Lecture 24: Apoptosis
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Apoptosis
distinctive and important mode of programmed cell death
Orderly, energy-dependent, and removes unwanted or damaged cells without harming neighbours
important for:
development
sculpting digit tissues
joint formation
homeostasis
eliminated damaged, excess, infected cells
depends on a proteolytic cascade mediated by Caspases
C. Elegans Apoptosis
Nobel Prize 2002: for their discoveries concerning genetic regulation of organ development and programmed cell death”
the lineage of the known cells of C. Elegans were followed in-vivo so they could be seen dying
mutants of C. elegans showed impaired/failed clearance of apoptotic cells
from this, the apoptotic pathway was built
Apoptotic Pathway
specification
killing
execution
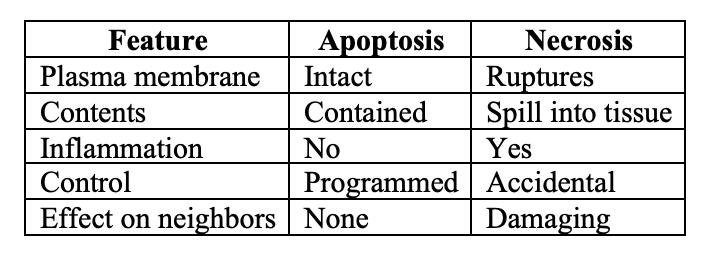
Necrotic vs. Apoptotic Cells
Necrotic cells
spill their contents into their neighbours
Apoptotic cells
die neatly, without damaging it neighbours
Caspases
cysteine asparate proteases
apoptosis depends on a proteolytic cascade mediated by caspases
cysteine proteases which use the sulfur atom in cysteine to preform the cleavage reaction
activated by cleavage at aspartic acids by other caspases
once activated, they cut strategic proteins in the cell next to asparate amino acids
may be either:
initiator
executioner
Initiator Caspases
Exist as inactive monomers
Activated by dimerization or self-cleavage
begin the apoptotic program by activating the executioner caspases
caspase 8 and 9
Executioner Caspases
Have short prodomains
Activated by initiator caspases
Cleave hundreds of cellular targets
Caspase 3,6, and 7
Irreversibility of Apoptosis
Caspases activate other caspases
Creates an amplifying cascade
Once started → cell is committed
CAD
caspase activated DNAse
catalyses the hydrolytic cleavage of DNA by releasing the brake on DNAses to degrade DNA
Extrinsic Pathway
1 of 2 main activation pathways
signalled from outside the cell
often via killer immune cells
mechanism:
Fas ligand binds Fas receptor
Fas receptors cluster
Death domains exposed
Recruit adaptor protein FADD
FADD recruits inactive initiator caspases
Large complex forms: DISC
Initiator caspases activate → apoptosis begins
Intrinsic Pathway
1 of 2 main activation pathways
signalled from the mitochondria inside of the cell
often in response to developmental signals or to injury (ex. DNA damage)
initiated by the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm
Mechanism
Cytochrome c binds Apaf-1
Apaf-1 oligomerizes
Forms large complex: apoptosome
Recruits inactive caspase-9
Caspase-9 dimerizes → activated
Executioner caspases activated
BcI-2
main regulators of the intrinsic pathway
pro-apoptotic or anti-apoptotic
balance between them determines cell fate
Control mitochondrial membrane permeability
Pro-apoptotic BcI-2
BcI2 proteins make holes into the mitochondrial membrane
Anti-apoptotic BcI-2
BcI2 proteins inactivate the pro-apoptotic BcI2
Inhibitors of Apoptosis
IAP
line of defense against inappropriate caspase activation
bind and prevent activation of some procaspases
Post-Apoptosis Cleanup
healthy neighbours phagocytose and digest apoptotic cells
cell competition is a fitness control mechanism in which less fit cells are eliminated from a tissue
PtdSer
Phosphatidyl Serine (PtdSer)
Normally located on inner membrane leaflet
Caspases inactivate flippases, therefore allowing PtdSer to appear on the cell’s outer surface
as a result, neighbouring cells recognize apoptotic cells
Apoptotic cells are then phagocytosed and digested
Ferroptosis
intracellular iron dependent form of cell death
distinct from apoptosis and necrosis
characterised by the accumulation of oxidatively damaged phospholipids