FBS 10 LEC 4
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
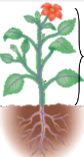
shoot system
Nodes (module)
Internodes (module)
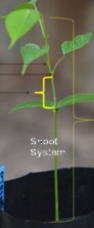
nodes
points at which
leaves attach
Internodes
stem
length between
nodes-
Apical/terminal bud
Axillary bud

Apical/terminal bud
located near the
shoot tip,
lengthens a shoot
Axillary bud
structure that can
form a lateral
shoot, or branch
apical dominance.
The presence of a terminal
(apical) bud is partly
responsible for inhibiting
the growth of axillary
buds, a phenomenon
called
apical dominance
Leaf primordia
are crowded
close together because their
internodes are very short.
intercalary meristems

Protoderm
The
outermost layer of cells in
the shoot tip forms the
epidermis;
Epidermal cells
Guard cells
Trichomes or hairs
Cuticle
Protoderm Epidermis,
which is made of:
Ground meristem
These cells slowly lose their ability
to divide, and they differentiate
mostly into parenchyma cells;
flank meristem
forms the
cortex (the cylinder of cells just
inside the epidermis),
rib meristem
forms the
pith (the core of cells in the center
of the stem)
Ground meristem
cortex & pith
The pith region of the
stem in some plants
may become hollow by
the breakdown of the
centrally located
parenchyma cells.
Procambium
produces the primary
vascular tissues
(primary xylem and
primary phloem);
scattered
In the stems of
monocots, the
vascular bundles tends _______throughout the stem
instead of being in a
ring.