GREAT DEPRESSION: Canada
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Mackenzie King
Liberal, laissez-faire prime minister at the beginning of the Great Depression during his first term (1925-1930). Later re-elected in 1935, but implemented more interventionist policies after re-election.
RB Bennett
Conservative, interventionist prime minister from 1930-1935 in Canada. He implemented several programs of public spending to combat the Depression, which later coalesced into his self-proclaimed "Bennett's New Deal" just before the election in 1935.
1935 Election in Canada
On October 14, 1935, the House of Commons of Canada were elected. Mackenzie King won a majority of the vote and beat RB Bennett.
Bank of Canada
Canada's central bank, created by RB Bennett.

British North America Act
United the territories and made them Canada! Like the U.S. Constitution, it delimits the authorities of the federal government and the provinces
National service Loan
Relief implemented by the Canadian federal government under RB Bennett to help struggling businesses and people during the economic crisis.
Canadian shield
A horseshoe-shaped, exposed portion of continental crust that makes up almost 50% of canada's land mass (roughly 3 million square miles). It contains important mineral resources
Bennett's New Deal
Introduced in January 1935, this was Bennet's last-minute way of trying to fix the economy by government intervention and public spending

Imperial Preference
Lowered import taxes for the United Kingdom and increased taxes on imports from other countries.
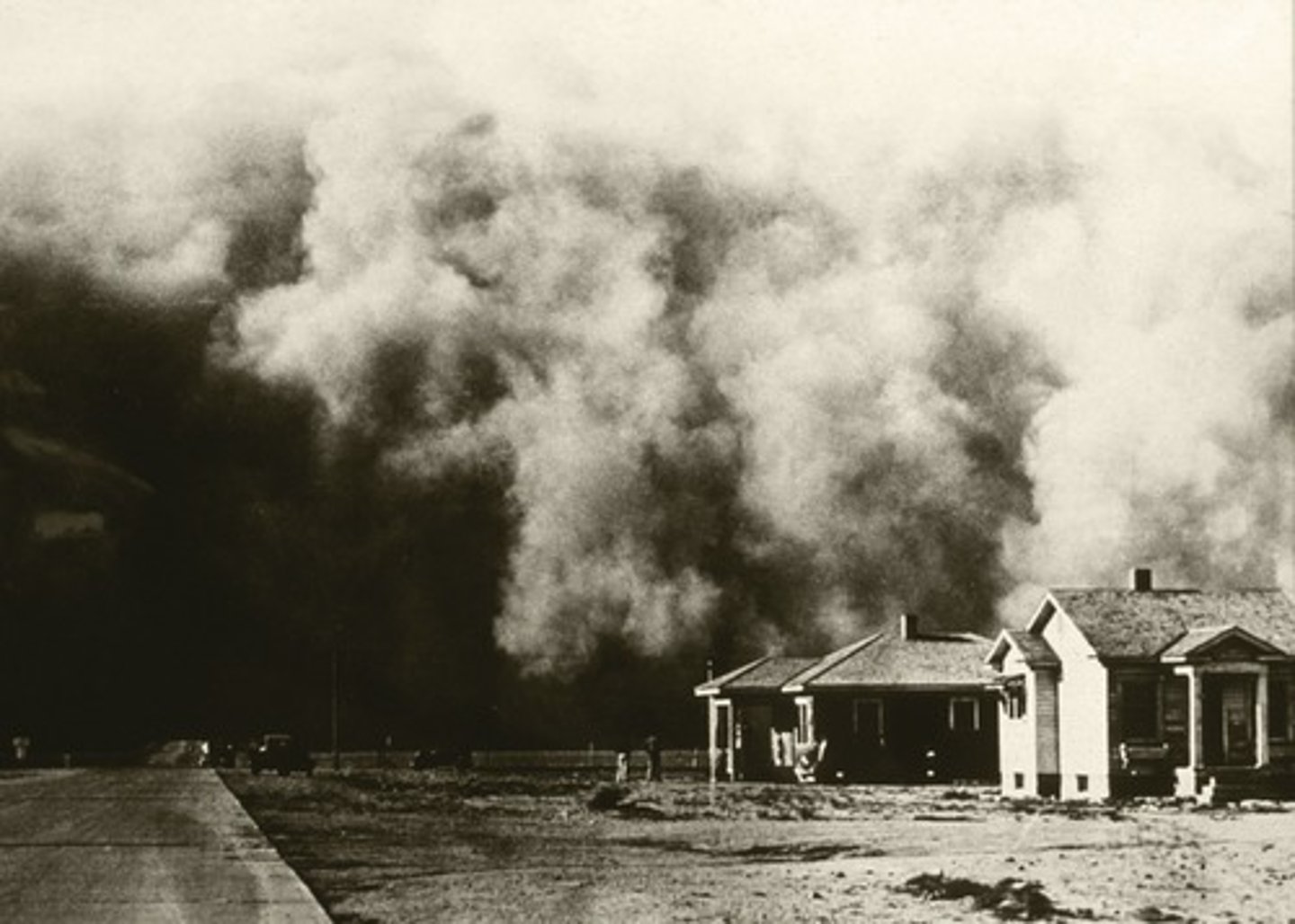
Dust Bowl in Canada
A time in the 1930s in which severe dust storms damaged the ecology and agriculture of the Canadian prairies.

National Employment Commission
made by MacKenzie King, in 1936, in attempts to examine unemployment in Canada and how the country can improve. It recommended greater government intervention and involvement in the economy
Bennett's Tariffs
Import taxes R.B Bennett implemented to bring economic relief to Canada. Many historians believe they caused greater economic distress
Prairie Provinces
The Canadian Prairies, which include Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta, are western regions in Canada that are rich in wheat and energy sources.
Branch Plants
In the early 20th century, US companies began building factories in Canada to avoid paying Canadian tariffs when shipping goods. Paper mills to harvest timber were especially prominent
Royal Twenty Centers
Nationwide camps to house male Canadians and also give them a job if they were single, unemployed, or homeless. They earned only twenty cents a day and conditions in the camps were terrible.
Canadian Liberal Party
One of the two main political parties in Canada that believed in limiting government involvement; equivalent to America's Republican Party
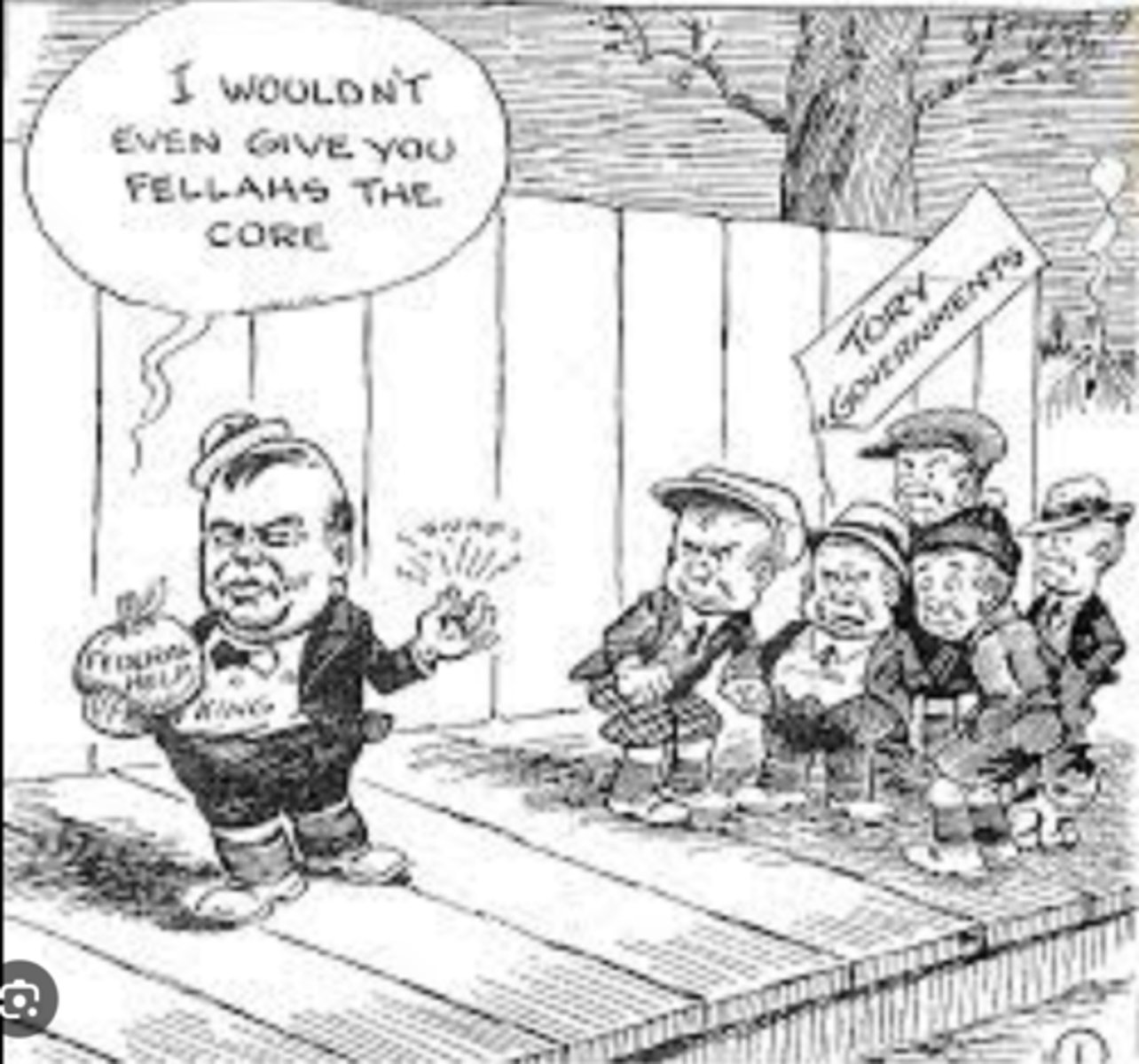
Five Cent Speech
in this address, PM Mackenzie King said that it was up to the provinces and municipal governments to deal with the depression, and that he would not give provinces led by Conservative leaders any money

Canadian Wheat Board
A federal Crown corporation established by RB Bennett to help grain farmers market their product in an aggressive way and to provide equitable returns to producers.
Farmers Creditors Arrangement Act
A law passed by RB Bennett to help debt-ridden farmers restructure their loans.
Prairie Farm Rehabilitation Act
An organization established by RB Bennett to seek solutions to ecological conditions of Dust Bowl. Similar to the Resettlement Organization or the Soil Conservation Service in the US.
Rowell-Sirois Report
a commission set up in 1937 to examine the Canadian economy and federal-provincial relations. It recommended the Canadian federal government assume responsibility for unemployment insurance and pensions