Software Development 😘
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Analysis
Evaluating a project’s practicality and likelihood of success from what the stakeholders state what they want from the finished product.
Requirements
The needs, capabilities and constraints that the project must meet to achieve an objective.
Design
Understanding how to meet the requirements to achieve said objective. Often using a test plan.
Design Aspects
Inputs
Outputs
Security features
Hardware compatibility
User interface
Implementation
Taking a conceptual software design and coding said software.
Testing
Assessing whether the software performs as anticipated and error-free.
Alpha Testing
Carried out by the software development teams to pinpoint and fix bugs.
Beta Testing
Carried out by a select group of users to use the user’s feedback in the next stage of development.
White Box Testing
A test carried out with the testers knowing the internal structure of the program usually being software development teams meaning that all possible routes are tested.
Black Box Testing
A test carried out with the testers not knowing the internal structure of the program which can be done in house or by end-users.
Deployment
The process of making a software available for its intended users.
Evaluation
Assessing the software to determine if it meets its defined goals, requirements and the end-user’s needs.
Criteria of Evaluation to consider
Robustness
Reliability
Portability
Maintainability
Maintenance
All modifications, improvements and updates made to the software after its initial deployment after being flagged up by end-users.
General steps of Software Development
Analysis
Requirements
Design
Implementation
Testing
Deployment
Evaluation
Maintenance
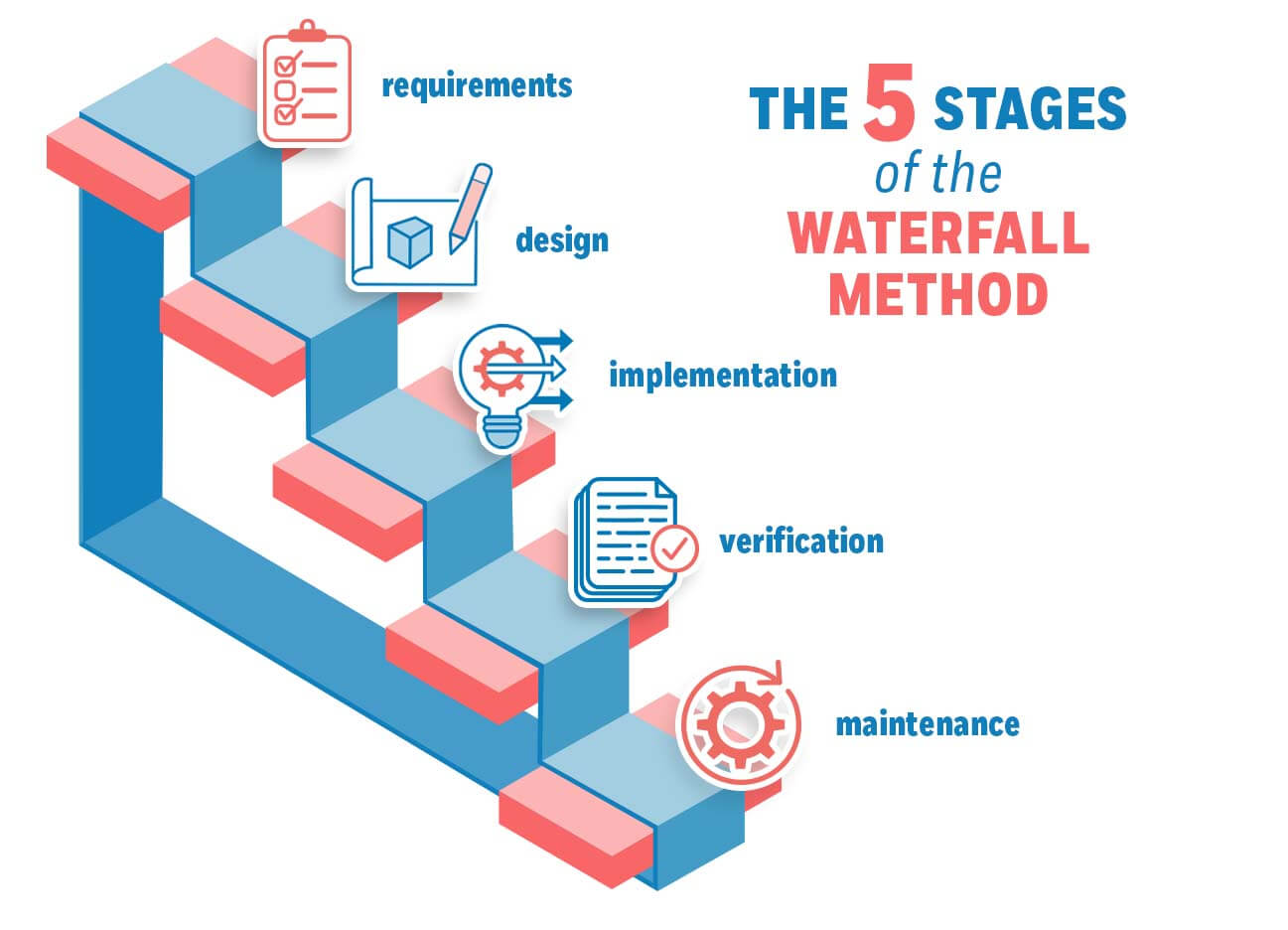
Waterfall Methodology
A traditional model based on a series of stages which are completed in sequence, in order to go back to a stage all previous stages must be revisited.
Advantages of Waterfall Methodology
Uses clear structure with defined sets of steps making it easier to manage, sets clear responsibilities and helps see if a project is running on schedule.
Each phase has a well devised start and end point with identifiable deliveries.
Disadvantages of Waterfall Methodology
Inflexible making it unsuitable for projects with changing requirements.
Users have little input except during the analysis and evaluation stage.
High Risk
In order to go back to a stage all previous stages must be revisited, making it time consuming.
Compatibility of Waterfall Methodology
Goes well with low risk projects which need little user input.
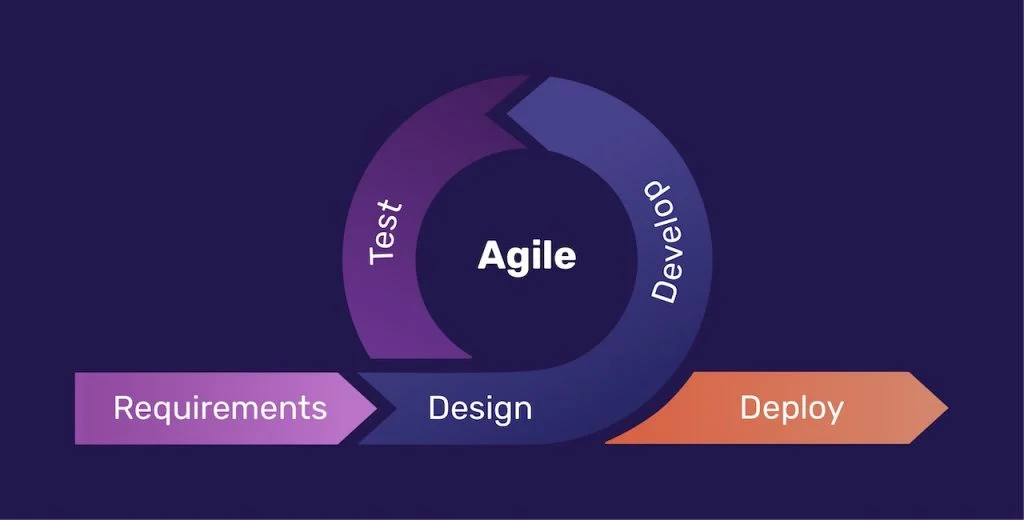
Agile Methodology
Improves flexibility by breaking down into sections to be developed in short sprints of 1 - 4 weeks before brief meetings, creating new prototypes to be delivered throughout the development cycle.
Advantages of Agile Methodology
More refined than RAD.
High code quality.
Flexible to changes.
Regular user input.
Easier to see if it’s on track
Focuses on the efficiency of programming
Fast paced
Disadvantages of Agile Methodology
Time frames are difficult to work with.
Needs close collaboration.
Time zones.
Requires consistent communication between the end-users and the programmer.
The goal changes each time
Not good with large companies
Compatibility of Agile Methodology
Small to medium sized, low-budget projects with short time frames
Extreme Programming
Aims to produce very high quality code by encouraging developers to adopt a set of common practices that focuses on the values of communication, feedback, courage and respect.
Advantages of Extreme Programming
Produces high quality code.
Constant user involvement, leading to high usability.
Promotes teamwork
Disadvantages of Extreme Programming
High cost of two people working on one project.
Time zones
Close collaboration needed
Not good with large companies
Compatibility of Extreme Programming
Small to medium sized projects with unclear initial requirements and strong end-user involvement
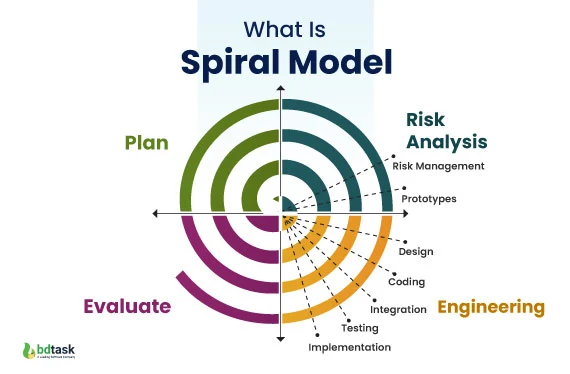
Spiral Methodology
A risk-managing driven methodology which focuses on analysing requirements, pinpointing and mitigating risks, development and testing and finally, evaluating before the next iteration.
Each decision is based on the risks.
Projects deemed too risky are terminated.
Advantages of Spiral Methodology
Isn’t a fixed process and can be in any order
Can be adopted to other methodologies
Going to be high quality with minimized risks
Disadvantages of Spiral Methodology
Expensive to hire specialist risk assessors.
Lack of focus on code efficiency.
Constant prototyping.
Needs to have objectives set out from the beginning.
Compatibility of Spiral Methodology
Large, risk-intensive projects with a high budget.
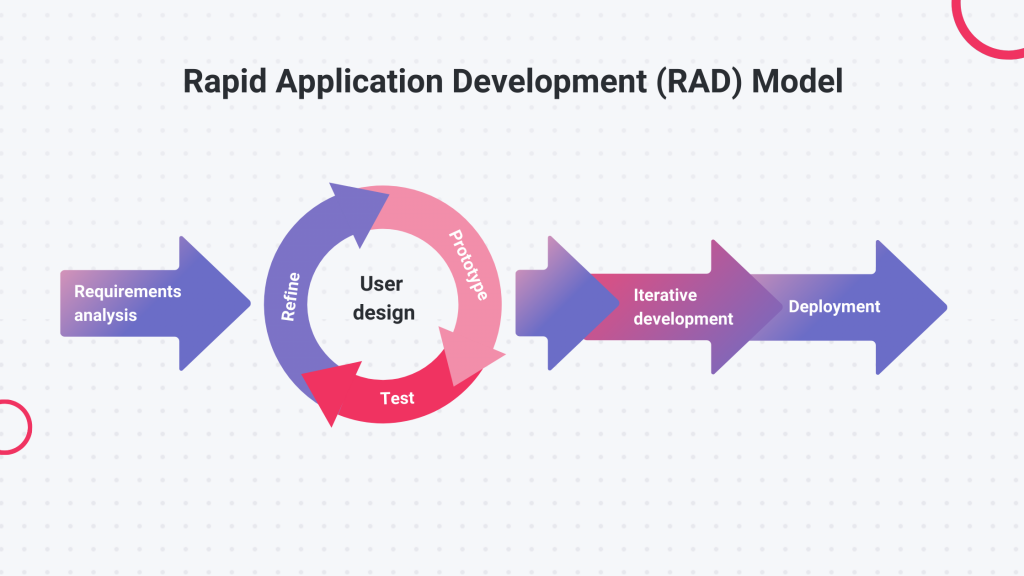
Rapid Application Development (RAD)
Uses partially functioning prototypes which are continually built on using end-users feedback to generate the next improved prototype, continuing until all the requirements are met and the end-users are satisfied, becoming the final product.
Advantages of RAD Methodology
Regular contact with clients.
Caters to changing user requirements.
Highly usable finished product.
Easy to use
Disadvantages of RAD Methodology
Time consuming because of prototype building.
Focuses on usability rather than programming reducing quality.
Not good for large companies.
Expensive to maintain.
Constant meetings with clients.
Compatibilty of RAD Methodology
Small to medium sized projects with unclear initial requirements.
Types of Methodologies
Waterfall
Agile
Extreme Programming
Spiral
Rapid Application Development