Physics: Waves
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Definition of a wave
Waves carry energy or information from one place to another
Transverse waves
e.g. light waves
Travel perpendicular to the direction of energy travel
Up and down movements
Longitudinal waves
e.g sound waves
Travel parallel to the direction of energy travel
Across movements
What is the term for short and long wavelengths in a Longitudinal Wave
Short: compression
Long: Rarefaction
What frequency can humans hear?
20 - 20,000 Hz
Definition of Frequency
The number of waves passing a point in a second
Definition of ‘period’
P - time period
Time taken to pass a point (seconds)
Time taken for one complete oscillation
Variables for the speed of ripples on water practical
Control - Travel length, height dropped from
Dependant - Time to travel 2m
Independent- Water Depth
Equation for speed
S=D/T
Speed = Distance / Time
What is the ‘normal’?
A line drawn perpendicular to the mirror/surface to help measure the angle
When light reflects off a flat surface in a straight line, what is this called?
specular
When light reflects off a rough surface in different directions, what is this called?
Diffused
Info about sound waves
Longitudinal (across)
Vibrations travel through air
Vibrations move to our ear drums which vibrate and cause the sensation of sound
Ultrasound
Above 20,000Hz (above human hearing)
Wave is partially reflected at the boundary between materials
What is ultrasound used for and how does it work?
Medical (foetus scan) - Sound waves bounce off skin, organs etc at different speeds. These echos are converted into images with a transducer.
Industrial (under oceans) - Time taken for reflections to reach a detector can be used to determine how far away a boundary is
Dog training (whistles)
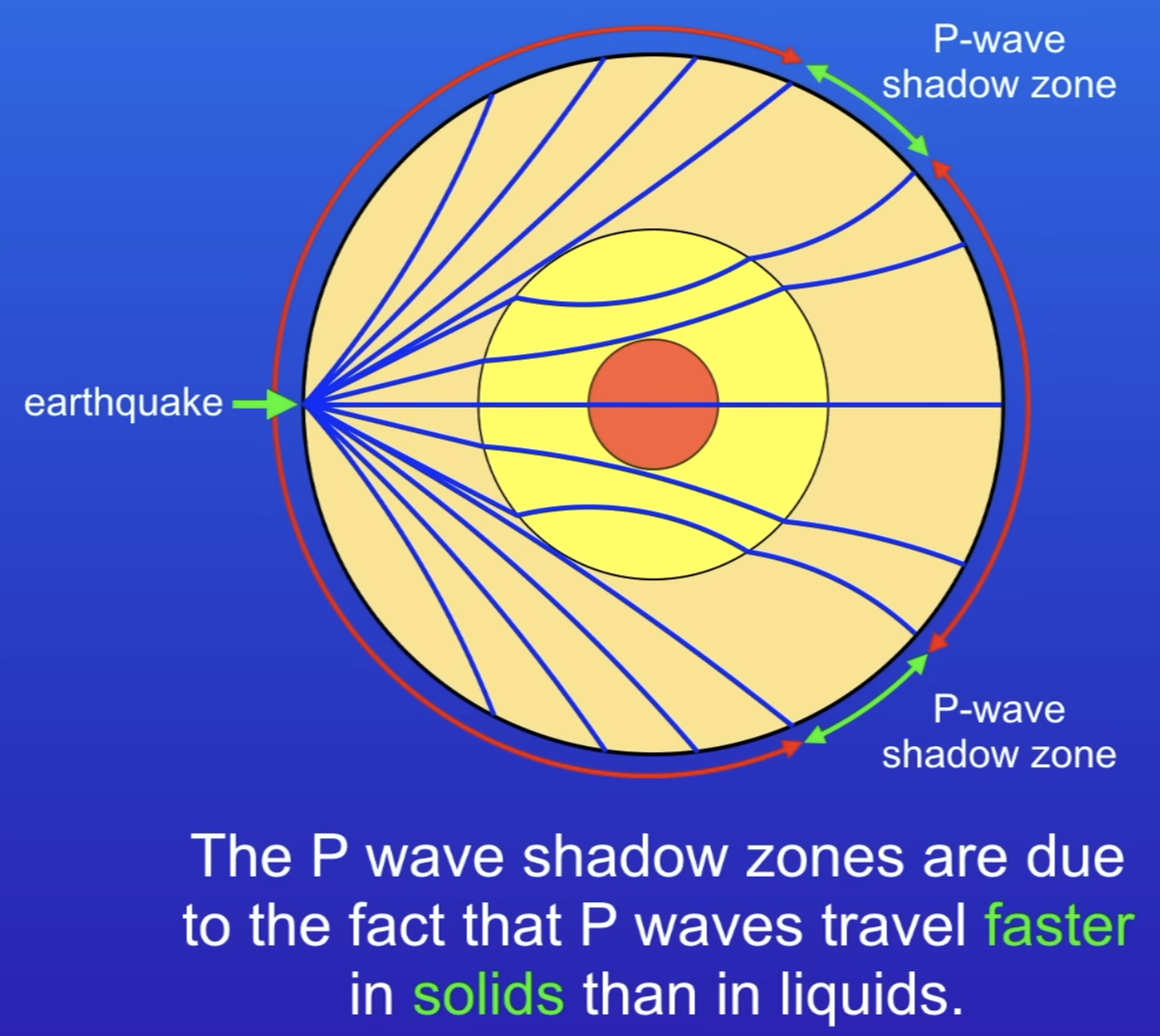
What are seismic waves? Explain P waves.
P waves - longitudinal, pass through solids and liquids. Travel faster
Because they travel at different speeds in solids and liquids, they refract going in and out of the outer core (its liquid) leaving shadow zones.
Faint P waves can be detected in the P wave shadow zones (shows that inner core is solid)
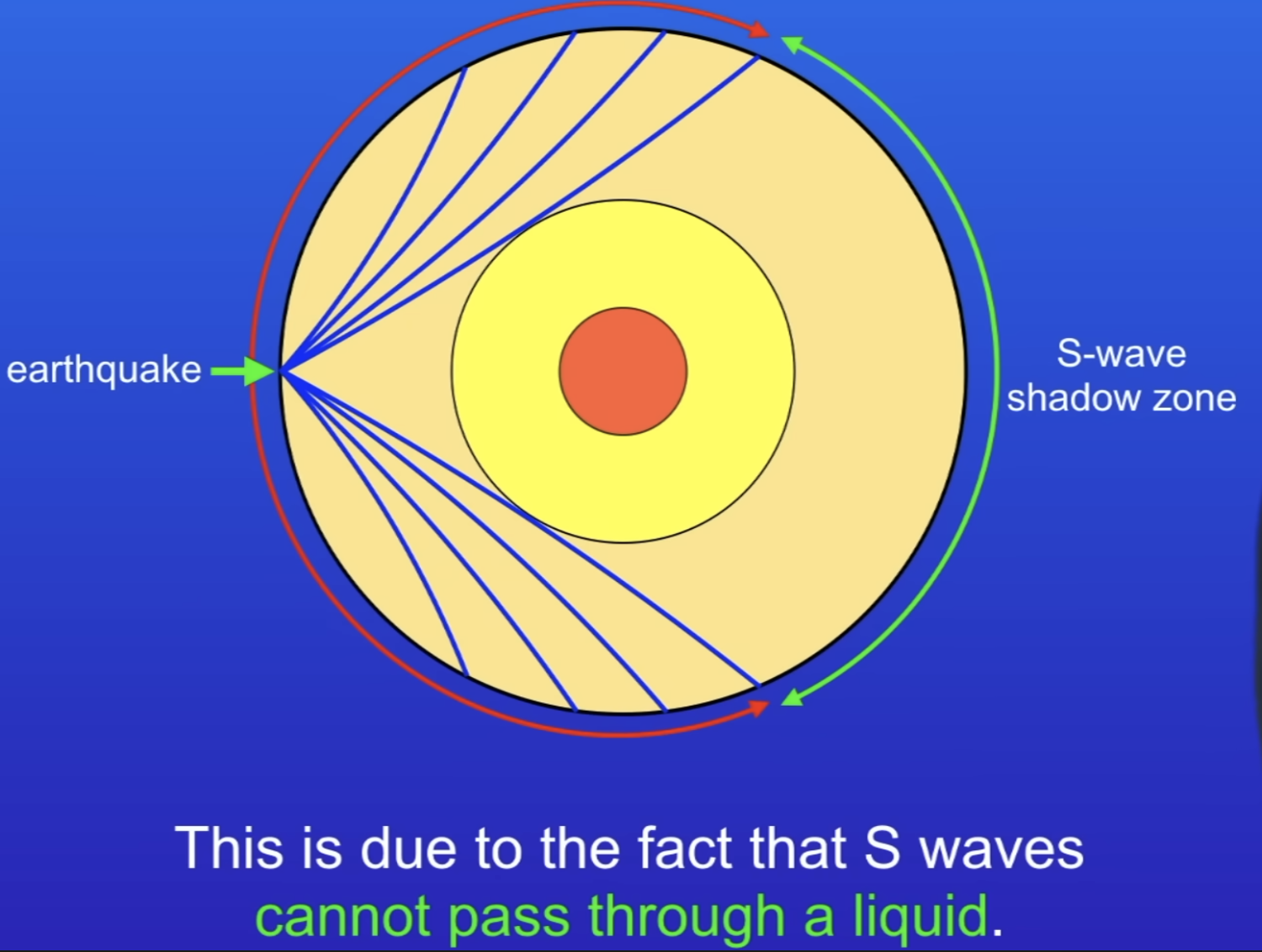
What are S waves?
Secondary waves - transverse, Only travel through solids.
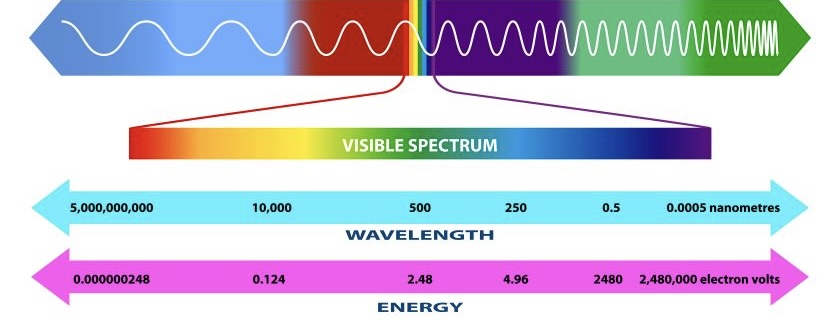
What is the Electromagnetic spectrum?
Moves energy from a source to an absorber
Lowest Freq:
Radio waves
Microwaves
Inferred Radiation
Visible light
Ultraviolet
X-ray
Gamma waves
Highest Freq
Wavelength
The distance from a point on a wave to the equivalent point on the next wave
(metres)
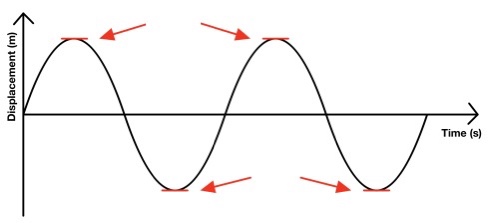
What Is the highest and lowest point on a wave called?
Peaks
Troughs
What can happen when a wave meets a boundary
Reflection
Transmission
Absorption
Refraction
What happens when waves are reflected off a surface
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
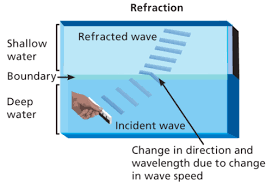
What does Refracted mean?
Wave is reflected off a surface and changes direction
What happens when light travels from a material with a low to one with higher refractive index?
The light bends towards the normal
What happens when light travels from a material with a high to one with lower refractive index?
The light bends away from the normal
Why does Refraction happen?
When a light wave enters a medium in which it travels slower at an angle,
The first part of the wave to enter slows down
The rest continues at a higher speed
the waves changes direction towards the normal
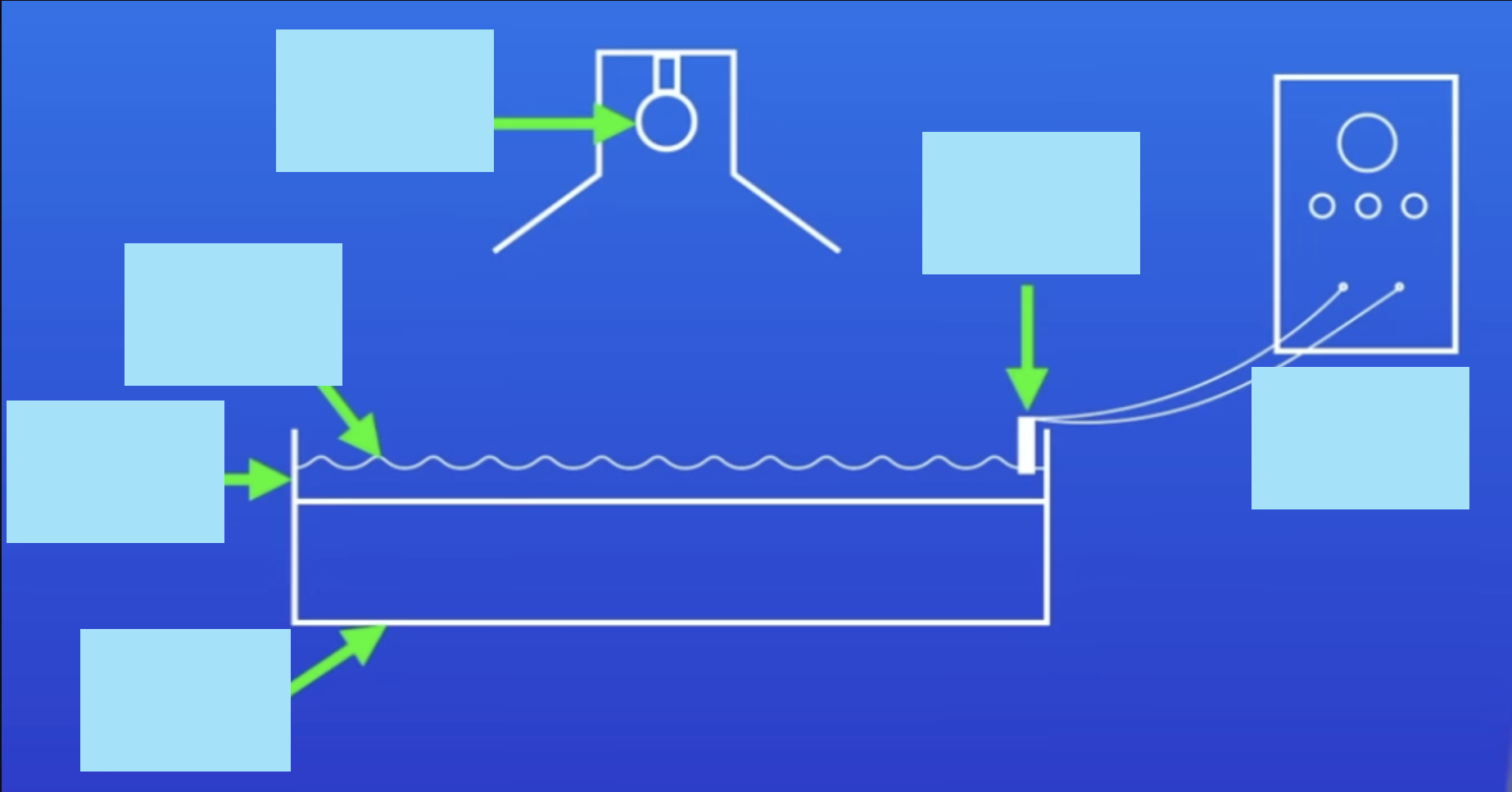
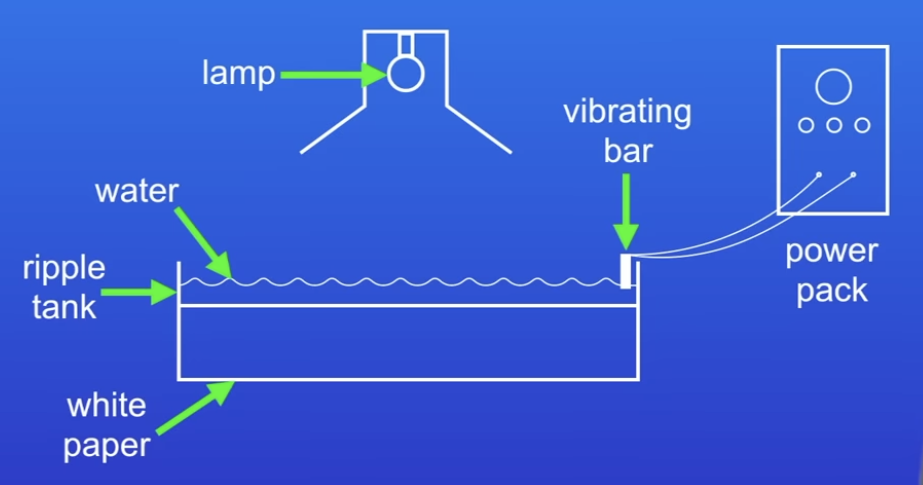
Label this ripple tank
Wave speed equation
v=f x λ
wave speed = freq x wavelength
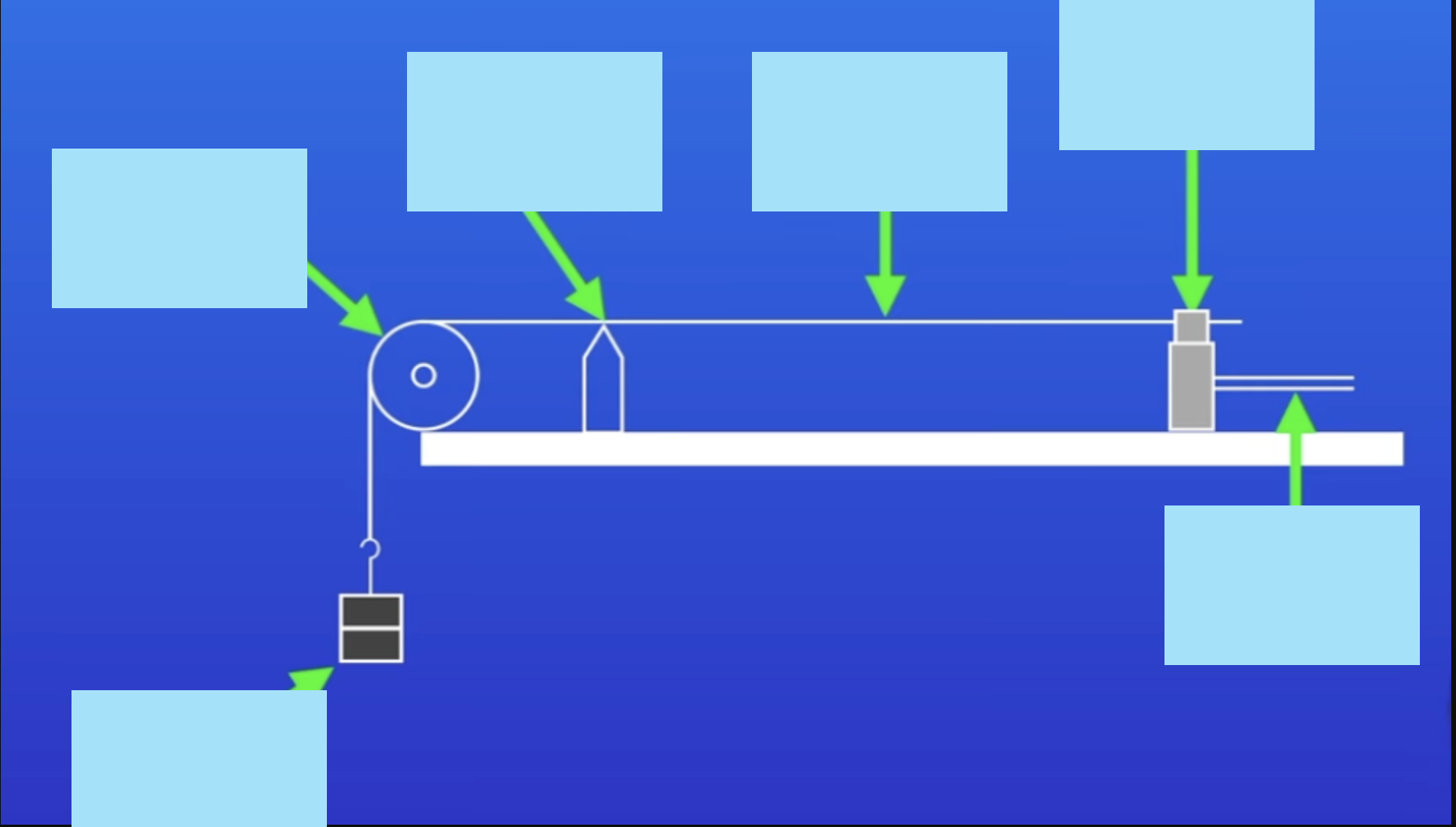
Label this diagram
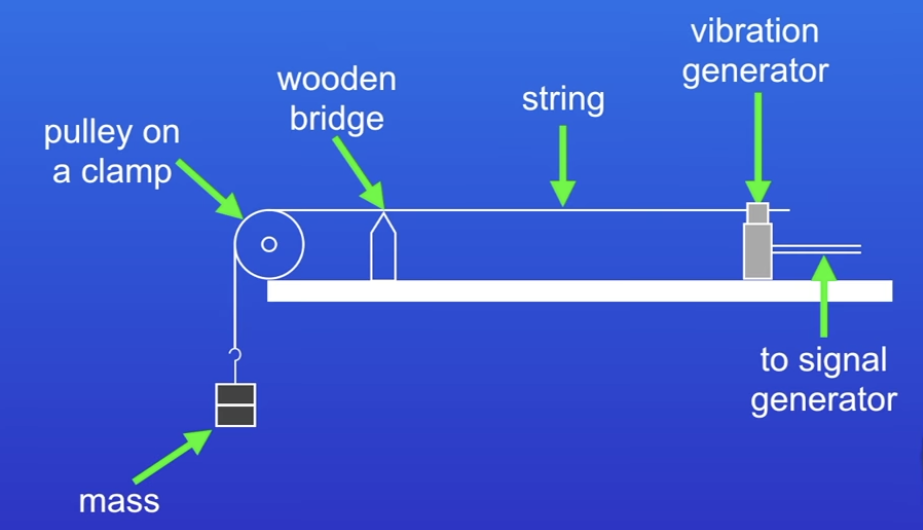
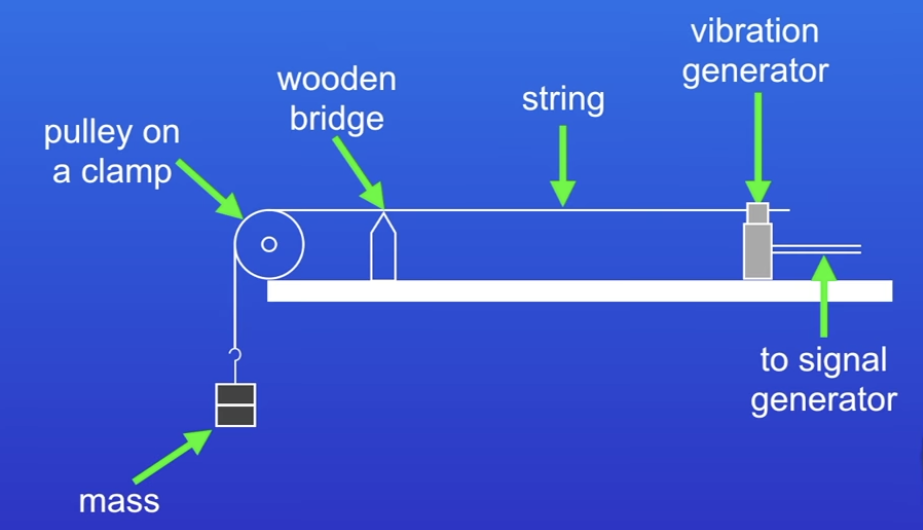
How to determine wavelength with this practical
Total Length / number of half wavelengths x 2
How to draw the reflected ray?
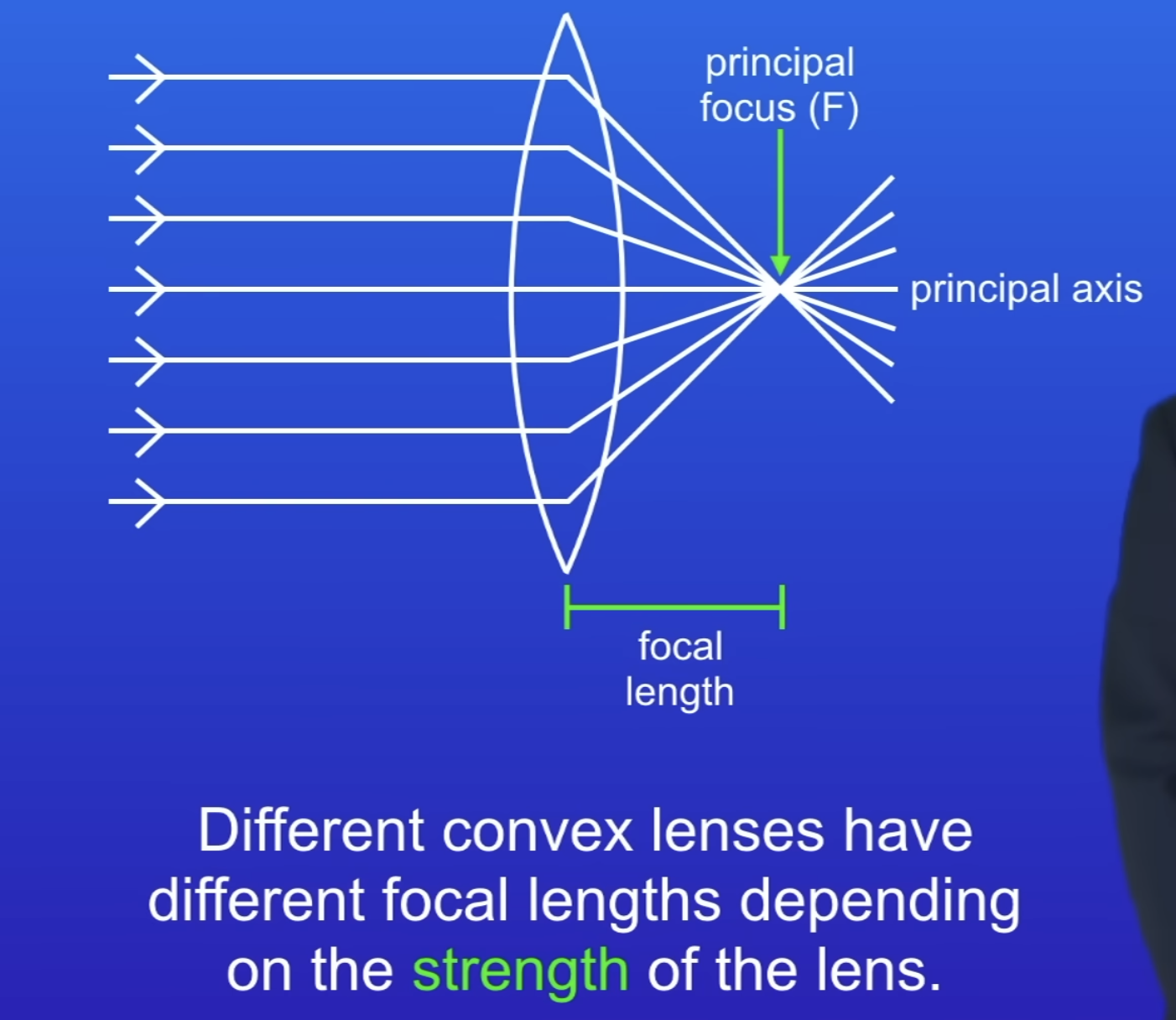
What is a convex lens?
How do you show this?

Method for angle of refraction with ray box
place a glass block on a piece of paper
draw around the glass block
use the ray box to shine a ray of light through the glass block
mark the ray of light entering & exiting
join the points to show the path of the complete ray through the block
draw a normal line at 90° to the surface
use a protractor to measure the angle of incidence & refraction
use a ray box to shine a ray of light at a range of different angles (of incidence)
increase the angle of incidence in 10° intervals
from 10° - 70°
What is the Leslie cube practical?
Discover how much infrared different surfaces absorb
Fill cube with hot water
Point infrared detector on each surface (same distances) can use thermometer but less accurate
Matt black → shiny black → white → shiny metallic (order of absorbsion)

Another method for the Leslie cube practical
drawing pin held on with vaseline
Falls off matt black side first because they absorb more infrared.
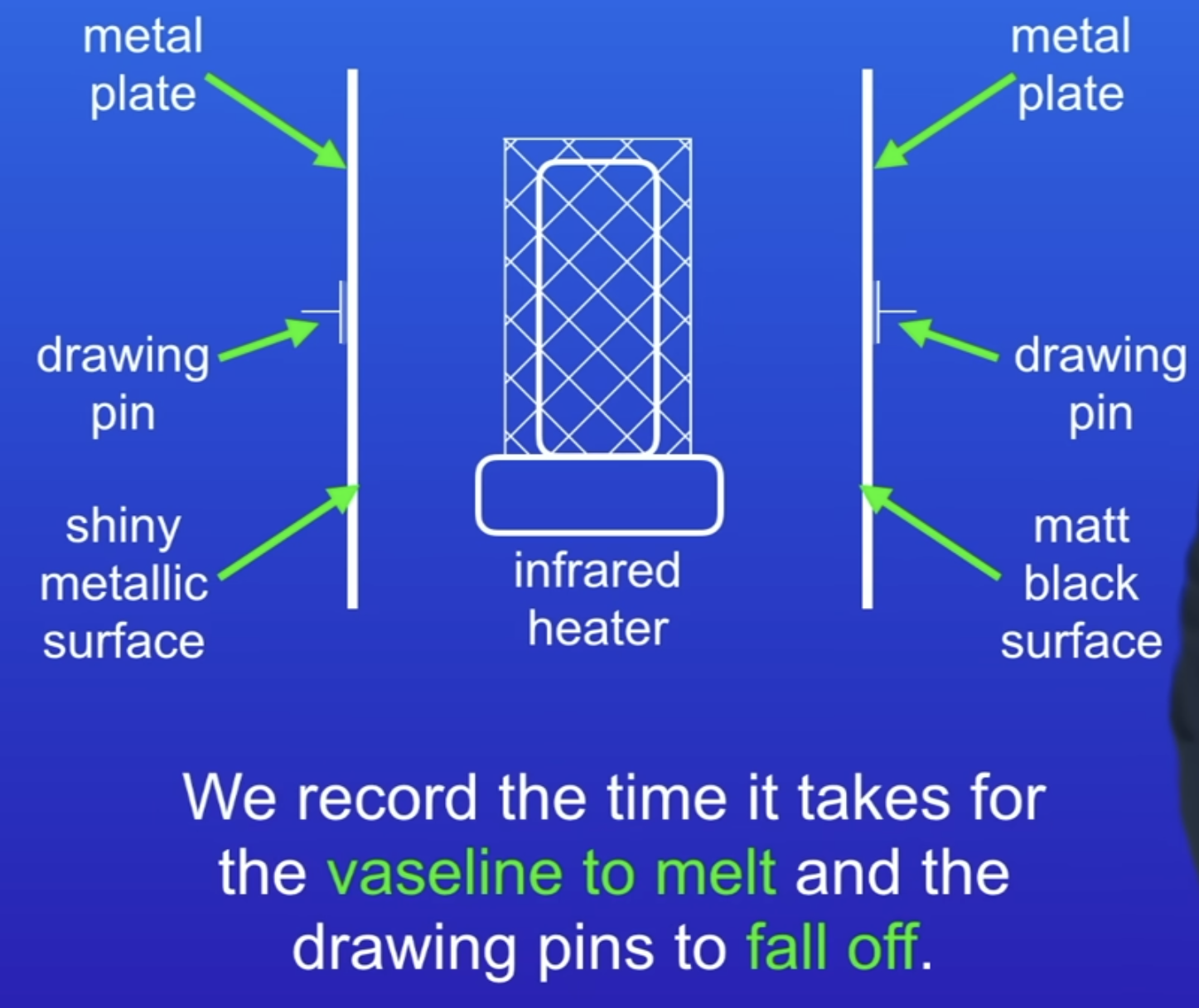
How are radio waves made?
When electrons oscillate in electrical circuits
Can be absorbed by electrical circuits in an aeriel, causing electrons in the circuit to oscillate
Creates an AC the same freq as the radio waves
Label a convex lens diagram
How to draw a ray diagram for a convex lens
Real - because it is inverted & rays meet at a point
Diminished - image is smaller than object
Virtual - if the rays don’t meet and they are connected with dotted lines beghind the arrows
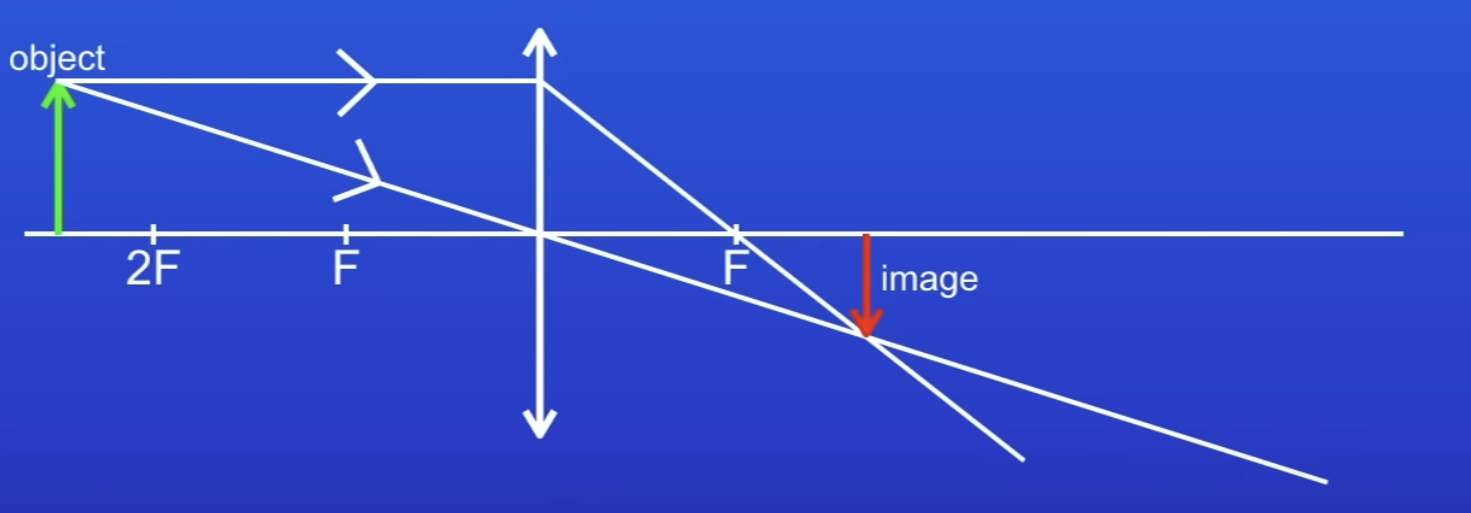
How to draw ray diagram of concave lens
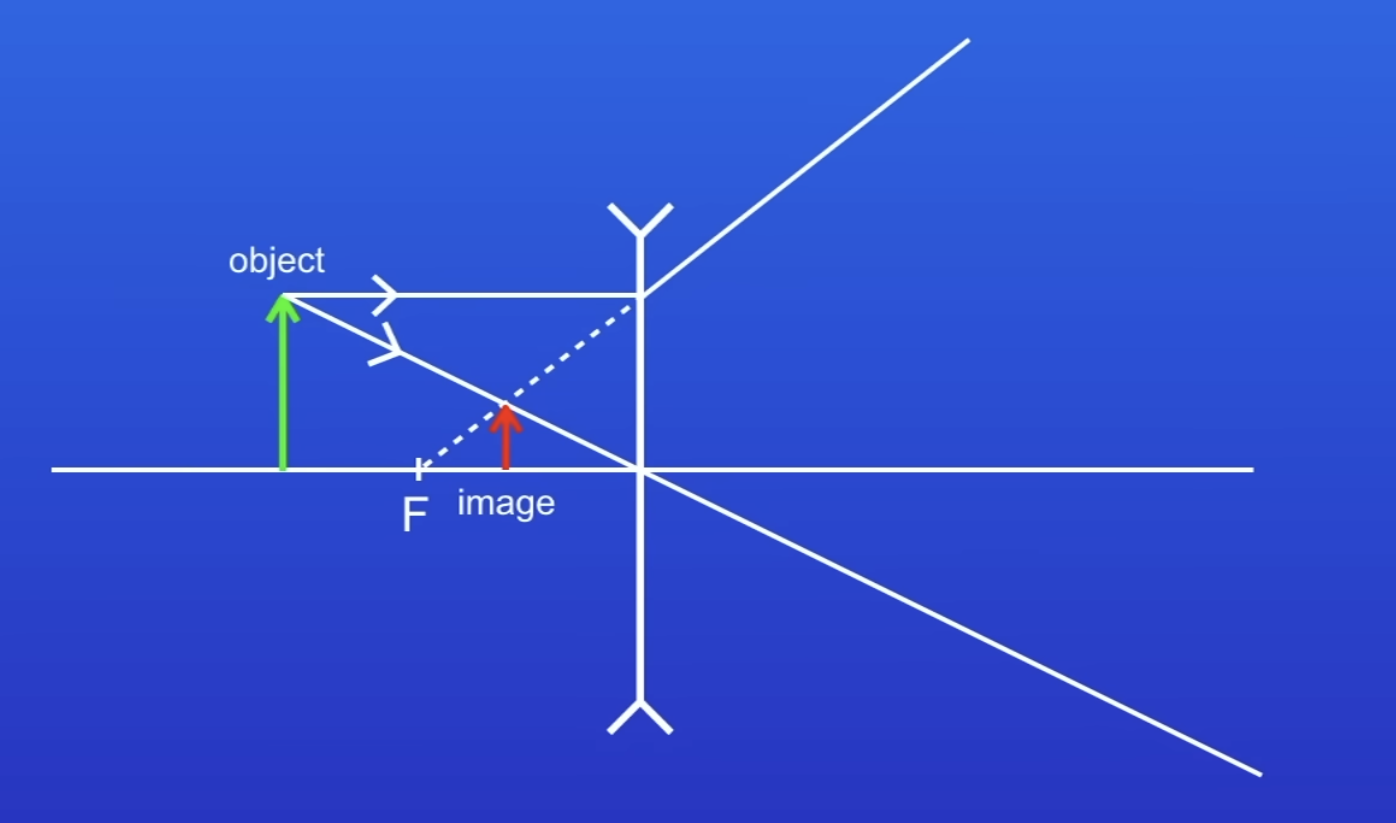
How to draw concave lens diagram
What is black body radiation
A perfect black body absorbs all radiation - none transmitted or reflected
Best emmitter for radiation