Cardiovascular System
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
epicardium
outside layer of the heart
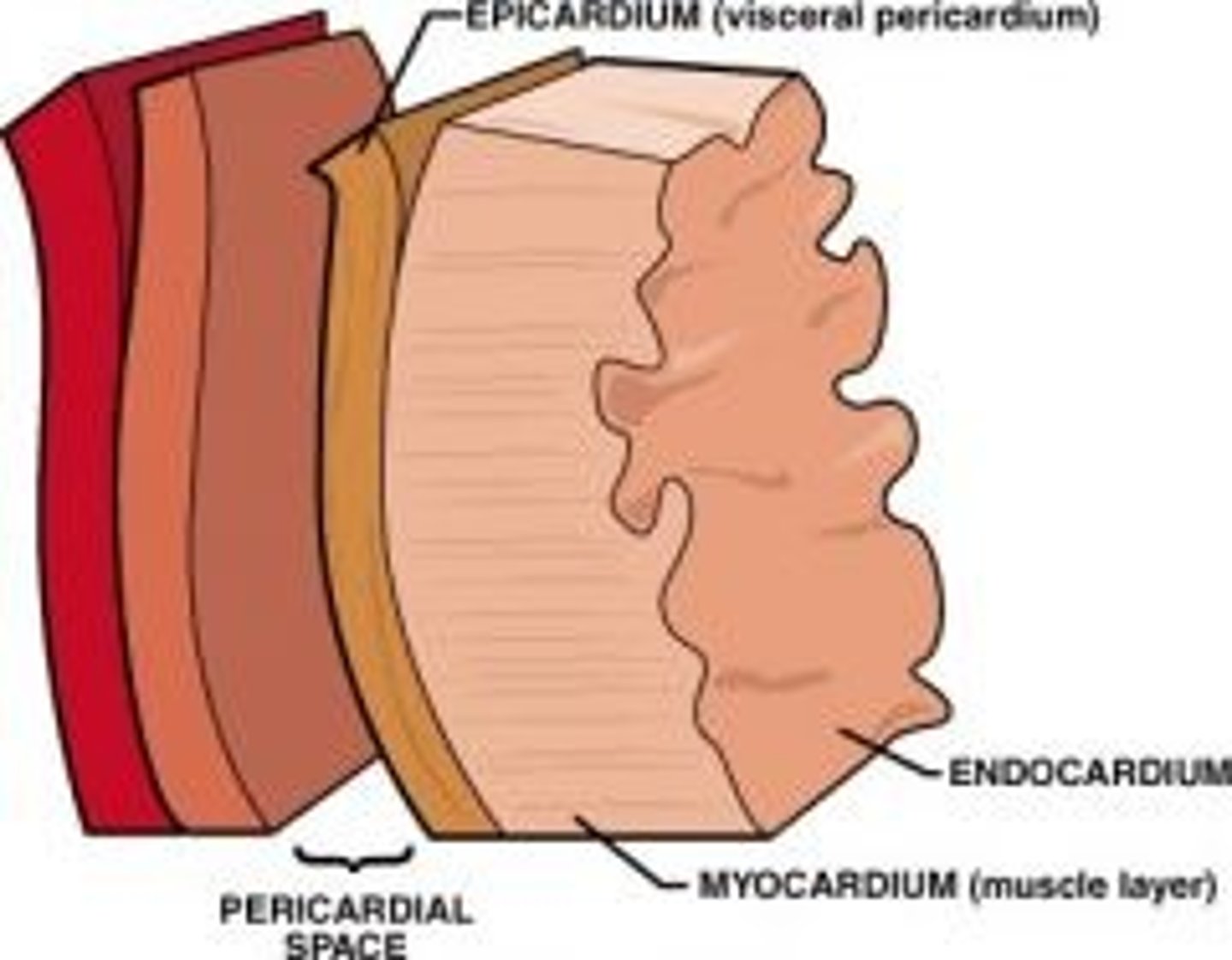
myocardium
middle muscle layer of the heart
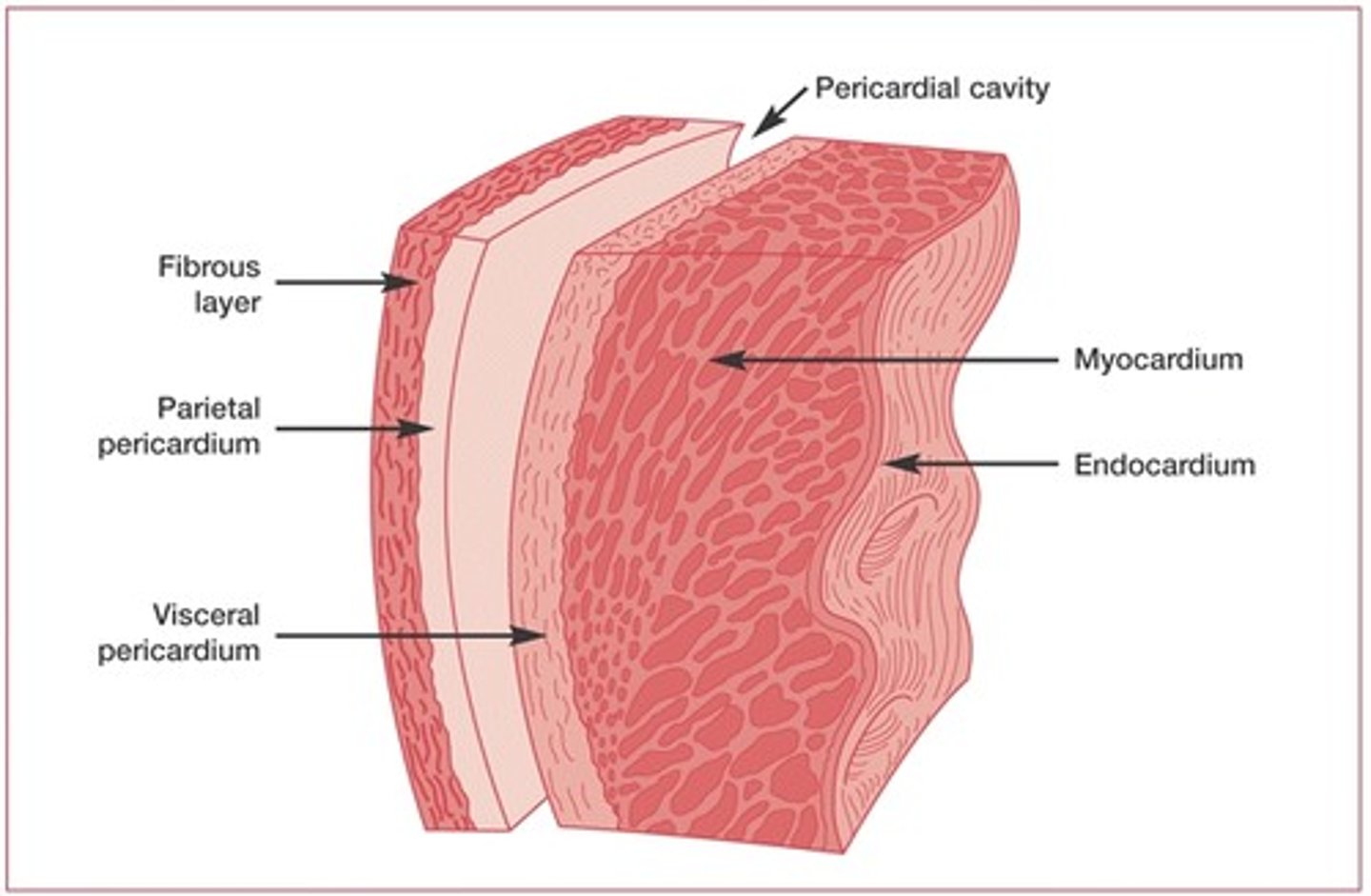
endocardium
inside layer of the heart
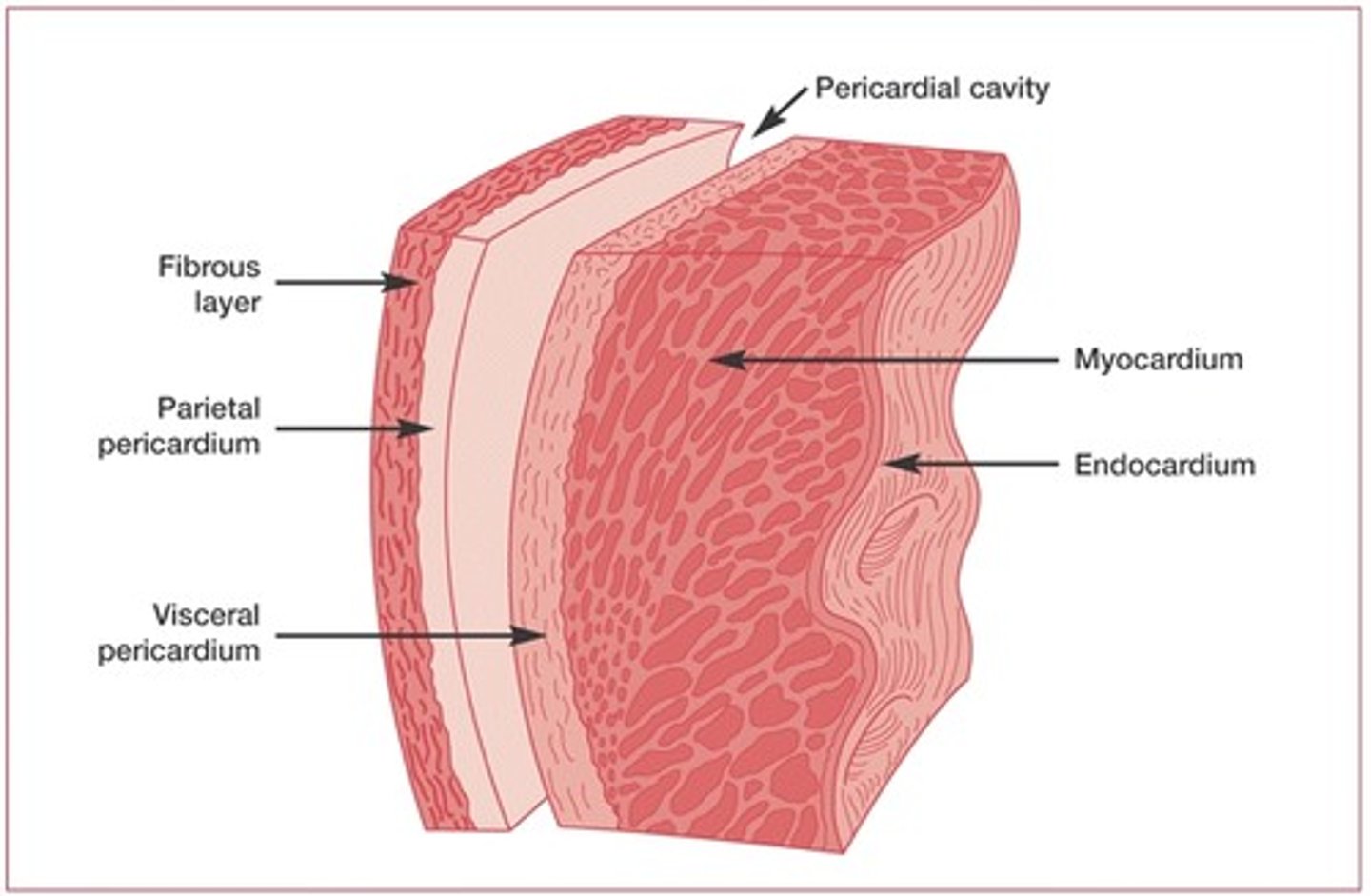
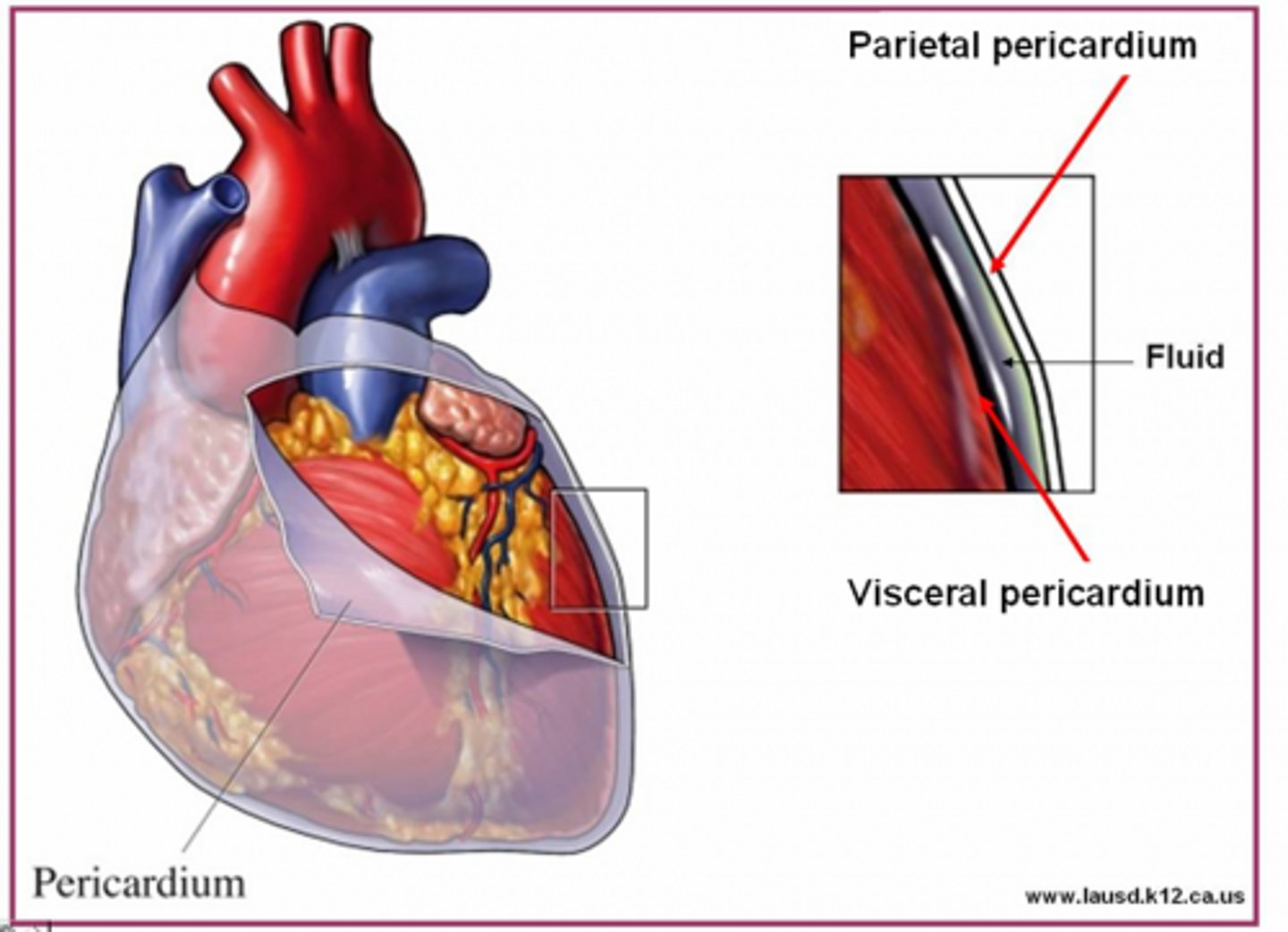
pericardium
sac surrounding the heart
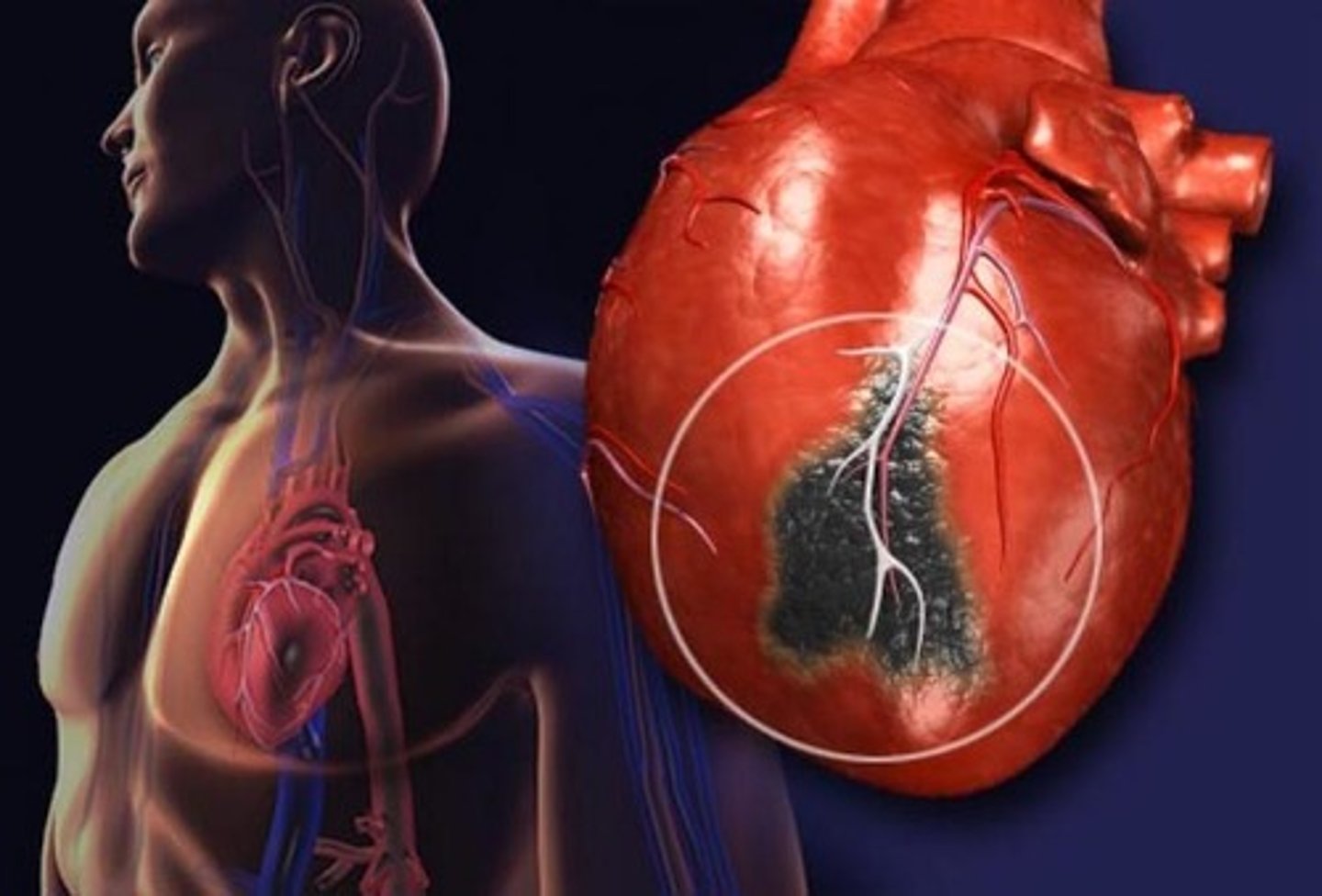
Myocardial infarction
heart attack
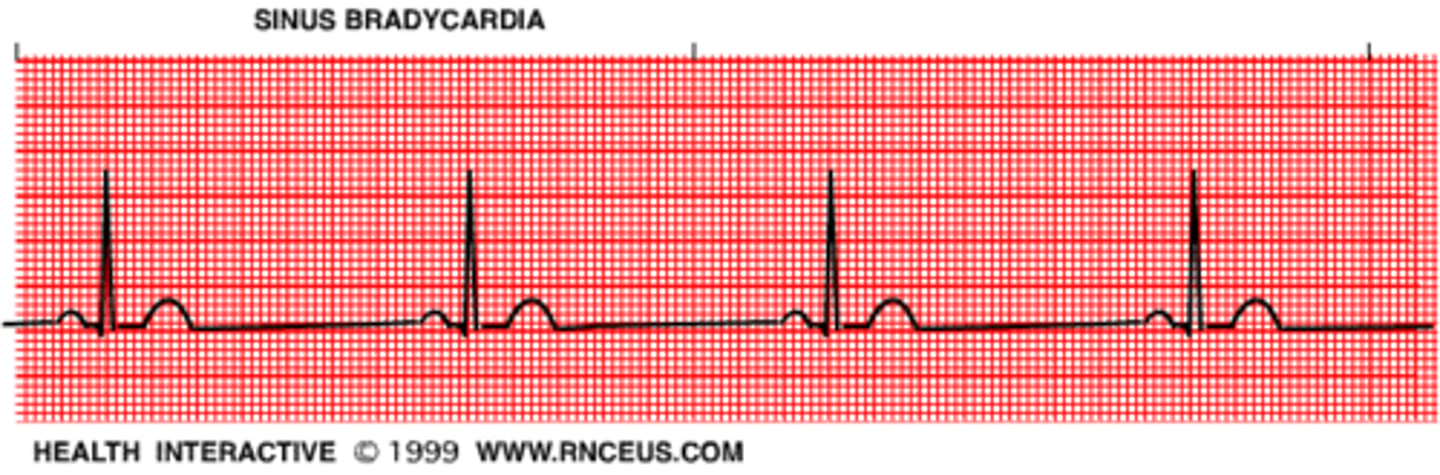
Bradycardia
slow heart rate, less than 60 bpm
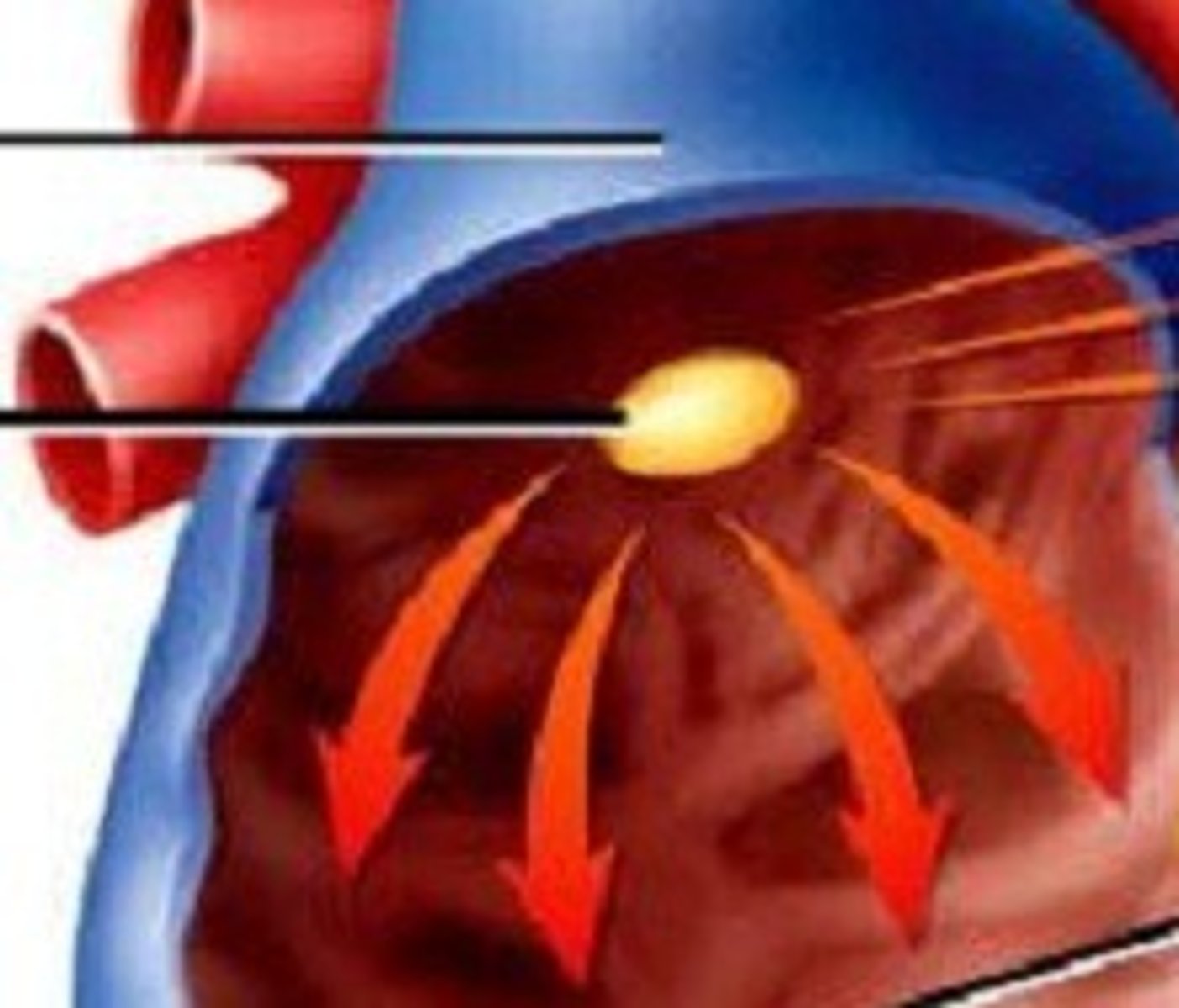
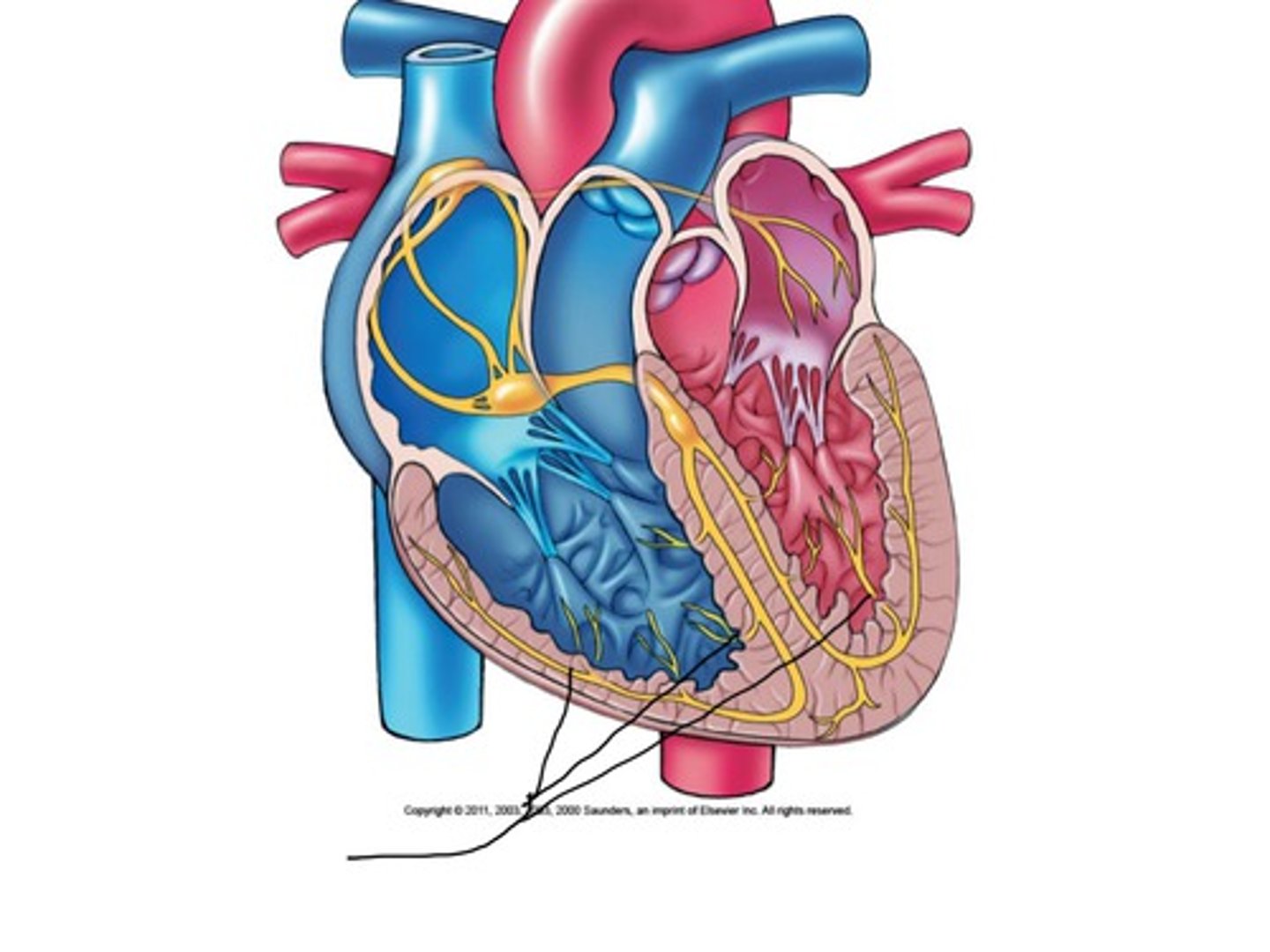
SA node
The pacemaker
AV node
At the bottom of the atria sends impulse to the ventricles, can pace at 40-60 bpm
Arrhythmia
Abnormal heart rhythm or heart rate
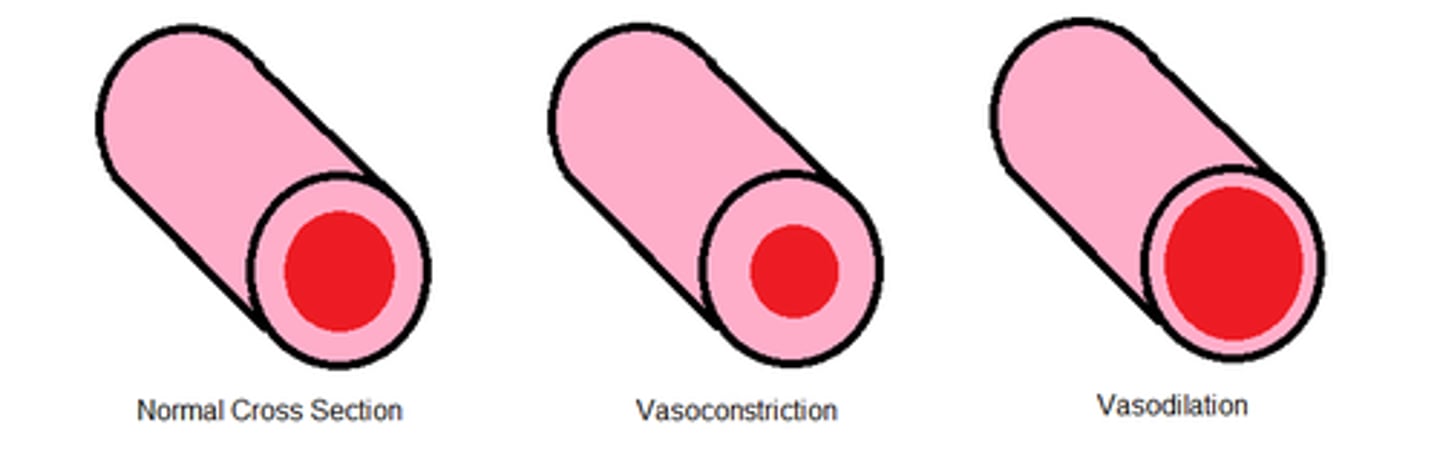
Vasoconstriction
Constriction of the veins
hypertension
high blood pressure, sustained 140/90

Systole
contraction phase of the heart
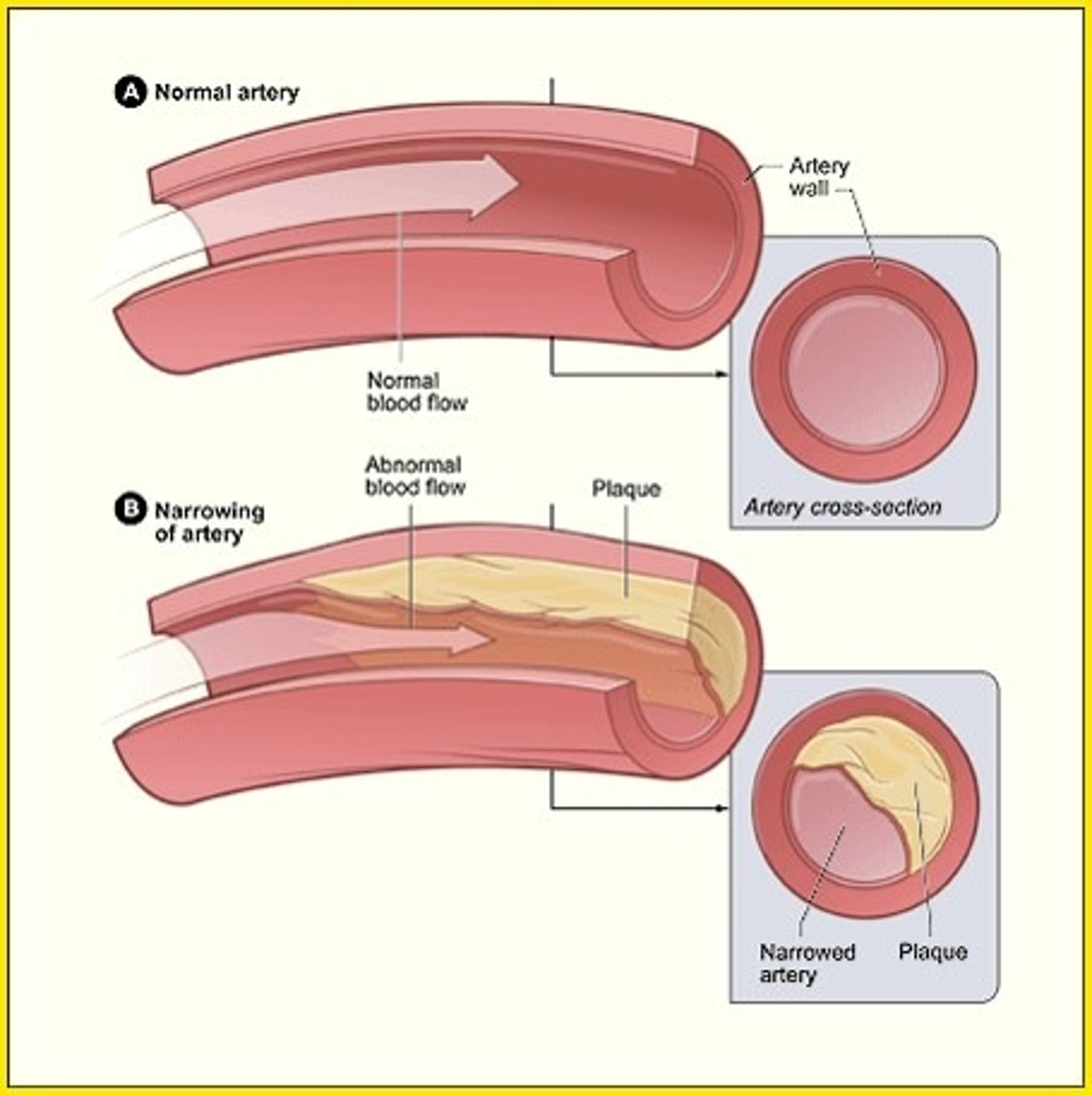
Coronary artery disease
artery that nourishes the heart muscle becomes thickened
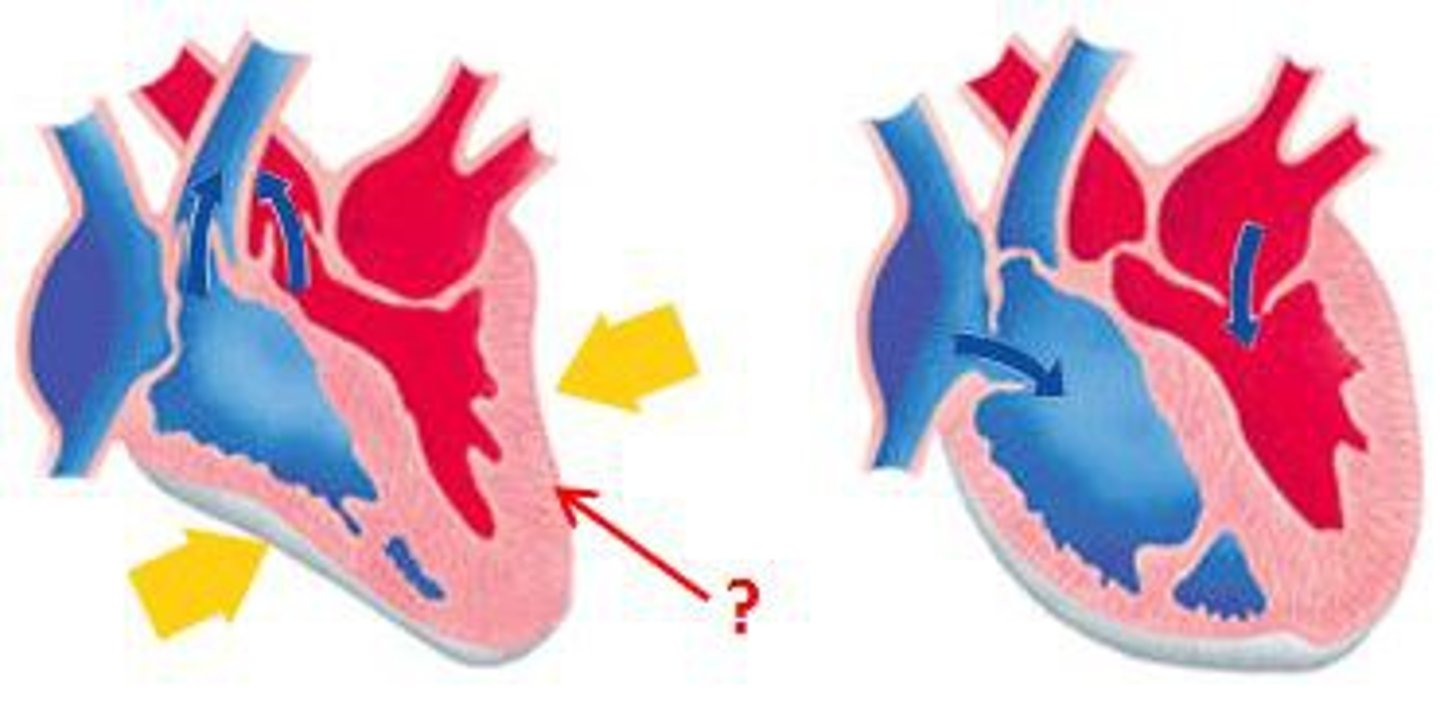
Pulmonary stenosis
a heart condition where the pulmonary valve, which controls blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs, becomes narrowed
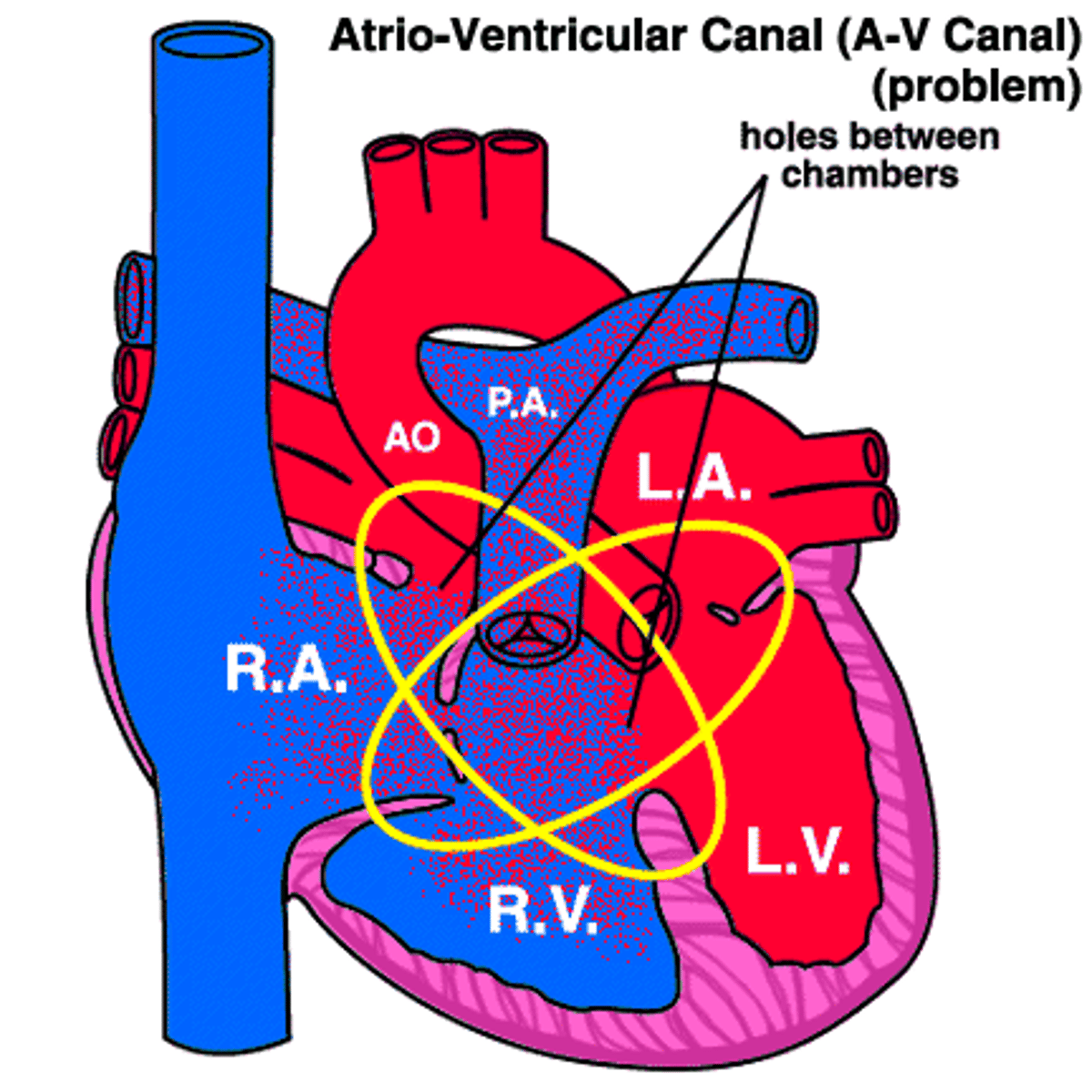
Atrial fibrillation
a heart condition that causes an irregular heartbeat.
atrioventricular (AV) valve
valve that separates the atrium from the ventricle
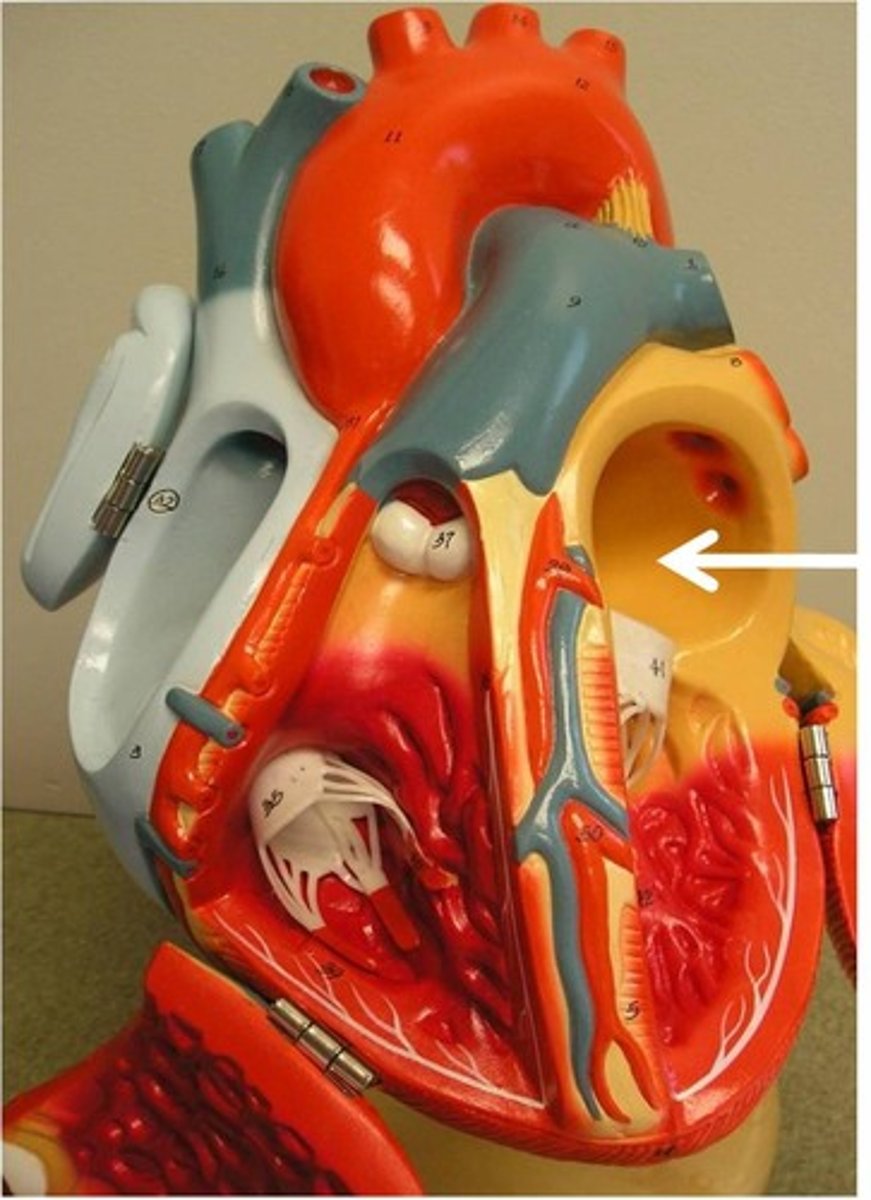
Aortic valve calcification
a condition where calcium deposits accumulate on the aortic valve
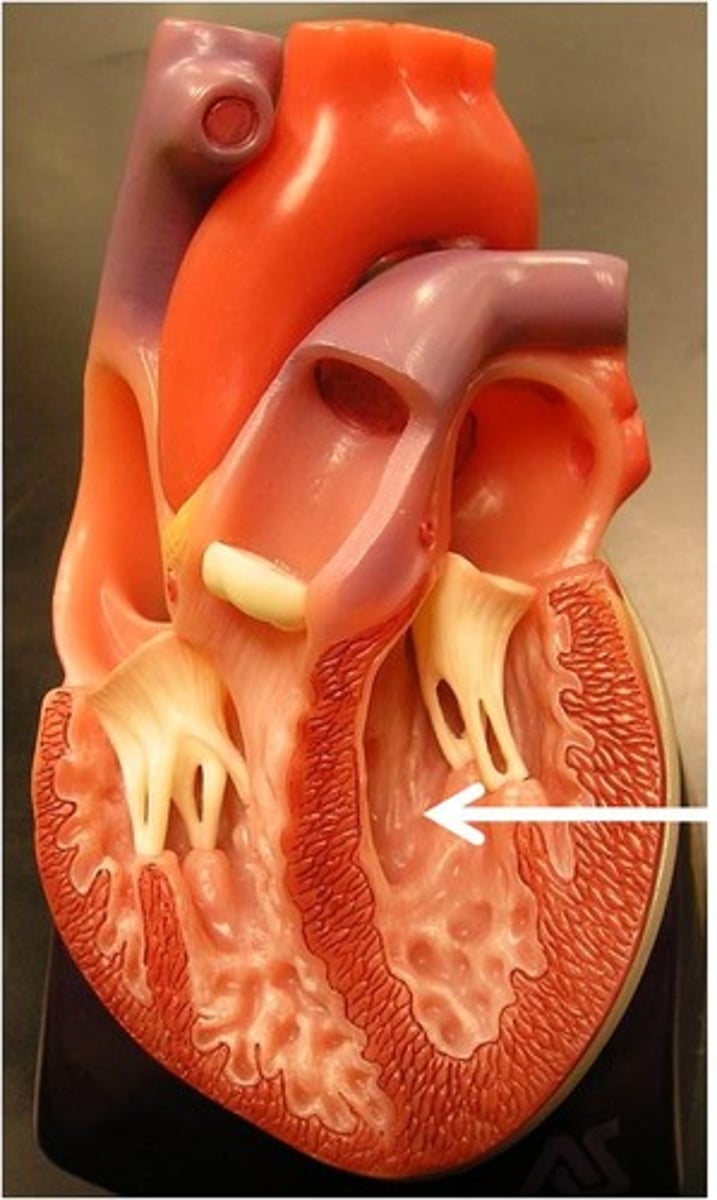
atrium
upper chambers of the heart
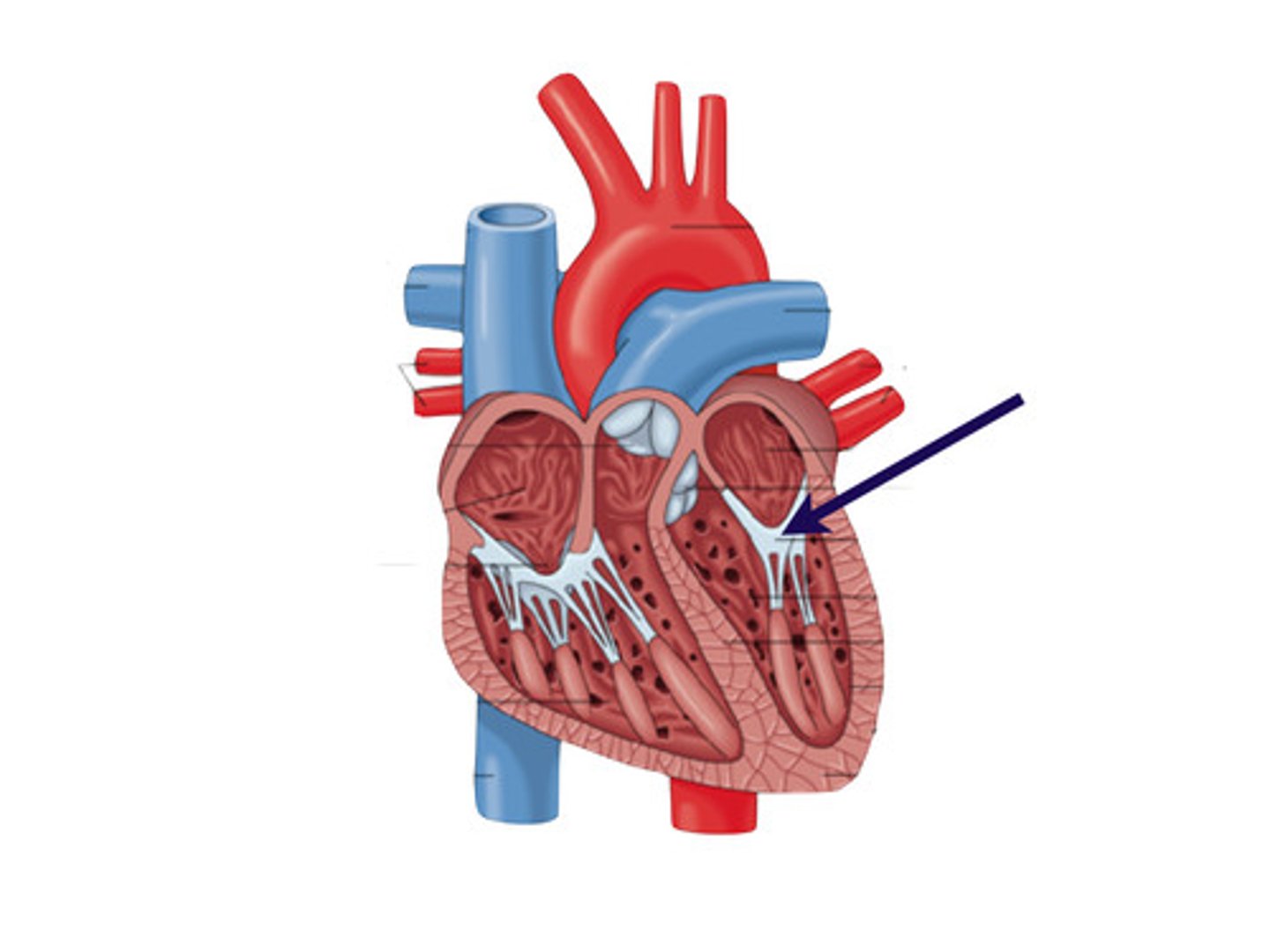
ventricle
lower chambers of the heart
right side of the heart
responsible for pulmonary circulation, moving deoxygenated blood to lungs
left side of the heart
responsible for systemic circulation, moving oxygenated blood to body
name of AV valve on left side
bicuspid/mitral AV valve
pulmonary semilunar valve
valve between right ventricle and pulmonary artery
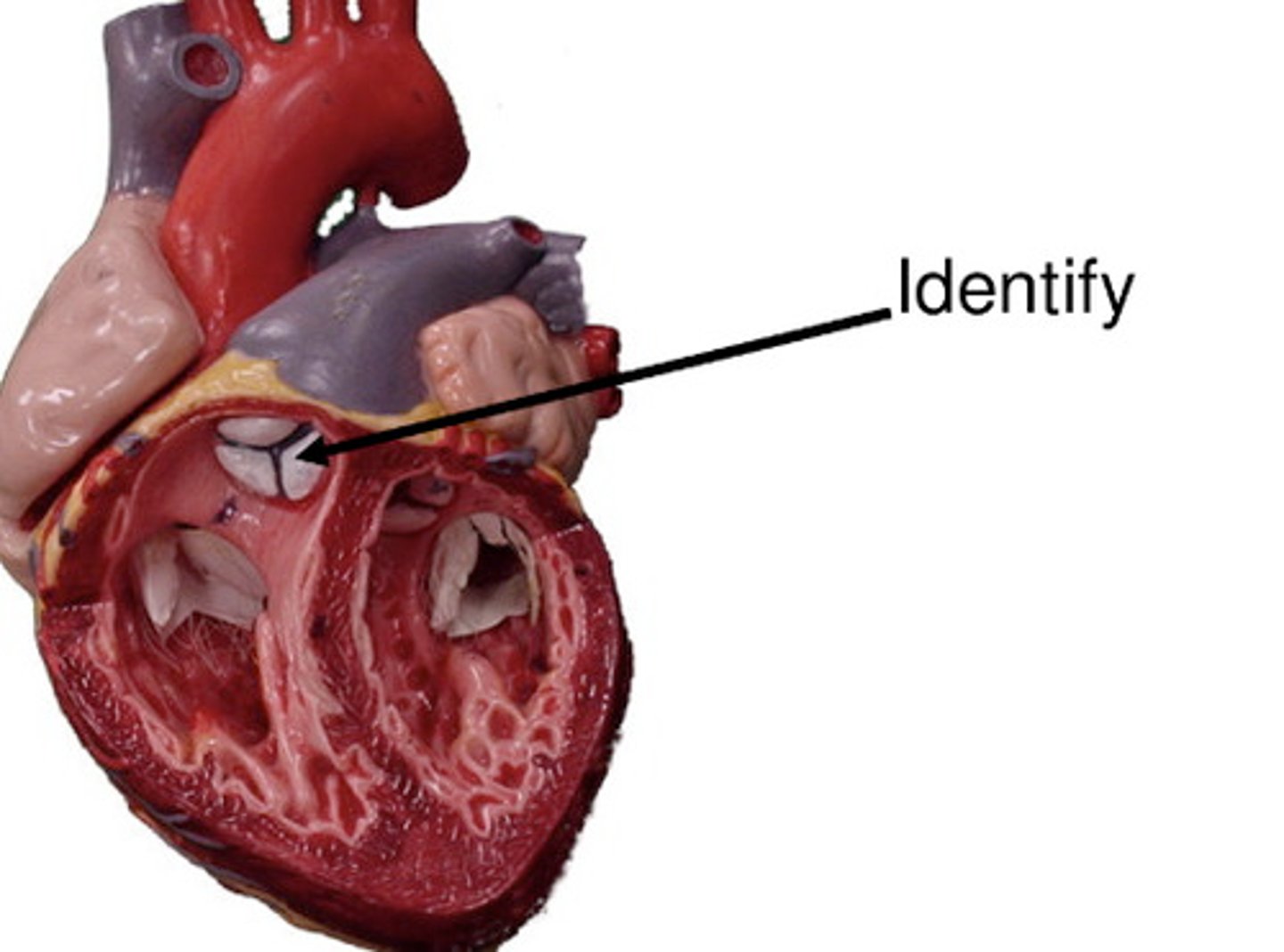
aortic semilunar valve
valve between left ventricle and aorta
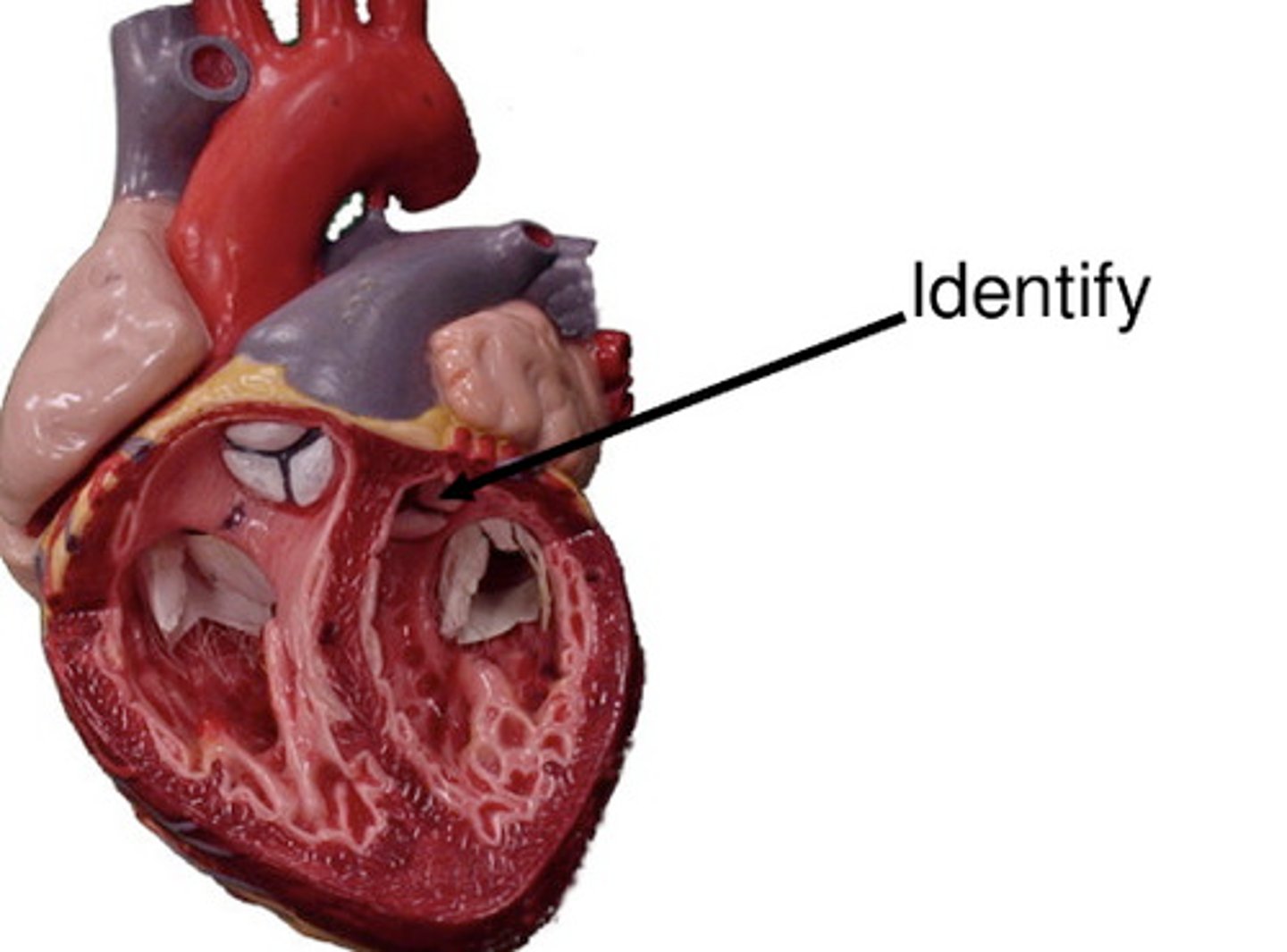
diastole
relaxation portion of blood pressure
Heart rate (HR)
number of times heart beats in one minute
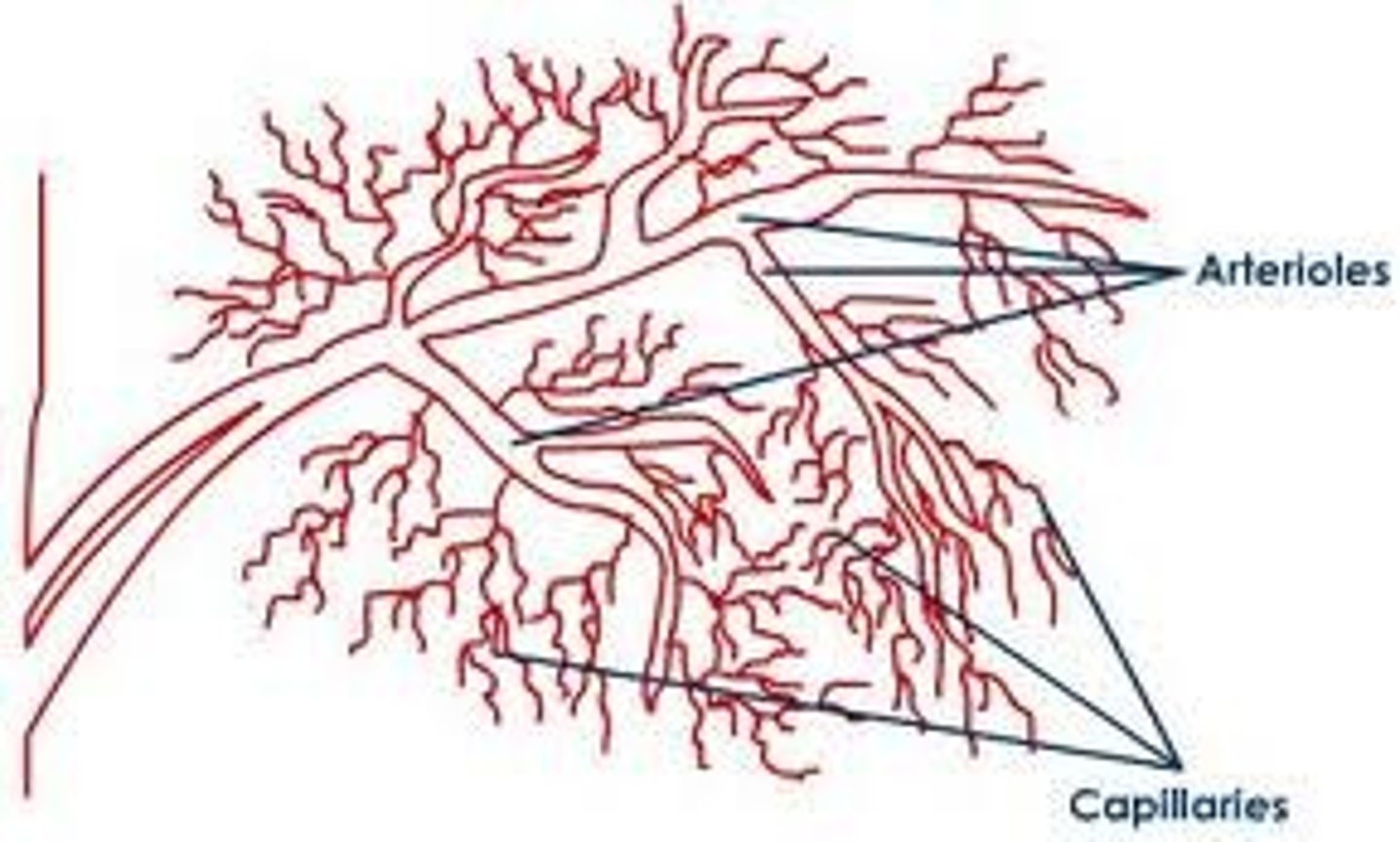
arteries/arterioles
vessels carry blood AWAY from heart
venules/veins
vessels carry blood TO the heart
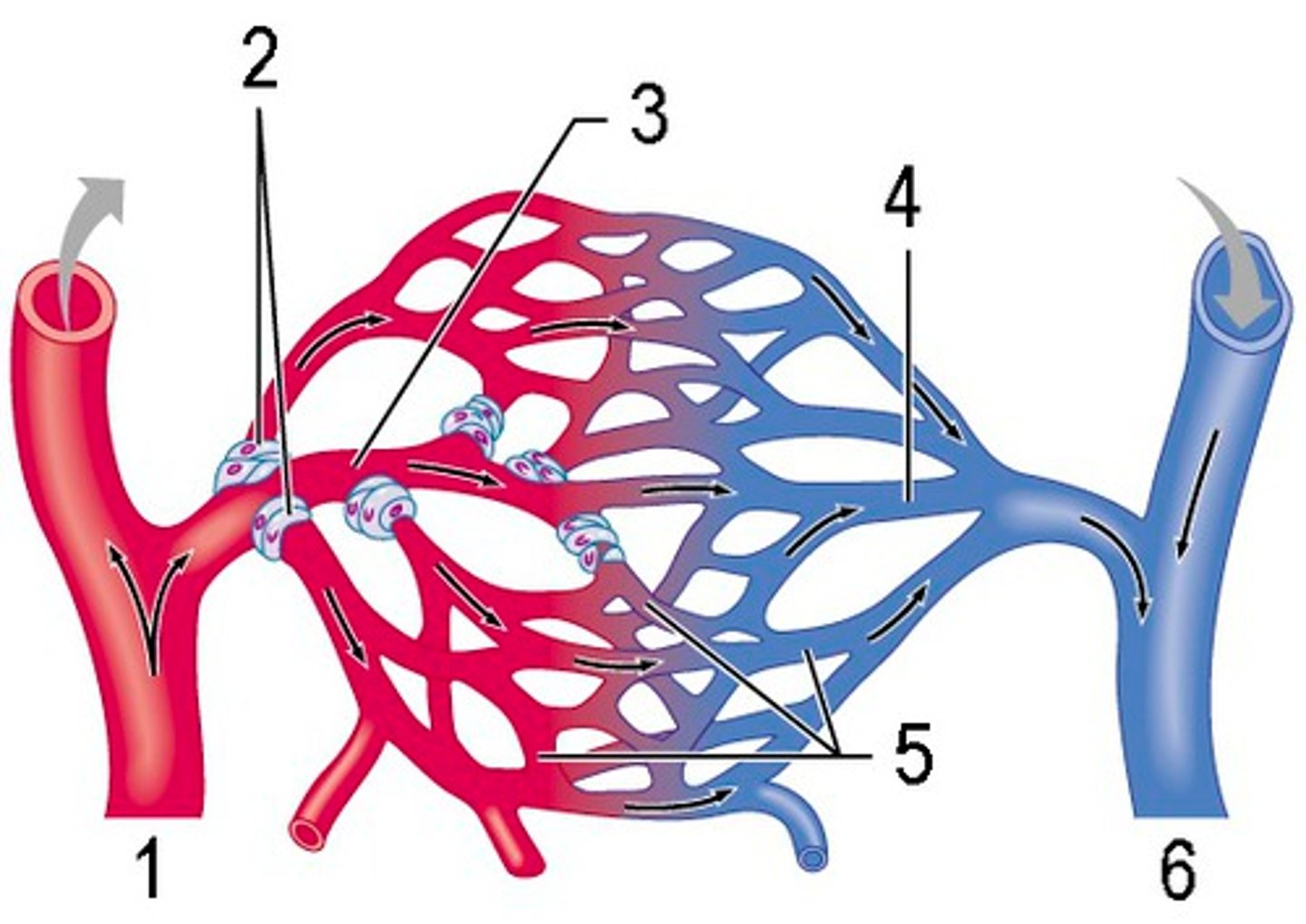
capillaries
blood vessels that are one cell thick, where nutrient/gas exchange occurs
aorta
largest artery in the body
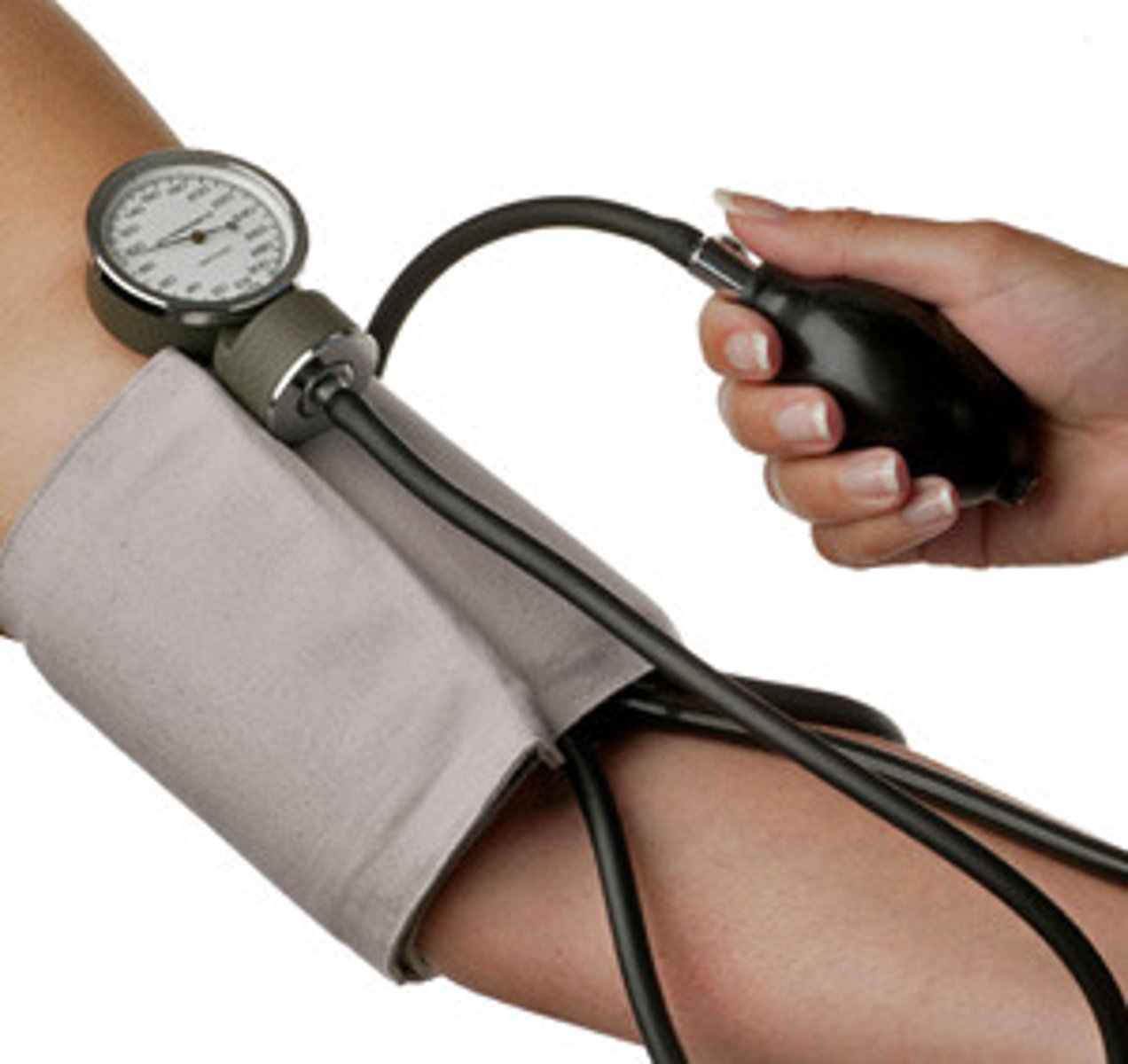
blood pressure
the force/pressure blood exerts on blood vessel walls
normal blood pressure
120/80 mmHg
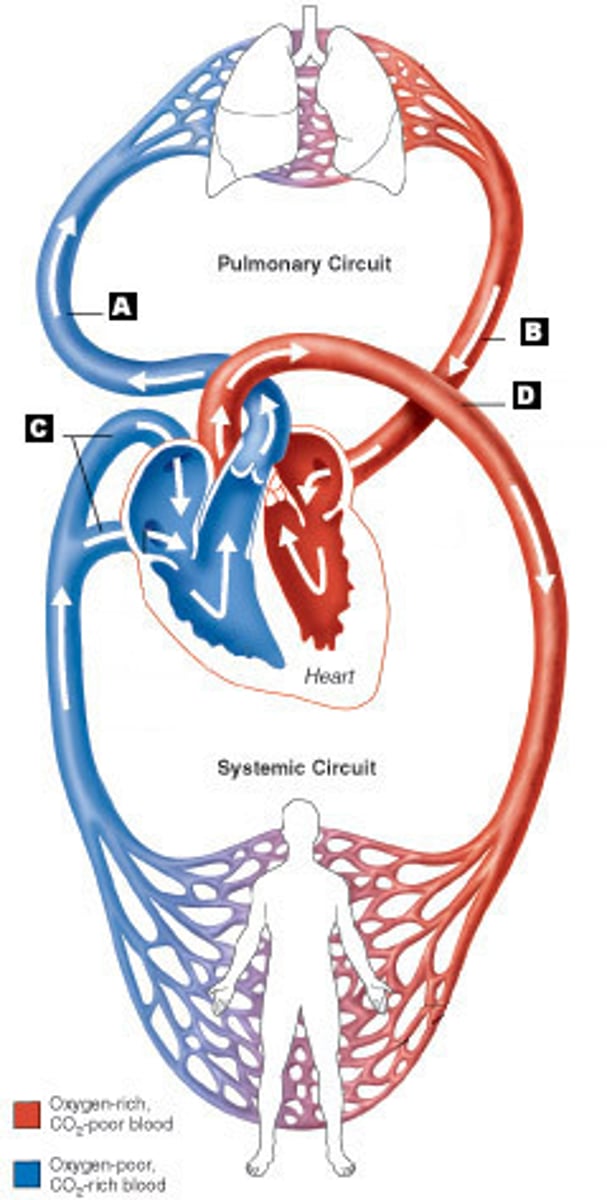
pulmonary circulation
blood flow from heart to lungs
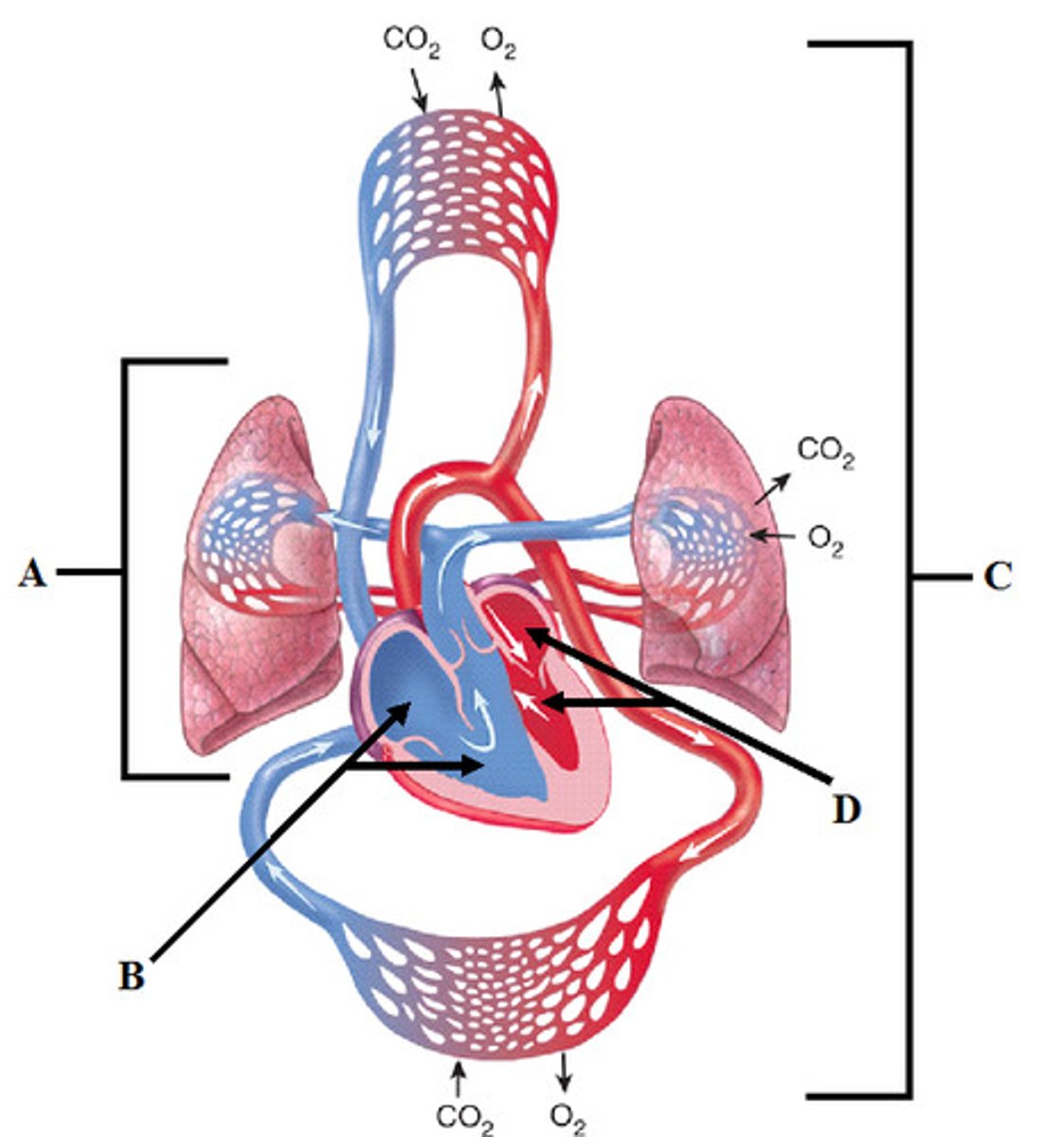
systemic circulation
blood flow from the heart to the all the parts of the body
pulmonary artery
the only deoxygenated artery, leaves the right ventricle
pulmonary vein
the only oxygenated vein, enters the left atrium
right atrium
where the superior & inferior vena cavae empty into
coronary artery
artery that nourishes the heart muscle
Functions of the circulatory system
-Transport gases, nutients and hormones
-Homeostasis- regulates temp, pH and electrolytes
-immunity (WBC, antibodies)
plasma
liquid component of the blood, is a straw colored mixture of 92% water, proteins, nutrients, electrolytes, and wastes
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells; transports gases
Hemoglobin
protein that binds oxygen
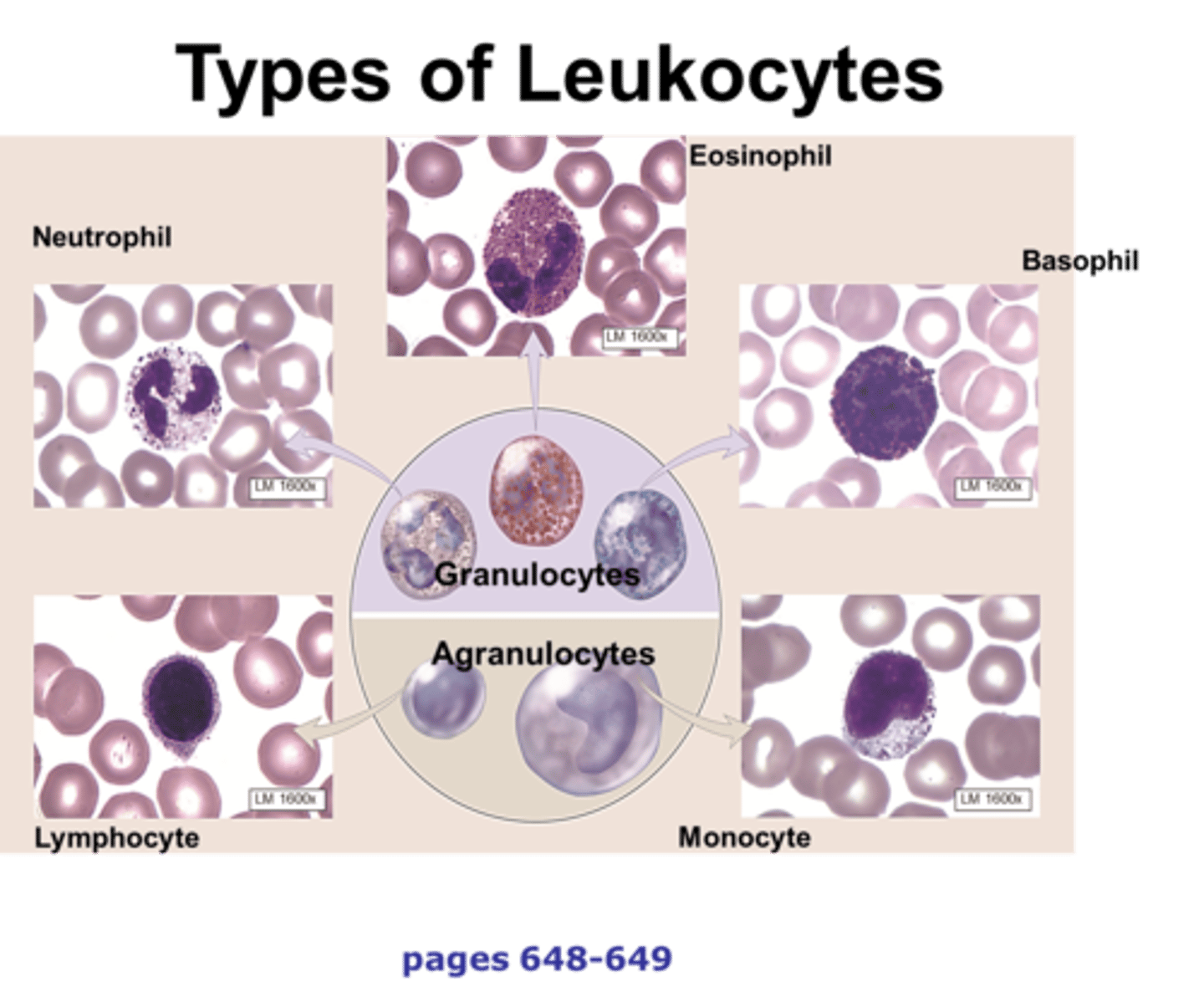
Leukocytes
White blood cells; fight disease and infection
thrombocytes
platelets; clot blood
spleen
organ that fliters blood, produces antibodies
Hematopoiesis
Formation of red blood cells
antigens
proteins found on the surface of red blood cells, determines blood type
agglutination
clumping of blood
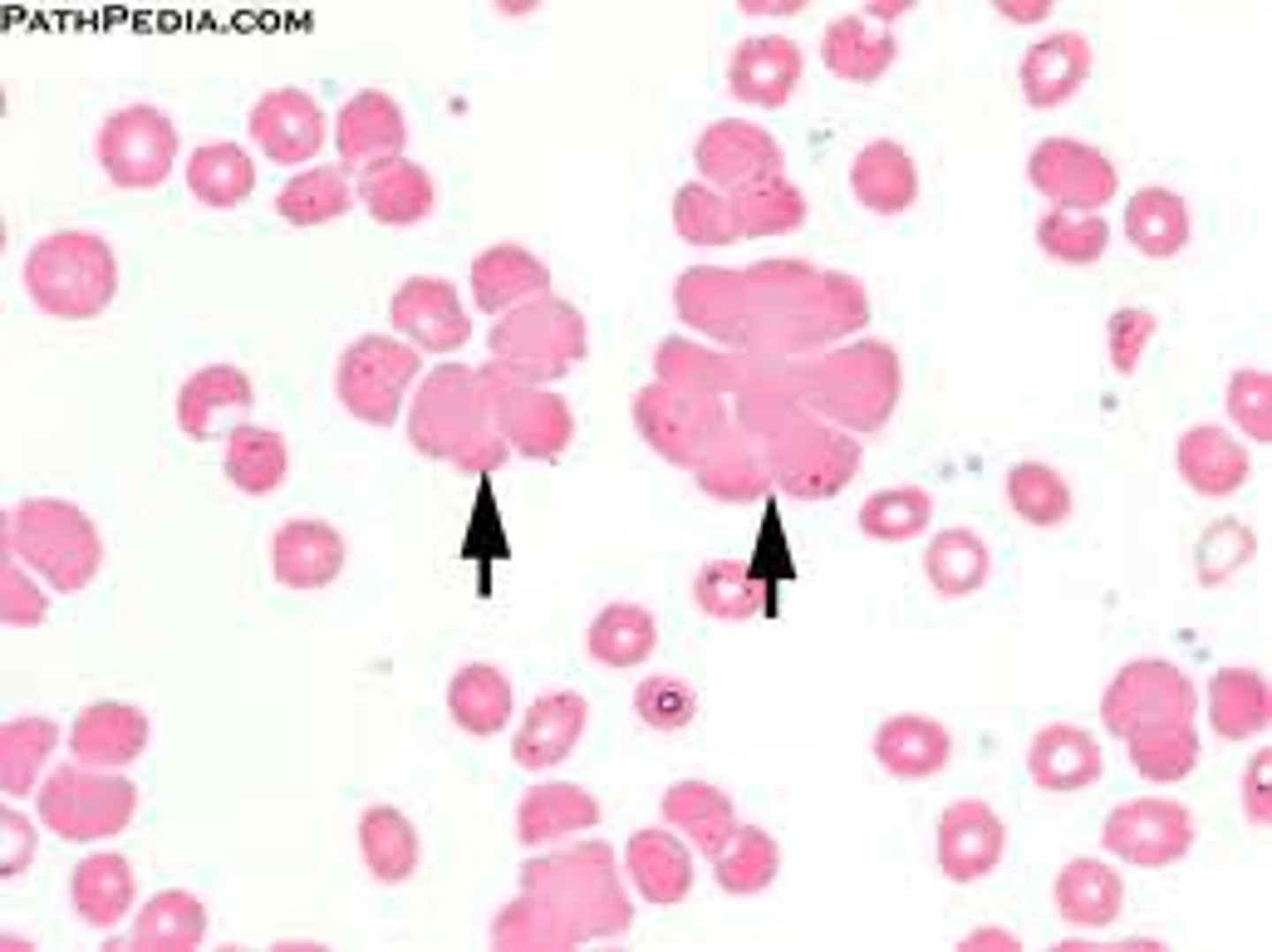
Blood types
A, B, AB, O (+/-)
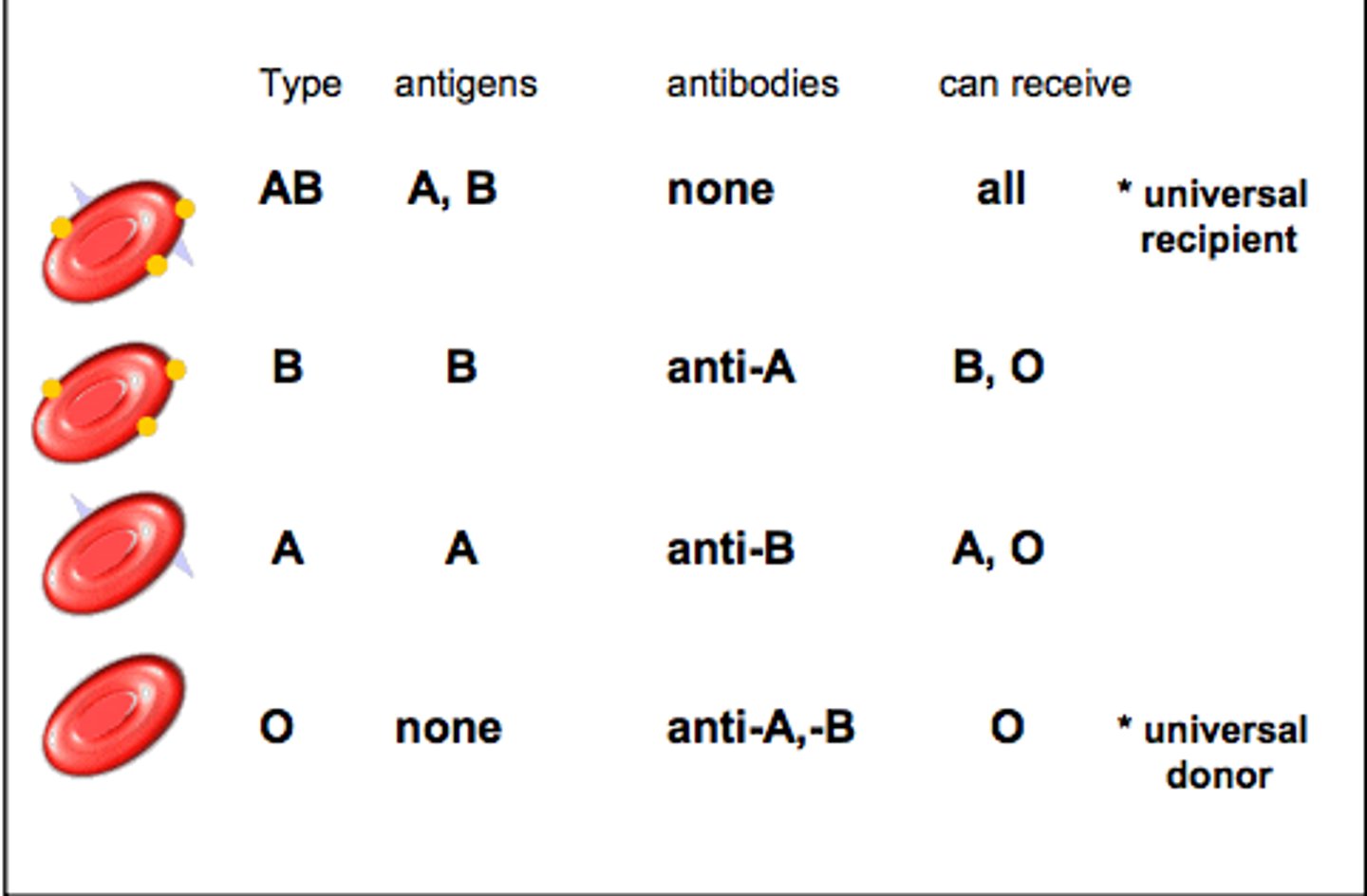
transfusion
transfer of blood from one person to another
Universal donor
O-
Universal recipient
AB+
Anemia
lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin
Leukemia
form of cancer that causes an overproduction and release of immature white blood cells
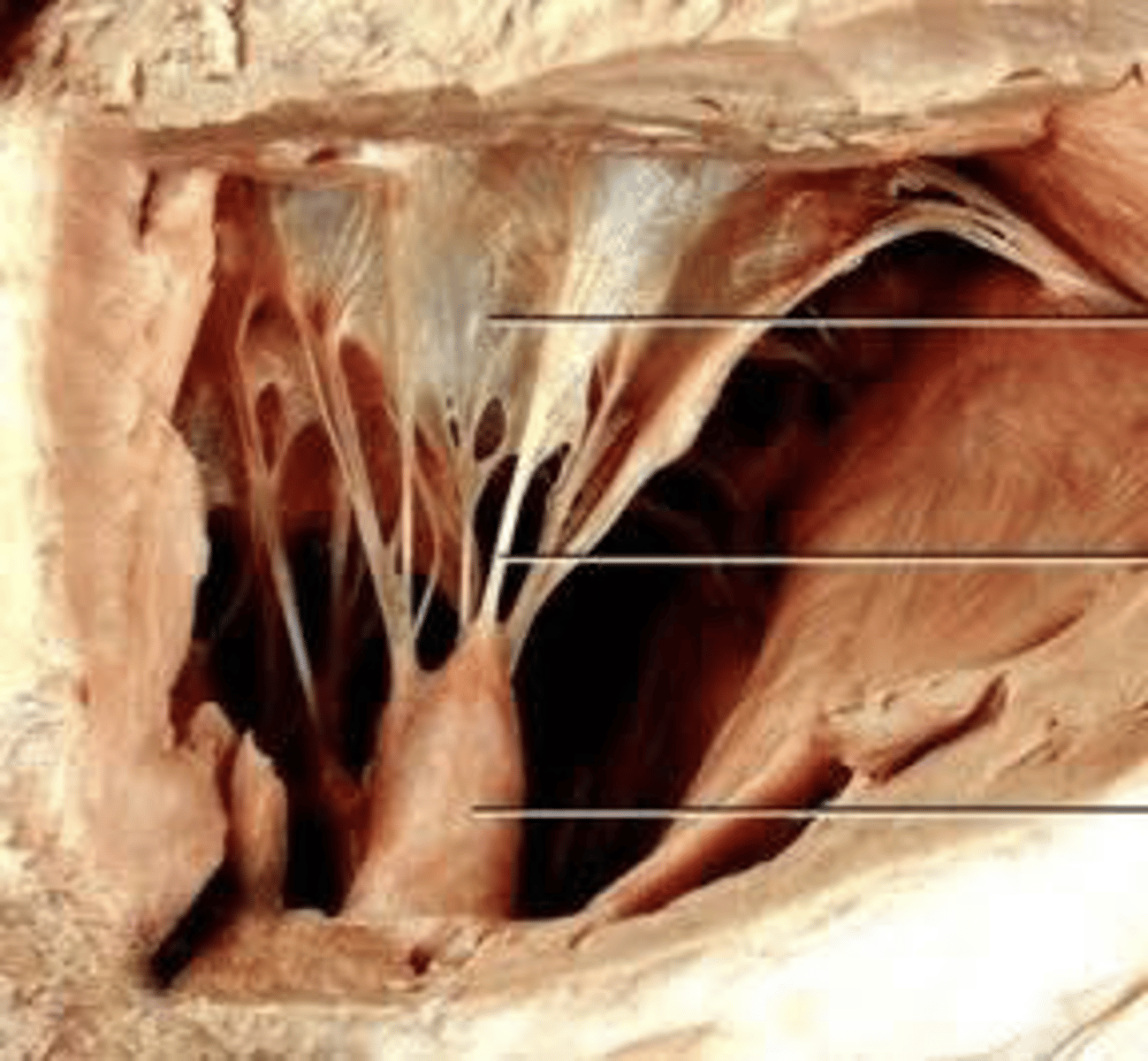
chordae tendịneae
"heartstrings" that keep valves from prolapsing and are attached to the papillary muscles.
Purkinje fibers
Nerves in the heart that carry the contraction impulse toward the apex of the heart, to the muscle of the right and left ventricles, causing them to contract.
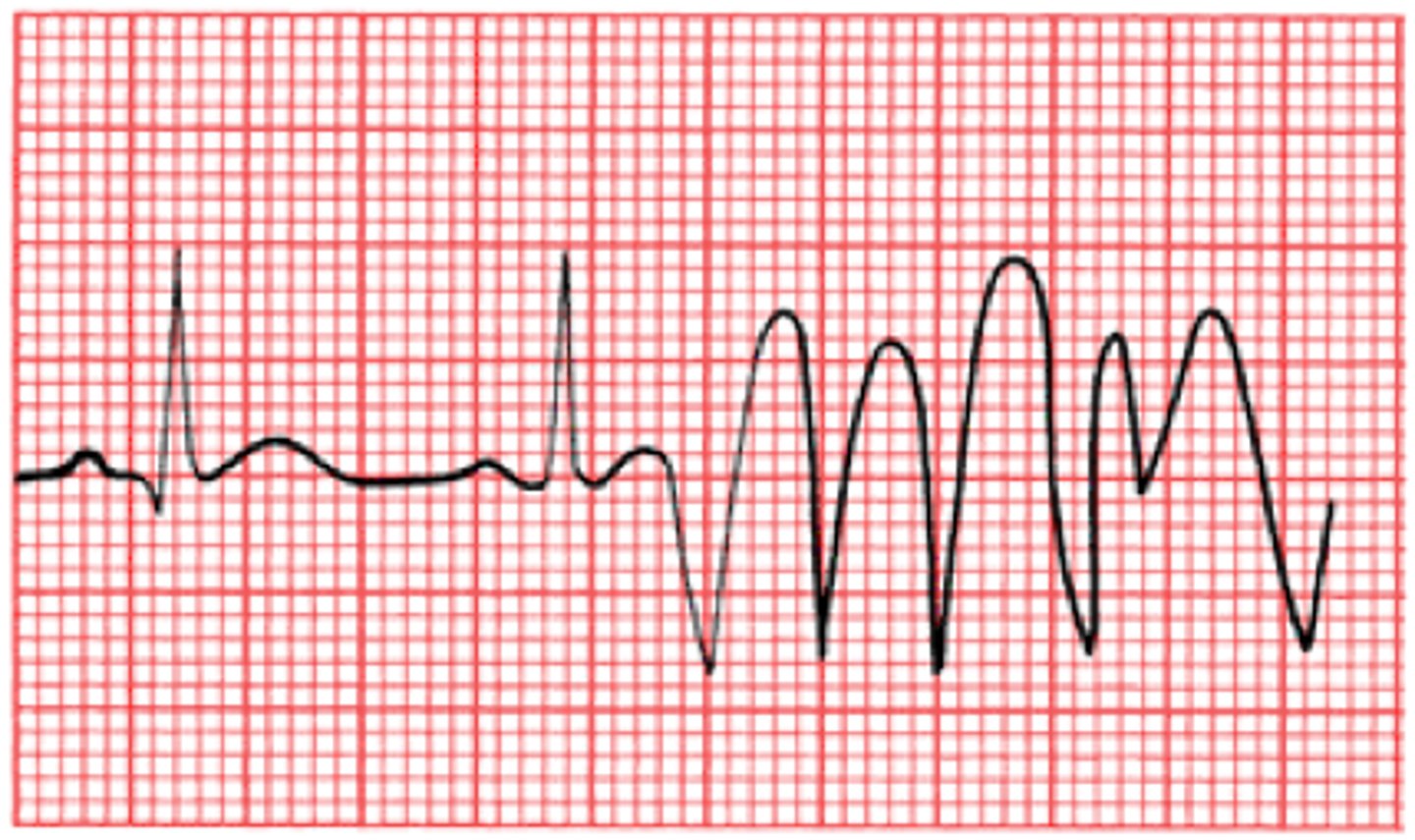
Fibrillation
Failure of the electrical system can cause the heart to beat irregularly
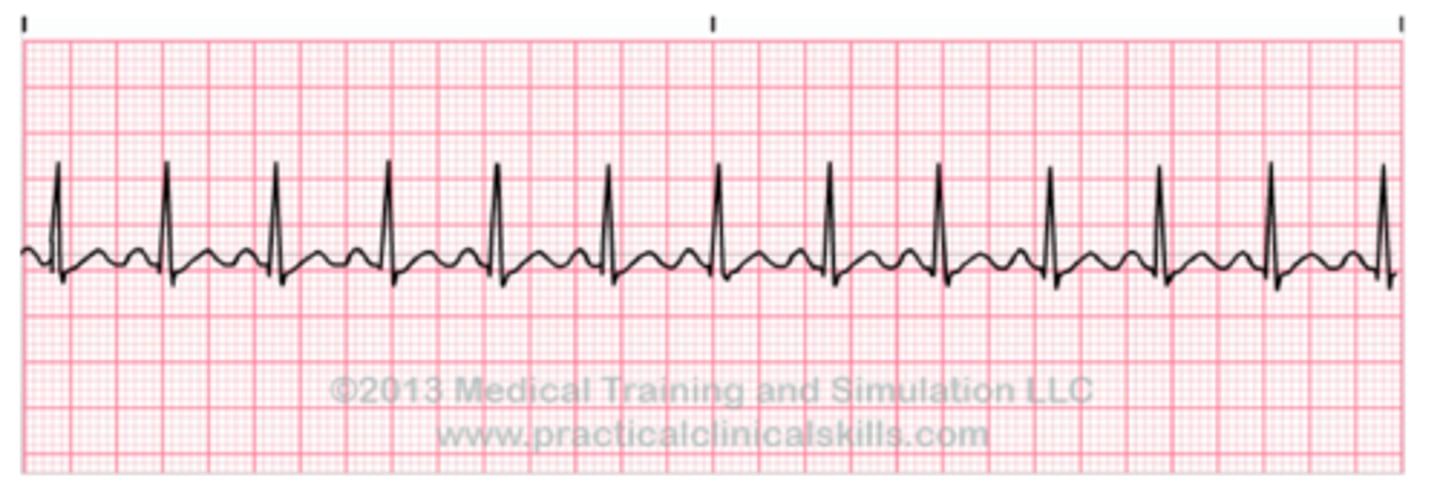
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
measure electrical impulses coming from the heart, creating a graph of the output.
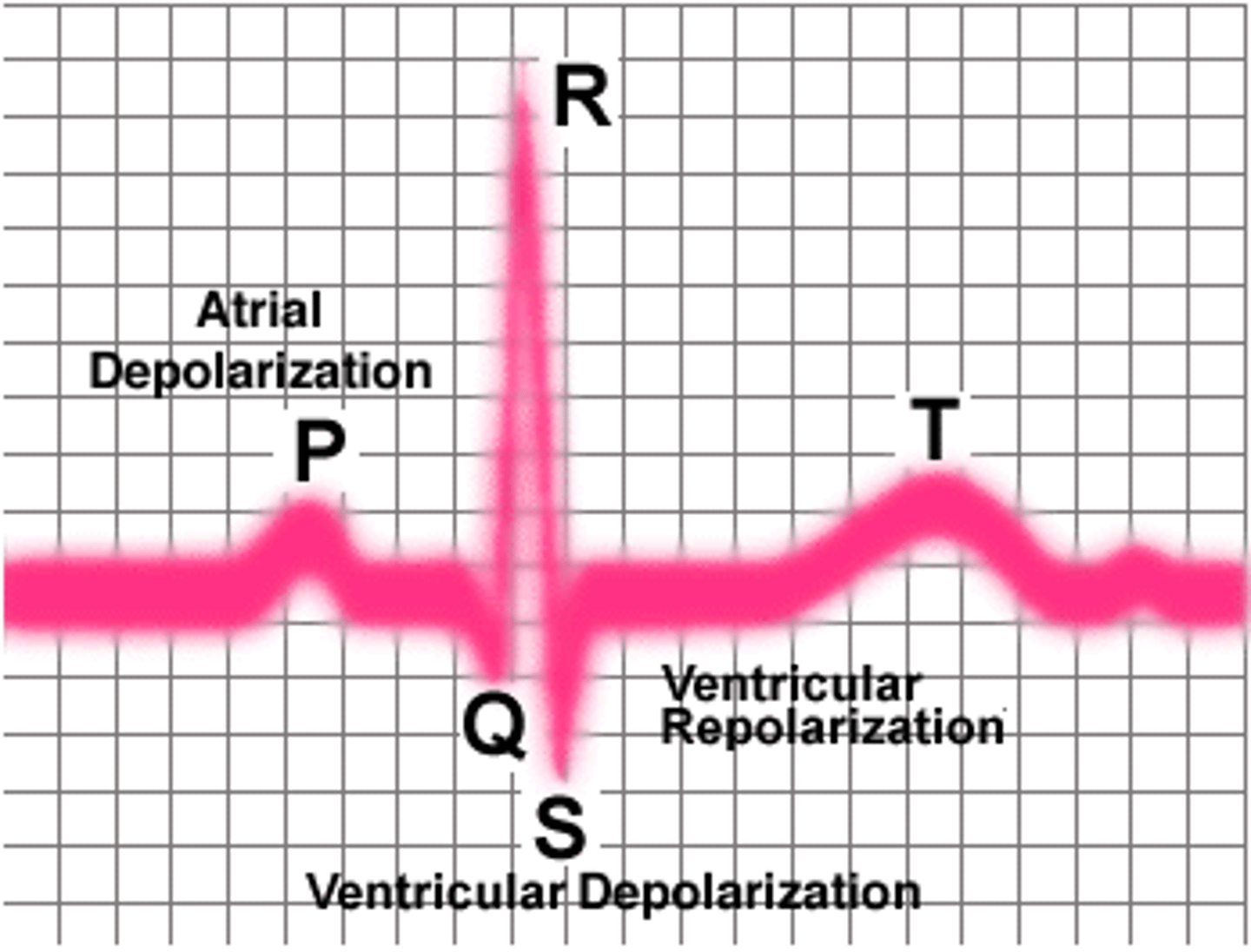
P wave
Atria contract (atrium depolarizes)
QRS wave
Ventricles contract (ventricle depolarizes)
T wave
Ventricles relax and reset (ventricle repolarizes)
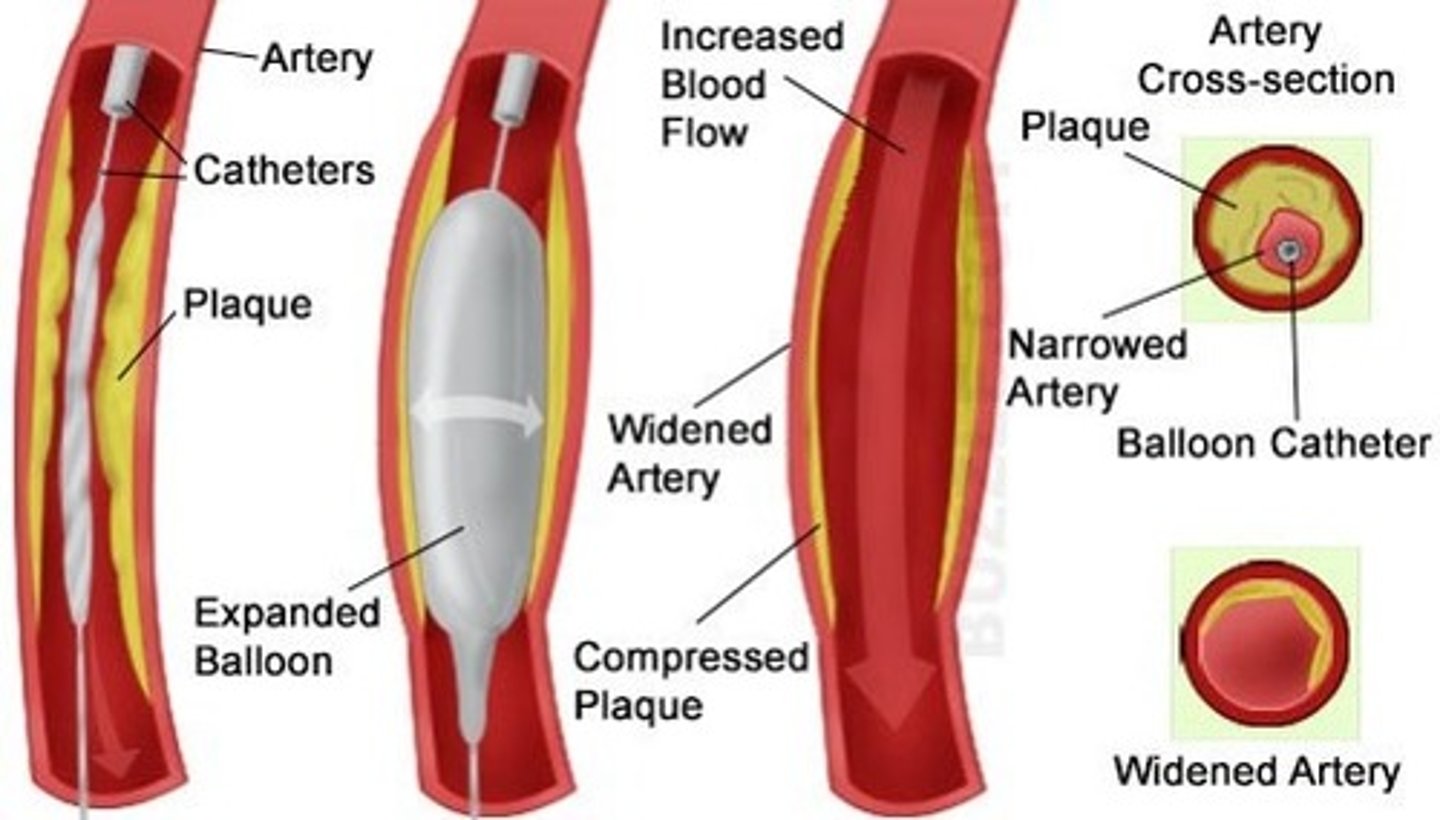
Angioplasty
a narrow balloon is inserted into the blocked vessel. It is then inflated, expanding the vessel.
Aneurysm
weakening of the wall of a blood vessel, causing it to bulge outwards. This can lead to:
The vessel bursting
or formatin of a thrombus
Sphygmomanometer
an instrument for measuring blood pressure