IB Chem Reactivity Mix
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Heat
A measure of the total energy of a substance and therefore depends on the amount of substance present.
Always transfers/flows from a higher temperature object to a lower temperature object.
Absolute temperature (K)
A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
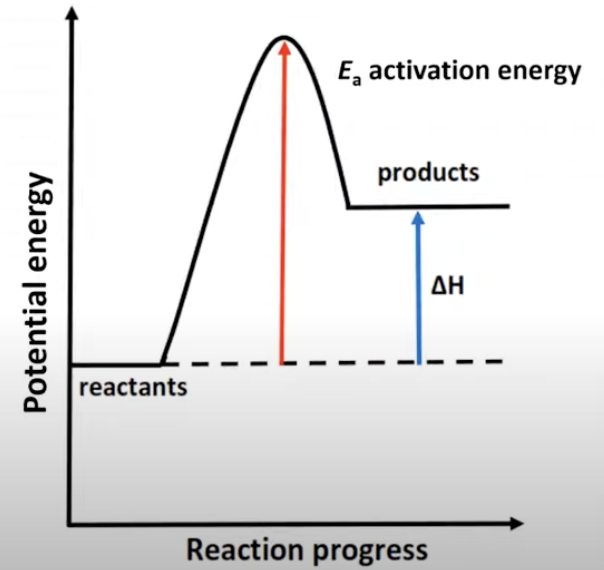
Exothermic reaction
Heat flows from the system to the surroundings.
The temperature of the reaction mixture and the surroundings increases as heat is released.
ΔH = negative < 0
Endothermic reaction
Heat flows from the surroundings into the system.
The temperature of the reaction mixture and the surroundings decreases as heat is absorbed.
ΔH = positive > 0
Enthalpy (H)
The heat absorbed or released in a chemical reaction that takes place at constant pressure.
Can be thought of as the heat content if a substance.
Cannot be measured.
Enthalpy change (ΔH)
Can be measured.
The change in enthalpy that occurs when a chemical reaction takes place.
q=mcΔT
q - heat (J)
m - mass (g)
c - specific heat capacity (J g-1 oC-1)
ΔT - temperature change
Average bond enthalpy
The energy required to break one mole of bonds in a gaseous molecule averaged over similar compounds.
ΔH=∑(bonds broken) - ∑(bonds formed)
(ΔH=reactants - products)
Enthalpy change of formation
One mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions.
ΔHꝊ=∑ΔHfꝊ(products) - ∑ΔHfꝊ(reactants)
Entropy (S)
The distribution of available energy among the particles in a system.
Standard entropy change (ΔSꝊ)
ΔSꝊ(reaction) = ∑ΔSꝊ(products) - ∑ΔSꝊ(reactants)
Spontaneous process
A process that occurs without adding energy (other than the energy required to overcome the energy barrier).
The change in entropy of ΔS(total) must be positive.
ΔS(total)=ΔS(system) + ΔS(surroundings)
Gibbs free energy (ΔG)
ΔG=ΔH-TΔS
Spontaneous reaction: -ΔG
Non-spontaneous reaction: +ΔG
Atom economy
% atom economy = molar mass of desired product / molar mass of all reactants x 100
The higher the atom economy for a chemical reaction, the less waste is produced and the more efficient the reaction is.
Gibbs free energy change (ΔGꝊ)
ΔGꝊ=∑ΔGfꝊ(products) - ∑ΔGfꝊ(reactants)
Data booklet: Table 12
Elements have a standard Gibbs free energy of formation value of zero
ΔGꝊ = -RT ln K
ΔGꝊ = standard change in Gibbs free energy in J
R = universal gas constant
T = temperature in kelvin
ln K = natural log of K
Rate of reaction
Unit: mol dm-3 s-1
Increase in product conc. over time OR decrease in reactant conc. over time
Factors that affect the rate of reaction
Temperature
Concentration
Particle size / surface area
Pressure
Catalysts
Activation energy: exothermic reaction
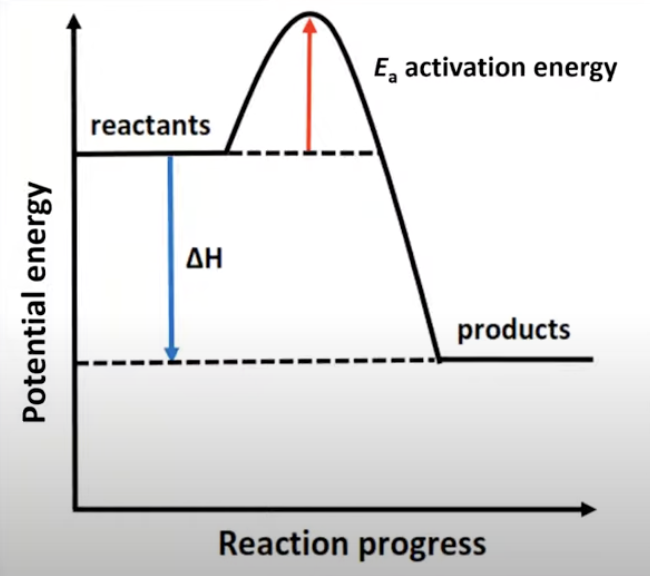
Activation energy: endothermic reaction