Meristems of primary growth
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
outcomes of primary growth
adds length
produces new organs
establishes patters of cell differentiation
apical meristem contains:
promeristem
primary meristems
promeristem in seed free plants
single apical cell
promeristem in roots (non seed free)
group of apical initials
quiescent center
inactive meristematic calls which divide rarely and are surrounded by the promeristem
columella
vertical files of cells in the root cap used for gravity sensing
open type meristem
root meristem where primary meristems are only distinguishable a ways away from the promeristem
closed type meristem
root meristem where primary meristems are recognizable immediately adjacent to the promeristem
trichoblast
specialized epidermis cells for producing root hairs
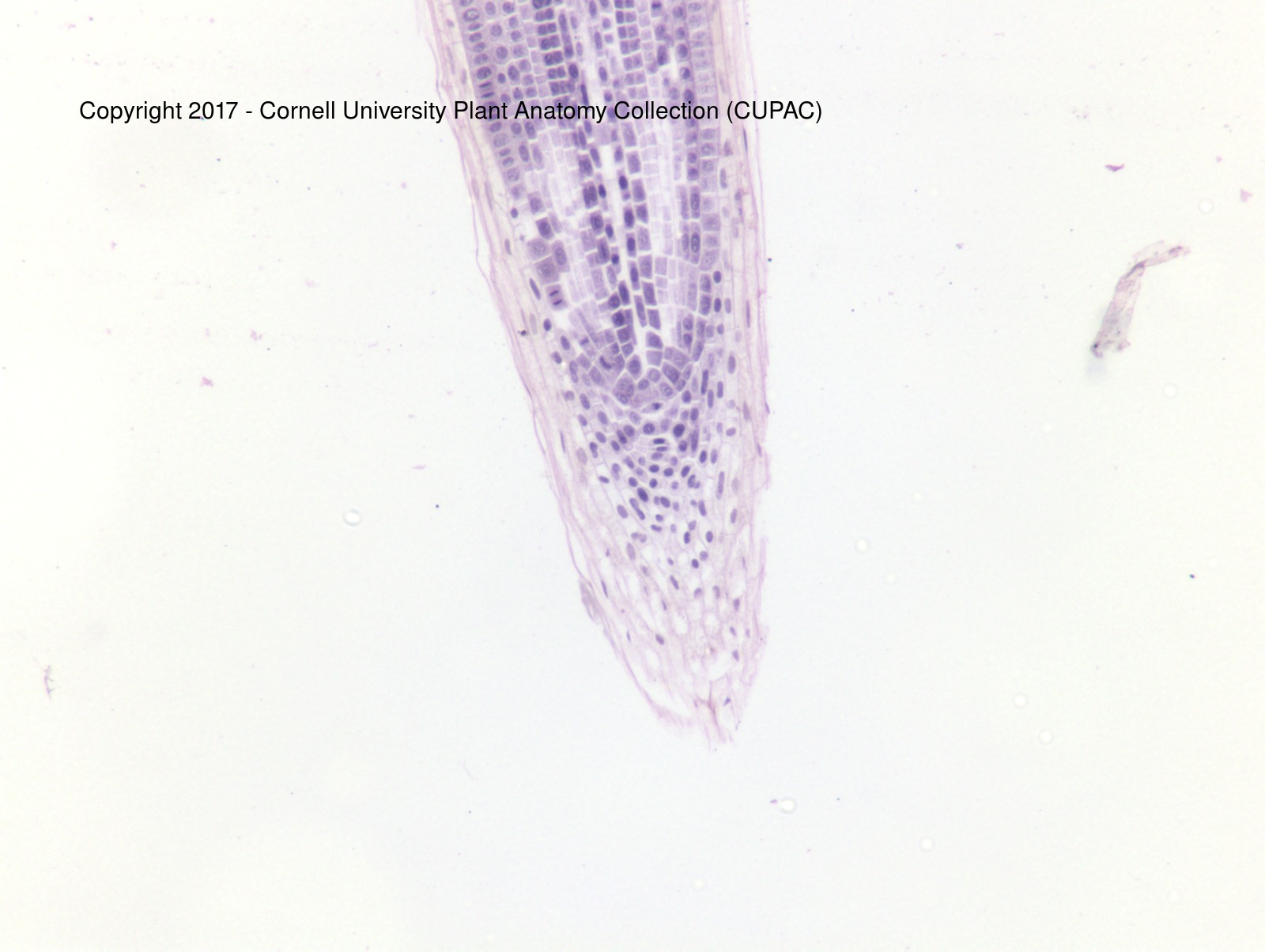
Equisetum root w/ apical cell and trichoblasts
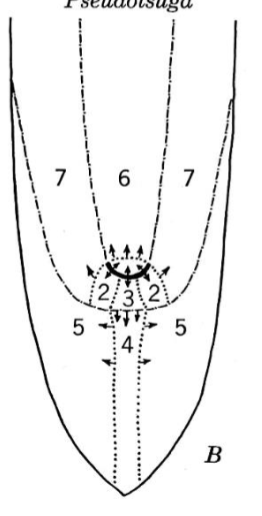
name the regions
black bar: permanent initials
1: central cylinder mother cells
2: cortical mother cells
3: columellar mother cells
4: columella
5: root cap
6: central cylinder
7: ground meristem and protoderm

Allium root tip; open type

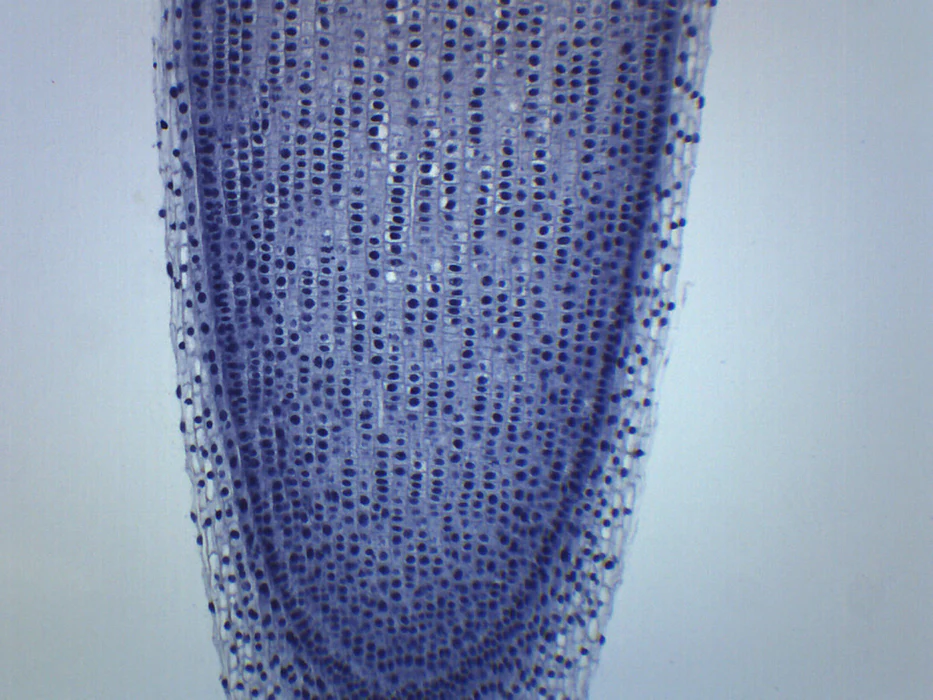
Zea root tip; closed type-Zea type
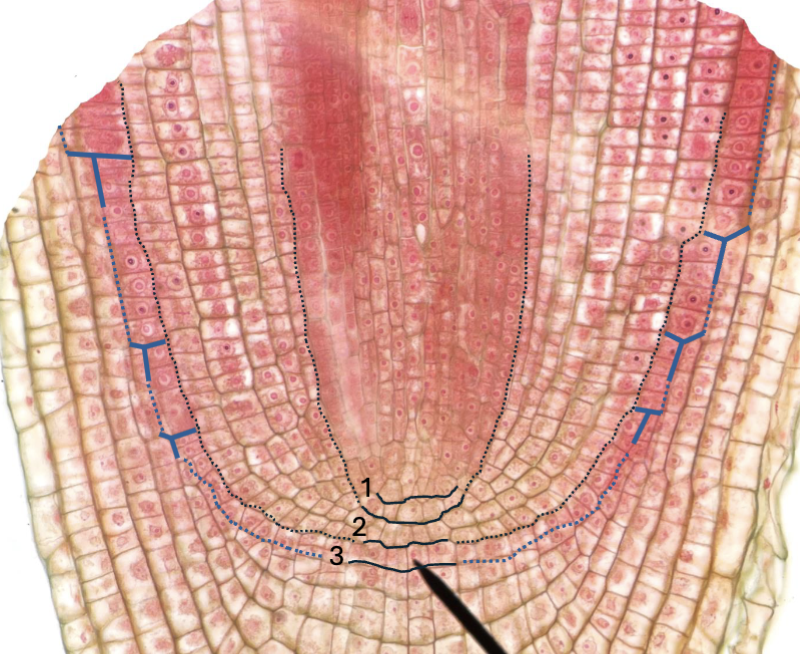
Raphanus root tip; closed type-Raphanus type
characteristic T/Y divisions
Difference between Zea and Raphanus type roots
Zea: 3 apical tiers which give rise to:
root cap
ground meristem and protoderm
central cylinder
Raphanus: 3 apical tiers which give rise to:
root cap and protoderm
ground meristem
central cylinder
central cell
cell representing quiescent center in Zea type roots, present between the top 2 tiers
statocytes
cells in root cap with amyloplasts (acting as statoliths) for gravity sensing
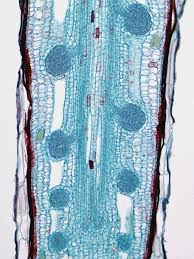
Pistia root tip; closed type-Raphanus type
lateral roots with root caps and primary meristems developing
shoot promeristem characteristics
outer layer enclosing a central region
in gymnosperms:
surface meristem
central mother cells
sometimes transition zone
in angiosperms:
tunica
corpus
sometimes transition zone
from top view:
central zone
peripheral zone
rib meristem
in shoots, central meristem which gives rise to pith
flank meristem
in shoots, peripheral meristem which gives rise to ground meristem, procambium, sometimes outer edge of rib meristem
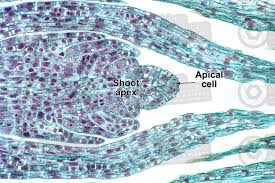
Equisetum shoot tip with apical cell
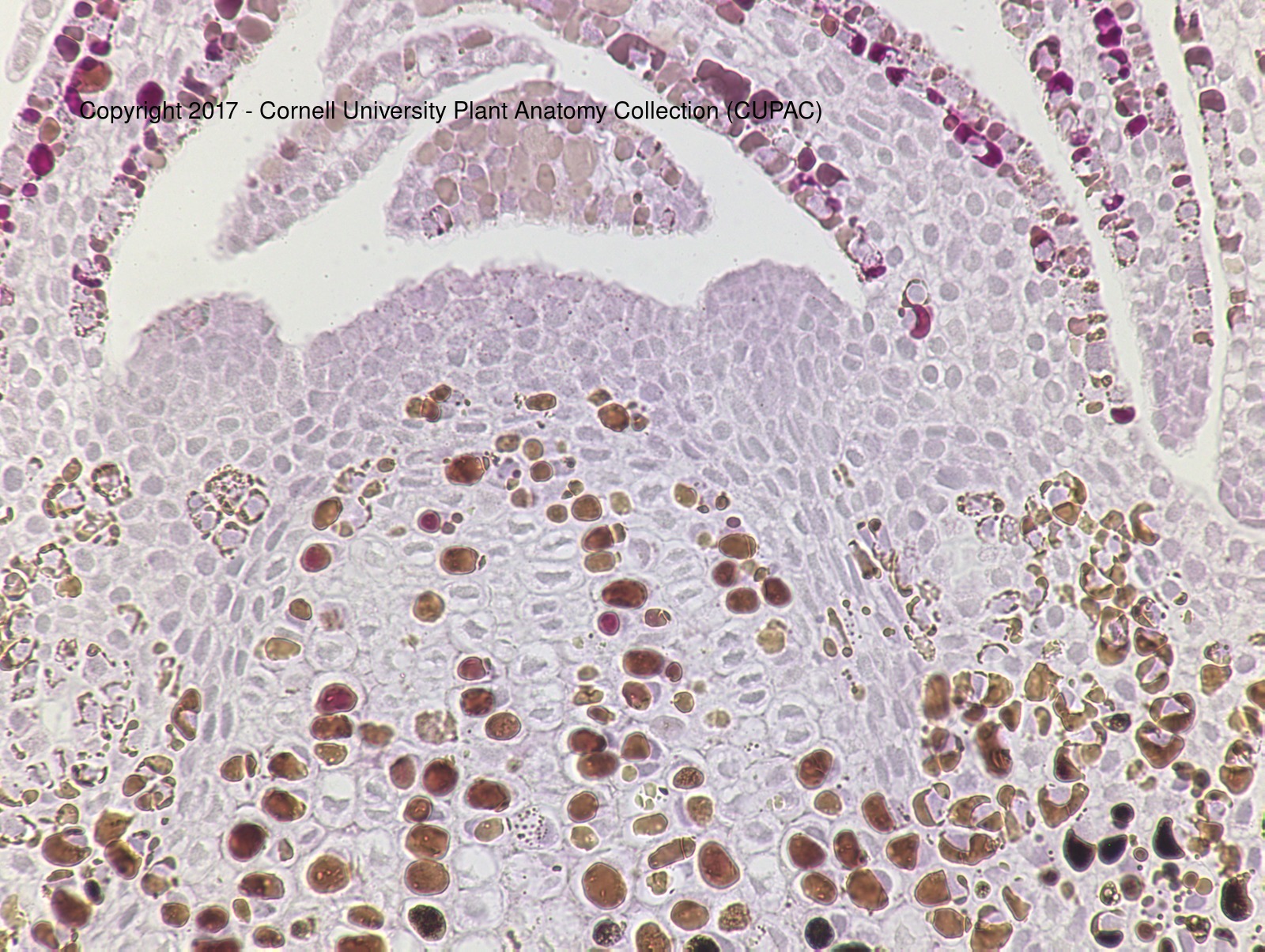
Pinus shoot tip
surface meristem
central mother cells
rib meristem surrounded by peripheral zone (flank meristem)
sometimes transitional zone
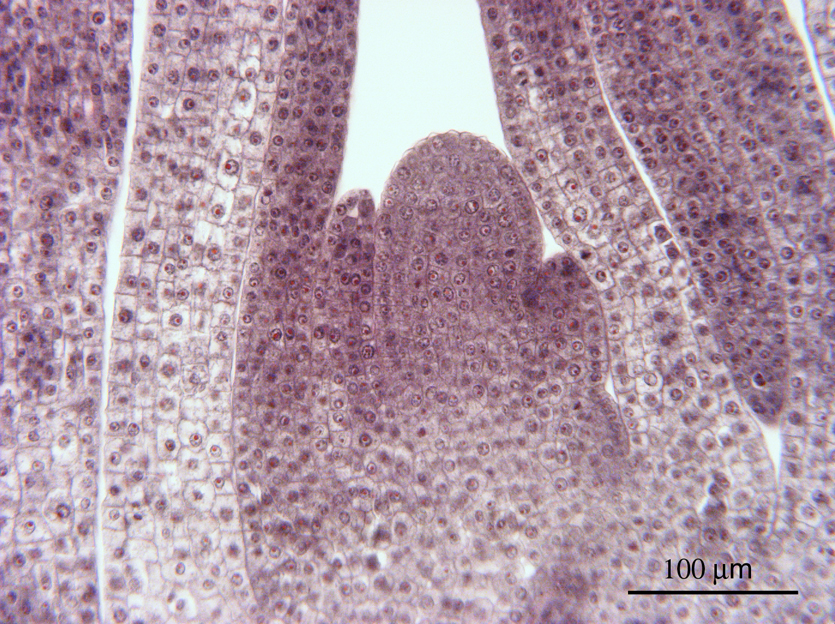
Zea shoot tip
1 tunica layer

Vinca shoot tip
5 tunica layers
transition zone under corpus
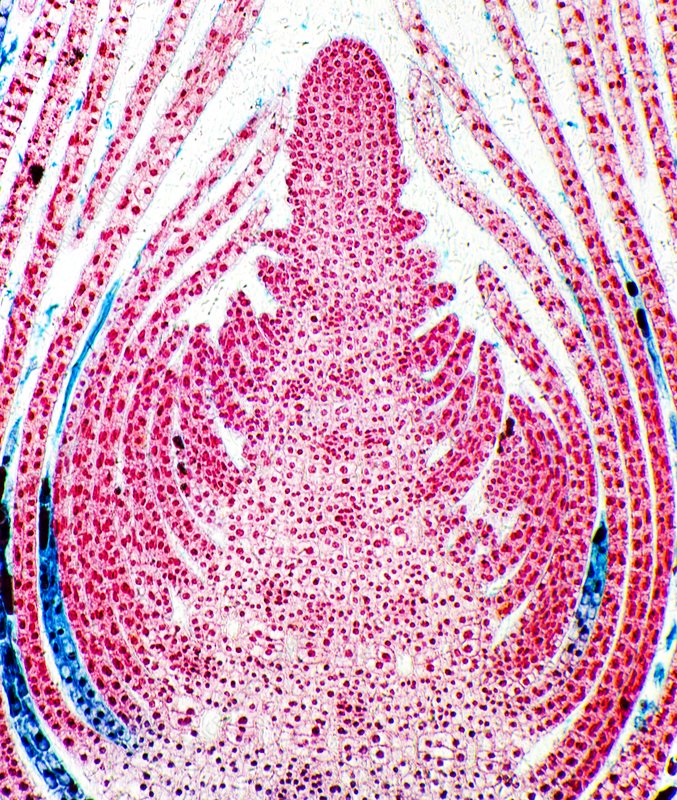
Elodea shoot tip
2 tunica layers
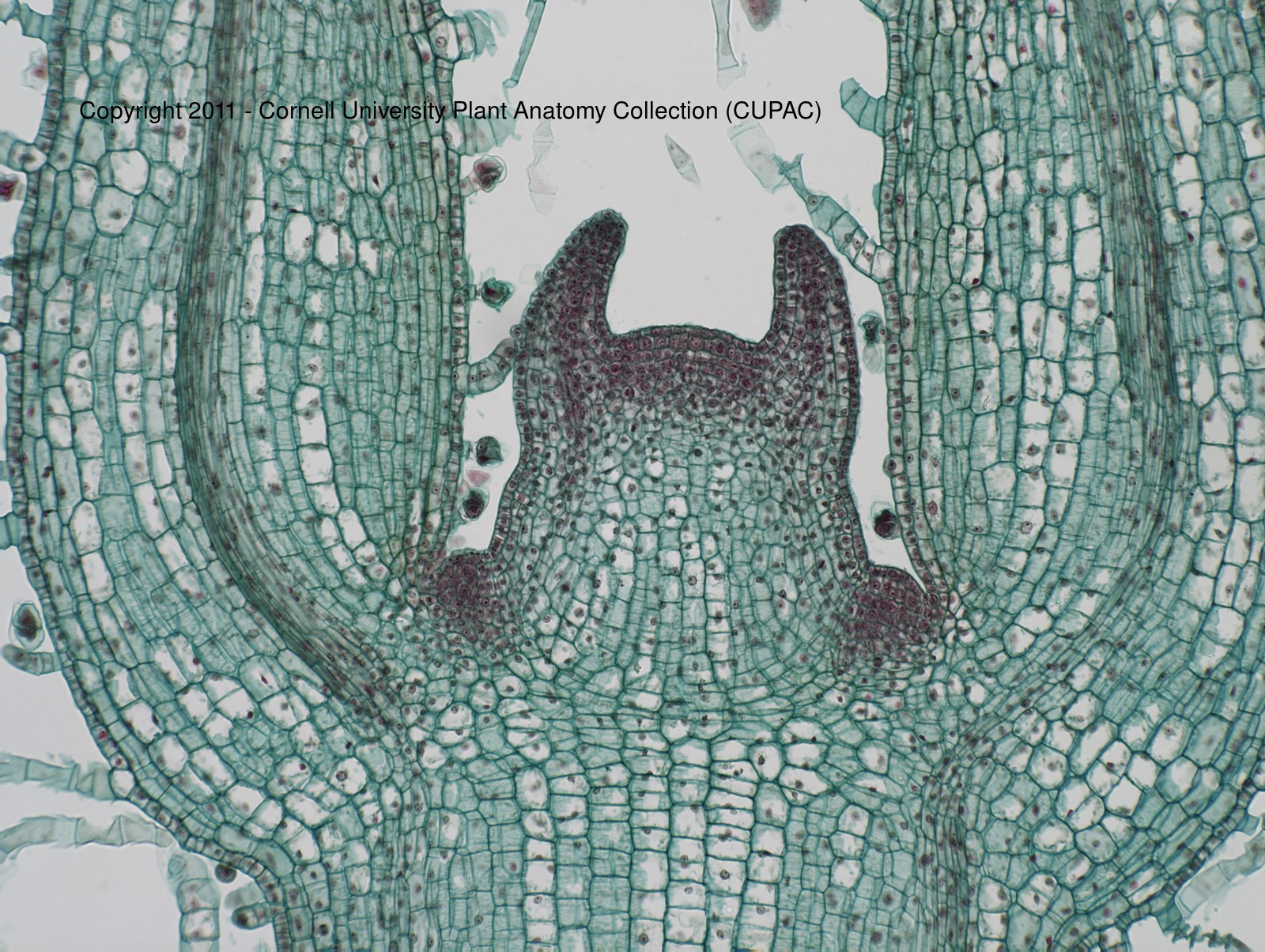
Coleus shoot tip
5 layer tunica

Equisetum intercalary meristem
base of each internode
rhexigenous protoxylem lacunae
holes in internodes containing secondary wall thickenings. Produced by tearing of stretched protoxylem tracheids from elongation of internodes