Stigma and Discrimination (Part 1)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
why is the study of stigma so important?
we are social beings
understand our own bias
to not make harmful assumptions based on one’s appearance
social inclusion/exclusion = effects on health
part of environmental factors that increase risk of premature death (29%)
stigma and definitions
negative attitudes
stereotype
prejudice
discrimination
negative attitudes
sociocultural conditioning that starts very young (5 yrs)
the beautiful body
emphasis on productivity and success
socioeconomic factors (disability = poverty, burden on the economy)
attribution “sick role”
disability = status degradation
stereotype
an unfair and untrue belief that many people have about all people or things with a particular characteristic
can be positive or negative
example
doctor: prestige, all knowing
women can’t drive
men in theatre are homosexual
all canadians are nice and polite
prejudice
to judge before
to formulate a rash and definitive judgement about a person or a group of people without sufficiently knowing them
preconceived idea on a person or a group of people
always based on a stereotype
ingrained in us by social environment
undoing them requires conscious acknowledgement and self-reflection
racism
type of prejudice
believing that race, skin colour, or culture makes people inferior or superior
class prejudice
type of prejudice
believing that certain economic classes are superior or inferior
prejudice =
beliefs
discrimination
to exercise prejudice in a direct or indirect manner, towards a person or a group of people
an action or a decision that treats a person or group negatively
race
age
disability
isolate and treat differently based on
origin
religious beliefs
age
gender
disability
real or supposed opinions
stereotypes =
generalizations
victims of discrimination
based on race, colour, national or ethnic origin and/or religion
women, people with disabilities and older adults
discrimination =
an act
direct discrimination
type of discrimination
direct action towards a person
example
a manager screens-out people with disabilities in the hiring process based solely on their disability status
indirect discrimination
type of discrimination
can happen through another person, another organization or policies/rules that may not have been created intending to exclude people with a disability but they do
example
an employer’s policy of not hiring people who have “gaps” in their résumés because they have been out of the workforce for a period of time off work for reasons related to a disability
in the literature on stigma theory
there is a consensus that fundamental components of stigma are
generalizations = stereotypes
beliefs = prejudice
acts = discrimination
examples of stigma (stereotype)
example
people with a disability are less competent than those without a disability
examples of stigma (prejudice)
example
individual believes the stereotype and judges that all people with disabilities are incompetent
examples of stigma (discrimination)
example
individual never hires a person with a disability
stigma as a social construct (susman/goffman)
it is not functional limitations of impairment that constitute the biggest challenge met by people with a disability, but rather the societal and social responses to them
two groups of people created
THEM (people w characteristic)
US (people w/o characteristic)
stigma and deviance
deviation from relevant or valued norms
not an inherent property
a person isn’t deviant until his/her acts or attributes are perceived as different
what is stigma?
is the possession of (or the belief that one possesses) some attribute, or characteristic that conveys a social identity that is devalued in a particular social context
example of stigma and context
example
context with a guy with a lab coat
hospital: less likely to experience stigma
bar: more likely to experience stigma
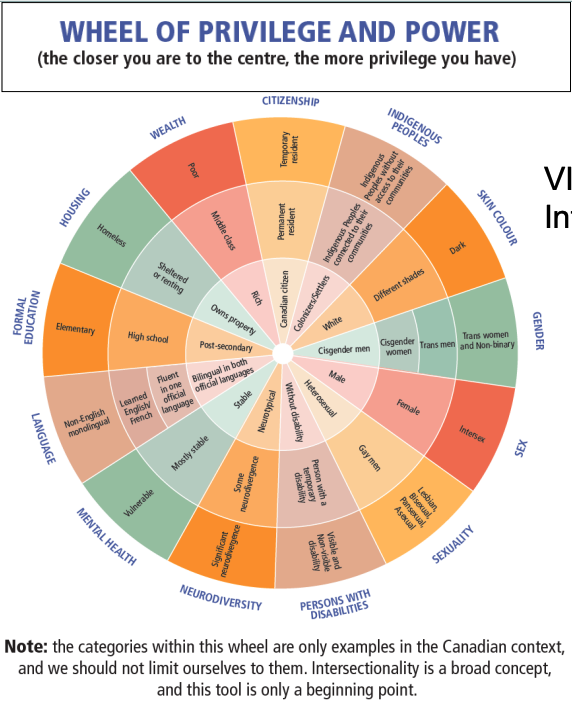
power imbalance
Judged on your sex, gender, wealth
People at the centre of the circle are more privileged in society and less discriminated
People farther from the centre are less privileged and therefore more discriminated and stigmatized
power in the sense that those without characteristic are more autonomous and make decisions for “them”
intersectionality
racialized people have higher rates of disability
often combined with lower-socioeconomic or immigrant status
face barriers accessing health services
people with disabilities are 2 to 4 times more likely to be victims of abuse
dimensions of stigma
multidimensional process
concealable
course of the mark
disruptiveness
aesthetics
origin
peril
concealable
dimension
how apparent the characteristic is to others
having been incarcerated
mental illness
fibromyalgia
course of the mark
dimension
whether the characteristic becomes more apparent with time
Parkinsons Disease
disruptiveness
dimension
does the characteristic interfere with social interactions
hearing impairment
aesthetics
dimension
degree to which the characteristic is unpleasant (unappealing) to others
people with an amputated limb
origin
dimension
perceived level of the individual’s responsibility in acquiring the characteristic
example
teen mom
lung cancer
obesity
peril
dimension
danger that others perceive towards the characteristic in social contexts
AIDS
Schizophrenia
COVID-19
4 big types of stigma
social/public stigma
self-stigma
label avoidance
structural stigma
public stigma
type of stigma
when the general public endorses stereotypes about disease and disability and then discriminates against them
strongly influenced by medias
ex. people living with HIV are contagious
self stigma
type of stigma
public stereotypes directed inwardly towards one’s self
ex. a person with intellectual disability
conscious that “most people” think that people with ID are stupid
agree with this stereotype “they’re right”
apply it to themselves “I am stupid”
label avoidance
type of stigma
the process whereby individuals decline or refuse to engage with specific types of services in order to avoid being labeled or stereotyped
ex. students with learning disabilities might refrain from requesting academic accommodations because they do not want to be stereotyped
structrual stigma
type of stigma
includes both intentional and unintentional private and public institutional rules, regulations and norms
ex. “interventions”: contentions and isolation for people with psychiatric or developmental disorders
the impact of public and structural stigma
impact
affect many life-domains
lead to discrimination of many people with a disability in the health system, criminal justice system, housing, employment and education
people with disabilities are susceptible of experiencing lesser physical and mental health resulting from the discriminatory chronic stress and lack of adequate social support
the impact of self-stigma
impact
may influence pursuit of life opportunities through its negative impacts on the individual’s self-concept
reduction in hope and self-esteem
disengagement from treatment (health)
reduction of quality of life
disengagement from educational career or social life
potentially suicide
impact of label avoidance
impact
closely tied to public stigma and self-stigma
avoidance of service use (including social services, medical treatment, and academic and work accommodations) because of a fear of public consequences of being labeled by others and or personal fear of acquiring a stigmatized label
impact of stigma (health)
impact
stigma may thwart (hamper)
acknowledgement and identification of health conditions
may be an obstacle (barrier)
help-seeking, service provision and treatment adherence
each individual is different in their experience and response to stigma and discrimination
disability ≠ stigma
not always the case a person with a disability is stigmatized
many studies show that people with a disability are not necessarily devalued or excluded from full participation in their community