Practical 6: Sensory Receptors and Perception
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Sensory Receptors
Specialised cells or structures that respond to specific types of physical energy and convey information to the brain.
Five Senses
Sight, hearing, taste, smell, touch.
Additional Sensory Modalities
Includes temperature, pain, vibration, proprioception.
Adaptation
Sensory system's insensitivity to constant stimulation.
Nociceptors
Pain receptors that do not adapt to continued stimulation and are responsible for signaling pain from various types of tissue damage or injury.
Visual Spectrum
Electromagnetic range visible to humans, 380-750 nm.
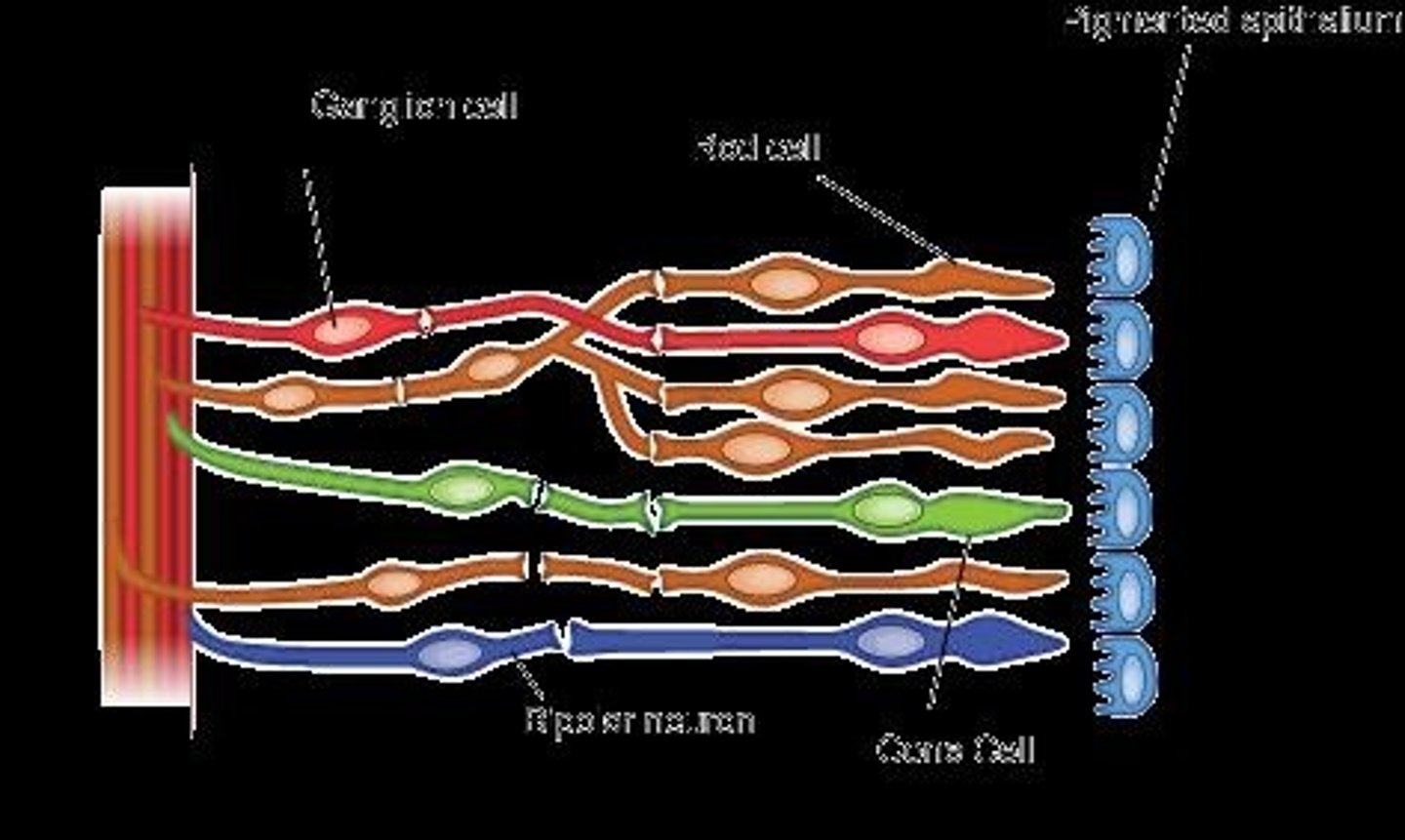
Cones
Retinal cells for color differentiation.
Rods
Retinal cells for light and dark contrast.
Fovea
Region of highest visual acuity in the retina.
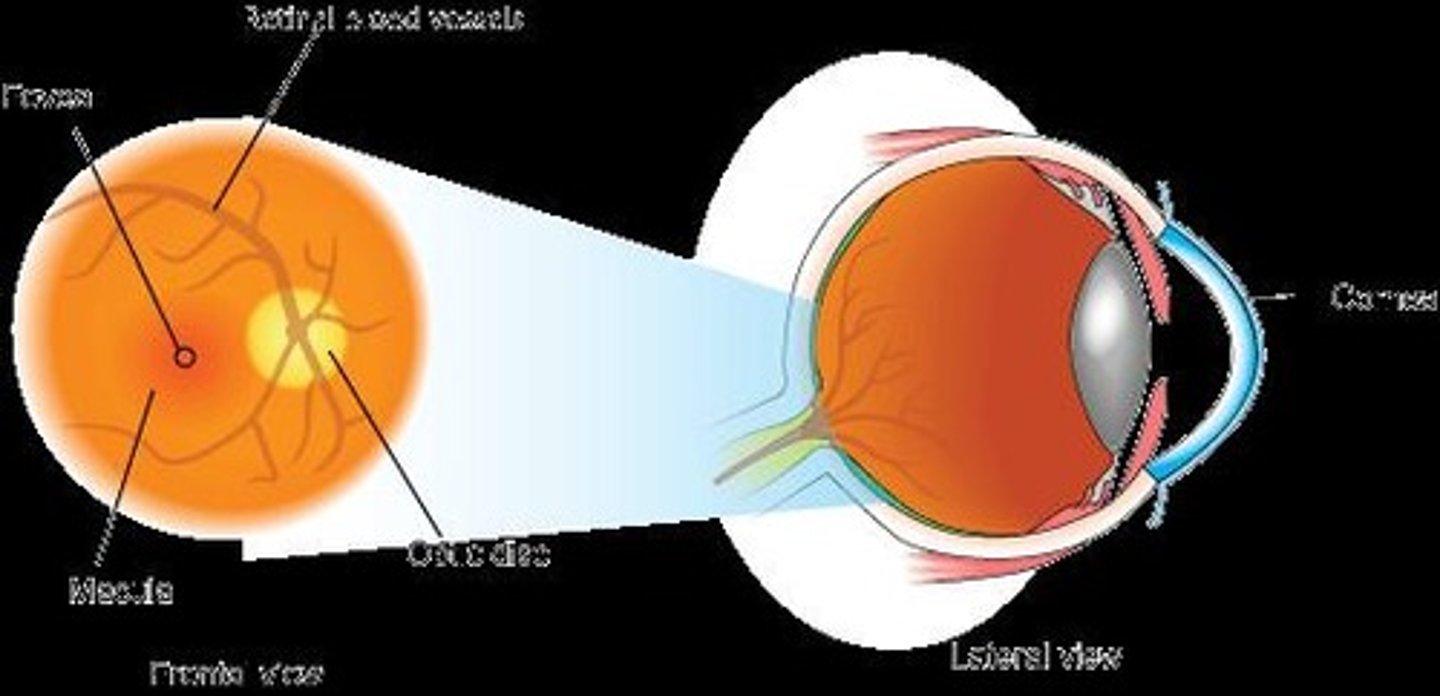
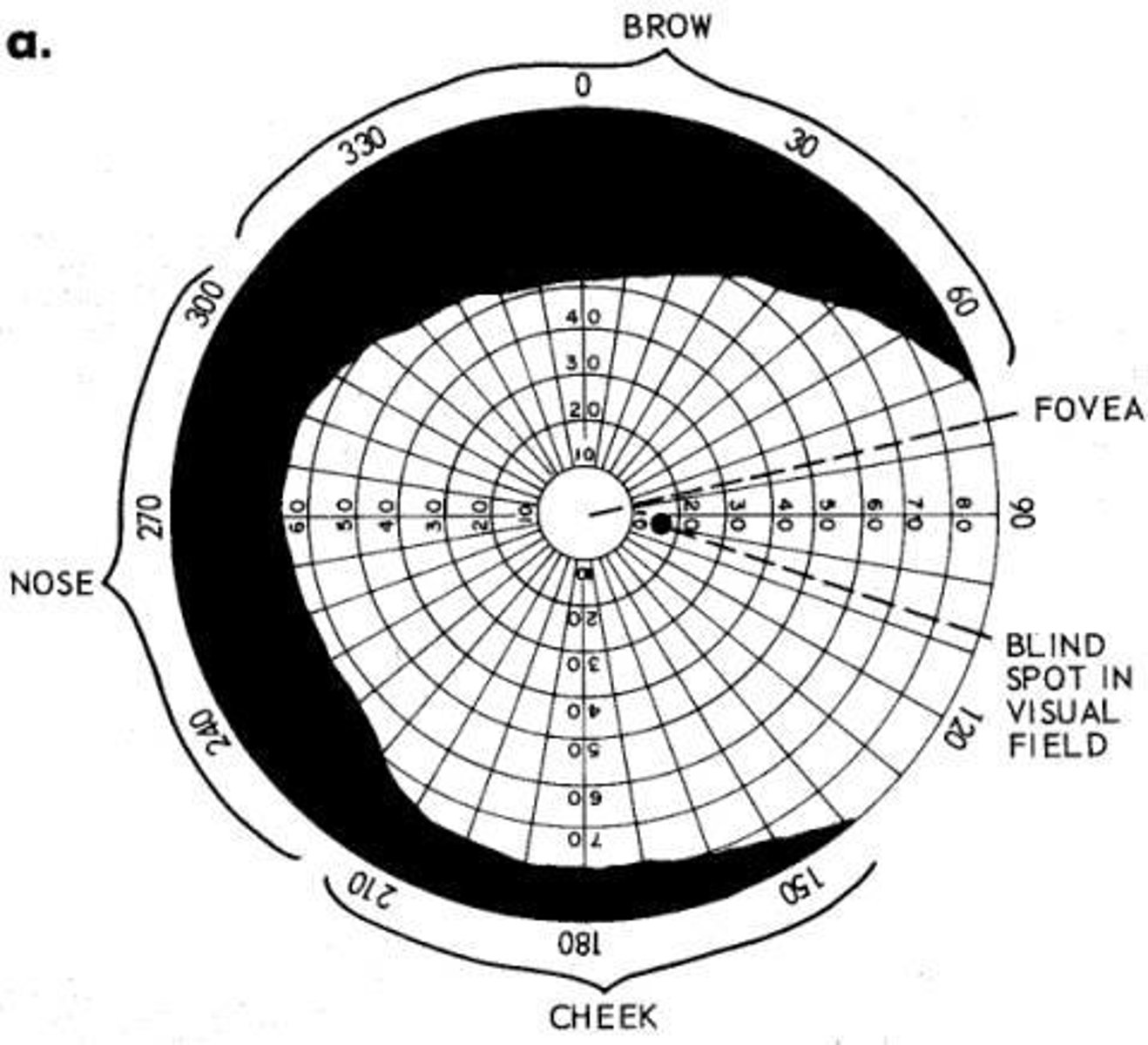
Blind Spot
Optic disc area devoid of receptors.
Color Vision
Perception based on cone sensor excitation.
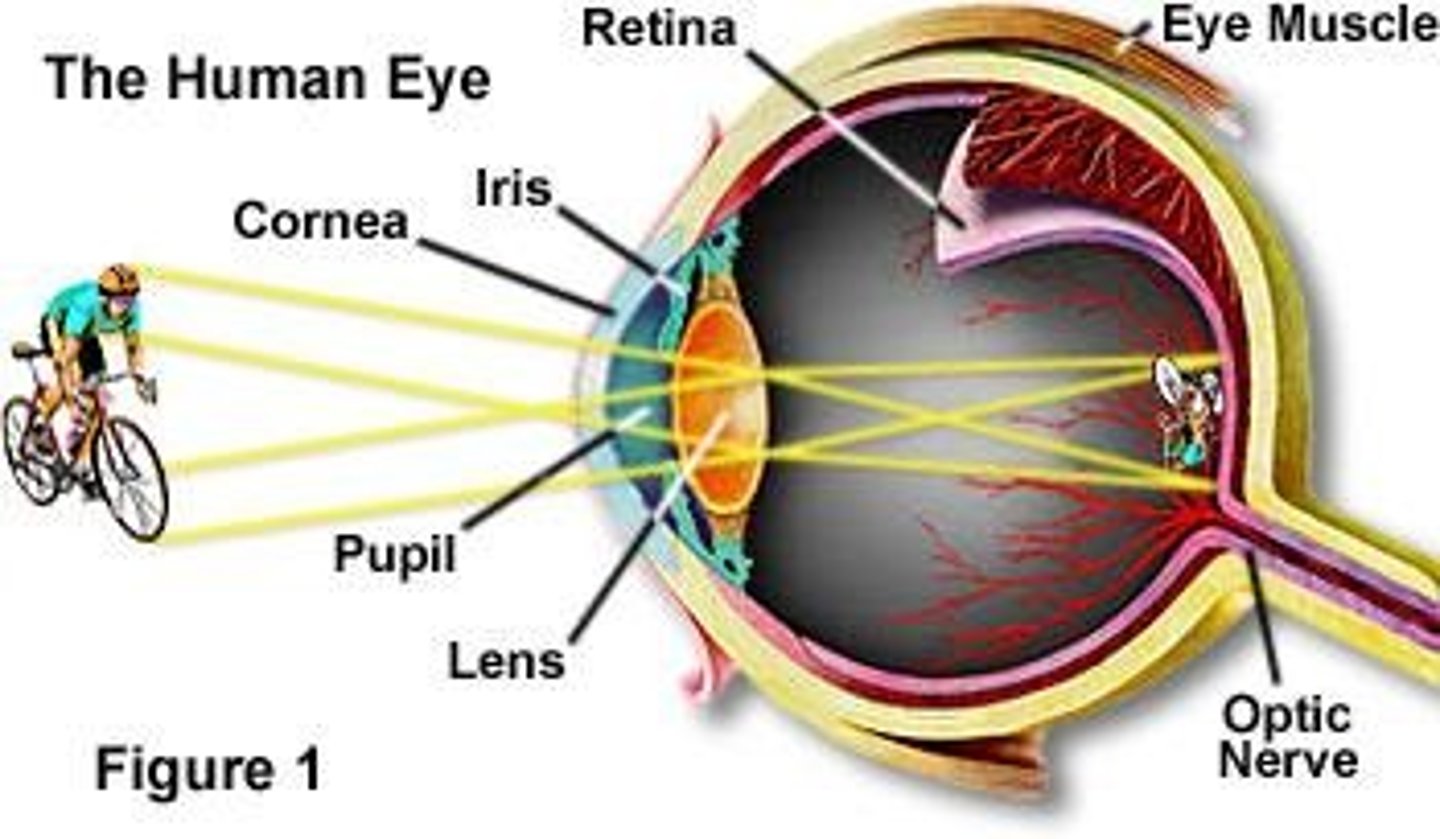
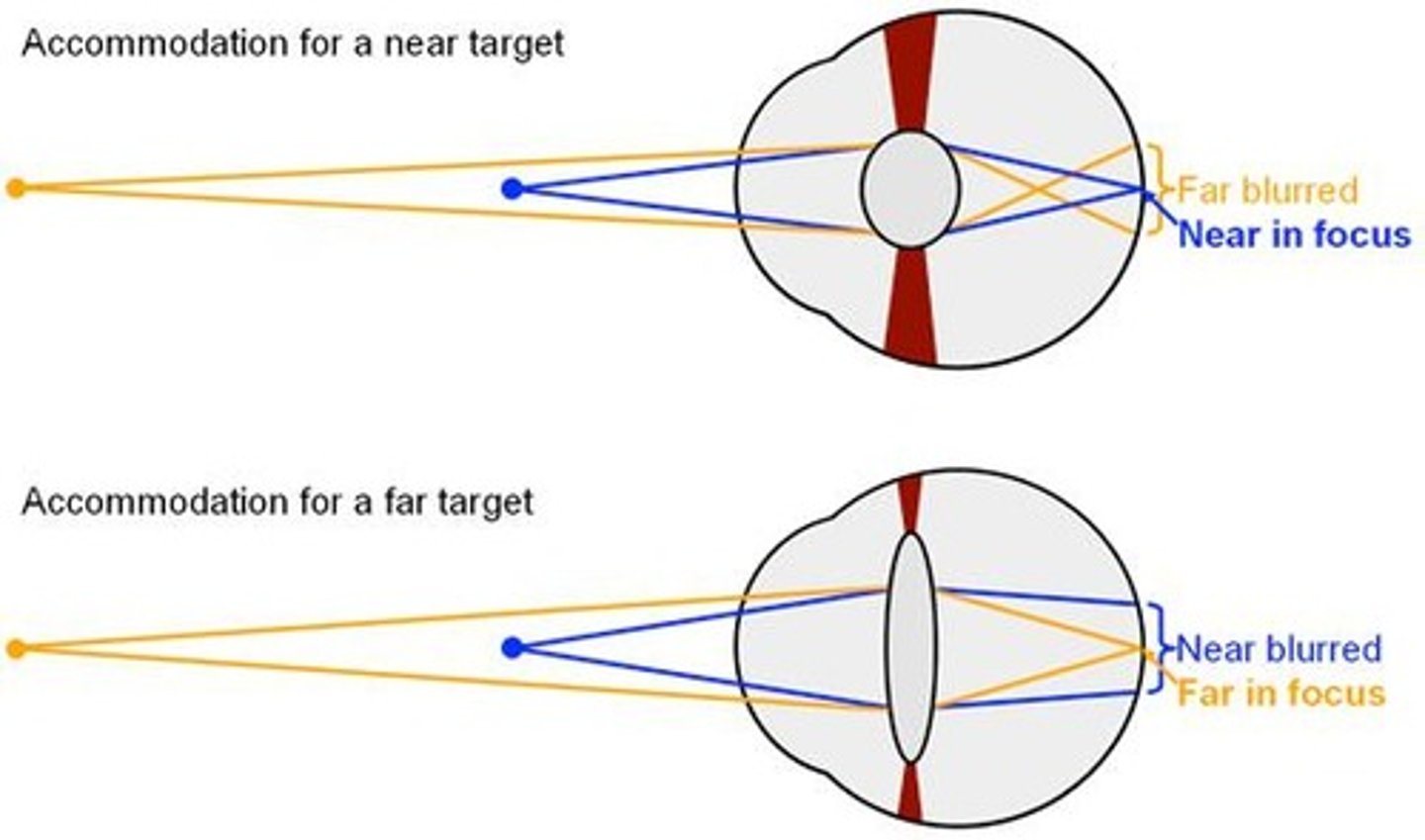
Accommodation
Eye's ability to change focus for distance.
Electromagnetic Energy
Energy detected by visual sensory receptors.
Photo Receptive Cells
Cells in the eye that detect light.
Infrared Detection
Ability to sense body heat by some snakes.
Ultraviolet Vision
Some insects can see beyond human capability.
Peak Sensitivity
Wavelengths where cones are most responsive.
Visual Acuity
Clarity or sharpness of vision.
Retina
Layer of photoreceptors at the back of the eye.
Stimulus Transduction
Conversion of physical energy into neural signals.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals released by receptors to activate neurons.
Tactile Receptors
Skin receptors that adapt quickly to stimuli.
Acetaminophen
Medication used to interrupt pain signals.
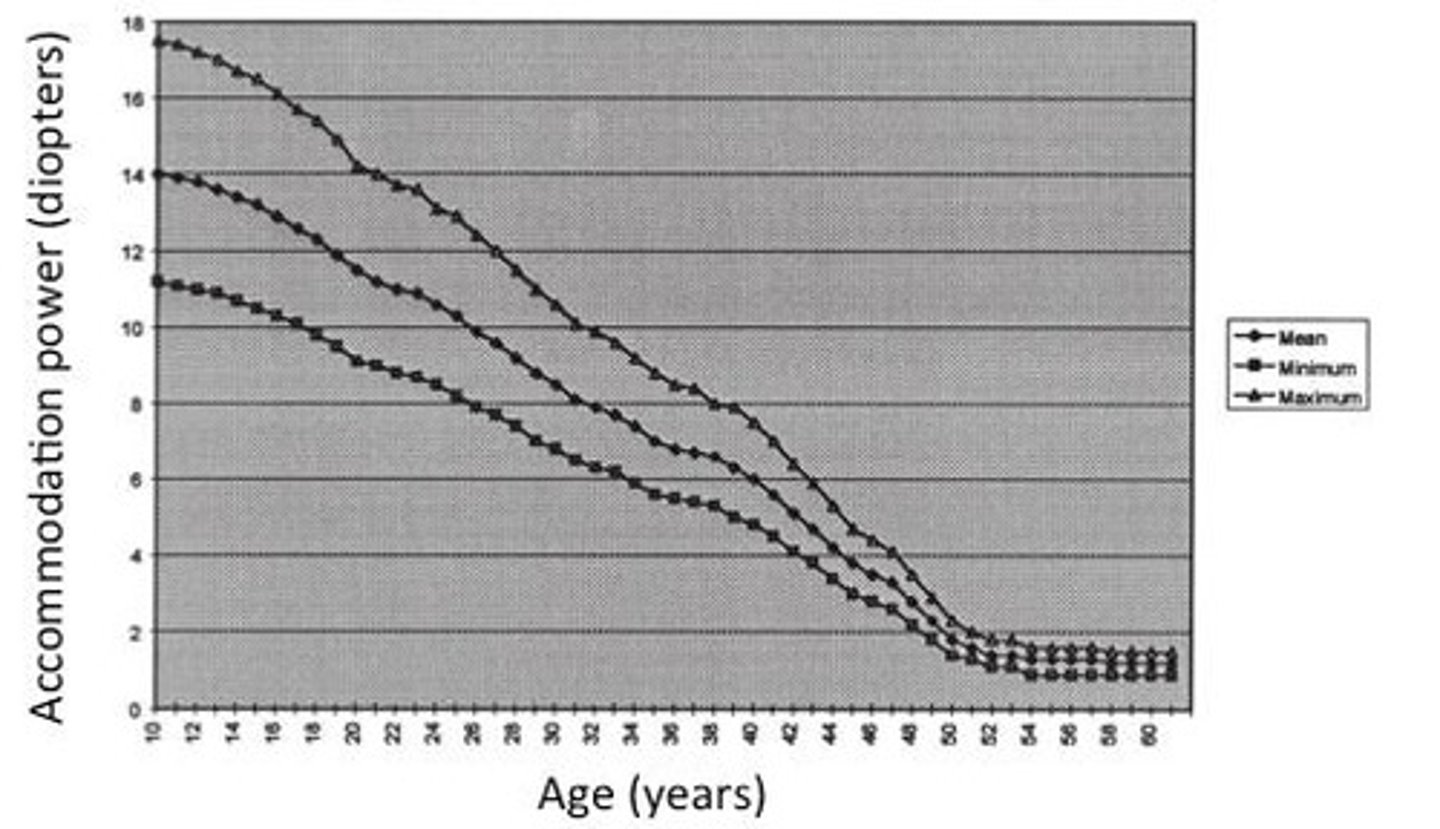
Near Point
Closest distance for clear vision of an object.
Diopter
Unit measuring lens power, equal to 1/m.
Optic Disc
Region where optic nerve exits the eye.
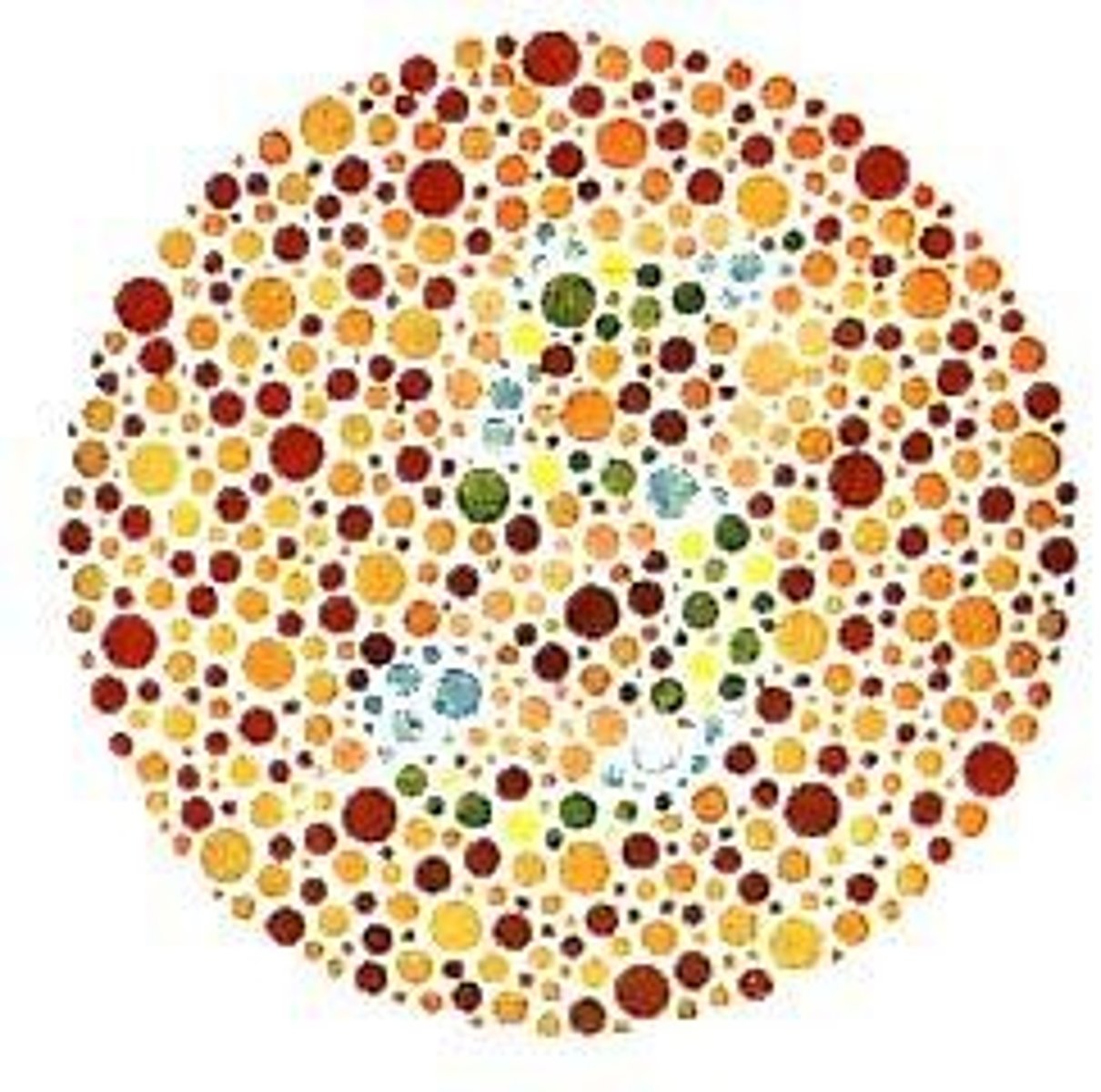
Color Blindness
Inability to distinguish certain colors.
Achromatopsia
Severe color blindness; sees only gray shades.
X-linked Recessive
Genetic trait often inherited through X chromosome.
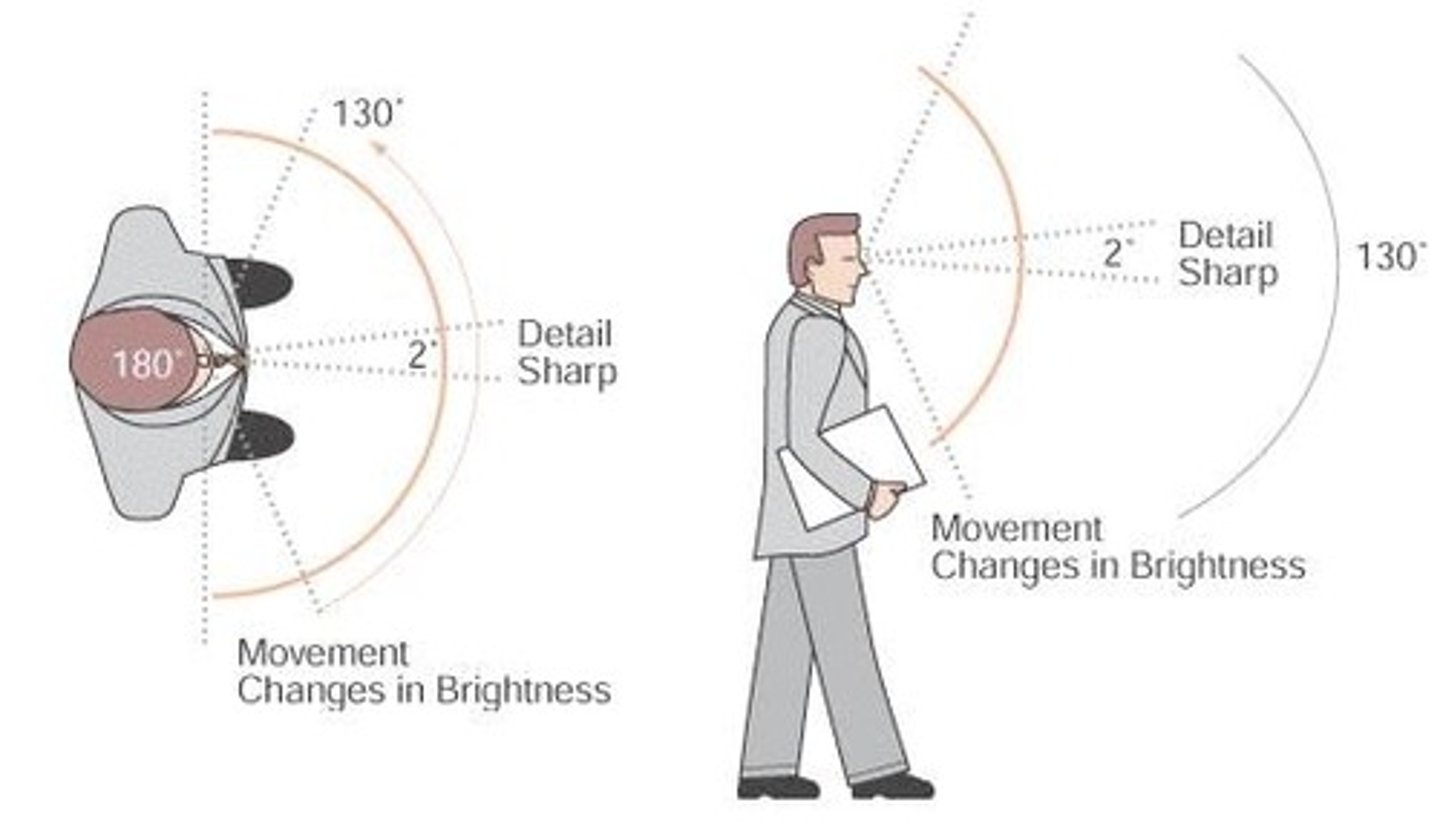
Visual Field
Total area visible when looking straight ahead.
Focal Length
Distance from lens to focus point.
Nystagmus
Involuntary eye movement, often jerky.
Accommodation Power
Measured in diopters; varies with age.
Retinal Blood Vessels
Supply blood to the retina, emerge at optic disc.
Lazy Eye
Condition where one eye fails to achieve normal vision.
Pen Test
Experiment to measure blind spot and visual field.
Color-Sensing Granules
Pigments in cones that detect color.
Irregular Margins
Uneven edges of the blind spot outline.
Measurement Technique
Using a tailor's tape for distance measurement.

Visual Focus Mechanisms
Three processes for adjusting focus on objects.
Protanopia
Complete red cone deficiency affecting color perception.
Deuteranopia
Complete green cone deficiency affecting color perception.
Protanomaly
Altered sensitivity in red cone function
individuals have difficulty distinguishing between reds and greens due to a reduced sensitivity to red light. .
Deutanomaly
Altered sensitivity in green cone function.
Tritanopia
Complete blue cone deficiency affecting color perception.
Red-green deficiency
Common color vision defect in males and females.
Equilibrioception
Perception of balance related to vestibular system.
Vestibular system
Inner ear system for balance and spatial orientation.
Semicircular canals
Fluid-filled structures detecting head rotation.
Utricle and saccule
Detect linear acceleration and gravity effects
organs located in the vestibular system of the inner ear, playing a crucial role in balance and spatial orientation. .
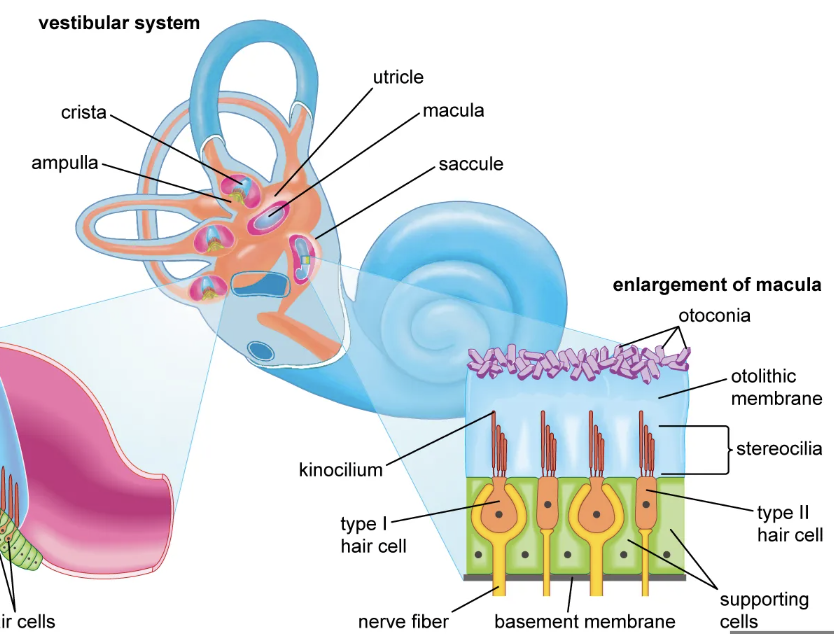
Crista ampullaris
Receptor apparatus in semicircular canals.
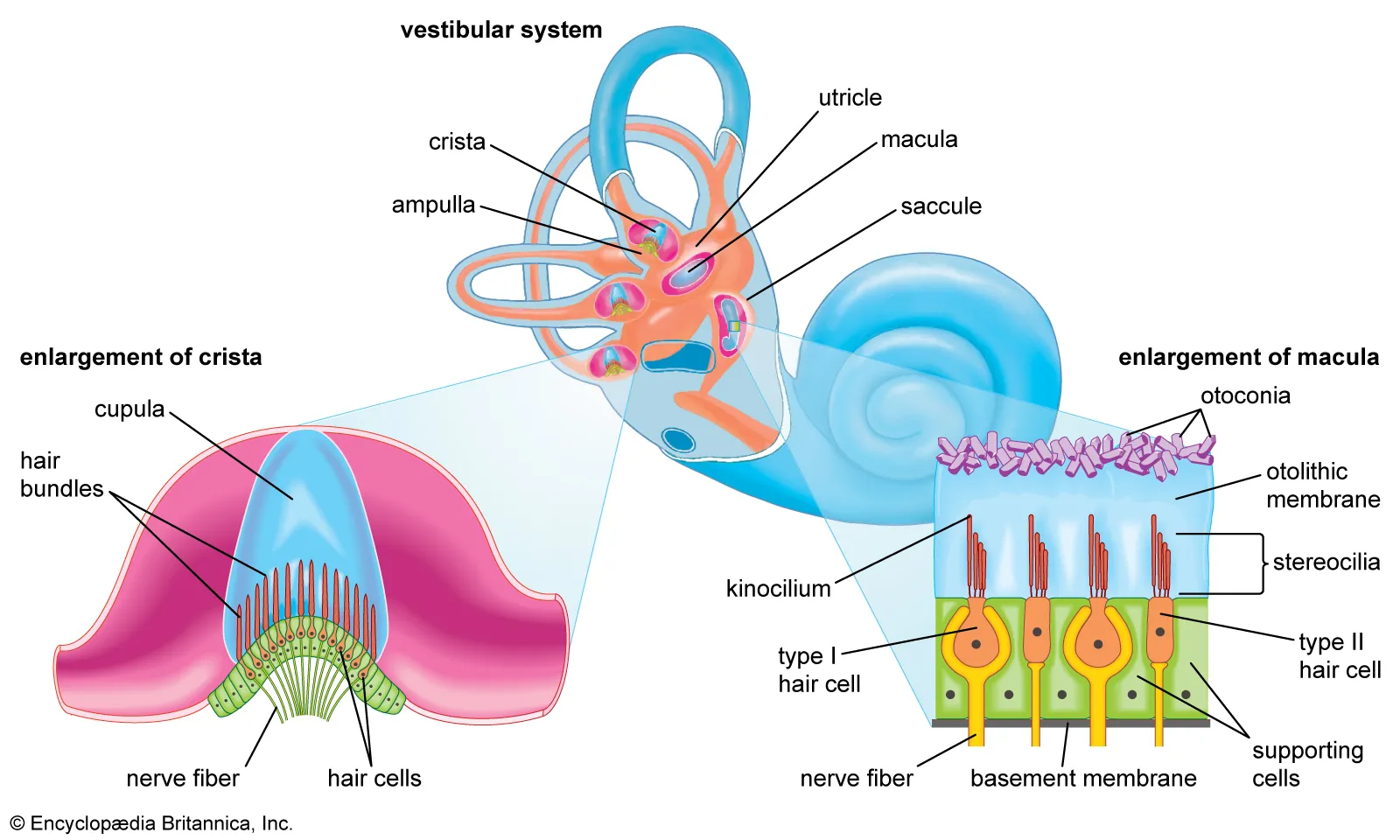
Otoconia
Calcium carbonate crystals aiding gravitational detection.
Hearing
Sense of sound perception through vibrations.
Audiometry
Test measuring frequency response of human hearing.
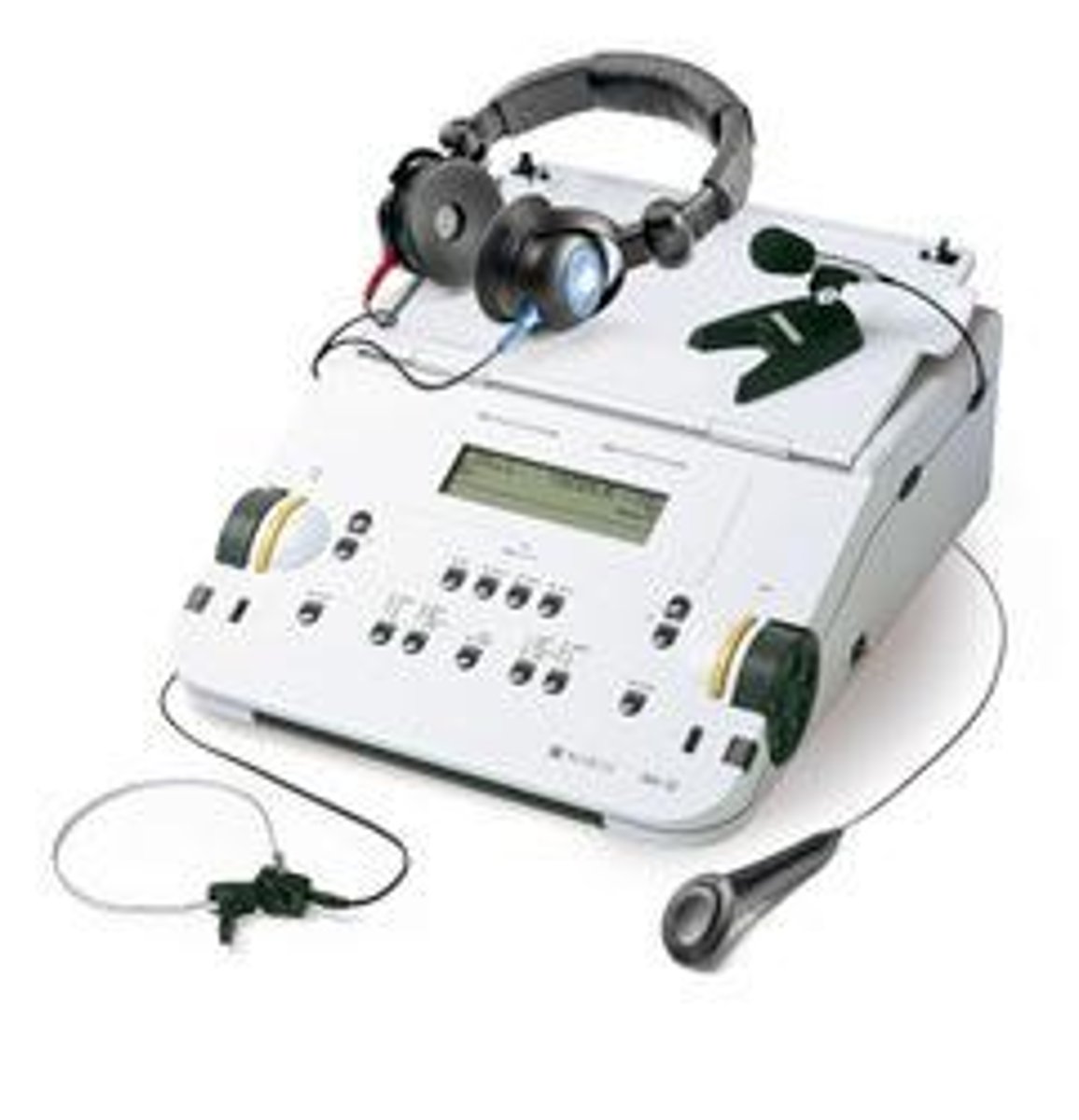

Pure-tone audiometer
Device generating sounds of specific frequencies.
Frequency range
Humans detect sounds from 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
Tactition
Detection of vibrations through body contact.
Sound frequency
Measured in Hertz (Hz), cycles per second.
Amplitude of sound waves
Measured in decibels (dB), sound intensity.
Audiograph
Graph plotting sound frequency against amplitude.
Hearing loss
Reduced sensitivity to sound frequencies over time.
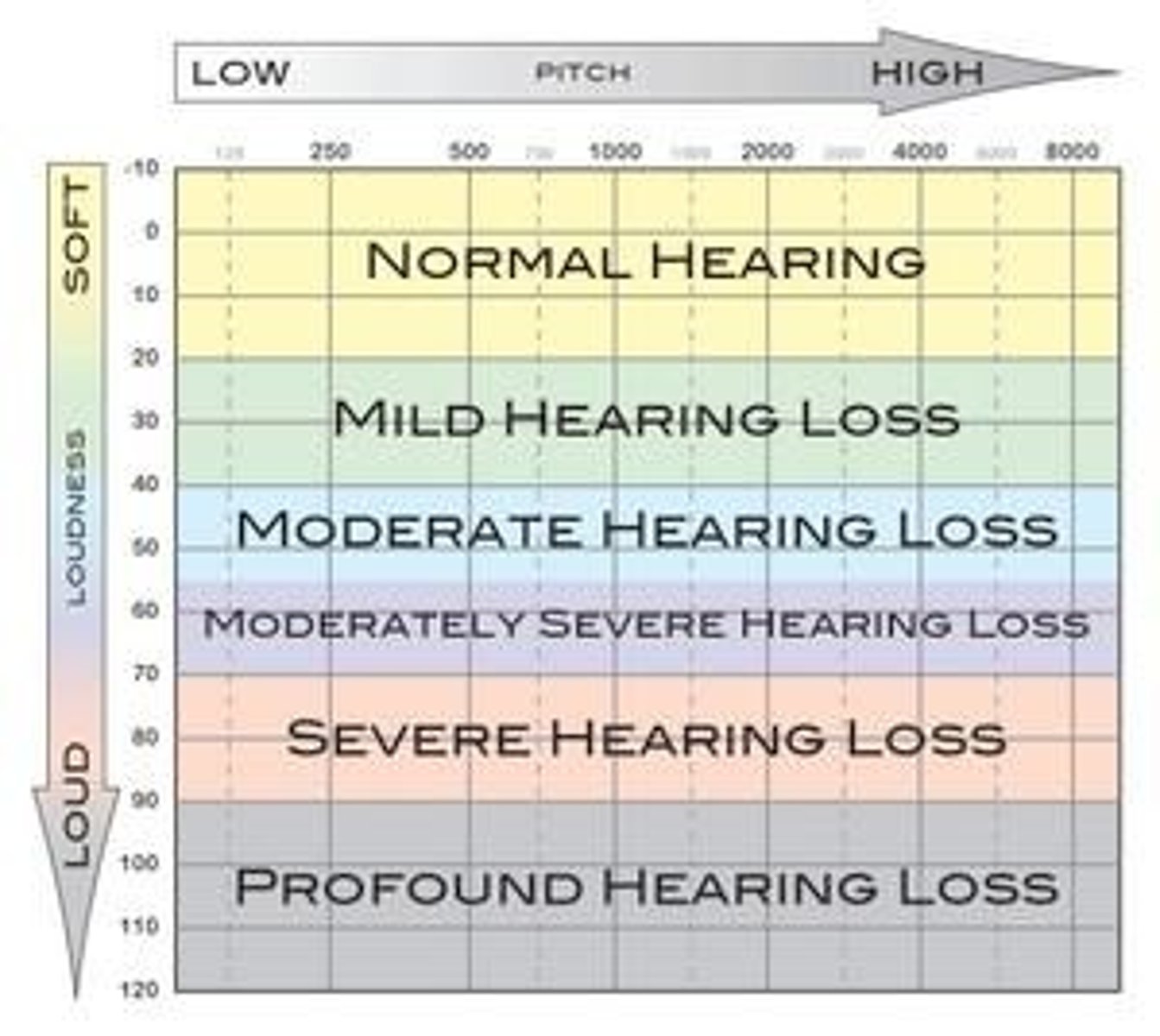
Age-related hearing loss
Common decline in high-frequency sensitivity with age.
Inner ear
Contains structures crucial for hearing and balance.
Frequency of Sound
Measured in Hertz (Hz), indicates sound pitch.
dB
Decibels, unit measuring sound intensity.
Proprioceptive Senses
Awareness of body position and movement.
Pacinian Corpuscles
Complex receptors for deep pressure and vibration.
Two-Point Discrimination
Ability to distinguish two close stimuli as separate.
Minimum Distance
Smallest separation to perceive two distinct points.
Density of Receptors
Varies across body parts, affecting sensitivity.
Thermoception
Sense detecting heat and cold temperatures.
Cold Receptors
Sensitive to temperatures below 37°C.
Warm Receptors
Sensitive to temperatures between 37°C and 45°C.
Achilles Tendon Vibration
Stimulates proprioception during balance tests.
Postural Swaying
Movement of body while maintaining upright position.
Demonstrator
Individual assisting in practical exercises for safety.
Wobble Board
Platform used to assess balance and stability.
Physiological Basis
Underlying biological mechanisms explaining sensory differences.
Statistical Difference
Comparison of data to determine significance between groups.
Standard Deviation (SD)
Measure of data variability around the mean.
Standard Error of the Mean (SEM)
Estimates accuracy of sample mean relative to population.
Temperature receptors
Found in subcutaneous skin layers, detect temperature.
Homeostatic thermoceptors
Regulate internal body temperature near hypothalamus.
Thermal illusion
Perception of temperature changes based on adaptation.
Ciliary muscle
Muscle that adjusts lens shape for focusing.
Zonule fibers
Connect ciliary muscle to the lens
They play a crucial role in adjusting the shape of the lens for focusing. .
Short sightedness
Inability to see distant objects clearly.
Far sightedness
Inability to see close objects clearly.
Perimetry
Test to measure visual field extent.
Color blindness
Difficulty distinguishing certain colors, often sex-linked.
Cone photopigments
Proteins in cones that detect color, located on X chromosome.
Dichromacy
Type of color blindness with two functioning cones.
Romberg's Test
Balance test assessing proprioception and vestibular function.
Proprioception
Sense of body position and movement.
Pacinian corpuscle
Rapidly adapting skin receptor for pressure.
Merkel disks
Slowly adapting skin receptors for light touch.
Ruffini endings
Slowly adapting receptors for skin stretch.
Meissner corpuscles
Rapidly adapting receptors for light touch.
Thermal adaptation
Decreased sensitivity to temperature after prolonged exposure.
Temperature-related injury
Damage to tissues from extreme temperature exposure.