AQA A level Chemistry 3.3.6: Organic analysis
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
How do you test for the presence of a carboxylic acid? (1)
Add sodium carbonate
What observation indicates the presence of a carboxylic acid in a sodium carbonate test? (1)
Effervescence is observed
What is the deduction if effervescence is observed when sodium carbonate is added to a compound? (1)
CO2 is formed from an acid-base reaction
What test is used to identify halogenoalkanes? (1)
Warm with NaOH followed by acidified silver nitrate
What observation indicates the presence of a chloroalkane in the halogenoalkanes test? (1)
A white precipitate forms.
What is the deduction when a white precipitate forms in the halogenoalkane test? (2)
1. NaCl is formed
2. Followed by AgCl
What observation indicates the presence of a bromoalkane in the halogenoalkanes test? (1)
A cream precipitate forms
What is the deduction when a cream precipitate forms in the halogenoalkane test? (2)
1. NaBr is formed
2. Followed by AgBr
What observation indicates the presence of an iodoalkane in the halogenoalkane test? (1)
A yellow precipitate forms
What is the deduction when a yellow precipitate forms in the halogenoalkane test? (2)
1. NaI is formed
2. Followed by AgI
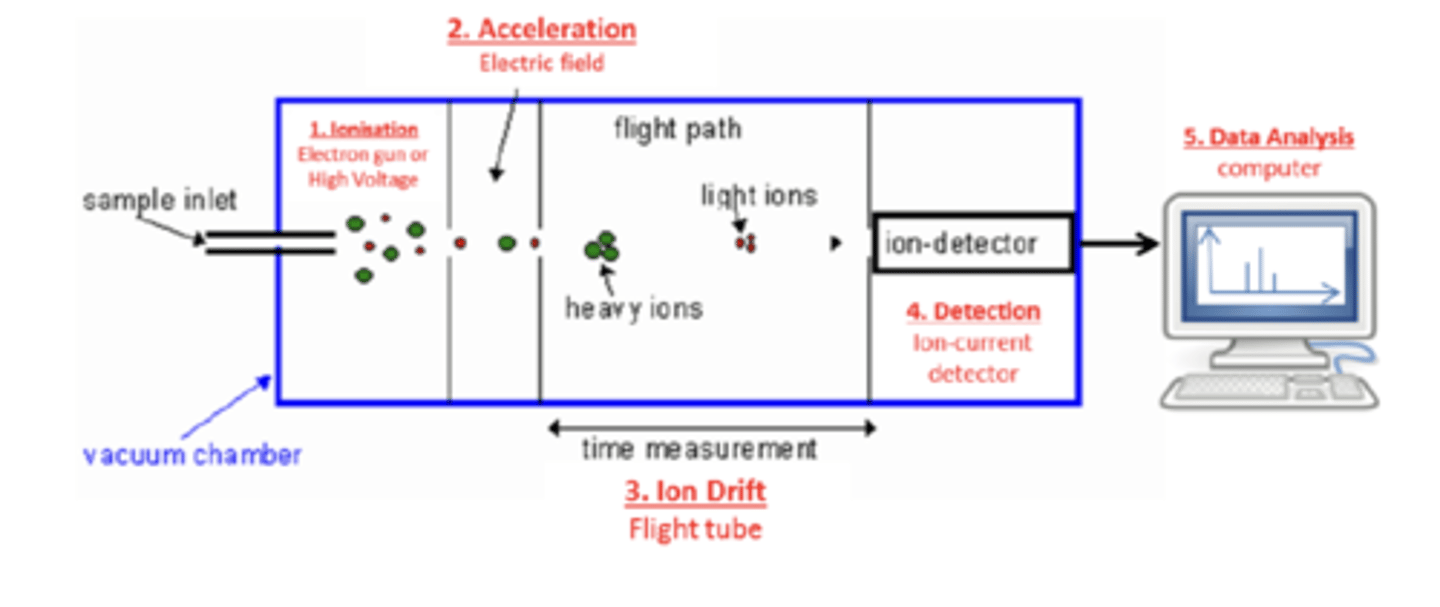
Draw a diagram of a time of flight (TOF) mass spectrometer (5)
What is the method of ionisation involving an electron gun called? (1)
Electron impact ionisation
How does electron impact ionisation work? (2)
1. High-energy electrons from an electron gun are fired at the sample.
2. These electrons knock off an electron from the sample, forming a positive ion.
What is the general equation for electron impact ionisation? (1)
X(g) -> X+(g) + e-
What is the key observation for Electron Impact Ionisation regarding the molecular ion peak? (1)
The Mr for the sample will be equal to the peak with the greatest m/z value
What is the principle of Electrospray Ionisation? (2)
1. The sample is dissolved in a volatile solvent and injected through a fine hypodermic needle at high voltage to form a fine mist.
2. Each particle is ionised by gaining a proton (H⁺)
Write the equation for Electrospray Ionisation. (1)
X(g) + H⁺ → XH⁺(g)
What is the key observation for Electrospray Ionisation regarding the molecular ion peak? (1)
The Mr for the sample will be equal to the peak with the greatest m/z value minus one.
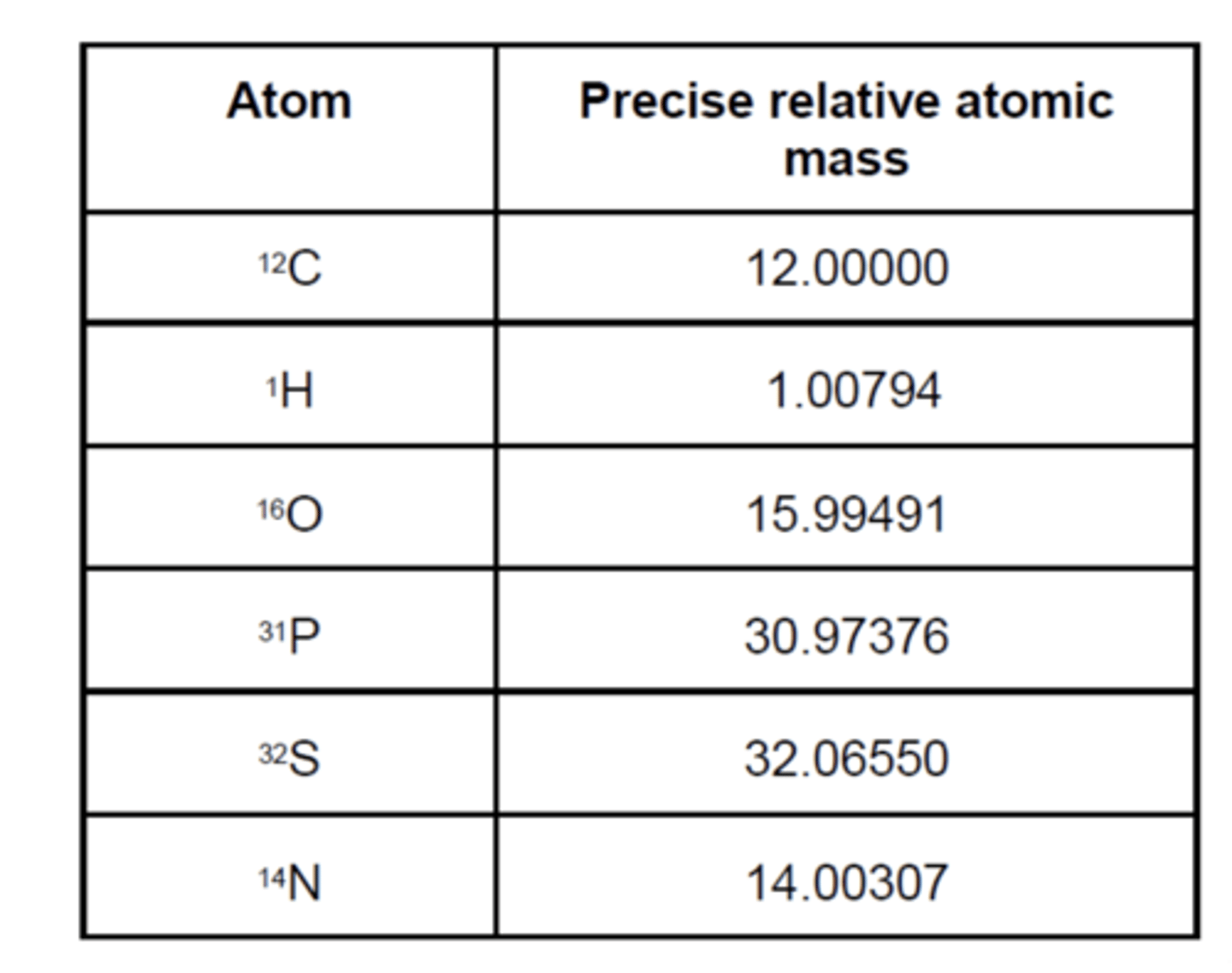
What is high-resolution mass spectrometry? (1)
- Measures masses to 4 or 5 decimal places
- Allowing determination of the molecular formula of a compound by using precise atomic masses.
What does Infra-red (IR) spectroscopy help identify in a compound? (1)
It helps identify the type of bonds in a compound
How does infra-red spectroscopy work to identify bonds? (3)
1. A chemical bond vibrates like two balls joined by a spring.
2. Stronger bonds vibrate faster, and heavier atoms make the bond vibrate slower.
3. Each bond absorbs infrared radiation at its own natural frequency
Draw a simple diagram of how IR spectrometer works (5)
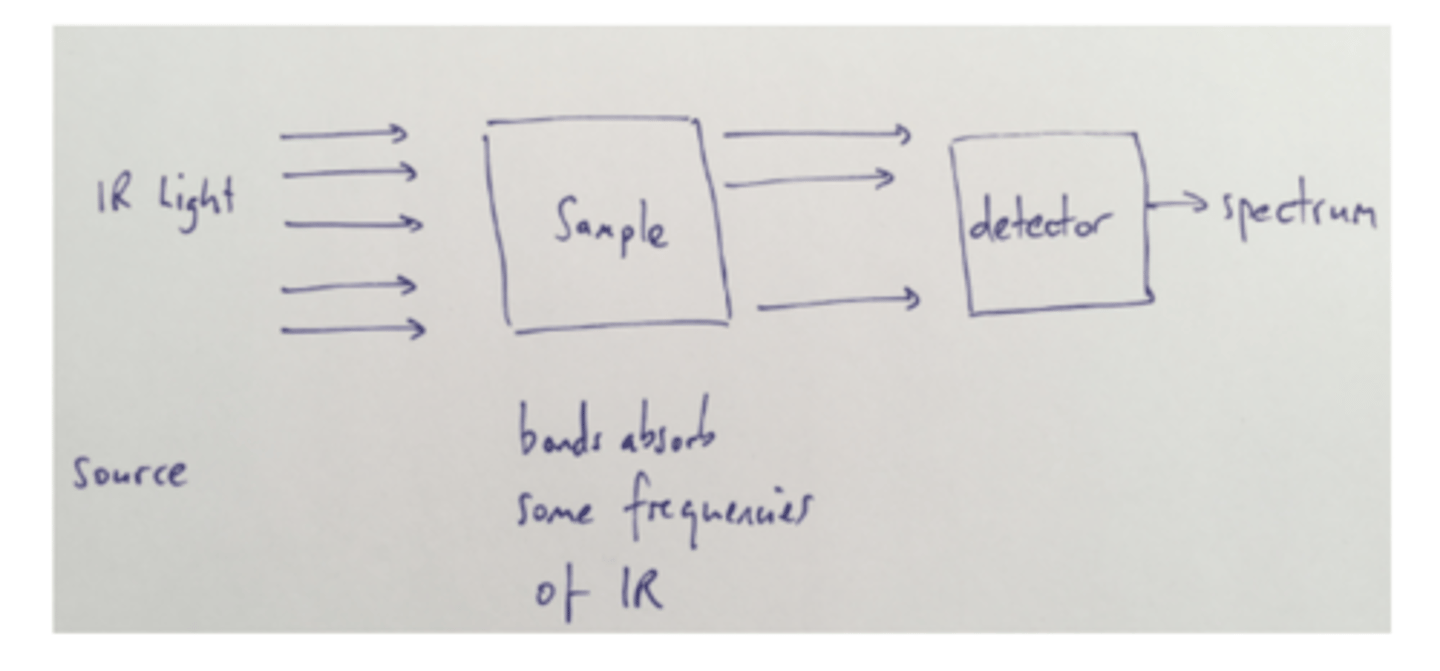
What happens in an IR spectrometer when a sample is analysed? (4)

Draw a typical IR spectrum diagram (4)
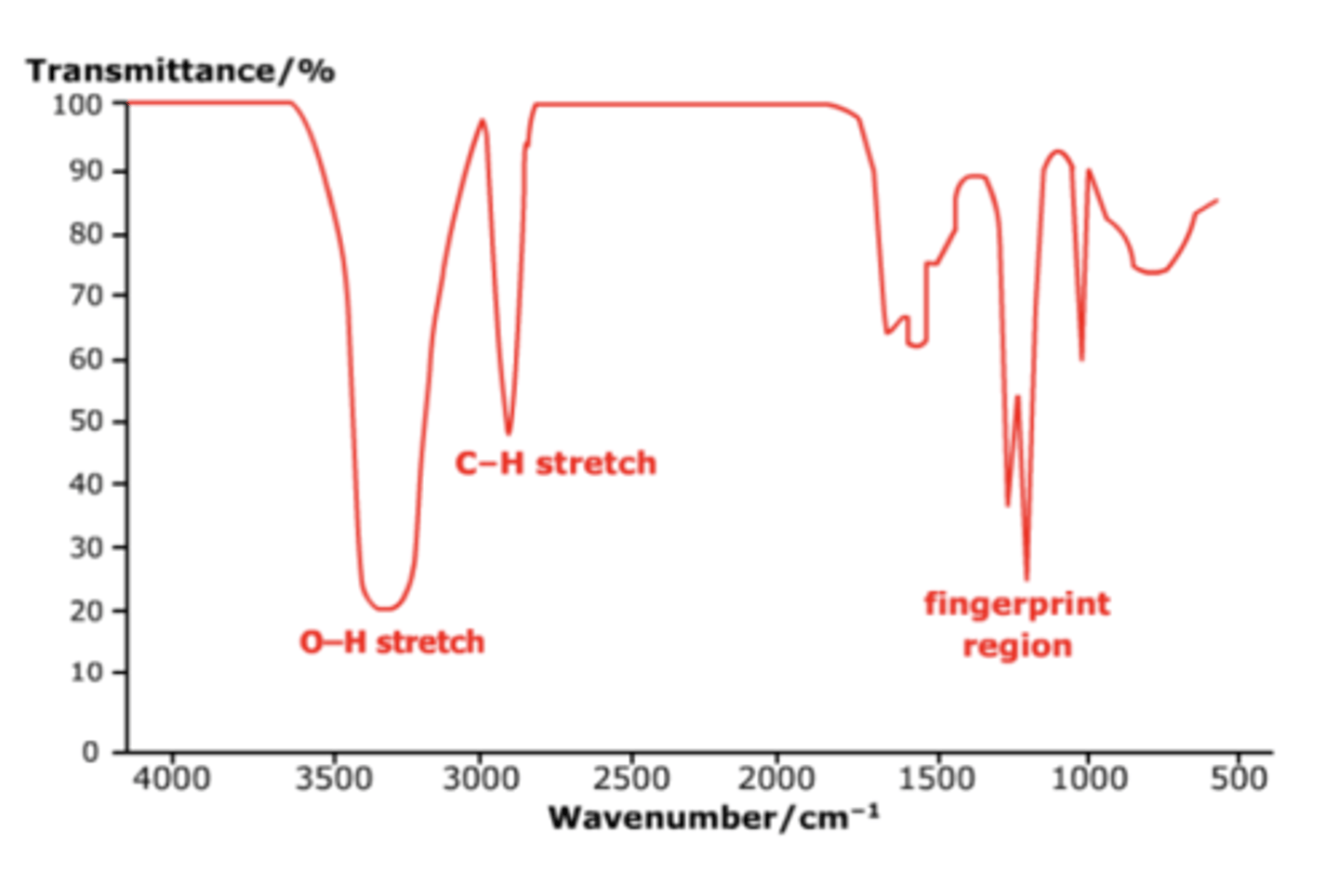
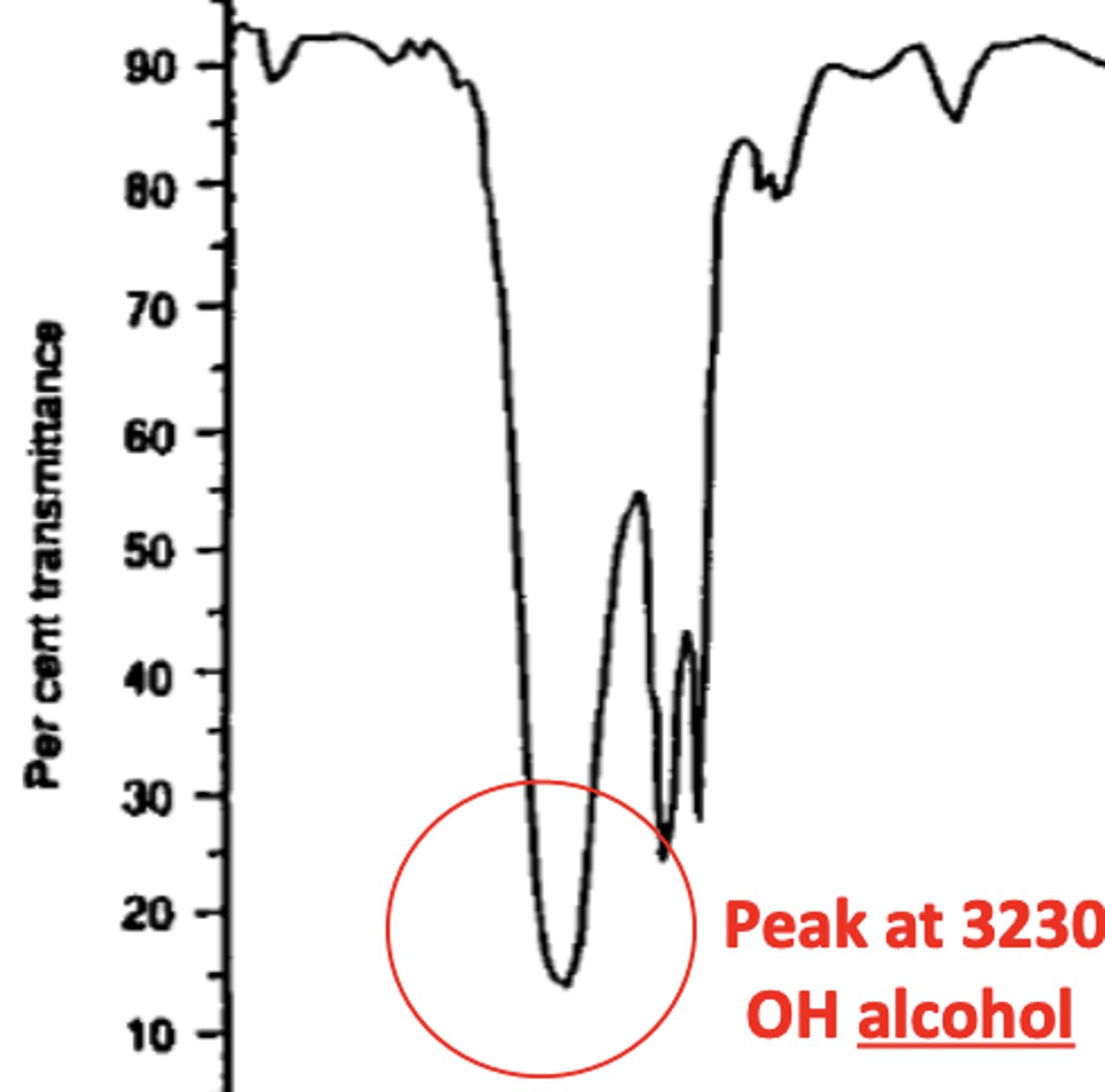
How does the peak for an OH alcohol bond look like in an IR spectrum? (1)
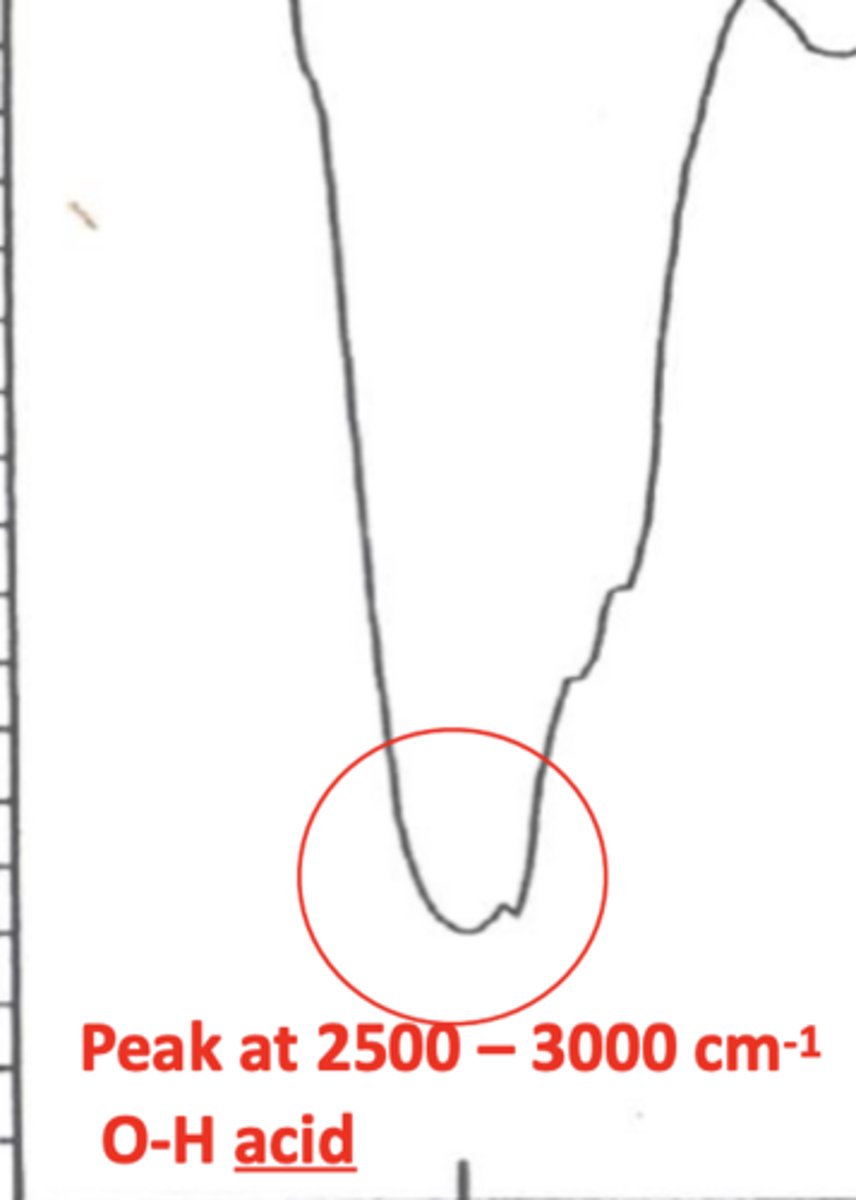
How does the peak for an OH acid bond look like in an IR spectrum? (1)
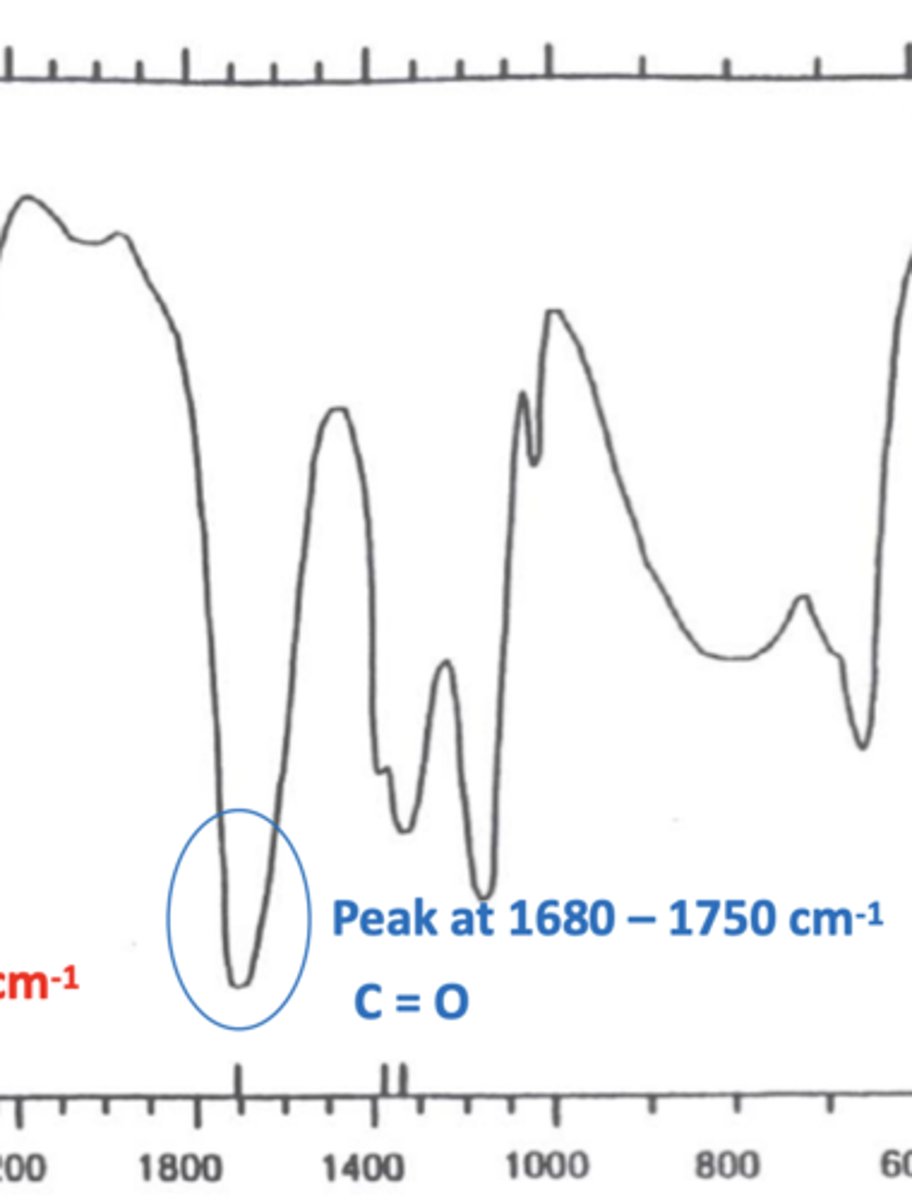
How does the peak for a C=O bond look like in an IR spectrum? (1)
What is the fingerprint region in an IR spectrum? (1)
The area of the IR spectrum below 1500 cm⁻¹, unique for each molecule, used to identify compounds
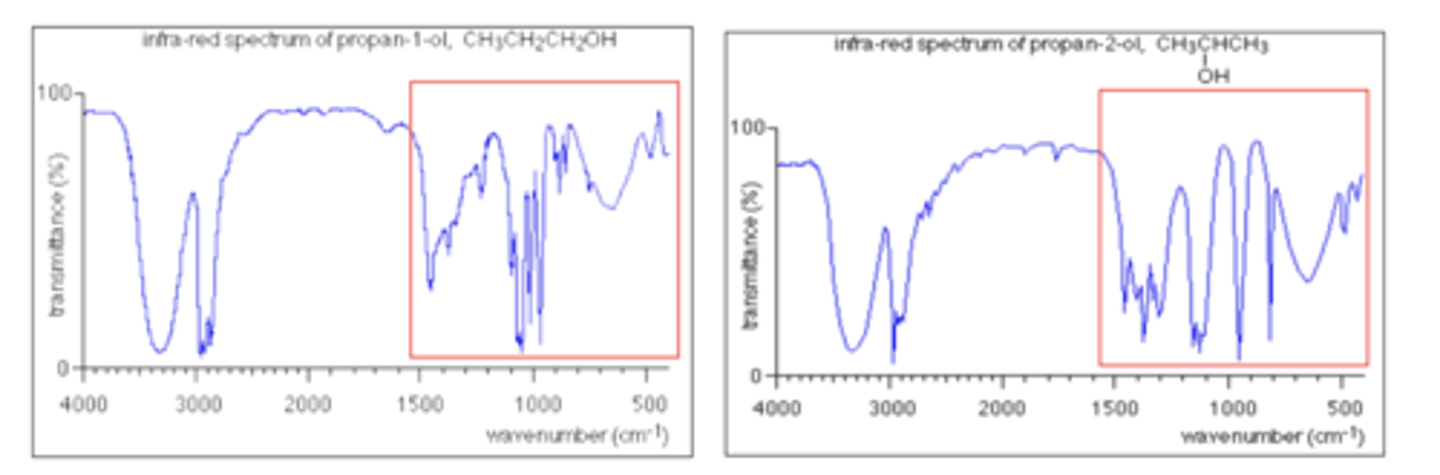
How can the fingerprint region confirm the identity of a compound? (1)
By matching the fingerprint region with a database of known compounds for an exact match
What do both spectra of propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol share in the 3230 - 3350 cm⁻¹ region? (1)
Absorption due to the O-H bond in alcohols.
How do the fingerprint regions of propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol differ? (1)
They have different patterns of peaks, which can be used to distinguish the two alcohols
How can IR spectroscopy help identify impurities in a sample? (1)
By revealing absorptions that should not be present in the pure compound
What are common impurities detectable in an IR spectrum? (1)
Water and leftover reactants
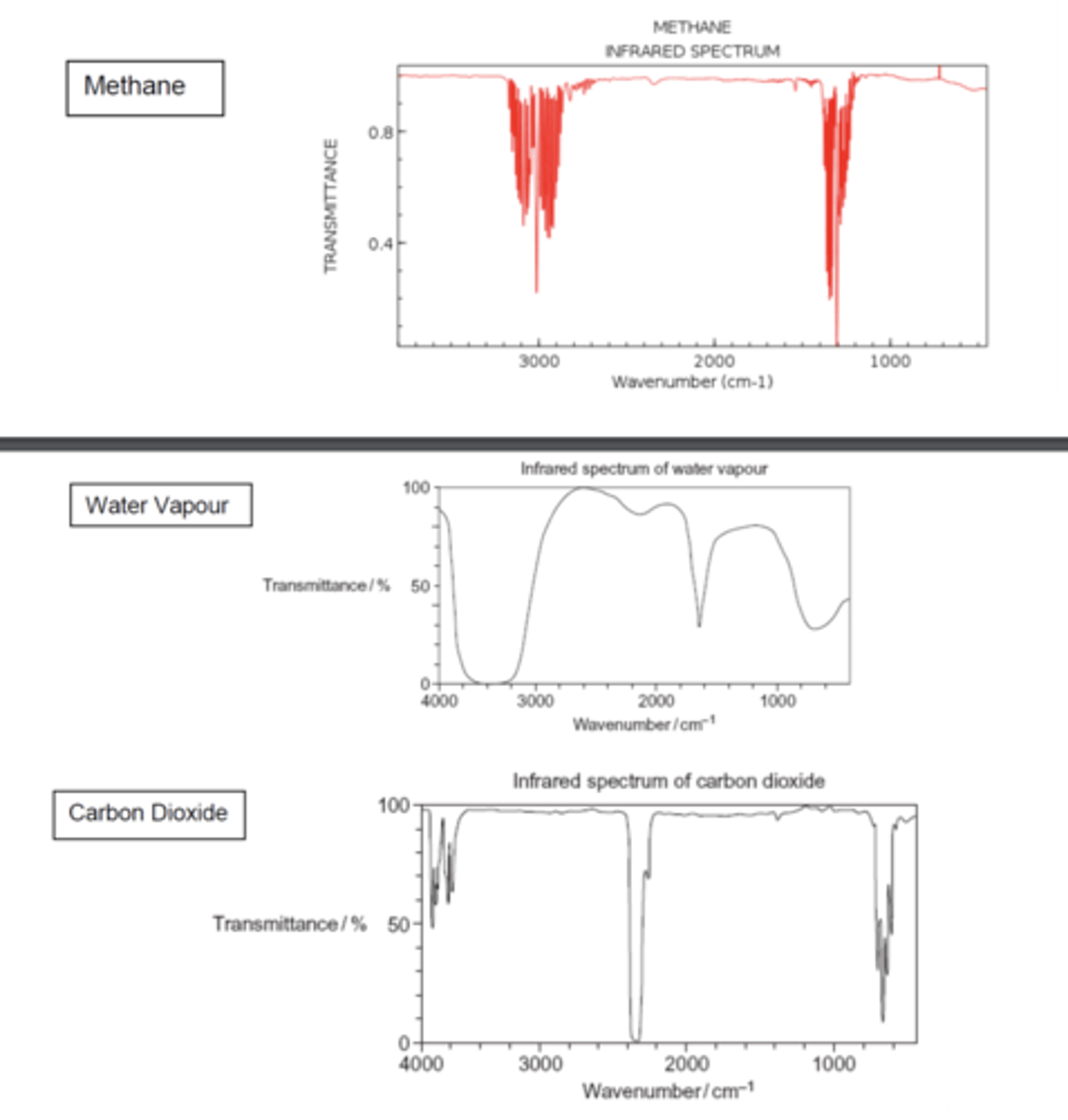
What is the role of greenhouse gases in trapping heat? (1)
Greenhouse gases absorb the most infrared radiation and trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere
Compare the infrared spectra of methane, water vapour, and carbon dioxide, highlighting their absorption of infrared radiation. (3)