water economics, forested watersheds
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
economic water demand
consumptive demand - drinking water, hygiene, sanitation
productive purposes - irrigation, industrial use, etc, production of goods/services
different types can use water of different qualities, potable or not
water supply treatment
water treatment for drinking water purposes
water distribution, treatment - needs to be pumped, delivered etc
often under central govt control, highly regulated - monopoly
how much do we pay for 1L of water in edmonton?
water tariifs - fixed cost for use, encourages lower use
then we pay additional for every 1 m3 of water, drainage fixed costs and variable per m3
wastewater fixed and variable and then total ends up about 77$/month or 0.008$/L
many places also have fixed rates instead
why is water so cheap in edmonton?
cost to produce the water doesn’t change in scarcity, doesn’t change with supply and demand - set by govt regulations
due to allocations then Epcor will always get the water
inelastic demand, access is essential and so socially cannot deny uses
its very local in nature and so water industries have a monopoly - costs only really include the infrastructure
water stress and value
southern AB among many other parts of the world are projected to experience stress by 2040
scarcity requires decisions to be made on uses and priority - knowing the value
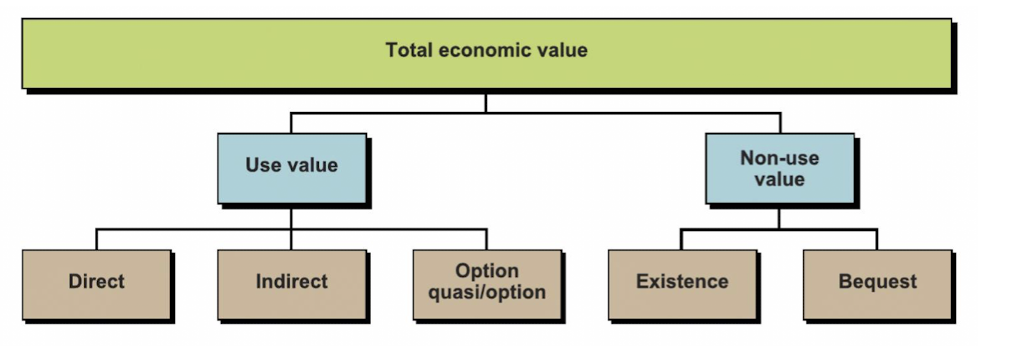
direct value of water
present and future use by individuals, associated with consumptive and productive use
for ex household or irrigation
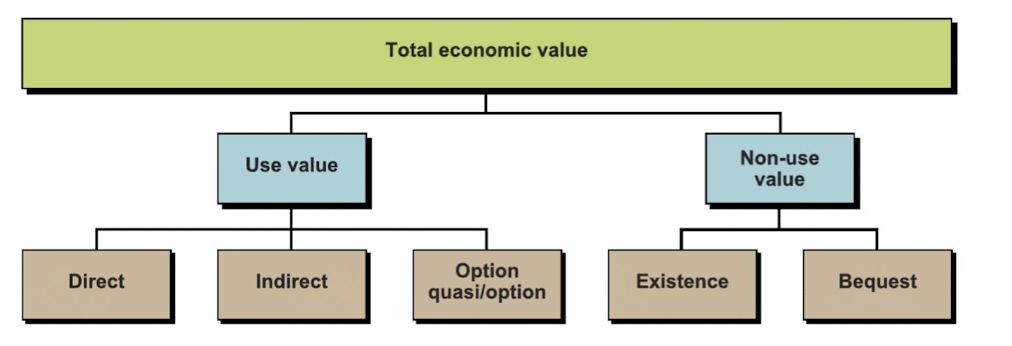
indirect value of water
benefits are derived from ecosystem functions - that are beneficial for humans
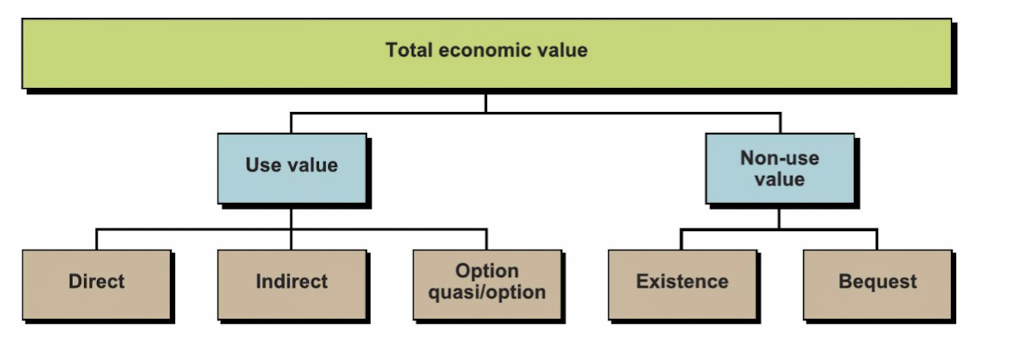
option value of water
value of preservation of resource, or potential future values of it even if it is not used today
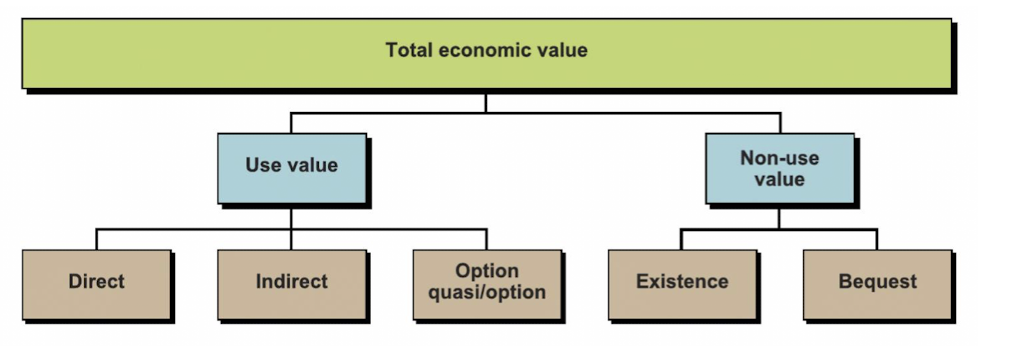
existence value of water
value of an ecosystem without any links to human use or future use
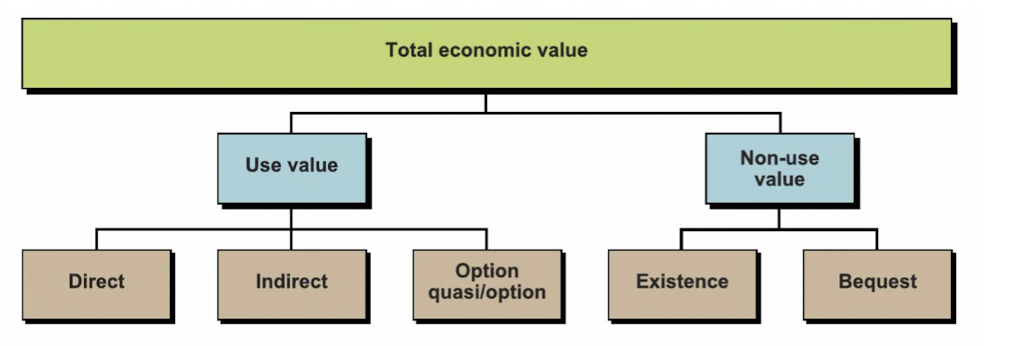
bequest value of water
the value in knowing that future generations will be able to enjoy the existence of an ecosystem
millenium ecosystem assessment
value of an ecosystem services are in the context of the value they provide to human well-being, overlapping with economic value
provisioning, regulating, cultural and supporting sevices are ranked based on value
provisioning services and value
food, water fibre, fuel, biochemical
applicable to direct use of water, and option values
regulating services and value
climate regulation, water and disease, purification, erosion reg, natural hazard reg, etc
applicable to indirect water values and option values
cultural services and value
spiritual, aesthetic, recreation and education
applicable to direct water use, option and non use values
habitat and supporting services and value
soil formation, primary production, nutrient cycling
values through other categories
example n. sask value according to millenium ecosystem assessment
provisioning services such as drinking water, sanitation, industrial manufacturing, and irrigation, processing
regulating such as sediment transport, flood control, GW recharge, local cooling, carbon storage, etc
cultural such as fishing, indigenous values/colonizer values, aesthetic values, ecological education, mental health
and supporting such as aquatic habitat and biodiv, downstream support to delta
values for wetland ecosystems
generally have high high ecosystem value - inherent
value of <$20 000, as determined by the cost of a simple (poor) restoration in 2014
not a value of ecosystem services or a deterrent of development
water allocations in southern alberta
closed basin, no new licenses may be issued but they can sell to willing buyer
in selling the govt may withhold 10% of transfer increased river flow
ensures economically efficient uses of water are promoted - with supply and demand dictating prices
so therefore new allocations depend on economic considerations not social
valuation techniques
when providing a dollar value to an ecosystem services, large variation no real answer
should biodiv, ecosystem services have a dollar value - perhaps aid in understanding for people who dont understand ecological impacts/science background
but changes so much with goals and who is involved
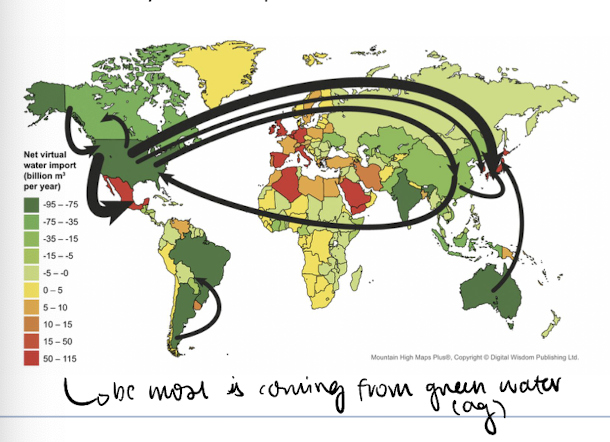
blue water - embedded virtual water
direct, clean water consumption of freshwater which is not returned to the watershed
for example use of potable water
green water - embedded virtual water
water used by soils and by plants during ag production - precipitation and irrigation
grey water - embedded virtual water
water used to deal with pollution during supply chains, the volume of freshwater it takes to assimilate pollutants and return the water back to its source
how much virtual water is in a 0.5L soft drink bottle
direct production and processing - blue and grey
indirect production like employees and sanitation - blue and grey
direct supply chain - green for sugar, blue/grey for packaging
indirect supply chain - energy, transport, infrastructure
ends up being around 200L of water, 90% from direct supply chain (green)
trade of virtual water
all products carry a water footprint, total of blue, grey, green water
global trade of goods also includes a global trade of water - many countries depend on the water use of other countries
forested watersheds
>70% of canadians source their water here, key habitat, recreational activities
quantity and quality of water from forested affected by timber harvest, site prep and planning, forest drainage, forest fertilization, wildfires, insect outbreaks, livestock grazing, urban development, construction for oil and gas
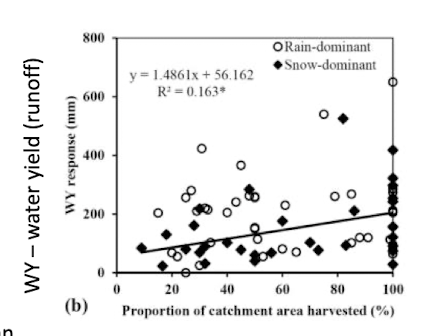
impacts on runoff generation and forest harvesting
forest harvesting leads to reduced ET and sometimes decreased capacity for infiltration, this causes increase runoff
this also changes in stream erosion and stream power increases
also differs due to regions, soil type and climate
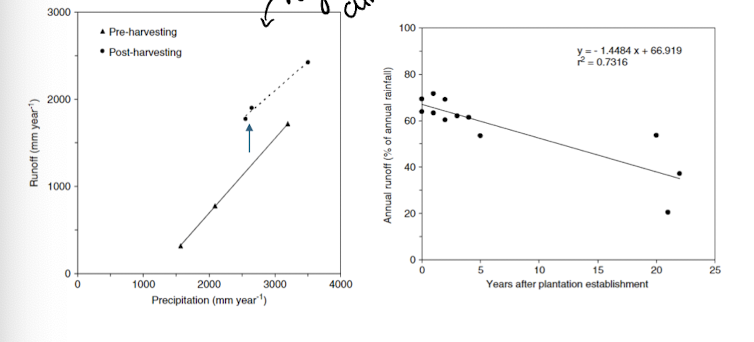
example la reina catchment, chile
post harvesting observed a large increase in total runoff which lasted for approx 20 years before it began to decrease
wildfires and runoff
similar situation to forest harvesting, increases runoff and reduces ET
fire severity can influence the magnitude of response of ET and thus runoff
also can cause soil clogging and water repellency of surface soils which will decrease infiltration capacity and increases overland flow, peak discharge
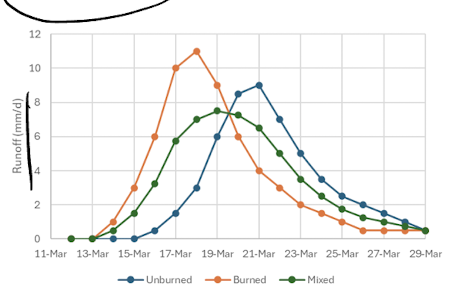
harvesting impact on snowmelt runoff/freshet
harvesting and wildfires lead to increase and earlier runoff during freshet - less shading means faster melt, wetter soils in fall means more ice and therefore less infiltration during snowmelt
in mixed catchments the stream flow is mixed with increased and decreased area, thus can be even lower peak flow over a longer time
insect outbreaks and runoff
rapid regrowth of understory veg with increased light can reduce impact of forest die off on ET
inconclusive evidence of total runoff generation
forestry and disturbances impact water quality
physical quality like sediment load, turbidity, temp, and dissolved O2
chemical quality like nutrients - natural or fert, heavy metals with sediment, pesticides/herbicides, fire retardant, dissolved O C, pH
things such as access roads, skid trails, stream crossings, slash piles can also impact
slash piles on water quality
decomposition releases nutrients but there are no plants to take up any nutrients and so it is washed away
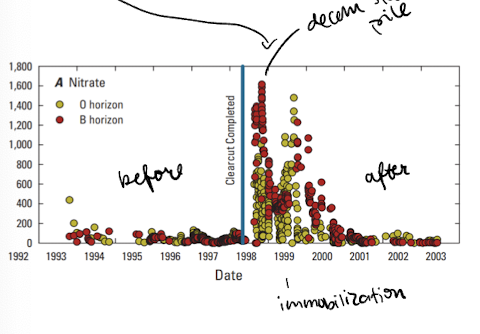
catskills mountain and water quality
in NY
timber harvest increased nitrate in soil water and streams due to reduced plant demand and increased production from slash piles
lasted 3 years
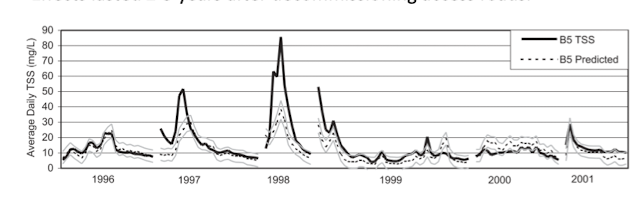
boreal BC and water quality
increased TSS after harvest in 1996
traced to landing with high erosion, effects lasted 2-3 after the decomission of access roads
example peachland BC
population about 5000, increased sediment loads due to forestry and forest roads led to extended periods of high turbidity that the water treatment plant was not designed to handle
new treatment needed to be built and cost 30 mil
best management in forest harvesting
monitor weather, avoid long/straight extraction routes, avoids slopes, maintain slash mats, avoid skidders on wet ground, keep away from streams, keep routes outside of buffer zones and valley bottoms, avoid long slopes, avoid buildup of slash piles near streams, use stone ramps to protect access routes, protect stream crossing, work away from wet terrain, replace upturned root plates near banksides, ensure runoff is away from streams, suspend operations when wet and muddy, phased felling - not all at once
so basically work away from moving water, avoid erosion heading to water
fires and water quality
release minerals, metals, into soil and potential runoff
burned infrastructure can be toxic and can leach into soil and GW
mudslide when rain, increase in temp when shade is lost, bacterial blooms can cause as a result - harming fish populations
forest fertilization
with nitrogen pellets is common and effective in BC and AB
can also add phosphate, sulfur, and boron
acts as diffuse mobilization of fertilizer into aquatic systems - eutrophication, lower DO
can last for years depending on climate but also highest in early days
herbicide is also common use
best management practices forest fert and herbicide
dont fert during wet weather/waterlogged/ frozen soils, dont apply in riparian buffer zones or near surface water/springs and wells, use hand application in buffer zones, dont apply when surface flow drains into/across buffer, treat dug drains as streams, increase buffer zone when using heli, dont ford streams w distributing, dont store fert bags in buffer zones, dont bury empty bags on site
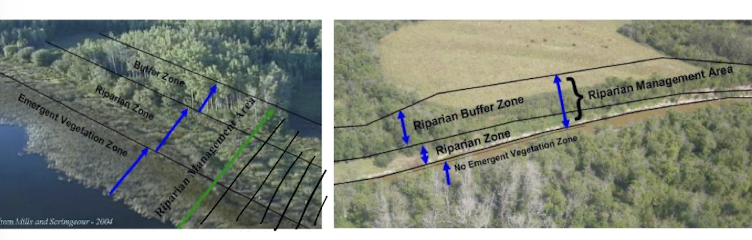
riparian zones and buffering
transitional areas that work to improve water quality, filter sediments, shade for temp control, and input OM for biota use
also reduce erosion, flood control, and habitat
require a buffer zone to industry work, but this is a trade off depending on the size of the stream
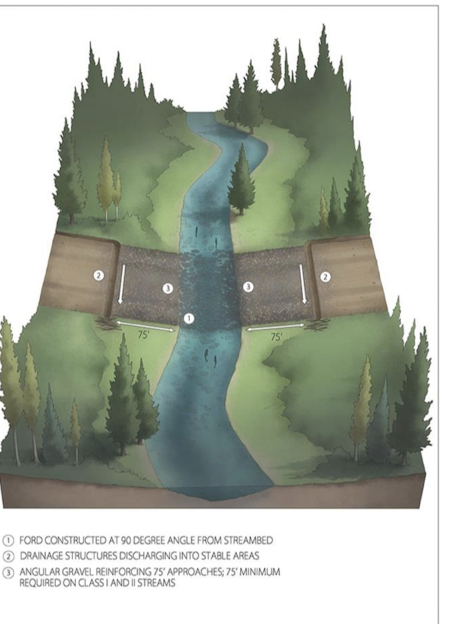
ford crossings
drainage structure, but high risk for erosion and sediment transport
coarse material covers crossing - geowebs or concrete
vehicle speed is a big factor
but fish migration or biota movement??
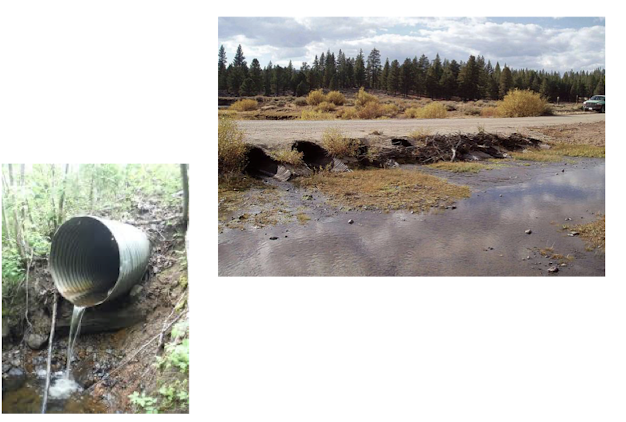
culvert crossings
most common type
lower risk for high sediment erosion
but they get blocked, require maintenance, when hanging they restrict fish and also undersizing can lead to wash out

best management in forestry operations
should be implemented throughout forest management cycle
pre operation planning, training and education of other workers and land owners
key ___ include - erosion control, rapid closure of access, sediment control at streams, improved stream crossings, riparian buffer zones and skid trail management and closure