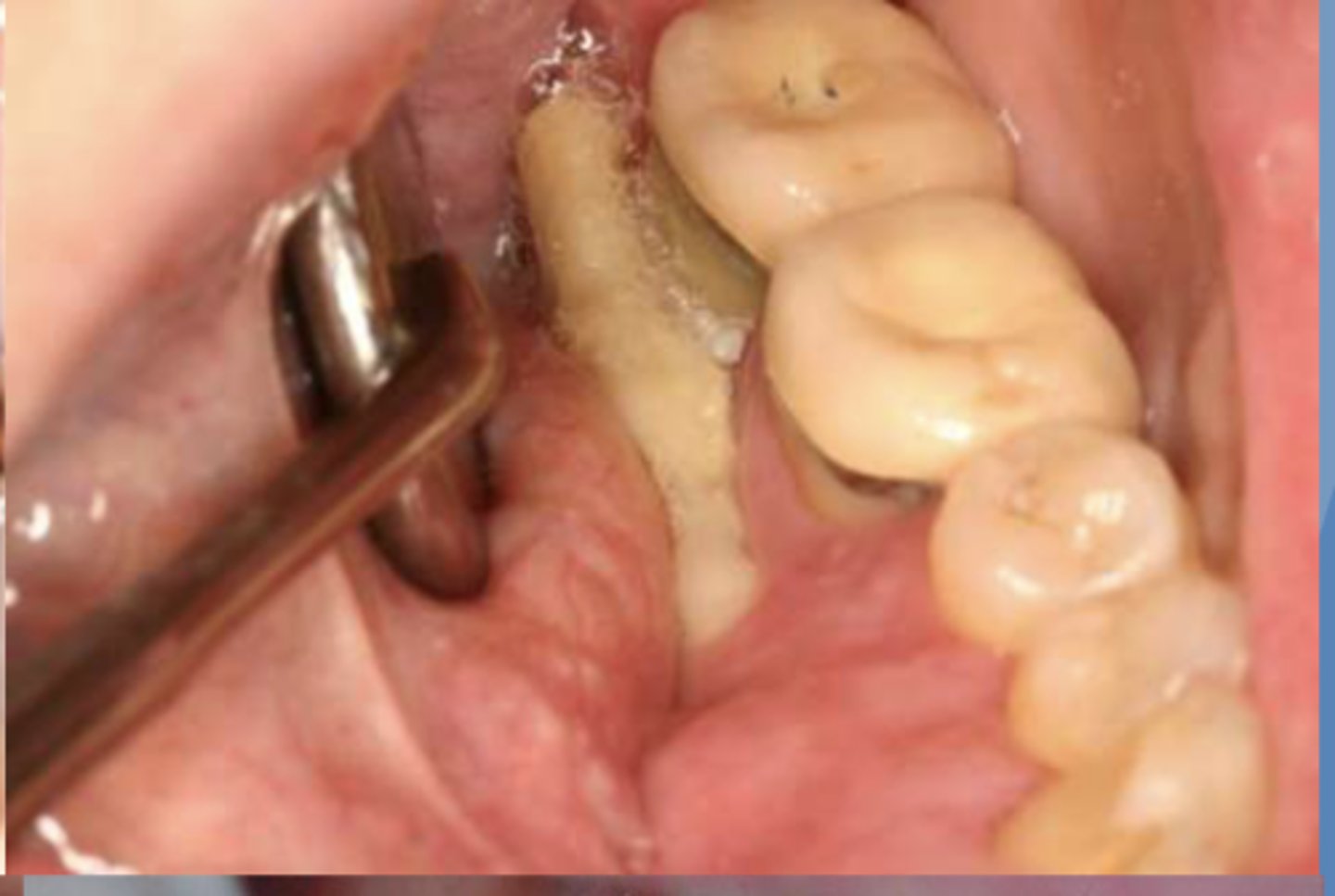
what do you suspect?
osteonecrosis/osteoradionecrosis/ MRONJ
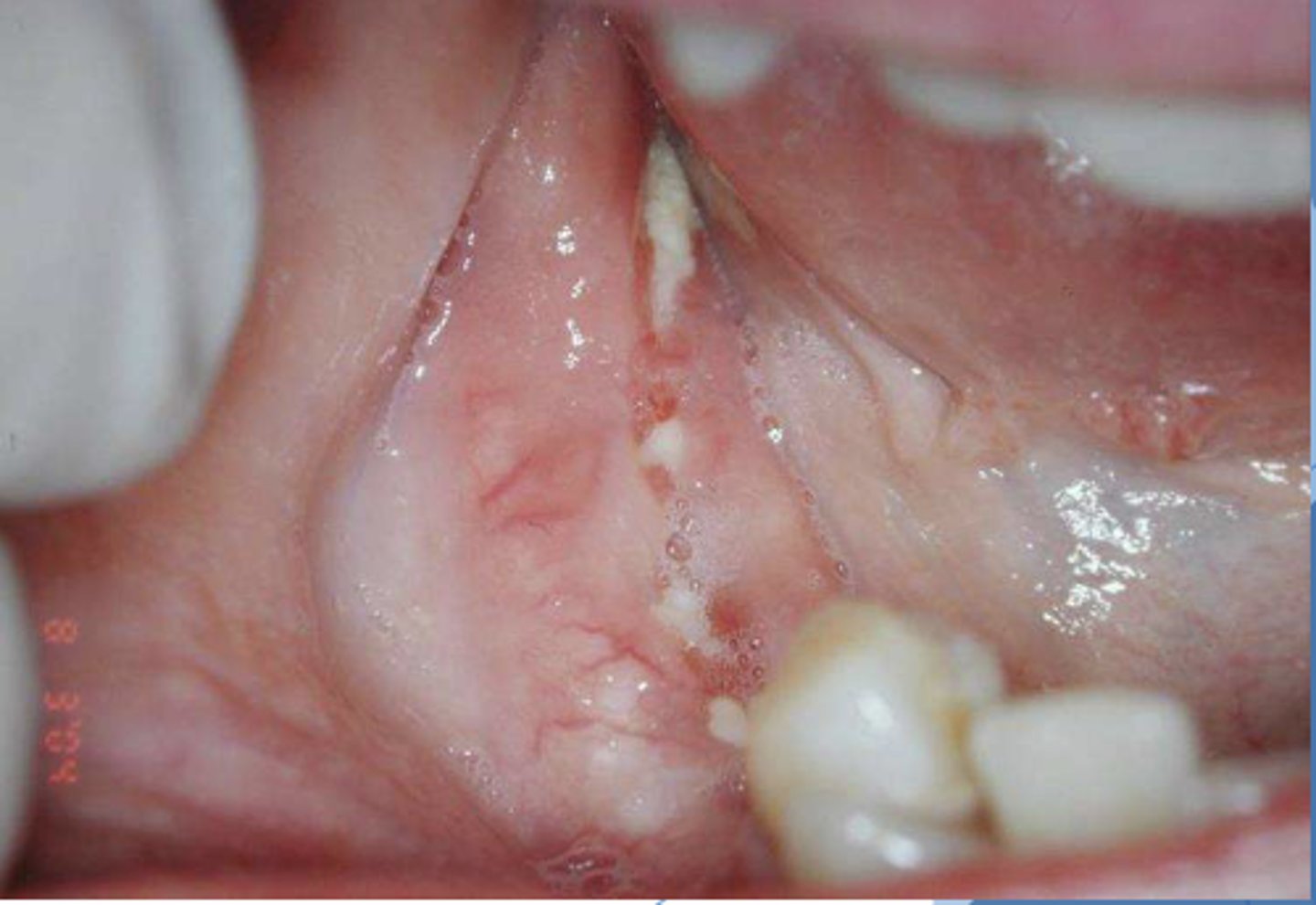
what do you suspect?
osteonecrosis/osteoradionecrosis/ MRONJ
Describe the AAOMS Staging of MRONJ
-stage 0 --> non-exposed
-stage 1 --> exposed asymptomatic
-stage 2 --> exposed symptomatic
-stage 3 --> extensive disease
what is stage 0 of the AAOMS staging of MRONJ?
non-exposed
what is stage 1 of the AAOMS staging of MRONJ?
exposed asymptomatic
what is stage 2 of the AAOMS staging of MRONJ?
exposed symptomatic
what is stage 3 of the AAOMS staging of MRONJ?
extensive disease
True or False: In MRONJ, increased radiopacity may be noted before clinical evidence of necrosis
True
True or False: The maxilla is affected more than the mandible by MRONJ
False ==> mandible affected more than the maxilla
*difference not as great as in osteoradionecrosis
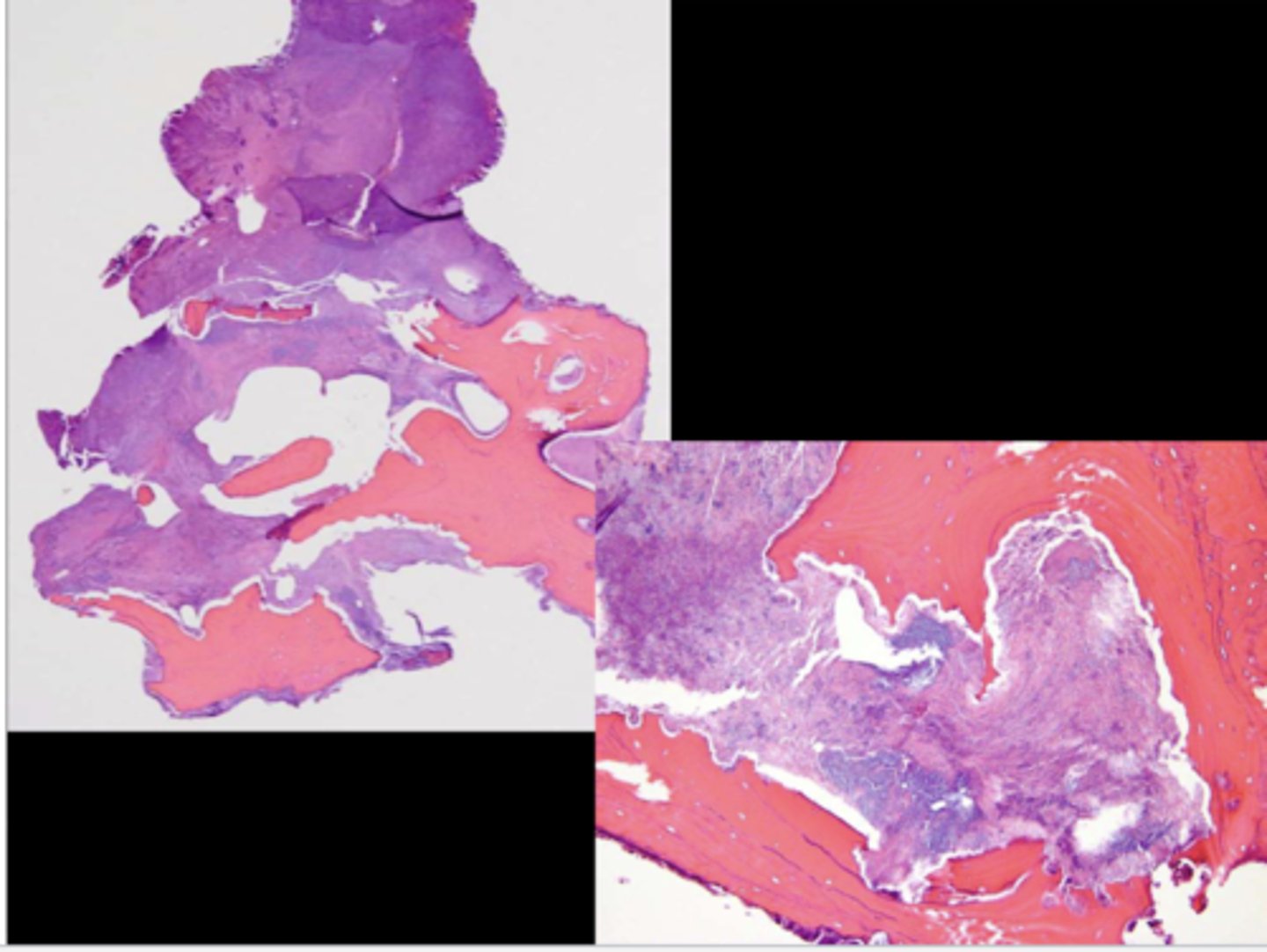
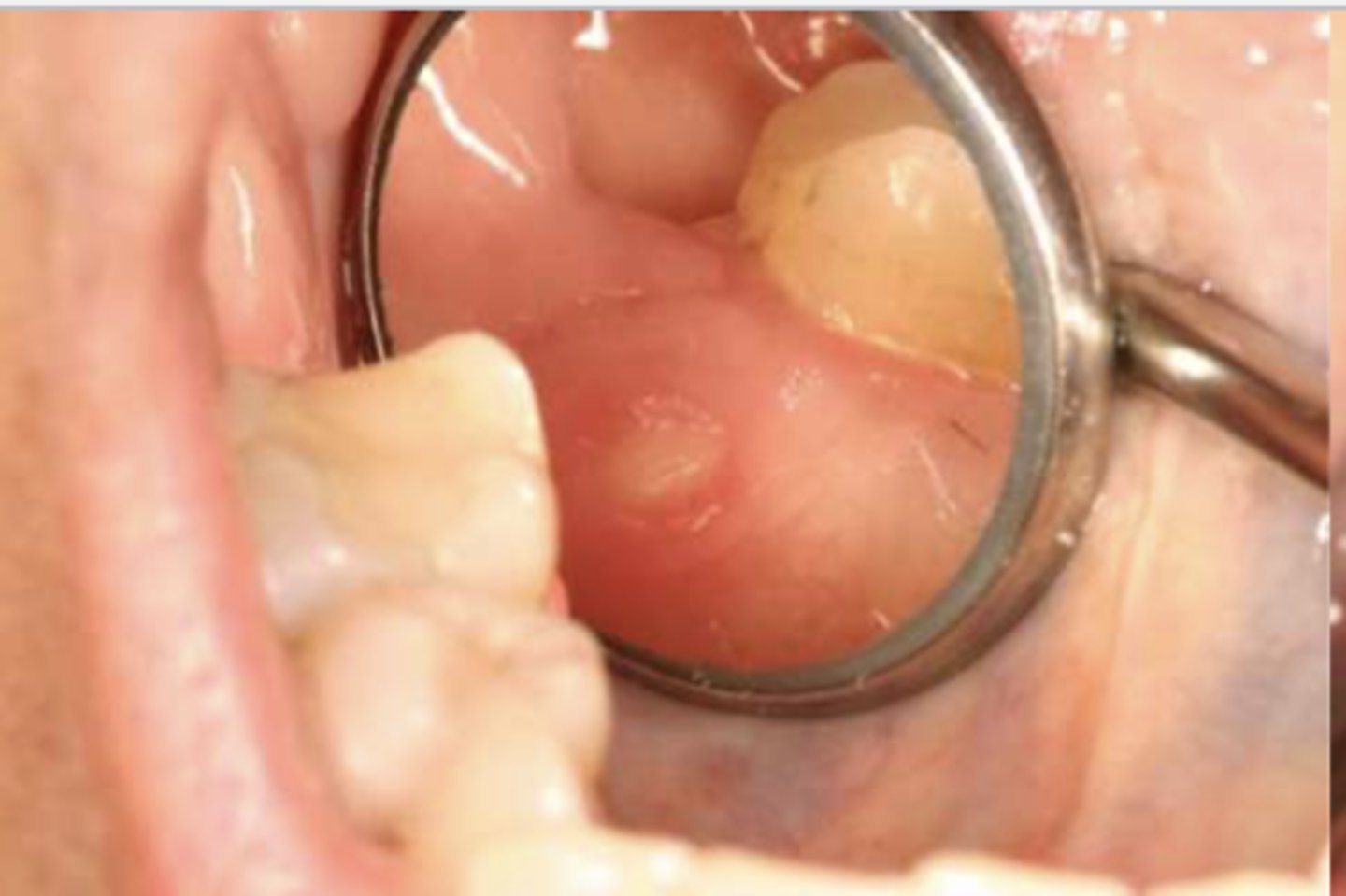
This is a histological image of what?
MRONJ
what is the best treatment for MRONJ?
prevention
how is MRONJ treated in asymptomatic patients? (3)
-chlorhexidine rinse
-smooth rough edges of exposed bone
-soft splint
how is MRONJ treated in symptomatic patients?
systemic antibiotic therapy & chlorhexidine
*hyperbaric oxygen hasn't been beneficial
what are the dental considerations for patients with MRONJ? (3)
-prophylactic dental care
-less invasive procedures recommended
-if multiple EXT needed, consider performing them by quadrant
what are the complications of radiotherapy (head & neck)? (7)
-saliva thickens at 1 wk
-salivary gland hypofunction
-mucositis occurs 1-2wks following irradiation --> desquamation & ulceration
-osteoradionecrosis
-hypofunction w/ or w/o xerostomia 1 month after radiotherapy --> irreversible damage
-increased incidence of cervical caries
-hypogeusia --> reduced taste sensation
what can occur 1-2wks after radiotherapy? (2)
-mucosiitis --> desquamation & ulceration
-saliva thickening (1wk)
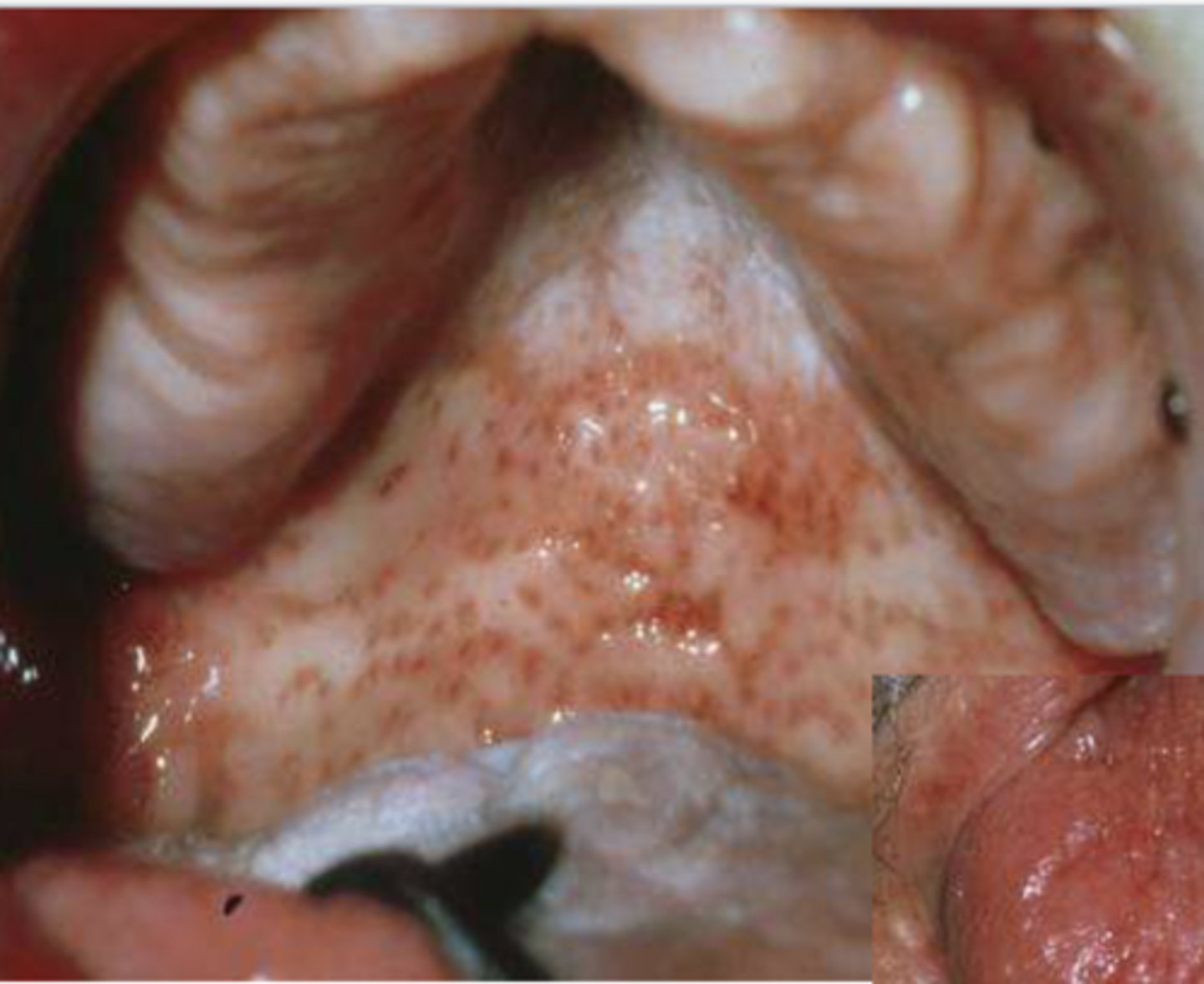
Patient reported undergoing radiotherapy 2 weeks ago. What do you suspect?
mucositis due to radiotherapy
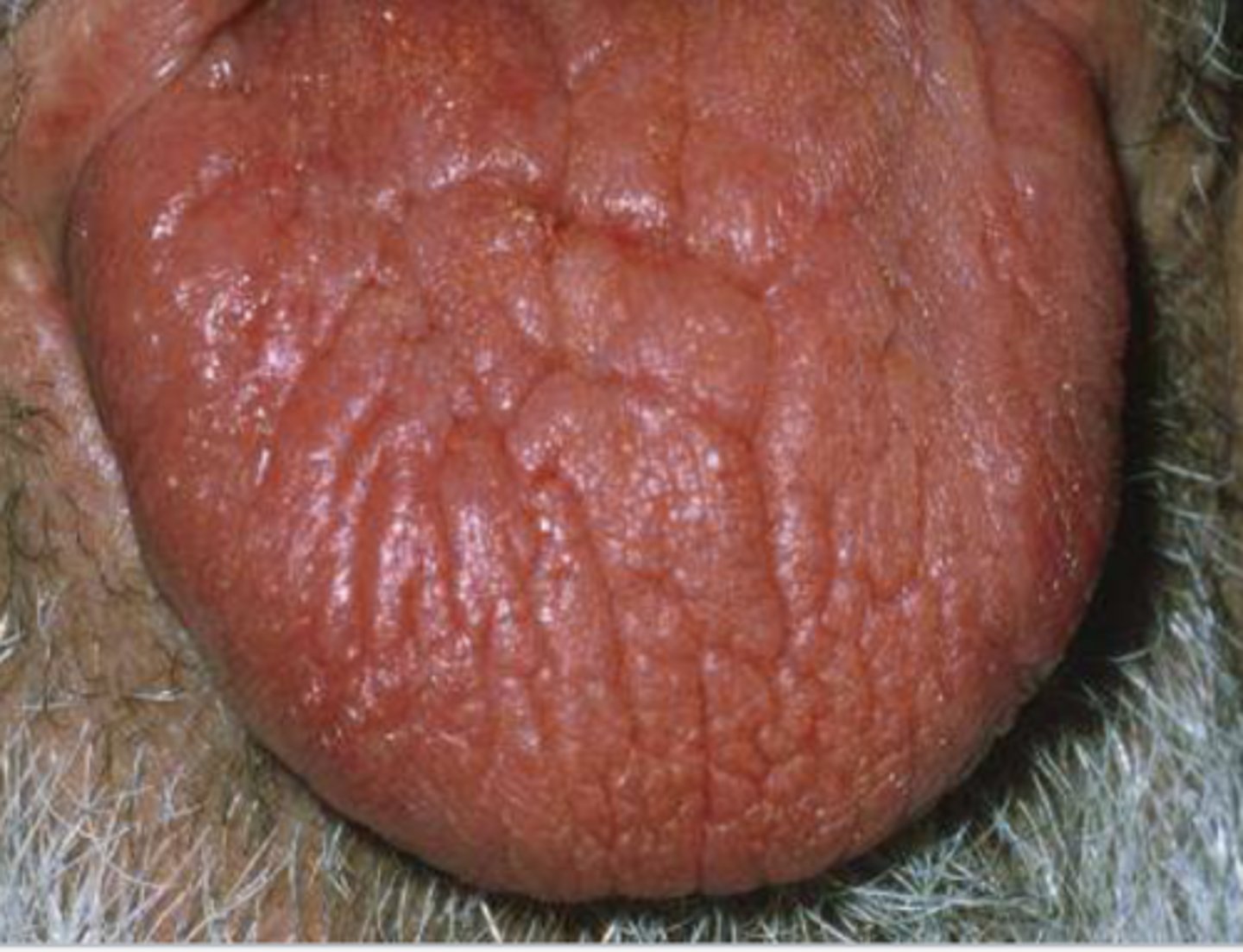
Patient reported undergoing radiotherapy a few weeks ago. What do you suspect?
mucositis of the tongue due to radiotherapy