current and static electricity
5.0(1)Studied by 16 people
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:54 PM on 12/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
current
the flow of electrons
2
New cards
voltage
how strong the current is in a circuit, difference in electrical potential between two points
3
New cards
resistance
resisting the flow of electrons
4
New cards
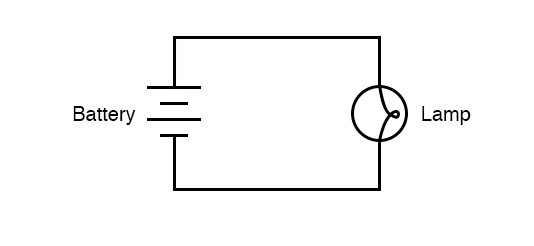
simple circuit
5
New cards
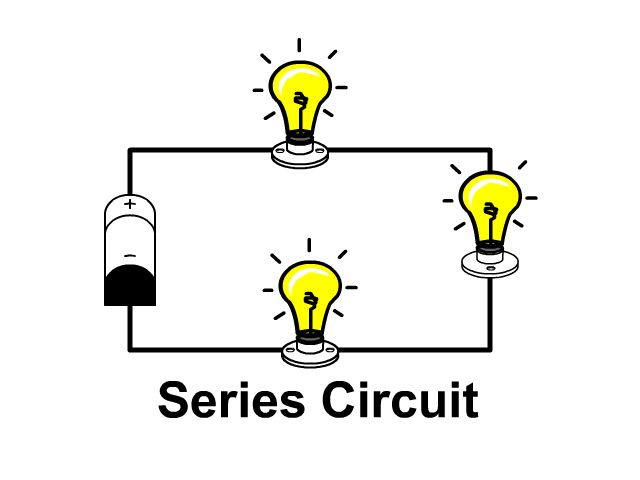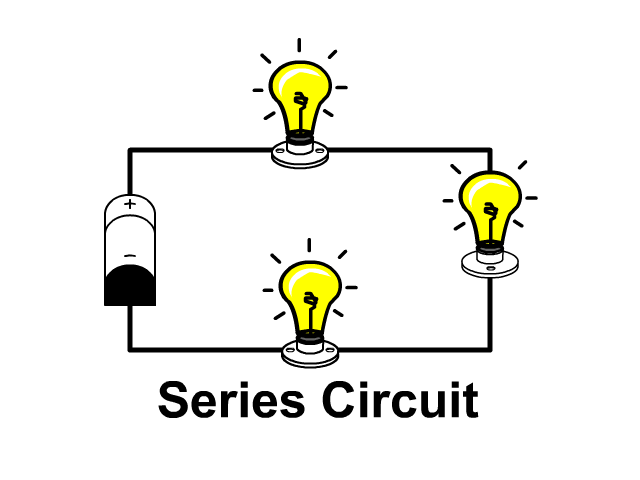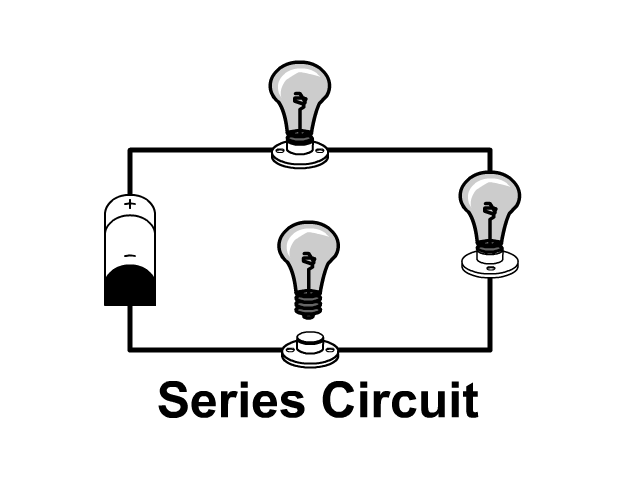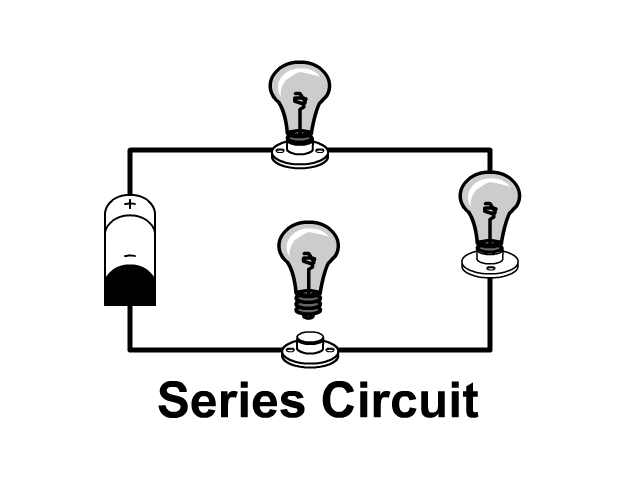
series circuit
6
New cards
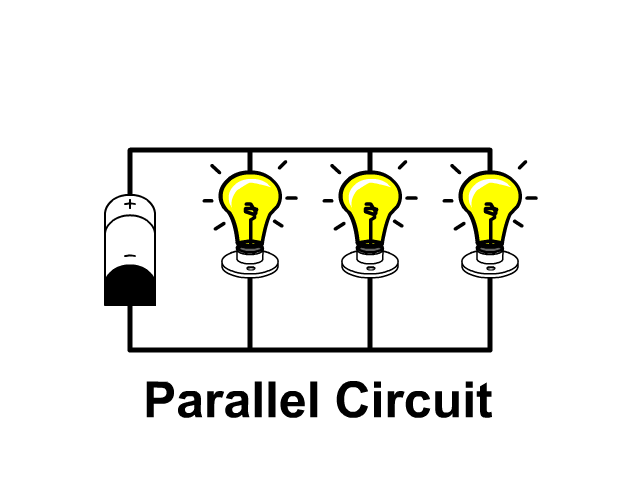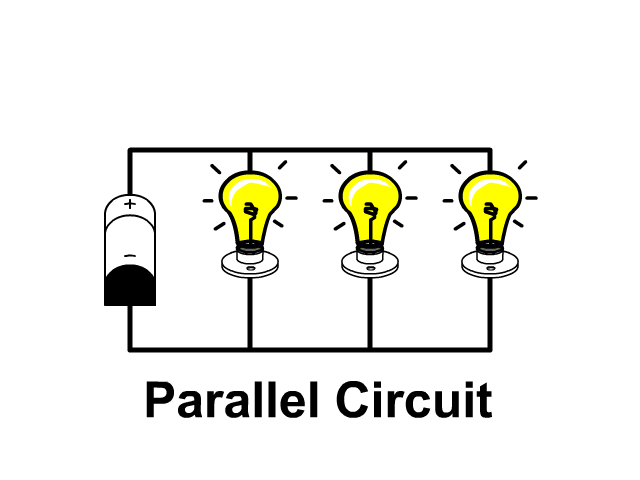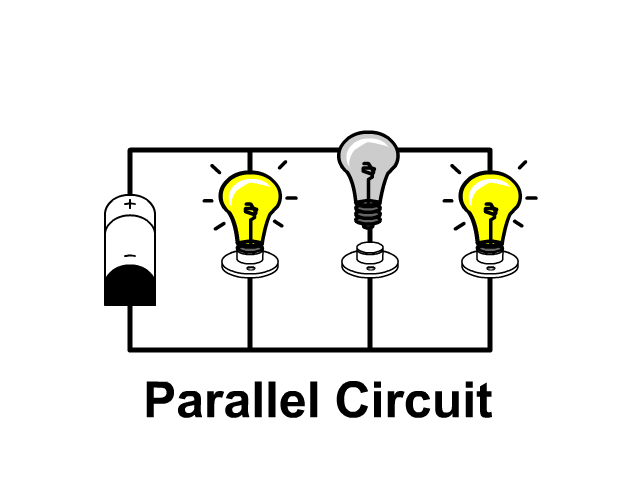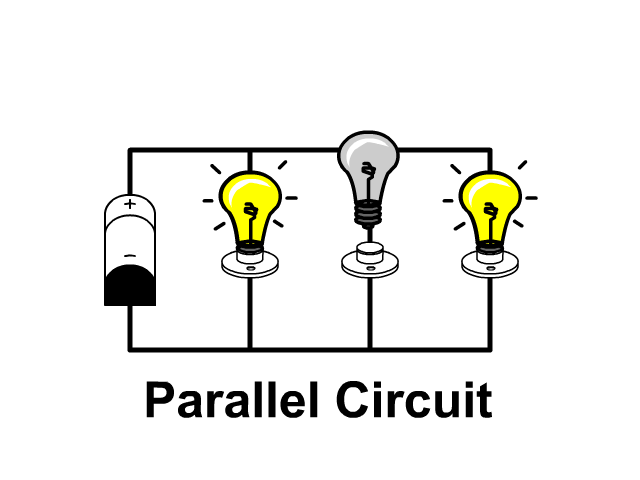
parallel circuit
7
New cards
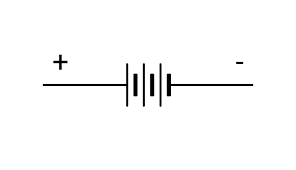
battery
8
New cards
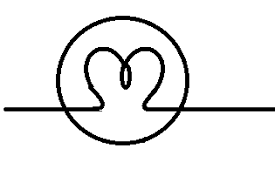
light
9
New cards
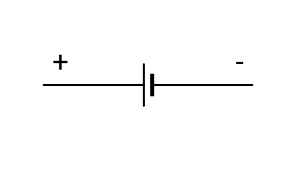
single battery cell
10
New cards

resistor
11
New cards
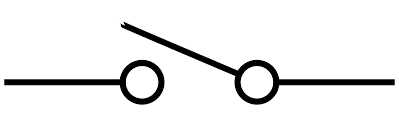
switch
12
New cards
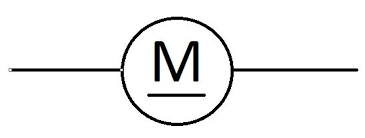
motor
13
New cards
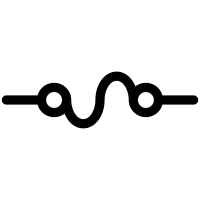
fuse
14
New cards
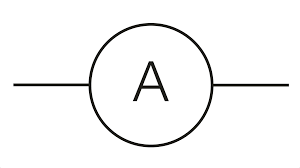
ammeter
15
New cards
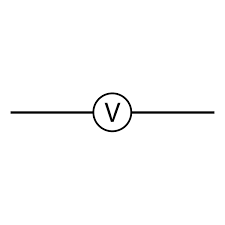
voltmeter
16
New cards
how to measure with an ammeter
turn the dial to a, insert black lead into com, and red lead into v, place the ammeter cords in the same way you'd place the wires in the circuit therefore the electrons will flow through the ammeter
17
New cards
how to measure with a voltmeter
turn the dial to v, insert black lead into com, and red lead into v, connect the voltmeter cords in parallel with the black lead first and red lead second
18
New cards
voltage and current (series circuit)
voltage = add up all the voltage values to get sum, current = to each other
19
New cards
voltage and current (parallel circuit)
voltage = to each other, current = add up all the current values to get the sum
20
New cards
the relationship between current and voltage
voltage pushes the current through the device
21
New cards
factors that affect resistance on a circuit diagram
material like copper has a lower resistance, length longer wires have a greater resistance, temperature heating a wire increases it's resistance
22
New cards
what causes a short circuit
when a low resistance path not fit to have electrons flow through it receives a high electrical current
23
New cards
ohms law
v = ir
24
New cards
law of attraction
like charges repel each other, opposing charges attract each other
25
New cards
insulator
keeps electricity in it's material and has a higher resistance for electrons to flow through
26
New cards
conductor
low resistance, lets electricity flow through it easily
27
New cards
static electricity
when two materials cause friction by rubbing together the negatively charged one loses electrons and becomes positively charged and the positively charged material gains electrons and becomes negatively charged