CC2 LEC LIVER FUNCTIONS
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
1. Excretion/Secretion
2. Metabolism
3. Detoxification
4. Storage
4 functions of the liver
Hepatic artery
Artery of the liver that receives blood to function
Portal vein
Receives blood to be detoxified
Bilirubin
– the major heme waste product and the principal pigment in the bile.
Bile
– made up of bile acids or salts, bile pigments, cholesterols.
Immunoglobulins
Adult Hb
All proteins are synthesized by the liver except? (2)
Albumin
The most important protein is synthesized by the liver. What is this protein?
Glycogen
Liver stores glucose in the form of?
Gluconeogensis
glucose formed from non glucose
True
The liver serves as a gatekeeper between substances absorbed the GIT and those released into the systemic circulation. (T/F)
First pass
every substance that is absorbed in the GIT must first pass through the liver
Liver microsomes via the cytochrome P-450 isoenzymes
Detoxification takes place in the?
ADEK
Fat soluble diseases
B-complex and C
Water soluble vitamins (2)
Yellow
Jaune means?
Jaundice
Oldest pathologic conditions reported.
• Used to describe the yellow discoloration of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes resulting from the retention of bilirubin.
3-5 mg/dL
Jaundice levels
PREHEPATIC JAUNDICE
• Occurs when the problem causing the jaundice occurs prior to liver metabolism.
• Usually seen in cases of Hemolytic anemia.
caused by: RBC Destruction
Serum bilirubin: Elevated B1
Urine bilirubin: Negative
Urobilinogen: Normal/Increased
Clinical cases: HDFN, Hemolytic anemia, Malaria
Unconjugated bilirubin
Bilirubin that is predominant in prehepatic jaundice
Hepatic jaundice
Occurs when the problem resides in the liver.
Intrinsic liver defect or disease.
Due to bilirubin metabolism disorders, transport defects or hepatocellular injuries.
caused by: Hepatocyte injury
Serum bilirubin: Both elevated
Urine bilirubin: Positive
Urobilinogen: Decreased
Clinical cases: Cirrhosis, Viral hepatitis
Gilbert’s Disease
Enzymatic defect
• Benign, autosomal recessive, hereditary disorder.
• Results from a genetic mutation in the gene UGT1A1 that produces UDPGT
The most common cause
• Intermittent unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, underlying liver disease due to a defective conjugation system in the absence of hemolysis.
Total bilirubin: ↑
Conjugated bilirubin: Normal
Unconjugated: ↑
GILBERT’S DISEASE
Total bilirubin: ?
Conjugated bilirubin: ?
Unconjugated: ?
Crigler-Najjar syndrome
Syndrome of chronic nonhemolytic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
Inherited disorder of bilirubin metabolism involving a gene defect.
More rare and more serious disorder that may result in death.
Total bilirubin: ↑
Conjugated bilirubin: ↓
Unconjugated: ↑
CRIGLER-NAJJAR SYNDROME
Total bilirubin: ?
Conjugated bilirubin: ?
Unconjugated: ?
Type 1 Criggler-Najjar
complete absence of enzymatic bilirubin conjugation
Type 2 Crigler-Najjar syndrome
– mutation causing severe deficiency of the enzyme responsible for bilirubin conjugation.
Dubin-Johnson Syndrome
A rare autosomal recessive inherited disorder caused by a deficiency of the canalicular multidrug resistance/multispecific organic anionic transporter protein (MDR2/cMOAT).
The removal of conjugated bilirubin from the liver cell and the excretion into the bile are defective.
Obstructive in nature. Conjugated bilirubin binds to albumin (delta bilirubin).
Total bilirubin: ↑
Conjugated bilirubin: ↓
Unconjugated: Normal
DUBIN-JOHNSON
Total bilirubin: ?
Conjugated bilirubin: ?
Unconjugated: ?
Dark-stained granules
Dubin-Johnson syndrome in liver biopsy sample, what is the color?
Rotor syndrome
reduction in the concentration of activity of intracellular binding proteins such as Ligandin
Total bilirubin: ↑
Conjugated bilirubin: ↓
Unconjugated: Normal
ROTOR SYNDROME
Total bilirubin: ?
Conjugated bilirubin: ?
Unconjugated: ?
Physiologic Jaundice of the Newborn
• Deficiency in the enzyme glucoronyl transferase, one of the last liver functions to be activated in prenatal life since bilirubin processing is handled by the mother of the fetus.
• This condition causes kernicterus: bilirubin build- up in the brain, deposited in the brain nuclei and degenerate nerve cells.
• Infants with this type of jaundice are usually treated with ultraviolet radiation to destroy the bilirubin as it passes through the capillaries of the skin.
Total bilirubin: ↑
Conjugated bilirubin: Normal
Unconjugated: ↑
PHYSIOLOGIC JAUNDICE OF THE NEWBORN
Total bilirubin: ?
Conjugated bilirubin: ?
Unconjugated: ?
Kernicterus
Physiologic Jaundice of the Newborn causes a condition called ________ which is bilirubin build-up in the brain
Lucey-Driscoll Syndrome
• Familial form of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia and may be caused by a circulating inhibitor of bilirubin conjugation in the baby’s or mother’s blood.
Posthepatic jaundice
Type of jaundice that results in biliary obstructive diseases, usually from physical obstructions that prevent the flow of conjugated bilirubin to the bile canaliculi.
caused by: Obstruction of bile flow
Serum bilirubin: Elevated B2
Urine bilirubin: Positive
Urobilinogen: Decreased
Clinical cases: Cholelithiasis, Tumor
Total bilirubin: ↑
Conjugated bilirubin: ↑
Unconjugated: ↑
POSTHEPATIC
Total bilirubin: ?
Conjugated bilirubin: ?
Unconjugated: ?
Crigler-Najjar syndrome
Only jaundice wherein conjugated bilirubin is DECREASED
Cirrhosis
• A clinical condition in which scar tissue replaces normal, healthy liver tissue.
• Can be caused by Chronic Alcoholism, Hepatitis B, C, D infection, autoimmune hepatitis, inherited disorders, drugs, toxins, etc.
• Cannot be easily reversed.
Tumors
• Cancers of the liver are classified as primary or metastatic.
Primary liver cancer
cancer that begins in the liver cells
Metastatic cancer
– occurs when tumors from other parts of the body spread towards the liver.
Hepatocellular adenoma
– benign tumor of the liver exclusive in females of child- bearing age.
Hemangiomas
– masses of blood vessels with no known cause.
Hepatocellular carcinoma
– most common malignant tumor, aka hepatocarcinoma and hepatoma
Hepatoblastoma
uncommon hepatic malignancy in children
Reye syndrome
• An acute illness characterized by non-inflammatory encephalopathy and fatty degeneration of the liver, with a clinical presentation of profuse vomiting accompanied with vary degrees of neurologic impairment such as fluctuating personality changes and deterioration in consciousness.
Ammonia
AST
ALT
Reye’s syndrome has 3x increase in which analytes? (AAA)
Syndrome
A term used to describe a group of disorders caused by infectious, metabolic, toxic or drug-induced disease found in almost exclusively in children.
Viral infection
Reye syndrome is often preceded by what type of infection?
Ethanol
the most important drug associated with hepatic toxicity
Alcoholic fatty liver
• Mildest category
• Slight elevations in AST, ALT and GGT.
• Fatty infiltrates are noted on vacuoles of the liver
• Affect young to middle-aged people with history of moderate alcohol consumption.
• Complete recover within 1 month is seen when the drug is removed.
Alcoholic hepatitis
• Common signs include fever, ascites, proximal muscle loss
• Moderately elevated AST, ALT, GGT and ALP
• Elevations in total Bilirubin > 5 mg/dL
• AST elevations are 2x the upper reference of normal value.
• AST/ALT Ratio (De Ritis ratio) greater than 2.
• Albumin is decreased and INR is elevated.
>5 mg/dL
Total bilirubin of a person with alcoholic hepatitis
Alcoholic cirrhosis
• The last and most severe stage
• Prognosis depends on the nature and severity of associated conditions such as gastrointestinal bleeding or ascites or ascites
• Common in males than in females
• Weight loss, weakness, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, jaundice, ascites, fever, malnutrition, and edema
• Increased LFTs, decreased albumin, prolonged prothrombin time
Liver biopsy
definitive method for diagnosis of alcoholic cirrhosis
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis viruses with a faecal-oral route of infection (tAE)
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis virus with the longest incubation period (2-6 months)
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
2 Hepatitis viruses with insidious (slow) onset
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis viruses with the highest acute mortality rate (30%) (D for die)
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis with the highest chance to progress to end-stage liver disease (25%)
Liver function tests
A panel of biochemical tests are that are often deranged in patients with various forms of liver disease and dysfunction.
Synthetic function
Conjugation and excretion
Detoxification function
LFTs assess these 3 functions of the liver
Total protein
Serum protein
Total Albumin-Globulin
Prothrombin time (Vitamin K response test)
Synthetic function tests (4) (TSTP)
Bilirubin tests
Urobilinogen
BSP Dye excretion test
Excretion and conjugation tests (3) (BUB)
Enzyme panels
Ammonia
Detoxification function tests (2) (EA)
Bilirubin 1
Unconjugated
Water-Insoluble
Non-Polar
Indirect Reacting
Hemobilirubin
Slow Reacting
Prehepatic
Bilirubin 2
Conjugated
Water-Soluble
Polar Direct
Reacting
Cholebilirubin
One-minute/Prompt
Post/Hepatic Bilirubin
Delta Bilirubin
Bilirubin bound to albumin
Longer half life (12-14 days)
0-0.2 mg/dL
Conjugated bilirubin reference range
0.2-0.8 mg/dL
Unconjugated bilirubin reference range
0.2-1.0 mg/dL
Total bilirubin reference range
<0.2 mg/dL
Delta bilirubin reference range
Total bilirubin - conjugated bilirubin
Formula for solving for indirect bilirubin
Van den Bergh reaction
the diazotization of bilirubin to produce azobilirubin
Evelyn Malloy method
• Coupling Accelerator: Methanol
• Main Reagent:
Diazo A = 0.1% sulfanilic acid + HCl
Diazo B = 0.5% Sodium Nitrite
Diazo Blank = 1.5% HCl
• Final Reaction: Pink to Purple Azobilirubin at 560 nm
Jendrassik and Groff method
• Coupling Accelerator: Caffeine Sodium Benzoate
• Main Reagent:
Diazo A = 0.1% sulfanilic acid + HCl
Diazo B = 0.5% Sodium Nitrite
Diazo Blank = 1.5% HCl
Buffer: Sodium Acetate
Alkaline pH provider: Alkaline Tartrate
Initial Reaction Terminator: Ascorbic acid
Final Reaction: Blue Azobilirubin at 600 nm
Urobilinogen
a colorless end product of bilirubin metabolism that is oxidized by intestinal bacteria to the brown pigment stercobilin for feces or urobilin for urine
2 hours after a meal
2 hour freshly collected urine or stool
PX prep for urobilinogen testing
Ehrlich’s method
Method used for testing urobilinogen (p-dimethyl aminobenzaldehyde reagent)
Bromsulpthalein dye excretion test
Test for hepatocellular function and potency of bile duct
It determines the ability of protein albumin to transport the exogenous dye to the liver where it is excreted in the bile.
Intravenously
How is BSP dye administered?
MacDonald (Single dose method)
Dose: 5mg/kg body weight of patient
Sample collection: After 45 minutes of IV dose
Normal/Expected results: After 45 minutes, ± 5% dye retention
Rosenthal White (Double dose method)
Dose: 2mg/kg body weight of patient
Sample collection: After 5 minutes and after 30 minutes of IV dose
Normal/Expected results: After 5 minutes: 50% dye retention, after 30 minutes: 0% dye retention
Kjeldahl method
TOTAL PROTEIN METHODS
– reference method; based on nitrogen content
Biuret method
TOTAL PROTEIN METHODS
most widely used; colorimetric at 545nm
Folin-Ciocalteu method
TOTAL PROTEIN METHODS
highest analytical sensitivity; deep-blue color
Lowry method
TOTAL PROTEIN METHODS
combination of Biuret and Folin-Ciocalteu methods
Turbidimetric and nephelometric
TOTAL PROTEIN METHODS
used in CSF and urine spx
UV absorption method
TOTAL PROTEIN METHODS
absorbance of proteins at 210nm due to peptide bonds
Refractometry
TOTAL PROTEIN METHODS
alternative test to chemical analysis; refractive index
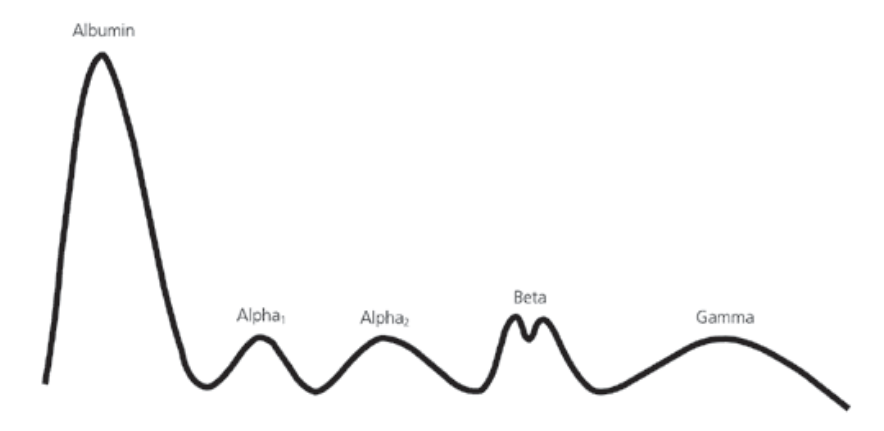
Electrophoresis
TOTAL PROTEIN METHODS
preferred in detecting abnormal proteins
Salt fractionation
TOTAL PROTEIN METHODS
separation of globulins and albumin
Serum protein electrophoresis
Principle: Migration of charged particles in an electrical field
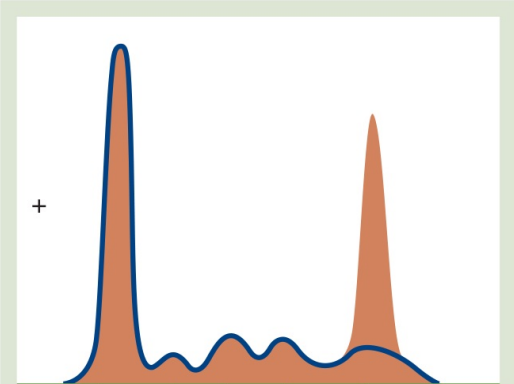
Multiple myeloma
SERUM PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS
Abnormal patterns:
Gamma spike
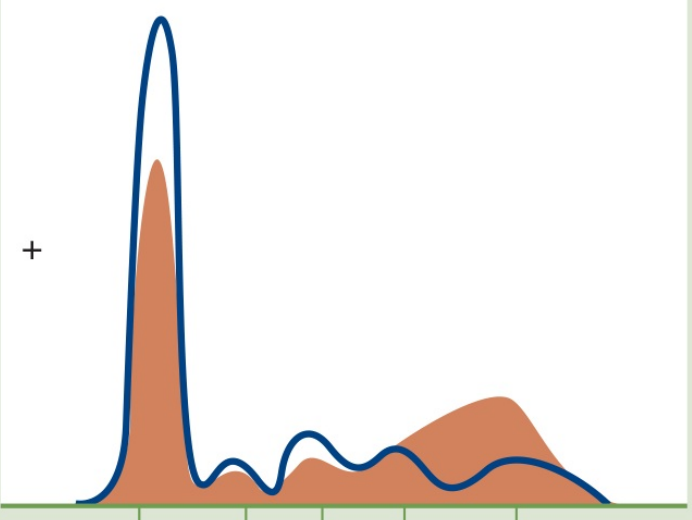
Hepatic cirrhosis
SERUM PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS
Abnormal patterns:
Beta-gamma bridging
Nephrotic syndrome
SERUM PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS
Abnormal patterns:
a2-globulin band spike
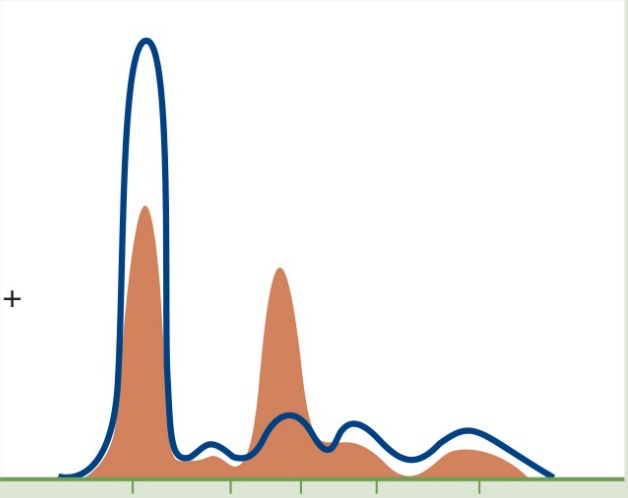
Juvenile cirrhosis (due to a1-antitrypsin deficiency)
SERUM PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS
Abnormal patterns:
a1-globulin flat curve
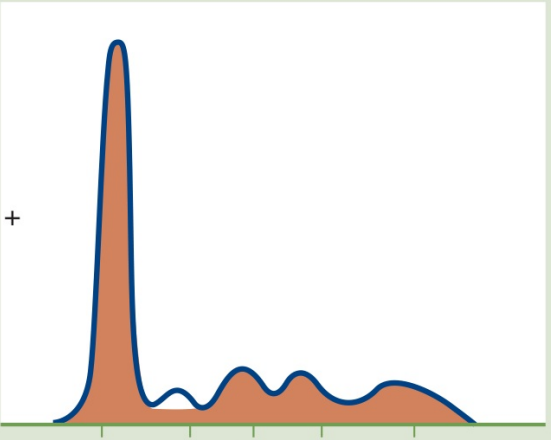
Inflammation
SERUM PROTEIN ELECTROPHORESIS
Abnormal patterns:
Spikes of a1, a2, and B globulin bands
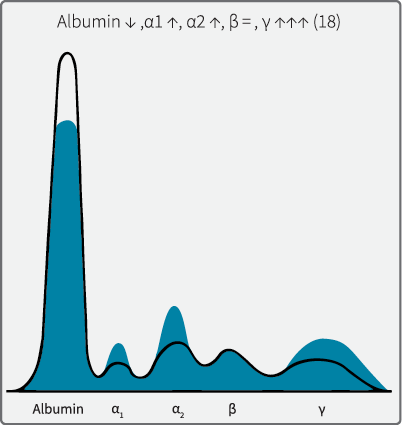
Albumin
Concentration is inversely proportional to severity of liver disease.
Decreased serum _________may be due to decreased synthesis.
Low in Hepatic Cirrhosis & Nephrotic Syndrome (along with low total protein).
What protein?