MUSCULOSKELETAL EXAMINATON HIP AND PELVIS (P2: HIP Anatomy and Subjective)
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
gg
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
True or False:
The hip joint is a multiaxial ball-and-socket joint that has minimal stability because of its similarity with the shoulder joint.
False:
The hip joint is a multiaxial ball-and-socket joint that has maximal stability because of the deep insertion of the head of the femur into the acetabulum
To allow sufficient movement and proper alignment to occur at the hip joint, the femur has a longer neck than the humerus and is (anteverted/retroverted?)
To allow sufficient movement and proper alignment to occur at the hip joint, the femur has a longer neck than the humerus and is anteverted
The __________ is formed by fusion of parts of the ilium, ischium, and pubis
The ilium, ischium and pubis grouped together is called what?
acetabulum
innominate bone or pelvis
True or False:
The normal acetabulum opens outward, backward, and downward
False:
The normal acetabulum opens outward, forward, and downward
Remember SAM (femur) and LIA (acetabulum)
Femur faces superoanteromedially (SAM)
Acetabulum faces Lateral, Inferior and Anteriorly (LIA)
True or False:
The femoral head is half of a sphere, and the acetabulum is two-thirds of a sphere.
False:
The acetabulum is half of a sphere, and the femoral head is two-thirds of a sphere.
Hip Joint
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Hip Joint
Resting position: 30° flexion, 30° abduction, slight lateral rotation
Close packed position: Full extension, medial rotation, abduction
Capsular pattern: Flexion, abduction, medial rotation (but in some cases, medial rotation is limited)
This is a dense, horseshoe-shaped fibrocartilaginous structure runs around the perimeter of the acetabulum and holds the femoral head in the acetabulum at extreme ranges of motion (ROM), stabilizing the hip.
Acetabular labrum


Other functions of the GOAT Acetabular LaBrum:
(no need to memorize just read through, you’ll remember)
It increases the articular surface area and volume of the acetabulum
provides proprioceptive feedback for dynamic stability
maintains a negative intra-articular pressure (i.e., a suction seal)
Allows femoral head to float protecting the cartilage
resists fluid flow by regulating synovial fluid, which enhances nutrition
acts as a shock absorber when assisting in force distribution during load bearing.
plays a secondary role in stabilizing the hip during lateral rotation
prevents anterior translation
How many percentage of patients with with labral pathology have associated bony abnormalities?
90%
True or False:
The labrum is avascular except at its center and therefore has poor healing potential.
False:
The labrum is avascular except at its margins and therefore has poor healing potential.

Mechanisms of injury to the LaBrum:
hip hyperabduction
twisting
falling
hyperextension
dislocation,
direct blow
motor vehicle accident

Labral tears can be seen in the following conditions:
femoroacetabular impingement (FAI)
hip dysplasia (e.g., Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease)
slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
trauma
osteoarthritis
iliopsoas impingement
Both of the following are occurrences of a labral tear:
an activity-induced or positional pain that fails to improve
a sudden twisting or pivoting motion with a click, pop, or locking sensation.
Which is more common?
A tear to the labrum may occur as an activity-induced or positional pain that fails to improve (most common).
What condition causes abnormal loading on the acetabular rim, which can lead to labral tears, damage to the chondral surface, and capsular laxity?
Hip dysplasia
twisting and pivoting movements, especially at the end range of rotation and falling, lead to labral fraying, chondral degeneration, or delamination and can ultimately lead to what condition?
Osteoarthritis.
The hip, already a stable joint because of its bony configuration, is supported by three strong ligaments, enumerate.
iliofemoral
ischiofemoral
pubofemoral ligaments
Which hip ligament is the strongest
iliofemoral ligament (Y ligament of Bigelow)
is considered to be one of the strongest ligaments in the body
iliofemoral ligament (Y ligament of Bigelow) prevents excessive hip _____________
Also prevents translation in what direction?
Extension
Anterior Translation
Aside from extremes of extension, the iliofemoral ligament also tightens during which hip motions?
lateral rotation and adduction
Repeated forced lateral rotation of the hip can lead to ___________ insufficiency
Repeated forced lateral rotation of the hip can lead to iliofemoral insufficiency
True or False:
If a patient has iliofemoral insufficiency, rotating (twisting) the hip can lead to feeling pain.
False:
If a patient has iliofemoral insufficiency, rotating (twisting) the hip can lead to a feeling of instability.
Which ligament is the weakest hip ligament?
ischiofemoral ligament
ischiofemoral ligament tightens during which hip actions
Extension
Medial rotation
Abduction
Repeated forced medial rotation of the hip can lead to ___________ insufficiency
Repeated forced medial rotation of the hip can lead to ischiofemoral insufficiency
The pubofemoral ligament prevents excessive ________ of the femur and limits ________ rotation, especially in (flexion/extension?).
The pubofemoral ligament prevents excessive abduction of the femur and limits lateral rotation, especially in extension
Pubofemoral limits what hip motions?
Lateral rotation and abduction.
All three ligaments also limit ________ rotation of the femur.
All three ligaments also limit medial rotation of the femur
This is the 4th ligament, intra-articular, strong and acts as a hip stabilizer.
Ligamentum Teres / Ligament of the head
The ligamentum teres acts as a hip stabilizer especially in these positions: (enumerate)
adduction
flexion
lateral rotation
when the hip is in its least stable position
What position cause the ligamentum teres to be lax?
abduction and medial rotation
True or False:
The ligamentum flavum provides a physical attachment of the head of the femur to the acetabulum
False
The ligamentum teres provides a physical attachment of the head of the femur to the acetabulum
The ligamentum teres prevents subluxation forces:
Prevents ________ subluxation during abduction
Prevents ________ subluxation during medial rotation
Prevents ________ dislocation during lateral rotation
The ligamentum teres prevents subluxation forces:
Prevents inferior subluxation during abduction
Prevents posterior subluxation during medial rotation
Prevents anterior dislocation during lateral rotation
True or False:
If the ligamentum teres is torn, macroinstability of the hip results, which can damage the labrum and cartilage, resulting in possible chondral lesions.
False:
If the ligamentum teres is torn, microinstability of the hip results, which can damage the labrum and cartilage, resulting in possible chondral lesions.
The instability is most evident in flexion, adduction, and lateral rotation of the hip (actions limited by the ligamentum teres)
Others feel that the ligamentum teres also has a proprioceptive role and may help to distribute synovial fluid over the femoral head via what effect.
Windshield-wiper effect
Tears of the ligamentum teres are associated with ___________
Dislocations
Partial tears arise from:
flexion/adduction stresses
hyperabduction
a fall on the ipsilateral knee with the hip flexed
sudden twisting injury
Basta partial tear pag hindi dislocation
an area of the femoral head where there is no cartilage; it provides an insertion point for the ligamentum teres and is the point in the acetabulum where the ilium, ischium, and pubis meet
Fovea Capitis
The arcuate ligament is part of the posterior capsule and reinforces the hip during extremes of what motions?
Flexion and Extension
a circular ligament, surrounds the neck of the femur and lies inferior to the femoral head
Zona Obicularis
The zona obicularis resists ________ distraction forces and aids in stabilization.
The zona obicularis resists inferior distraction forces and aids in stabilization.
True or False:
Under low loads, the hip joint surfaces are congruous; under heavy loads, they become incongruous.
False:
Under low loads, the hip joint surfaces are incongruous; under heavy loads, they become congruous.
Forces on the Hip: (read)
Standing: 0.3 times body weight
Standing on one limb: 2.4–2.6 times body weight
Walking: 1.3–5.8 times body weight
Walking up stairs: 3 times body weight
Running: 4.5+ times body weight
True or False:
congenital hip dysplasia is seen in infancy, primarily in males although its effect is often greater in adolescents and young adults.
False:
congenital hip dysplasia is seen in infancy, primarily in girls although its effect is often greater in adolescents and young adults.
Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease is more common in (girls/boys?) of how many years?
Boys
3 to 12 years old
True or False:
elderly women are more prone to osteoporotic femoral neck fractures.
True
no shit sherlock
True or False:
In young people, issues related to physeal injuries state of skeletal maturity and morphological abnormalities have clinical features similar to or associated with labral tears and chondral injuries.
True
Typically, __________ hip symptoms are worse with activities.
Typically, mechanical hip symptoms are worse with activities
Patients may also complain of dyspareunia (i.e., painful sexual intercourse)
The labrum may be injured with lateral rotation when the hip is ________________.
The labrum may be injured with lateral rotation when the hip is hyperextended
Labrum may also be injured due to traction from the (what muscle?), occurring primarily during kicking or sprinting
or (what muscle contraction?), primarily occurring during a change of direction
Labrum may also be injured due to traction from the rectus femoris, occurring primarily during kicking or sprinting
or iliacus contraction, primarily occurring during a change of direction
Hip injuries may cause mechanical symptoms:
clicking
giving way
locking
catching
Labral injuries cause an abnormal gait with a shortened _______ phase.
Stance Phase
Labral tears rarely occur in isolation. what is/are commonly associated with labral tears?
Chondral lesions
True or False:
Femoral neck stress fractures occur when excessive or repetitive stress is applied to the cortical bone in the femoral neck
False:
Femoral neck stress fractures occur when excessive or repetitive stress is applied to the trabecular bone in the femoral neck
Femoral Neck Stress Fractures categorized as:
______________ sided
Occur at the _____________ neck
Unlikely to _____________
Femoral Neck Stress Fractures categorized as:
compression sided
Occur at the inferomedial neck
Unlikely to displace
___________ fractures occur at the superolateral neck and, and are more likely to be displaced
Traction-sided fractures occur at the superolateral neck and, and are more likely to be displaced
True or False:
The traction type is usually treated conservatively, whereas the compression type, is a high risk stress fracture that may require surgical intervention.
False:
The compression type is usually treated conservatively, whereas the traction type, which may displace, is a high risk stress fracture that may require surgical stabilization
True or False:
Acute groin injuries are usually due to high running loads, changes in direction, or kicking
True
With a posterior dislocation (most common):
hip is slightly (extended/flexed?)
adducted/abducted?
(laterally/medially?) rotated
leg (shortened/lengthened?)
With a posterior dislocation (most common):
hip is slightly flexed
adducted
medially rotated
leg shortened
Opposite for anterior dislocation
True or False:
Hip dislocations warrant examinations of the sciatic and femoral nerves + examination of the knee
True
In the presence of a dislocation, reduction should be performed within how many hours?
6 hours
Microinstability or atraumatic instability occurs with repetitive microtrauma from axial loading and ________ rotation and is associated with _______.
Microinstability or atraumatic instability occurs with repetitive microtrauma from axial loading and lateral rotation and is associated with FAI.
True or False:
If the static stabilizers are compromised, then the dynamic stabilizers must work harder to stabilize the joint
True
Causes modification of biomechanics leading to abnormal movement patterns
if a patient presents with an internally snapping hip , a labral tear, and a pincer-type FAI, it is called?
triple impingement
If the hip is at fault, the patient may demonstrate what sign?
hint : if asked to show where the pain is, the patient will cup a hand above the greater trochanter with the fingers gripping the anterior groin, describing the pain as deep in the joint
“C” Sign
True or False:
In older adults, osteoarthritis and spondylitis should be considered first.
False:
In older adults, osteoarthritis and fractures should be considered first.
Anterior or groin pain may be related to:
Intra-articular / extra-articular hip problems?
apophysitis in children where?
Tendinitis of which muscle / muscle group?
FAI, labral or chondral injuries, or athletic pubalgia (no question for this #freebie)
Anterior or groin pain may be related to:
Intra-articular hip problems
apophysitis in children at ASIS or AIIS
Tendinitis of the iliopsoas or adductors
FAI, labral or chondral injuries, or athletic pubalgia
Lateral hip pain may be related to:
Intra-articular / extra-articular hip problems?
adductor/abductor injuries?
____________ pain syndrome
____________ dysplasia
Lateral hip pain may be related to:
extra-articular hip problems
abductor injuries
Greater trochanteric pain syndrome
acetabular dysplasia
Isolated posterior buttock pain is usually related to:
_____________ pathology
issues with the _______ nerve
superficial/deep gluteal pain syndrome?
Isolated posterior buttock pain is usually related to:
lumbar or sacroiliac pathology
issues with the sciatic nerve
deep gluteal pain syndrome
True or False:
Hip intra-articular pain including labral tears, FAI, and L4 nerve root pain is felt mainly in the groin and along the front or medial side of the thigh to the knee.
True
It is often described as a sharp, stabbing pain often accompanied by catching, locking, or clicking.
True or False:
Buttock pain, on the other hand, is associated with posterior labral tears and lumbar spine problems.
True
Gradual onset of pain usually indicates ____________
osteoarthritis
Adductor pain may be the result of overactive adductors caused by pelvic _________
Adductor pain may be the result of overactive adductors caused by pelvic instability
Pain when doing resisted sit-ups, hip flexion, or adduction may indicate ____________
Pain when doing resisted sit-ups, hip flexion, or adduction may indicate athletic pubalgia
True or False
Pain from the lumbar spine may commonly be referred to the back or medial aspect of the hip.
False:
Pain from the lumbar spine may commonly be referred to the back or lateral aspect of the hip.
This hernia is commonly caused by a deficient inguinal canal posterior wall, nerve entrapment, or adductor tendonopathies
Sports Hernia
Sports Hernia Pain:
MAY have an insidious onset
unilateral/bilateral?
description of pain?
location of pain?
Radiates to?
Aggravating movements?
Sports Hernia Pain:
MAY have an insidious onset
unilateral
Dull, aching or sharp, burning
Groin
Radiates to proximal thigh, low back, lower abdominal muscles, perineum and/or scrotum.
Sudden acceleration, cutting or kicking
True or False:
Lateral hip pain may be due to a trochanteric bursitis or tear of the gluteus medius tendon, most commonly in younger patients.
False:
Lateral hip pain may be due to a trochanteric bursitis or tear of the gluteus medius tendon, most commonly in older patients.
True or False:
Lateral hip pain may also simulate L5 nerve root pain; therefore assessment of the lumbar spine should also be considered for lateral or posterior symptoms
False:
Lateral hip pain may also simulate L4 nerve root pain; therefore assessment of the lumbar spine should also be considered for lateral or posterior symptoms
Lateral hip pain may also be referred to the knee or back and may_____________ on walking.
Lateral hip pain may also be referred to the knee or back and may increase on walking.
Clicking is common with labral tears when the hip moves into ________________
Clicking is common with labral tears when the hip moves into medial or lateral rotation.
What is snapping in and around the hip called
extra-articular sound.
Coxa saltans
Most common cause of coxa saltans
Slipping of the iliopsoas tendon
over the osseous ridge of the lesser trochanter or anterior acetabulum
Causes of coxa saltans:
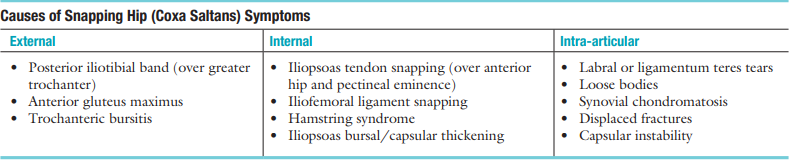
If due to the iliopsoas tendon or iliofemoral ligament
(internal coxa sultans):
snapping often occurs at approximately ___° of flexion
hip is moving from _________ to ___________
especially with the hip __________ and _________rotated
If due to the iliopsoas tendon or iliofemoral ligament
(internal coxa sultans):
snapping often occurs at approximately 45° of flexion
hip is moving from flexion to extension
especially with the hip abducted and laterally rotated
external coxa saltans:
felt more laterally/medially?
occurs when the hip is brought from the _____, _______, and _______ rotated position into _______and _______ rotation
during hip _______ and _________
especially if the hip is held in __________ rotation
it may be made worse if the ____________ bursa is inflamed.
external coxa saltans:
felt more laterally
occurs when the hip is brought from the flexed abducted and laterally rotated position into extension and medial rotation
during hip flexion and extension
especially if the hip is held in medial rotation
it may be made worse if the trochanteric bursa is inflamed.
Common age of intra-articular snapping?
20 and 40 years of age
Where is the complaint of sharp pain in intra-articular snapping?
groin and anterior thigh
especially on pivoting movement
Passively, clicking may be felt and heard when the extended hip is ____________ and _____________ rotated.
Passively, clicking may be felt and heard when the extended hip is adducted and laterally rotated.
Bursitis that often results from abnormal running mechanics with the feet crossing over midline, a wide pelvis and genu valgum, or running on running tracks with no banking.
Trochanteric Bursitis
Pain on sitting may be due to pinching of an inflamed ______ bursa or an FAI
Pain on sitting may be due to pinching of an inflamed psoas bursa or an FAI
In this condition sciatic nerve may be compressed, the piriformis muscle is tender, and hip abduction and lateral rotation are weak.
piriformis syndrome / deep gluteal space syndrome
END
P2 SOON?