PSYC 241 - Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/181
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:17 PM on 2/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
1
New cards
social psychology
the scientific study of how people think about, influence, and relate to one another
2
New cards
three main areas of social psychology
* social influence (culture, conformity)
* social thinking (judgements/attitudes)
* social relations (helping, aggression)
* social thinking (judgements/attitudes)
* social relations (helping, aggression)
3
New cards
social thinking
judgements we make, how we perceive ourselves and others
4
New cards
social influence
influence of culture, conformity, persuasion and biology on behaviour
5
New cards
social relations
how we behave towards others, how we behave differently based on the group
6
New cards
subjectivity
researchers interpreting information using their own mental categories
7
New cards
hindsight bias
tendency to exaggerate, after learning an outcome, one’s ability to have foreseen how something turned out
8
New cards
research in social psychology is based on two things…
* theory
* hypothesis
* hypothesis
9
New cards
theory
an organized set of principles used to explain observed phenomena (but not accepted as a fact)
10
New cards
hypothesis
an “educated guess” about the nature of the relationship among the variables being tested
11
New cards
nonexperimental method
examining existing, naturally occurring relations, in the world without manipulation of variables
12
New cards
archival study (nonexperimental method)
examining existing records of past events, looking at multiple things that have already happened
13
New cards
case study (nonexperimental method)
a detailed examination of a single event or person
14
New cards
survey study (nonexperimental method)
participants complete questionnaires in order to collect a large number of responses
15
New cards
observational study (nonexperimental method)
participants behaviors are observed (sometimes covertly), often in a naturalistic setting without manipulation
16
New cards
correlation does not =
causation
17
New cards
independent variable
the factor that is manipulated, differs between groups
18
New cards
random assignment
participants are randomly assigned conditions/groups
19
New cards
purpose of randomly assignment
ensures that the only thing that differs between groups is the independent variable, greater accuracy
20
New cards
dependent variable
the outcome that is measured, thing that you think is affected by the independent variable
21
New cards
limitations of experiments
* cannot feasibly manipulate some variables (age, gender, sexual orientation)
* cannot ethically manipulate some variables (drug usage, trauma)
* cannot ethically manipulate some variables (drug usage, trauma)
22
New cards
internal validity
the extent to which differences between groups in an experiment can be unambiguously attributed to the independent variable, rather than to other factors
23
New cards
external validity
the degree to which one can generalize results obtained in one set of circumstances to another set of circumstances
24
New cards
spotlight effect
the belief that others are paying more attention to our appearance than they really are
25
New cards
illusion of transparency
the illusion that our concealed emotions leak out and can be easily read by others
26
New cards
factors that influence the self
* self-esteem
* social self
* self-knowledge
* self-concept
* social self
* self-knowledge
* self-concept
27
New cards
self-concept
how a person answers the question “Who am I?” provides a glimpse of their self-concept
28
New cards
self-schema
beliefs about self that organize and guide the processing of self-relevant information
29
New cards
self-concept is formed by…
* social comparison
* other people’s judgements
* culture
* self-knowledge
* other people’s judgements
* culture
* self-knowledge
30
New cards
planning fallacy
we have the tendency to underestimate how long it will take to complete a task
31
New cards
impact bias
we overestimate the enduring impact of emotion-causing events
32
New cards
dual attitudes
differing implicit (automatic) and explicit (consciously controlled) attitudes toward the same object
33
New cards
self-esteem
person’s overall self-evaluation or sense of self-worth
34
New cards
self-serving bias
tendency to perceive yourself favorably
35
New cards
defensive pessimism
the adaptive value of anticipating problems and harnessing one’s anxiety to motivate effective action
36
New cards
false consensus effect
the tendency to overestimate the commonality of one’s opinions and one’s undesirable or unsuccessful behaviours
37
New cards
false uniqueness effect
the tendency to underestimate the commonality of one’s abilities and one’s desirable or successful behaviors
38
New cards
temporal comparisons
comparisons between how the self is viewed now and how the self was viewed in the past or how the self is expected to be viewed in the future
39
New cards
self-handicapping
protecting one’s self-image with behaviours that create a handy excuse for later failure
40
New cards
impression management
we manage the impressions we create to shore up our self-esteem and verify our self-image
41
New cards
self-presentation
the act of expressing yourself and behaving in ways designed to create a favorable impression or an impression that corresponds to your ideals
42
New cards
self-monitoring
being attuned to the way you present yourself in social situations and adjusting your performance to create the desired impression
43
New cards
self-presentation theory
a theory positing that we are eager to present ourselves in ways that make a good impression
44
New cards
learned helplessness
the hopelessness and resignation learned when a human or animal perceives no control over repeated bad events
45
New cards
individualistic cultures
value individuality, autonomy, and self-reliance; place the individual first (Canada, USA, Australia)
46
New cards
collectivist cultures
value fitting in, cooperation, and social harmony; place the group first (China, Korea)
47
New cards
individualism-collectivism influences
* our sense of self
* our sense of self-esteem
* social cognition
* our sense of self-esteem
* social cognition
48
New cards
system 1 (unconscious)
functions automatically and out of our awareness; fast, error prone, responsible for everyday decisions
49
New cards
system 2 (conscious)
requires our conscious attention and effort and is deliberate and controlled; slow, reliable, responsible for complex decisions
50
New cards
priming
activating particular associations in memory, typically without awareness
51
New cards
schemas
mental concepts or templates that intuitively guide our perceptions and interpretations of our experience
52
New cards
expertise
people may intuitively know the answer to a problem
53
New cards
heuristics
simple, efficient thinking strategies that enable quick judgements
54
New cards
representativeness heuristic
the tendency to presume, sometimes despite contrary odds, that someone or something belongs to a particular group if resembling (representing) a typical member
55
New cards
availability heuristic
a cognitive rule that judges the likelihood of things in terms of their availability in memory
56
New cards
counterfactual thinking
imagining alternative scenarios and outcomes that might have happened, but didn’t
57
New cards
illusory correlation
a perception of a relationship where none exists or a perception of a stronger relationship than actually exist
58
New cards
regression toward the average
the statistical tendency for extreme scores or extreme behavior to return toward the person’s average
59
New cards
belief perseverance
persistence of your initial conceptions, as when the basis for your belief is discredited but an explanation of why the belief might be true survives
60
New cards
misinformation effect
incorporating “misinformation” into one’s memory of an event, after witnessing an event and then receiving misleading information about it
61
New cards
misattribution
mistakenly attributing a behaviour to the wrong cause
62
New cards
attribution theory
theory of how people explain the behaviour of others
63
New cards
dispositional attribution
attributing behaviour to the person’s disposition and traits
64
New cards
situational attribution
attributing behaviour to the environment
65
New cards
spontaneous trait inference
an effortless, automatic inference of a trait after exposure to someone’s behaviour
66
New cards
fundamental attribution error
the tendency for observers to underestimate situational influences and overestimate dispositional influences on others’ behavior
67
New cards
explanations for attribution error
* actor-observer difference;
we observe others from a different perspective than we observe ourselves
* cultural differences
we observe others from a different perspective than we observe ourselves
* cultural differences
68
New cards
behavioral confirmation
people’s social expectations lead them to act in ways that cause others to confirm their expectations
69
New cards
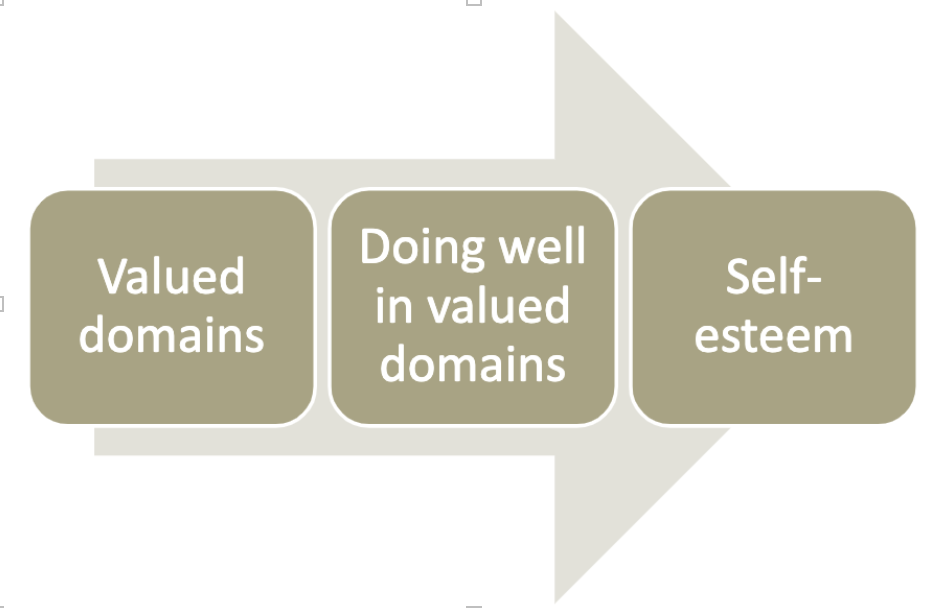
bottom up self-esteem
70
New cards
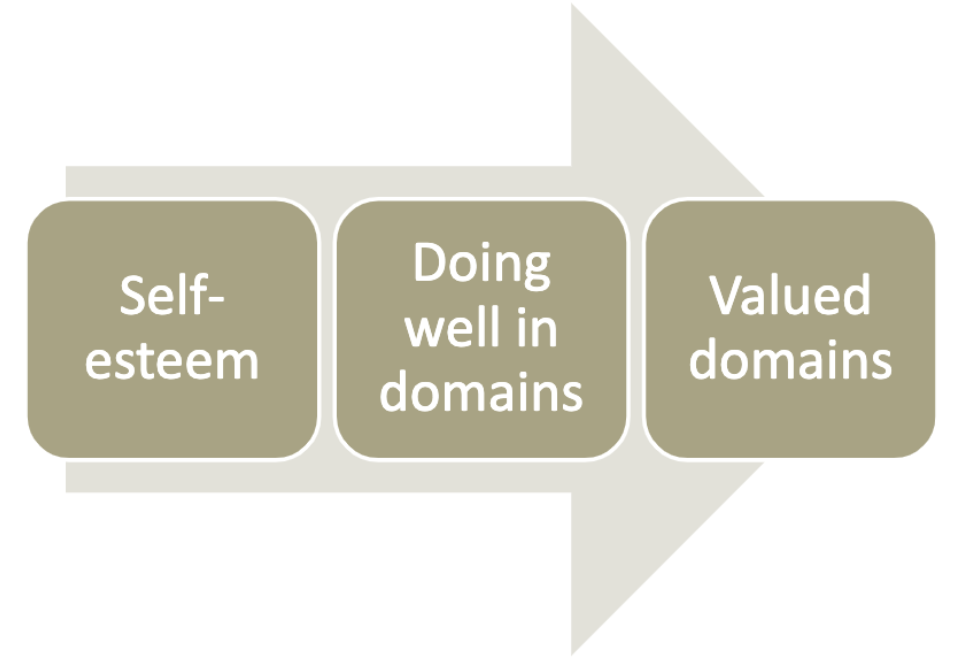
top down self-esteem
71
New cards
confirmation bias
look for evidence that supports your belief, rather than looking for contradictory evidence
72
New cards
actor-observer effect
refers to a tendency to attribute one's own actions to external causes while attributing other people's behaviors to internal causes
73
New cards
fixed mindset
intelligence/ability is innate
74
New cards
growth mindset
intelligence/ability is developed
75
New cards
attitude
a favorable or unfavorable evaluative reaction toward something or someone, exhibited in one’s beliefs, feelings, or intended behavior
76
New cards
IAT (implicit association test)
a computer-driven assessment of implicit attitudes that uses reaction times to measure people’s automatic associations between attitude objects and evaluative words, where easier pairings (and faster responses) are taken to indicate stronger unconscious associations
77
New cards
role
a set of norms that define how people in a given social position ought to behave
78
New cards
norms
rules for accepted and expected behavior that prescribe “proper” behavior
79
New cards
foot-in-door technique
a tactic for getting people to agree to something; people who agree to an initial request will often still comply when the requester ups the ante, people who receive only the costly request are less likely to comply with it
80
New cards
door-in-the-face technique
after someone first turns down a large request (the door in the face), the same requester counteroffers with a more reasonable request
81
New cards
three possible sources for the effect of action on attitudes
* self-presentation theory
* cognitive dissonance theory
* self-perception theory
* cognitive dissonance theory
* self-perception theory
82
New cards
self-presentation theory
assumes that, for strategic reasons, we express attitudes that make us appear consistent
83
New cards
cognitive dissonance theory
assumes that to reduce discomfort, we justify our actions to ourselves;
tension that arises when we are simultaneously aware of two inconsistent cognitions
tension that arises when we are simultaneously aware of two inconsistent cognitions
84
New cards
self-perception theory
assumes that our actions are self-revealing (when uncertain about our feelings or beliefs, we look to our behaviour, much as anyone else would);
when unsure of our attitudes, we infer them much as would someone observing us—by looking at our behavior and the circumstances under which it occurs
when unsure of our attitudes, we infer them much as would someone observing us—by looking at our behavior and the circumstances under which it occurs
85
New cards
attitude
psychological tendency that is expressed by evaluating a particular entity with some degree of favor or disfavor
86
New cards
tripartite theory (ABC’s of attitudes)
affect (love sushi), behaviour (frequent orders), cognition (sushi is good for you)
87
New cards
explicit measures of attitudes
self report survey, bogus pipeline
88
New cards
problems with explicit measures for attitudes
bias
89
New cards
social desirability bias
the tendency of survey respondents to answer questions in a manner that will be viewed favorably by others
90
New cards
explicit attitudes
measured with explicit measures where the true measure is known to the participant
91
New cards
implicit attitudes
measured with implicit measures (e.g. reaction time), the true measure is not really known to the participant
92
New cards
____ is important when measuring attitudes
specificity
93
New cards
specificity matching
asking these specific questions to get an accurate measure of behavior
94
New cards
intentions
represent whether a person believes that he or she will engage in a specific behavior
95
New cards
implementation intentions
hen individuals identify precisely when and where the behavior is to be performed
96
New cards
effort justification
justifying the time, effort, or money that one has devoted to something (especially when the effort was unpleasant or disappointing)
97
New cards
persuasion
the process by which a message induces change in beliefs, attitudes, or behavior
98
New cards
two paths leading to persuasion
central route & peripheral route
99
New cards
central route
occurs when motivated people focus on the arguments and think systematically about an issue
100
New cards
persuasion through central route is best done through…
strong, compelling, thoughtful arguments