EOY biology revision tuesday
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Name the 7 food groups
Carbohydrates
fats/lipids
protein
vitamins
minerals
fibre
water
What is the test and result for starch
iodine solution, brown to blue,black
What is the test and result for glucose
Benedict’s solution, heat it at 80 degrees for 5 mins, blue to green to yellow to orange to red
What is the test and result for protein
Biuret solution, blue to lilac
What is the test and result for lipids
ethanol and water, pour ethanol then water, clear to cloudy white
What is lipids made of
3 fatty acids and a glycerol
What are proteins made of
amino acids
What are sources, function, and deficiency disease for Vitamin A
Source-carrot, milk, butter, liver, sweet potato
Function- good eyesight, healthy
Deficiency disease- sore eyes, poor night vision, unhealthy skin
What are sources, function, and deficiency disease for vitamin C
Source-Oranges, lemons, limes
Function-Tissue repair, resistance to disease
Deficiency disease- scurvy
What are sources, function, and deficiency disease for vitamin D
Source- fish, oil, milk, butter, made in body by sunlight
Function- Strong bones and teeth
Deficiency disease- rickets (soft bones)
What are the sources, function, and deficiency disease for calcium
Source- Milk, Green veg
Function- Strong bones and teeth
Deficiency disease- soft bones
What are the sources, function, and deficiency disease for iron
Source- Liver, meat, cocoa
Function- Healthy red blood cells
Deficiency disease- anaemia
What is digestion
Breaking down large insoluble molecules into small soluble molecules.
What is absorbtion
Taking soluble molecules from the gut into the bloodstream
What is assimilation
Food molecules absorbed are taken into cells of tissues and used for respiration or growth and repair.
What is egestion
Waste material called faeces leaves the body via the anus. Composed of undigested food, water, enzymes, dead cells, bile pigments and mucus.
What is the function of the gall bladder
Stores bile
What is the function of the small intestine
The main site for absorption of soluble products of digestion.
What is the function of the anus
Undigested waste leaves here
What is the function of the pancreas
Produces enzymes for digestion that enter the small intestine to aid the breakdown of food
What is the function of the rectum
To store faeces before it leaves the anus
What is the function of the oesophagus
Connects the mouth to the stomach. Muscles squeeze food down by peristalsis.
What is the function of the stomach
Food is churned and mixed and hydrochloric acid and enzymes are produced that break down protein.
What is the function of the mouth
Teeth chew food which is mixed with saliva. Saliva contains the enzyme called amylase which brakes down starch
What is the function of the epiglottis
Covers the trachea when swallowing to stop food entering the airways.
What is the function of the large intestine
Absorbs water from faeces leaving undigested food.
What is the function of the appendix
No purpose in humans
What is the function of the duodenum
The first 30cm of the small intestine. connects the stomach to the small intestine.
What is the function of the liver
Produce bile
What are enzymes
They make reactions happen faster.
What are the 2 main types of Enzymes and what do they do
Breakers-Speed up reactions that break down large molecules
Buildings-Speed up reactions where small molecules join together to make larger ones
How do enzymes work
Enzymes are made up of long chains of amino acids. These chains are folded to produce a shape called the active site. Other molecules called substrates fit into the active site and a reaction takes place.
What 2 things affect enzymes
Temperature and pH
What is a source and deficiency disease of iodine
Source-fish
Deficiency disease-goitre
What happens if the temperature is too high for an enzyme
The enzyme will denature meaning the substrate wont fit.
What are the 2 roles of bile
To neutralise stomach acid and make conditions in the duodenum slightly alkali.
Emulsifies fats giving them a greater surface area for lipase to act on.
Where is carbohydrase produced, secreted, what is its substrate and what are the products of the enzyme reaction.
Produced- salivary gland
Secreted- mouth
Substrate- carbohydrates
Products- glucose
Where is protease produced, secreted, what is its substrate and what are the products of the enzyme reaction
Produced- pancreas and stomach
Secreted- stomach, small intestine
Substrate- protein
Products- amino acids
Where is lipase produced, secreted, what is its substrate and what are the products of the enzyme reaction.
Produced- pancreas
Secreted- Small intestine
Substrate- fats
Products0 fatty acids, glycerol
What adaptions does the small intestine have to speed up digestion
Villi for large surface area
A thin lining
A good blood supply
How thick is one villi
One cell
What do villi have on them
micro-villi
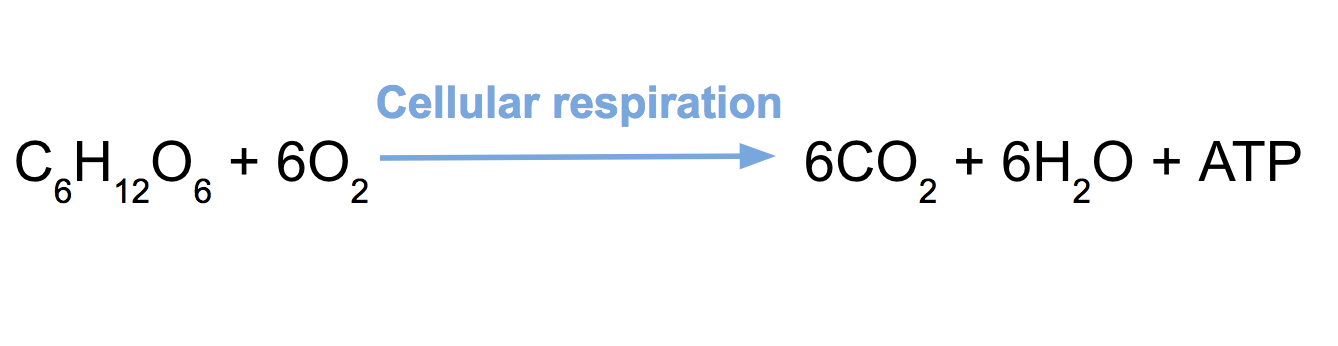
What is the word and symbol equation for aerobic respiration
Glucose + oxygen - carbon dioxide + water
What are the percentages for inspired and expired air
Oxygen-Inspired,21% Expired,16%
Carbon dioxide-Inspired,0.04% Expired,4%
Nitrogen-Inspired,78% Expired,78%
Water vapour- Inspired, variable Expired, saturated
What is anaerobic respiration
Respiration without using oxygen takes place in the cytoplasm. it produces less energy than aerobic.
What does anaerobic respiration produce and what effect does this have
It produces lactic acid because the glucose is only partly broken down. This accumulates in muscles causing pain and fatigue.
What is oxygen debt
After exercise we carry on breathing deeply. This is to bring oxygen into the body to break down the lactic acid.
Where is lactic acid broken down
The liver
What is fermentation
In the absence of oxygen, yeast and plants can respire anaerobically
what is the word Equation for fermentation
glucose- alcohol + carbon dioxide (energy)
What is the trachea
Tube that connects mouth to lungs
What are the ribs
outer cage of muscles that protect the lungs
What are intercostal muscles
Muscles between ribs allowing them to expand with the lungs
What are the bronchi
the first branch of the trachea. The trachea branches into 2 sections. 1 for each lung.
What are bronchioles
They branch from the bronchi and spread through the lungs
What are alveoli
They are ‘the leaves on the tree’ Little sacks that have a large surface area to diffuse oxygen into the blood
What is the pleural membrane
A protective layer for the lungs
What is pleural fluid
Helps to cushion the lungs.
What is the diaphragm
The main breathing muscle
What are the cells in the trachea that waft mucus towards the throat called
Ciliated epithelial cells
What is the mechanism of breathing and how does it work
The lungs inflate when the diaphragm is pulled down. This is because the lungs lose pressure so the air outside moves from area of high pressure to an area of low pressure.
What is the independent variable
The thing that you change in an experiment
What is the dependent variable
The thing that you measure in an experiment
What are the control variables
The things that you keep the same
What is the definition of accuracy
How close something is to the true value
What three things do cigarettes contain and how do they affect the lungs
Nicotine- Makes arteries narrower
Carbon monoxide- Stops red blood cells from carrying oxygen
Tar- Causes lung damage and lung cancer due to it sticking to the lungs
What is the difference between a human and a fish circulatory system
Fish system- Single circulatory system. The blood travels through the heart once for every complete circuit
Human system- Double circulatory system. The blood passes the heart twice in one circuit. More efficient.
What is blood made from and in what percentages
55%plasma
45%blood cells
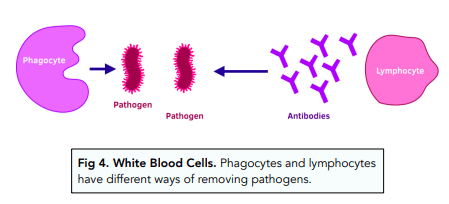
What are the 2 types of white blood cell and what do they do.
Phagocytes- ‘Cell eaters’ engulf bacteria using enzymes.
Lymphocytes- Send antibodies to fight the bacteria.
How do vaccines work
They inject a dead or weak version of a virus into your blood. The white blood cells then fight it. The memory cells are then stored away and when the same virus comes back the antibodies can be produced very quickly because of the memory cells.
What are features of an artery
They carry blood from the heart
Carry blood at high pressure
Have thick wall
No valves
blood flows in pulses
carry oxygenated blood
What are features of a vein
Carry blood to the heart
carry blood at low pressure
have thinner walls
have valves
have little elastic fibres
no pulses
deoxygenated blood
What do valves do
Stop blood from going backwards in veins
What is the hole that blood flows through in a vein and artery called
lumen
What do capillaries do
They exchange substances between blood and the surrounding cells. Oxygen, digested food an other substances pass from the blood into the cells. Carbon dioxide and other waste substances pass from the cells into the blood. They have thin walls tomake diffusion easier.
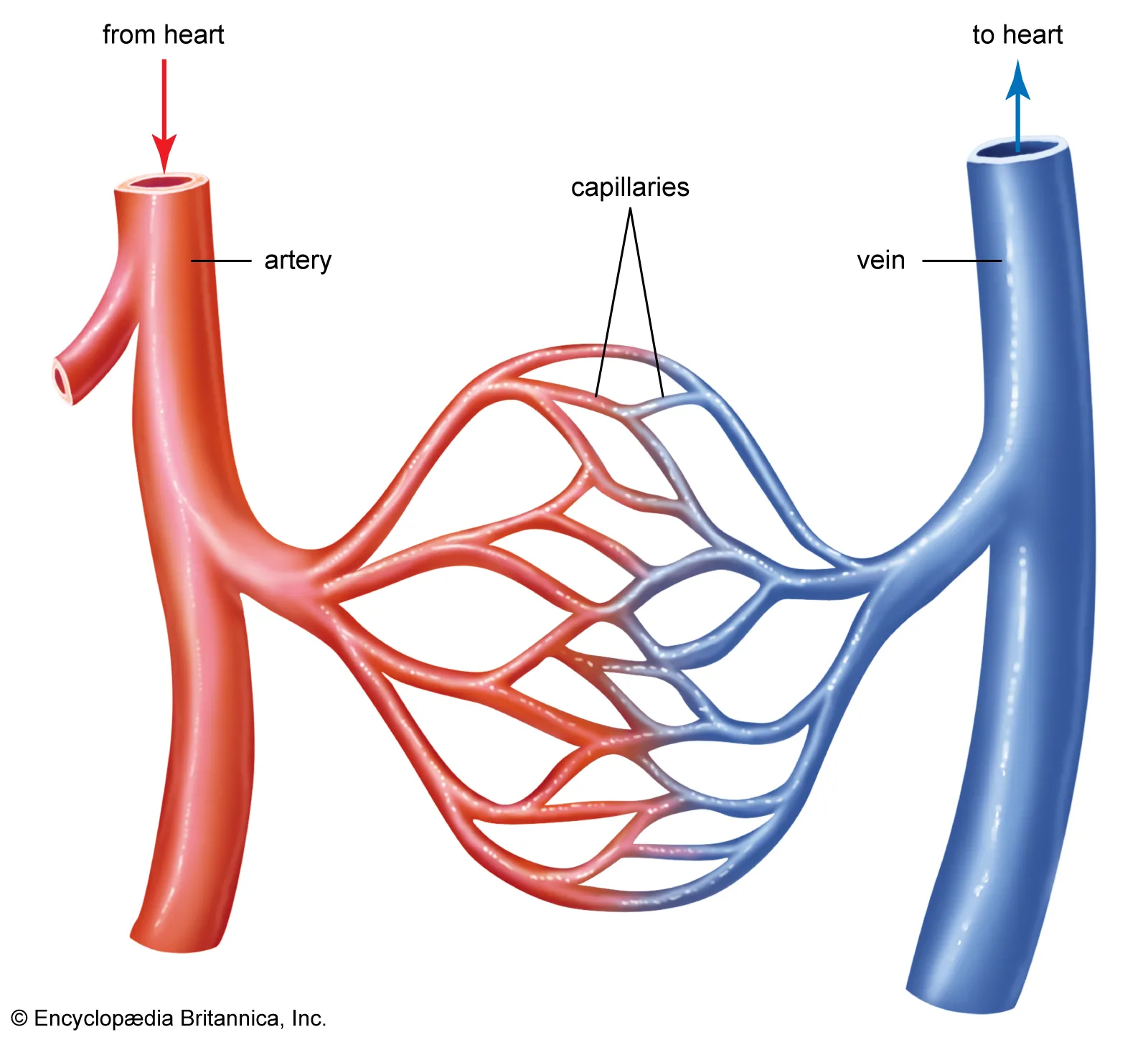
How wide is a capillary
the width of a red blood cell
How thick is a capillary wall
one cell
Heart diagram
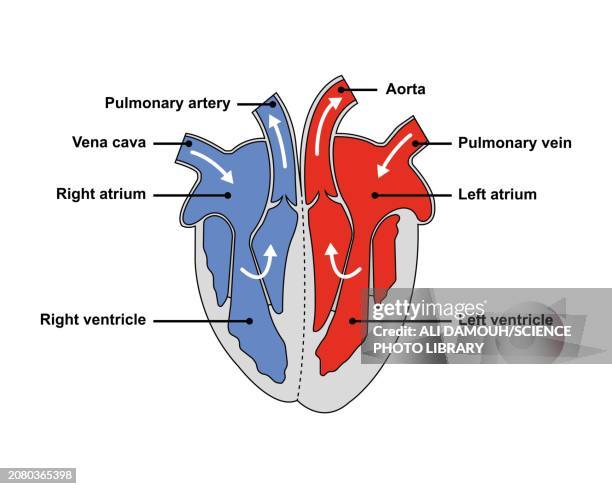
Where is the aorta going to
Around the body with oxygenated blood
Where is the vena cava coming from
The body carrying de oxygenated blood
Where is the pulmonary artery going to
The lungs with de oxygenated blood
Where is the pulmonary vein coming from
The lungs with oxygenated blood
Where is the tricuspid valve
between the right atrium and the right ventricle
Where is the bicuspid valve
Between the left atrium and the left ventricle
Where are the semi-lunar valves
Between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and also between the left ventricle and the aorta.
What is the cardiac cycle and what is each stage
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in one heartbeat
Diastole- when the muscle are relaxed. Blood flows into the atria from the veins.
Atrial systole- when the atria contract and force blood into the ventricles
Ventricular systole- is when the ventricles contract forcing blood out into the arterys.