Magnetism & Electromagnetism
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts, definitions, and principles related to magnetism and electromagnetism as per Edexcel IGCSE Physics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are the two poles of a magnet?
North and South poles.
What does the law of magnetism state?
Two like poles repel, and two opposite poles attract.
What are magnetically soft materials?
Materials that are easy to magnetize and lose their magnetism quickly, such as iron.
What are magnetically hard materials?
Materials that are difficult to magnetize and do not easily lose their magnetism, such as steel.
What happens when a magnetic material is placed in a magnetic field?
It can temporarily become a magnet, inducing magnetism.
What defines a magnetic field?
The region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet or a magnetic material.
How are magnetic field lines depicted?
Field lines go from the north pole to the south pole and do not touch or cross each other.
What is the right-hand thumb rule?
It is used to determine the direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying wire.
What is Fleming's Left-Hand Rule used for?
To determine the direction of the force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field.
What is the motor effect?
The phenomenon where a wire carrying current experiences a force in a magnetic field.
How can the strength of an electromagnet be increased?
By increasing the current in the coil or adding more turns to the coil.
What creates a uniform magnetic field?
A uniform magnetic field is created when the magnetic field lines are evenly spaced and parallel.
What effect does increasing the amount of current have on the magnetic field?
It increases the strength of the magnetic field.
What occurs when opposing poles of two magnets are brought close together?
They attract each other.
What materials are considered magnetic?
Iron, cobalt, nickel, and steel.
What is the motor effect?
The motor effect is the phenomenon where a current-carrying conductor experiences a force when placed in a magnetic field.
What causes the force in the motor effect?
The force is caused by the interaction between the magnetic field and the electric current flowing through the conductor.
How does the direction of force in the motor effect relate to current and magnetic field?
The direction of the force can be determined using the right-hand rule, which states that if the thumb points in the direction of current and the fingers point in the direction of the magnetic field, the palm points in the direction of the force.
What is a split ring commutator?
A split ring commutator is a device used in electric motors to reverse the direction of current in the coil, allowing for continuous rotation.
How does a split ring commutator function?
It consists of two segments that alternate the connection of the coil to the power supply as the coil rotates.
What is the purpose of a split ring commutator in an electric motor?
Its purpose is to ensure that the torque acting on the coil is always in the same rotational direction.
What is the role of brushes in relation to a split ring commutator?
Brushes maintain electrical contact with the split ring commutator, allowing the current to flow into the motor coil.
What materials are typically used for split ring commutators?
Split ring commutators are often made from conductive materials such as copper to facilitate efficient current flow.
What happens to the direction of current in a motor due to the split ring commutator?
The split ring commutator reverses the direction of current every half turn, enabling continuous rotation.
In what types of devices are split ring commutators commonly used?
They are commonly used in DC motors and generators.
What is the relationship between magnetic fields and electric currents in the context of the motor effect?
A magnetic field exerts a force on electric currents, which is the principle behind how electric motors operate.
Why is the motor effect important in practical applications?
It enables the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy, making it essential for motors and actuators.
What determines the magnitude of the force experienced by the conductor in the motor effect?
The magnitude depends on the strength of the magnetic field, the amount of current flowing, and the length of the conductor within the field.
How does changing the direction of current affect the motor effect?
Changing the direction of current reverses the direction of the force experienced by the conductor.
What factors can enhance the motor effect in a conductor?
Increasing the current, strengthening the magnetic field, and using longer conductors can enhance the motor effect.
What is Faraday's Law in the context of electromagnetism?
Faraday's Law states that a change in magnetic flux through a circuit induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the circuit.
How do AC motors differ from DC motors regarding commutation?
AC motors do not require commutation, as they can operate with alternating current directly.
What is electromagnetic induction?
Electromagnetic induction is the process of generating an electric current by changing magnetic fields.
Why are electric motors widely used in various applications?
They provide a reliable and efficient means of converting electrical energy into mechanical motion.
What physical principles govern the operation of electric motors?
They operate based on electromagnetic principles, specifically the interaction of current and magnetic fields.
What is back EMF in electric motors?
Back EMF is the electromotive force generated in the opposite direction to the applied voltage when a motor is running.
How does back EMF affect motor performance?
It limits the current flowing through the motor and helps prevent the motor from overheating.
What are some applications of the motor effect?
The motor effect is used in devices such as electric fans, pumps, and industrial machinery.
What is inductive reactance?
Inductive reactance is the opposition to alternating current due to the inductance of a coil, impacting motor performance.
How does resistance in the motor circuit affect performance?
Higher resistance can reduce current flow and decrease motor efficiency, leading to less torque.
What is torque in the context of electric motors?
Torque is the rotational force produced by the motor, related to the current and magnetic field strength.
How can the speed of an electric motor be controlled?
The speed can be controlled by adjusting the voltage or current supplied to the motor.
What is a universal motor?
A universal motor can operate on both AC and DC power, making it versatile for various applications.
What role do capacitors play in motor circuits?
Capacitors can improve the performance and efficiency of motors by providing phase shift in AC circuits.
What is the efficiency of an electric motor?
Efficiency is the ratio of mechanical output power to electrical input power, typically expressed as a percentage.
Flemings Left Hand Law
thumb - force
pointer finger - magnetic field
middle finger - current
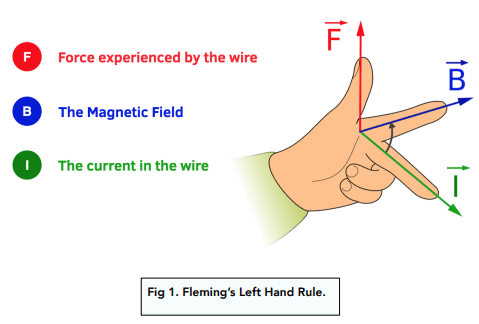
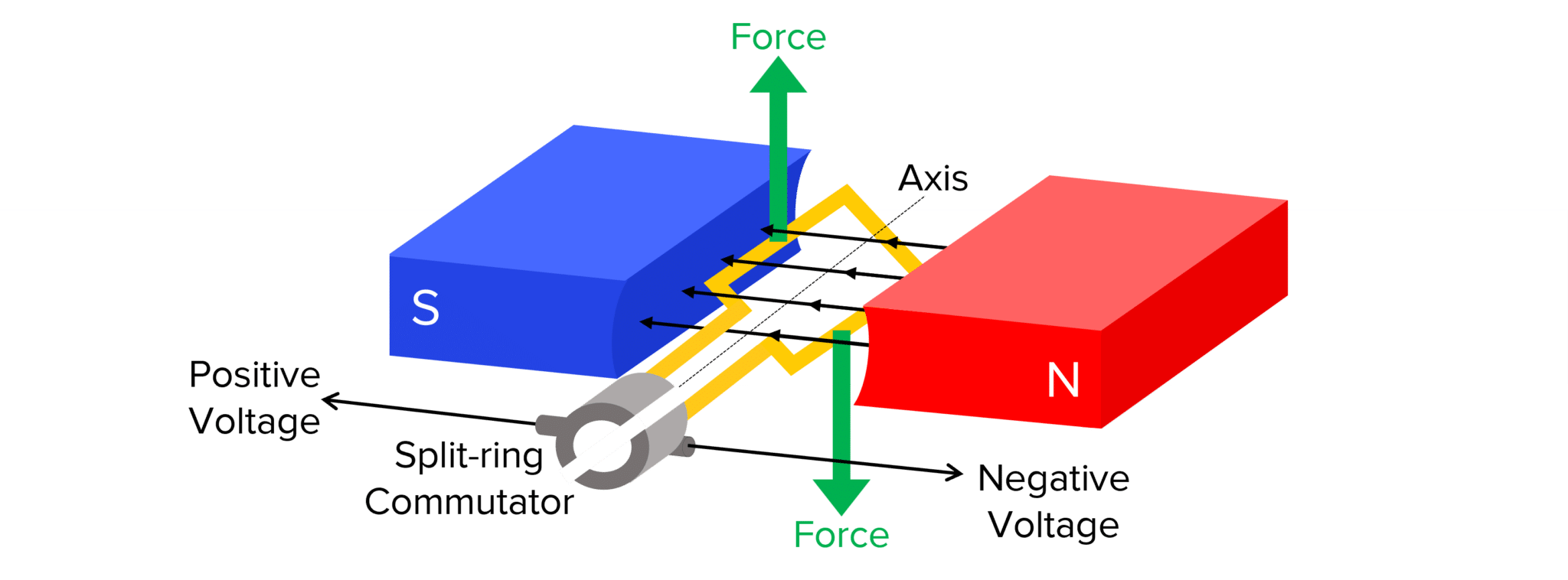
Motor effect
Electric current in a conductor causes something to become an electromagnet
This INTERACTS with a permanent magnet (the fields overlap
To produce a force predicted by Fleming’s Left hand rule.
2 forces act in opposite directions to cause motion in the conductor.
Current direction changes every half turn using a split ring commutator
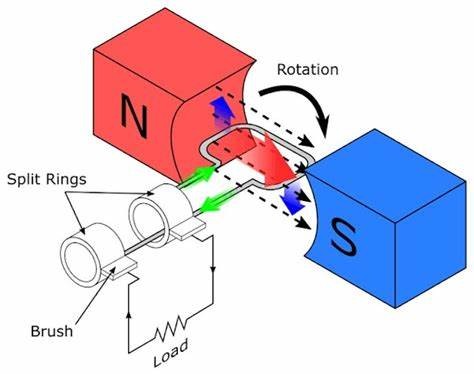
Generator effect
Force - relative motion between a magnet and a conductor
Conductor 'cuts' magnetic field lines
A potential difference (voltage) is INDUCED across the ends of the conductor
If a complete circuit, induced current flows
Generator - coil spins inside a magnet due to applied force, cutting through field lines in opposite directions in each revolution. Output is alternating current
