Topic 6 - Phototrophy - Biology 241 - University of Calgary
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:35 PM on 10/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
1
New cards
• 6CO2 + 6H2O ---> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the overall reaction for photosynthesis?
2
New cards
• Polar covalent bonds in the reactants.
What bonds are broken during photosynthesis?
3
New cards
• Non-polar covalent bonds in the products.
What bonds are formed during photosynthesis?
4
New cards
• H2O is oxidized and it becomes O2 since the bonding electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen have moved further away from the O atoms in O2.
What reactant in photosynthesis is oxidized? What is its product?
5
New cards
• Carbon is reduced and it becomes CO2 since the bonding electrons between the carbon and oxygen in the carbon dioxide have moved closer to the C atoms in glucose.
What reactant in photosynthesis is reduced? What is its product?
6
New cards
• Photosynthesis.
What occurs in the chloroplast?
7
New cards
• Outer membrane.
• Inner membrane.
• Inner membrane.
What two membranes does the chloroplast consist of?
8
New cards
• Space around the thylakoids.
Stroma
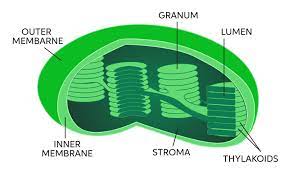
9
New cards
• One of the stacks of thylakoids found in chloroplasts.
Granum
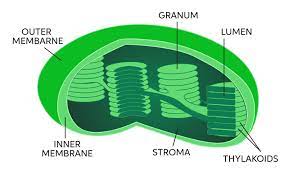
10
New cards
• Membrane-bound compartments inside chloroplasts that are the site of light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Thylakoids
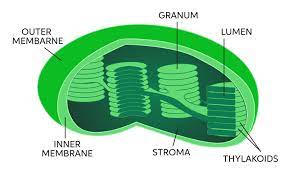
11
New cards
• To allow for pigments, ETC complexes, and ATP synthase.
Why do thylakoid structures contain high SA?
12
New cards
• Light dependent reactions.
• Light independent reactions.
• Light independent reactions.
What are the two photosynthetic processes?
13
New cards
• Reactants: Sunlight + H2O + NADP+ + ADP
• Products: ATP + NADPH + O2
• Products: ATP + NADPH + O2
What are the reactants and products in light dependent reactions?
14
New cards
• Reactants: ATP + NADPH + CO2
• Products: Glucose + NADP+ + ADP
• Products: Glucose + NADP+ + ADP
What are the reactants and products in light independent reactions?
15
New cards
• High energy.
A small wave length results in what type of energy?
16
New cards
• Low energy.
A long wavelength results in what type of energy?
17
New cards
• Photon.
• Frequencies.
• Frequencies.
Light is a _________ that resonates as different ____________.
18
New cards
• Reflected (what we see).
• Transmitted (pass through).
• Absorbed (photons absorb electrons, gaining energy).
• Transmitted (pass through).
• Absorbed (photons absorb electrons, gaining energy).
When a photon strikes an object, it can be... (3)
19
New cards
• Those efficient in absorbing photons.
What types of molecules produce pigments?
20
New cards
• Their chemical structure allows their electrons to absorb solar energy.
How does a molecule that can efficiently absorb photons produce pigments?
21
New cards
A) Specific
Pigments absorb photons of _________ wavelengths.
A) Specific.
B) Similar.
C) Varying.
A) Specific.
B) Similar.
C) Varying.
22
New cards
• Must exactly match the energy needed to excite the electron to a higher orbital.
What requirements must a wavelength meet to be absorbed?
23
New cards
• Electrons can jump 2 energy levels.
Blue Light (450nm) Characteristics
24
New cards
• Nothing.
• Doesn't absorb photons, so they are reflected or transmitted instead.
• Doesn't absorb photons, so they are reflected or transmitted instead.
Green Light (550nm) Characteristics (2)
25
New cards
• Electrons jump 1 energy level.
Red Light (700nm) Characteristics
26
New cards
• Falls back down to ground state and releases heat/light.
• Transferred to different pigment molecule.
• Transfers to electron acceptor.
• Transferred to different pigment molecule.
• Transfers to electron acceptor.
What are the three fates of an excited electron?
27
New cards
• Thylakoid membrane.
Where are photosynthetic pigments embedded?
28
New cards
• Main pigment.
• Capture of energy.
• Capture of energy.
Chlorophylls (2)
29
New cards
• Accessory pigments.
• Extends wavelength range absorbed.
• Protects from sunburn.
• Extends wavelength range absorbed.
• Protects from sunburn.
Carotenoids (3)
30
New cards
• Shows what pigments absorb what wavelengths.
Absorption Spectrum (Spectrophotometry)
31
New cards
• What wavelengths the chloroplasts are photosynthesizing.
Action Spectrum
32
New cards
• Photosystems.
What are pigment molecules organized into?
33
New cards
• A reaction center pigment.
Antenna pigments are grouped around...
34
New cards
• Reaction center in which not all electrons are transferred and electrons fall back.
When excited, the antenna pigments channel energy to the...
35
New cards
• Transfer of solar energy from one pigment molecule to other in an antenna complex.
Inductive Resonance
36
New cards
• Jump.
Photons do not leave the pigment, instead they __________ around.
37
New cards
• Light is absorbed by the antennae pigments.
• Energy is passed to the reaction center.
• The reaction center reduces a primary electron acceptor.
• Energy is passed to the reaction center.
• The reaction center reduces a primary electron acceptor.
What happens when reaction centers reduce a primary electron acceptor? (3)
38
New cards
• The reduction of a primary electron acceptor.
What powers light dependent reactions?
39
New cards
• Photosystem II.
Which photosystem produces PMF?
40
New cards
• Prokaryotes.
Does anoxygenic photosynthesis occur in eukaryotes or prokaryotes?
41
New cards
• At a time before oxygen was present in the atmosphere and when there were less organic molecules.
How did anoxygenic photosynthesis evolve?
42
New cards
• Anoxygenic photosynthesis.
What was the first metabolism that utilized an ETC?
43
New cards
• Cyclic electron flow (does not split the water for oxygen).
What type of process does anoxygenic photosynthesis use?
44
New cards
• Cytosol and on the cell membrane.
Where does oxygenic photosynthesis in prokaryotes occur?
45
New cards
• Chloroplasts.
• PSII, PSI, Calvin Cycle.
• PSII, PSI, Calvin Cycle.
Cyanobacteria have a photosynthetic mechanism similar to what? What makes them similar?
46
New cards
• Oxygenating the entire planet.
Oxygenic photosynthesis is responsible for...
47
New cards
G3P (3C) + G3P (3C) ---> Glucose (6C)
What is the formula for the conversion of G3P to glucose?
48
New cards
• Used in glycolysis for aerobic respiration.
• Polymerized into starch/cellulose for cell walls.
• Used to synthesize amino acids, nucleic acids, and lipids for us to eat.
• Polymerized into starch/cellulose for cell walls.
• Used to synthesize amino acids, nucleic acids, and lipids for us to eat.
What is glucose used for? (3)
49
New cards
• It uses energy to raise an electron to a higher energy level (P680*), and through oxidation and reduction processes from P680* to electron acceptors, it finally leaves behind P680+ which is highly oxidizing and can split apart water molecules. The oxidization of water molecules allows for P680 to regenerate.
When photosystem II is hit with solar energy, what happens in the reaction center P680?
50
New cards
• P680* reduces the primary electron acceptor that passes electrons to PQ.
• PQ (taxi) grabs H+ from the stroma.
• PQ reduces the cytochrome b6f complex and releases H+ into the thylakoid lumen.
• b6f reduces plastocyanin (taxi).
• PQ (taxi) grabs H+ from the stroma.
• PQ reduces the cytochrome b6f complex and releases H+ into the thylakoid lumen.
• b6f reduces plastocyanin (taxi).
How is the PMF produced by photosystem II? (5)
51
New cards
• Hydrophobic.
Is PQ hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
52
New cards
• Hydrophilic.
Is b6f hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
53
New cards
• The antenna.
Where does photosystem I get its energy from?
54
New cards
• It uses the energy from each photon to raise an electron to a higher energy level (P700*), and through oxidation and reduction processes, from P700* to electron acceptors, it finally leaves behind P700+, which then oxidizes plastocyanin, regenerating P700.
What happens when the energy from the antenna reaches photosystem I?
55
New cards
• The inner surface of the thylakoid.
Thylakoid Lumen
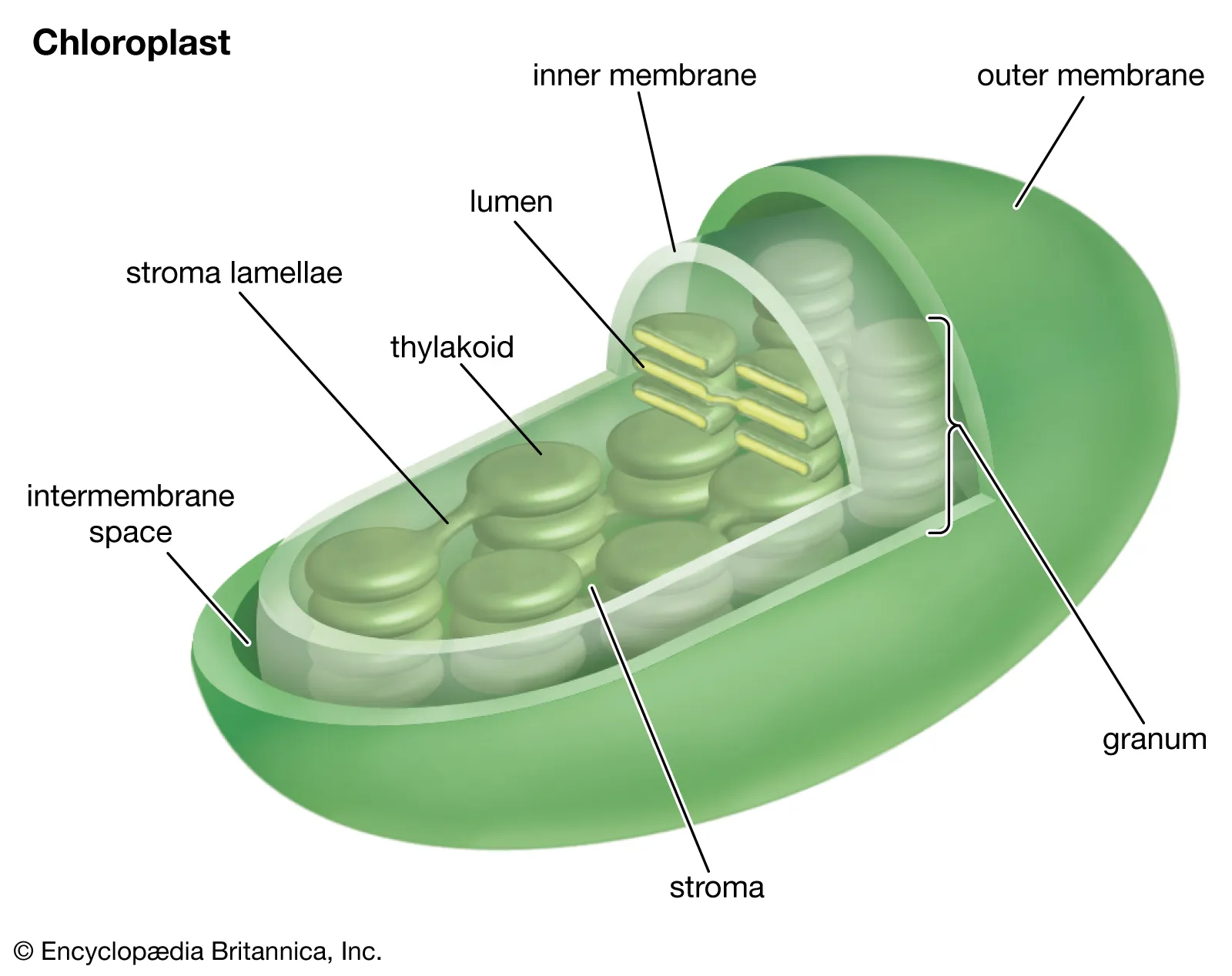
56
New cards
• P700* donates electrons to a primary electron acceptor which passes electrons to the protein ferredoxin.
• Ferredoxin reduces NADP+ reductase which in return, reduces NADP+ to NADPH in the stroma.
• Ferredoxin reduces NADP+ reductase which in return, reduces NADP+ to NADPH in the stroma.
How does photosystem I produce NADPH? (2)
57
New cards
• Hydrophilic.
Is ferredoxin hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
58
New cards
• Thylakoid membrane.
Where can we find photosystem II inside the chloroplast?
59
New cards
• Stroma.
Where can we find photosystem I inside the chloroplast?
60
New cards
• Nothing happens.
What happens if a wavelength is not exact and specific?
61
New cards
• Collection of proteins that interact with pigments.
Reaction Center
62
New cards
• Pigments that are grouped around reaction center (RC).
Antenna Pigments
63
New cards
• It reaches the reaction center.
Inductive resonance occurs until...
64
New cards
• It grabs a H+ from the stroma when reduced.
What does PQ do?
65
New cards
• Passes electrons to P700.
What does plantacyanin (PC) do?
66
New cards
• False.
Photosystem 2 does not produce the PMF, true or false?
67
New cards
• True.
P680 replaces its lost electrons by splitting H2O, true or false?
68
New cards
• True.
Photosystem I produces NADPH, true or false?
69
New cards
• Reduces NADP+ reductase.
What does ferredoxin do?
70
New cards
• Reduces NADP+ to NADPH.
What does NADP+ reductase do?
71
New cards
• Releasing protons in the thylakoid lumen when H2O is oxidized.
• Moving protons from the stroma into the lumen when PQ shuttles electrons.
• Using protons in the stroma to reduce NADP+ to NADPH.
• Moving protons from the stroma into the lumen when PQ shuttles electrons.
• Using protons in the stroma to reduce NADP+ to NADPH.
Both photosystems produce a strong proton electrochemical gradient, they do this by: (3)
(Hint: Think about the functions of PQ, b6f, ferredoxin, and NADP+ reductase.)
(Hint: Think about the functions of PQ, b6f, ferredoxin, and NADP+ reductase.)
72
New cards
• The use of solar energy to generate PMF to power ATP synthase.
Photophosphorylation
73
New cards
• Stroma side of the membrane.
ATP is generated on the...
74
New cards
• Chemical energy.
What type of energy is in ATP and NADPH?
75
New cards
• Creates the PMF.
• Reducing powers.
• Reducing powers.
The electron transport chain performs two actions:
76
New cards
• False, the energy from PSII generates enough energy to power the ETC only.
The energy from photosystem II is enough to power an ETC and generate enough energy to reduce NADP+, true or false?
77
New cards
• True.
Photosystem I reenergizes electrons enough to reduce NADP+, true or false?
78
New cards
• The stroma.
The Calvin cycle occurs in...
79
New cards
• ATP.
• NADPH.
• NADPH.
What two products of the light-dependent reaction does the Calvin cycle use?
80
New cards
• ATP.
Does the Calvin cycle use more NADPH or ATP?
81
New cards
• Cyclic electron flow.
What is the solution to a buildup of NADPH in the Calvin cycle?
82
New cards
• To generate balance between the ATP and NADPH energy budget.
• Protects both photosystems from damage due to stromal overreduction.
• Protects both photosystems from damage due to stromal overreduction.
What is the function of the cyclic electron flow? (2)
83
New cards
• Fixation.
• Reduction.
• Regeneration.
• Reduction.
• Regeneration.
What are the three phases in the Calvin Cycle?
84
New cards
• 3 CO2.
• 9 ATP.
• 6 NADPH.
• 9 ATP.
• 6 NADPH.
What are the reactants of the Calvin cycle?
85
New cards
• 1 G3P.
• 9 ADP.
• 6 NADP+.
• 9 ADP.
• 6 NADP+.
What are the products of the Calvin cycle?
86
New cards
• Use carbon dioxide to create sugar for plants.
What is the purpose of the Calvin cycle?
87
New cards
• Hydrophilic
Is PC a hydrophobic or hydrophilic electron taxi?