
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Isoptera
Order that termites are from
Hymenoptera
Order of ants, bees, wasps
What did termites evolve from
cockroaches
Termite facts
About 3000 species
Found almost everywhere (not Antartica)
Important detritivores and pests
queens can live up to 50 years
there is a kind
Sociality of termites
All are eusocial
Sociality in relatives of termites
Wood roaches (Cryptocercus) is subsocial
German cockroaches are gregarious (fond of company)
How does gene distribution differ in termites compared to Hymenoptera
Termites, unlike Hymenoptera, are not haplodiploidy
sisters are not ¾ related
no more related to each other (1/2) than they would be to their own offspring (1/2)
Holometabolous
complete metamorphosis, a type of insect development with four life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult
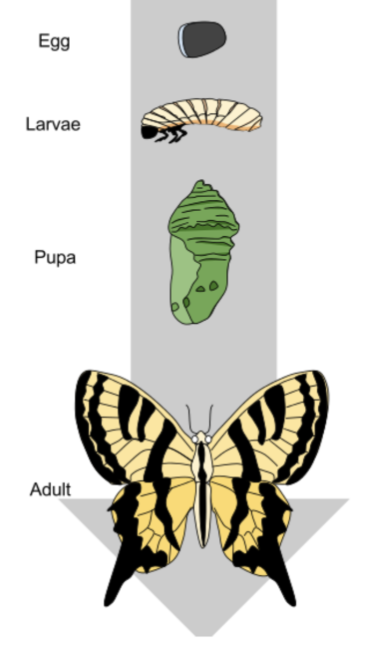
Hemimetabolous
insects that go through incomplete metamorphosis, or gradual changes, as they develop into adults
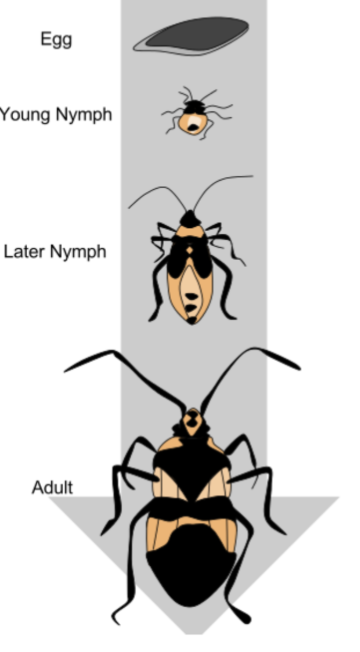
Describe the metamorphosis of termites
They are hemimetabolous with a lot of variation
Parthenogenetically
A type of asexual reproduction where an embryo develops from an egg without fertilization
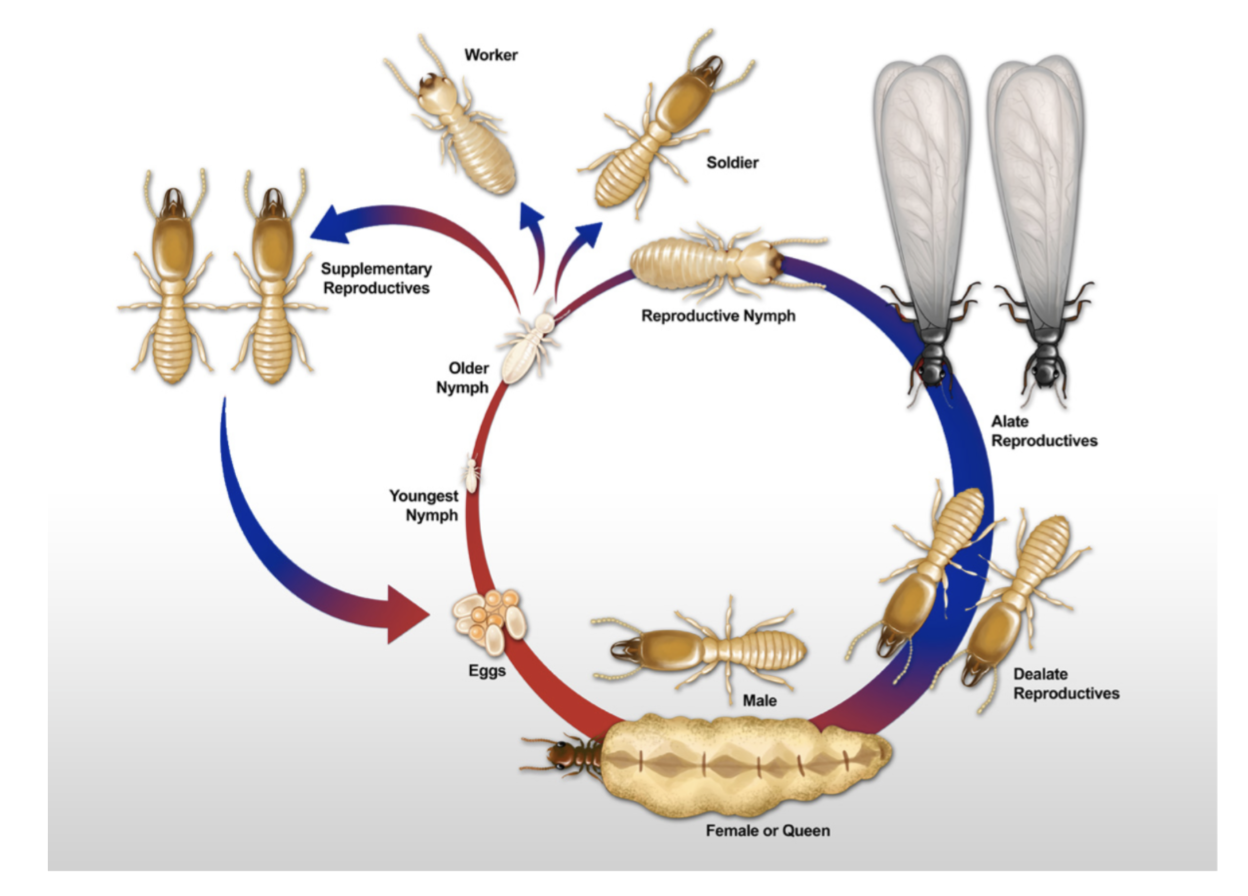
How does termite reproduction work
Sexually produced offspring are differentiated into workers and alates
Asexually produced offspring through parthenogenesis are differentiated into secondary queens
Drywood termites
Air dwellers (don’t require much humidity)
nighttime swarmers
found in costal regions and southwestern states
often found in attic wood
Subterranean termites
Live in mud tubes (require moisture)
daytime swarmers
found in warm, southern states
often found close to foundation
causes 95% of termite damage in US
Discuss the phylogeny of termitoidae
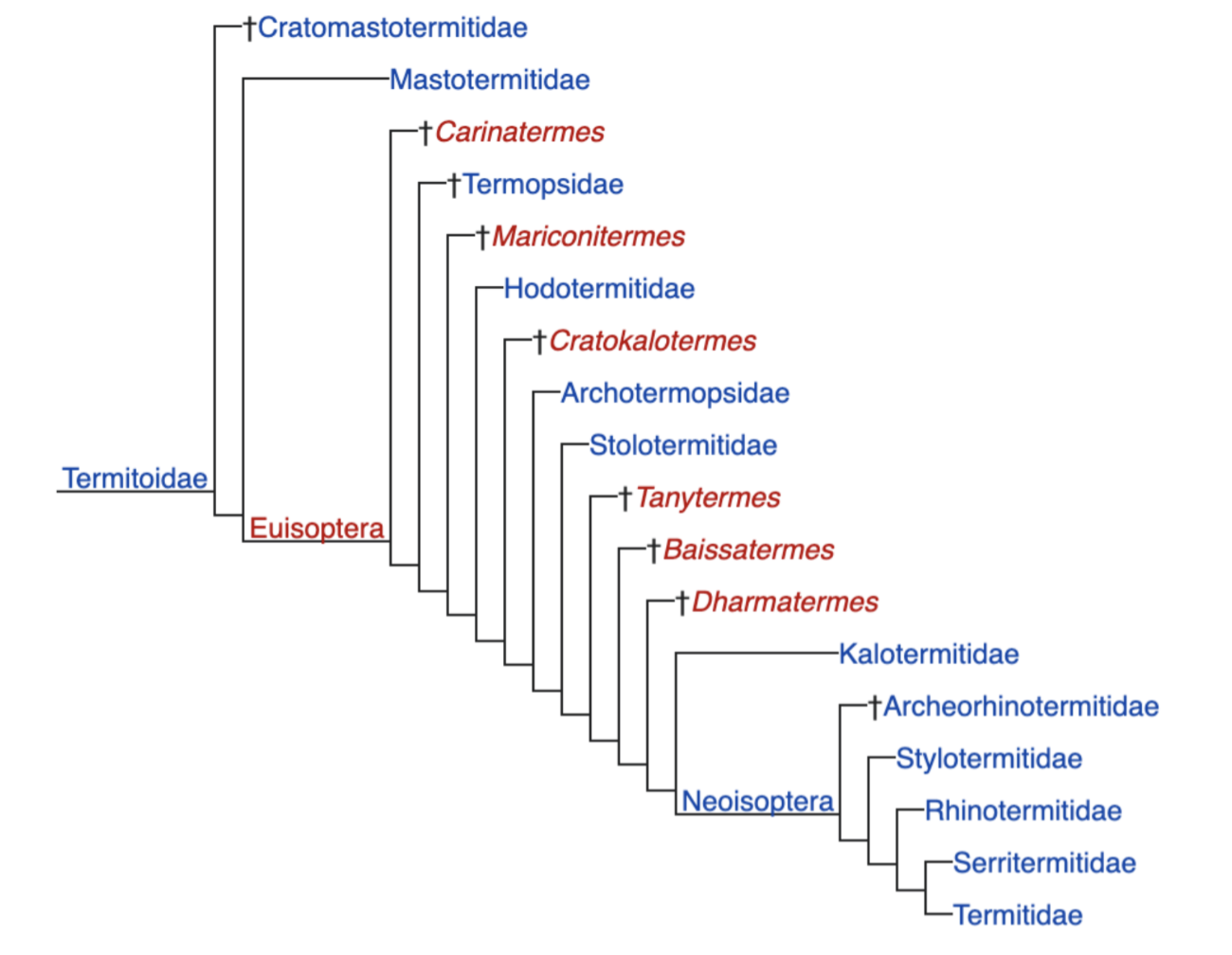
Basal termites (earliest branching lineage) is most fossilized
Newer termites are still alive
Mastotermes darwiniensis
A lower termite
only in Australia
only member of the family
most basal extant termite
has some cockroach like morphology and behavior
can kill trees and be pests
Hodotermitidae
A lower termite
few dozen species
“old world”
harvester termite
nest in soil
Archotermopsidae
A lower termite
few dozen species
damp wood termites; less of a pest
range restricted in the US
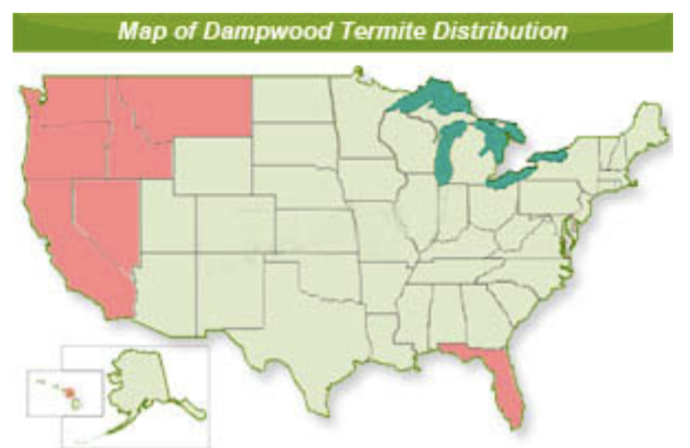
Dampwood termites
primarily infest damp, decaying wood, meaning they are attracted to wood with high moisture content
less likely to damage structural wood
Kalotermitidae
A lower termite
few hundred species
found around the world
dry wood termites
nest in fresh wood
do well in arid (dry) environments
more of a pest problem
Neoisoptera
New Isoptera, classified as higher termites
distinguished from lower order due to a frontal gland called fontanelle contains a sticky substance that entraps their enemies
also because they have a bacteria in their hind gut rather than protistans
wood digesting termites due to a protozoa, other microorganisms, and enzymes that digest cellulose in the gut
complex endosymbiotic interactions
not many things can eat wood
process of digesting lignocellulosic material
Material is mixed with salivary gland enzymes
Comminuted with the muscular gizzard
Reduced glucose is reabsorbed via midgut
Partially digests wood particles pass into the hindgut paunch
Hydrolyze remaining polysaccharides using cellulase and hemicelluloses
Lower termites: done through cellulolytic flagellates
Higher termites: done through cellulolytic bacteria
Short chain fatty acid is reabsorbed by the host
Feces that is lignin-rich is produced