DPT 745 (Lecture 8)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Does the hyoid articulate with any other bone?
No it does not!
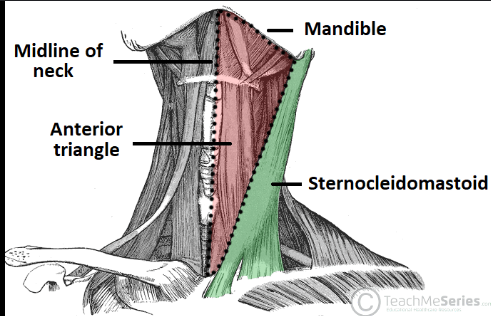
What form the anterior triangle of the inferior border?
mandible, midline of neck, jugular notch of manubrium
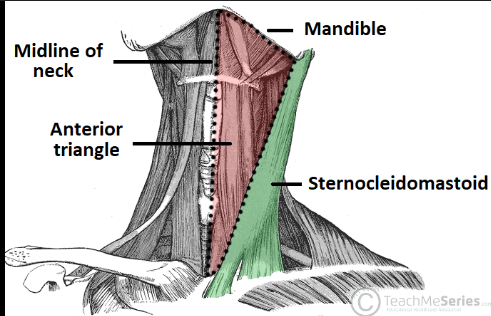
What forms the anterior triangle of the anteriorborder?
SCM, platysma (roof) pre-tracheal fascia (floor)
What form the posterior triangle of the posterior border?
SCM, middle 1/3 of clavicle, anterior border of trapezius, platysma (roof), deeper musculature (floor)
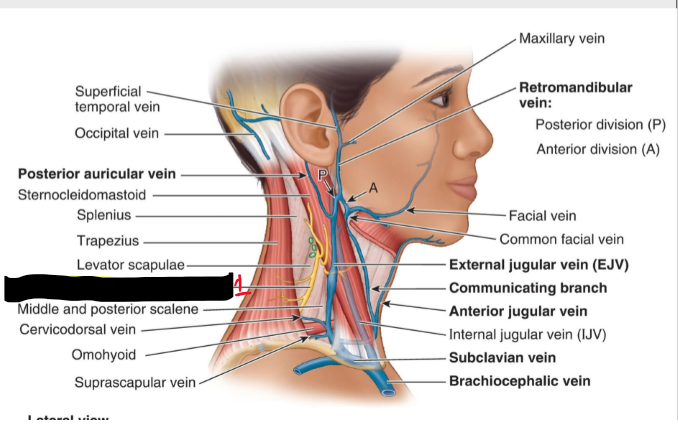
![<p>Name the Structure (1) [Posterior Triangle]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/14cbad2c-4a25-4a32-82d7-a63fd89afc66.png)
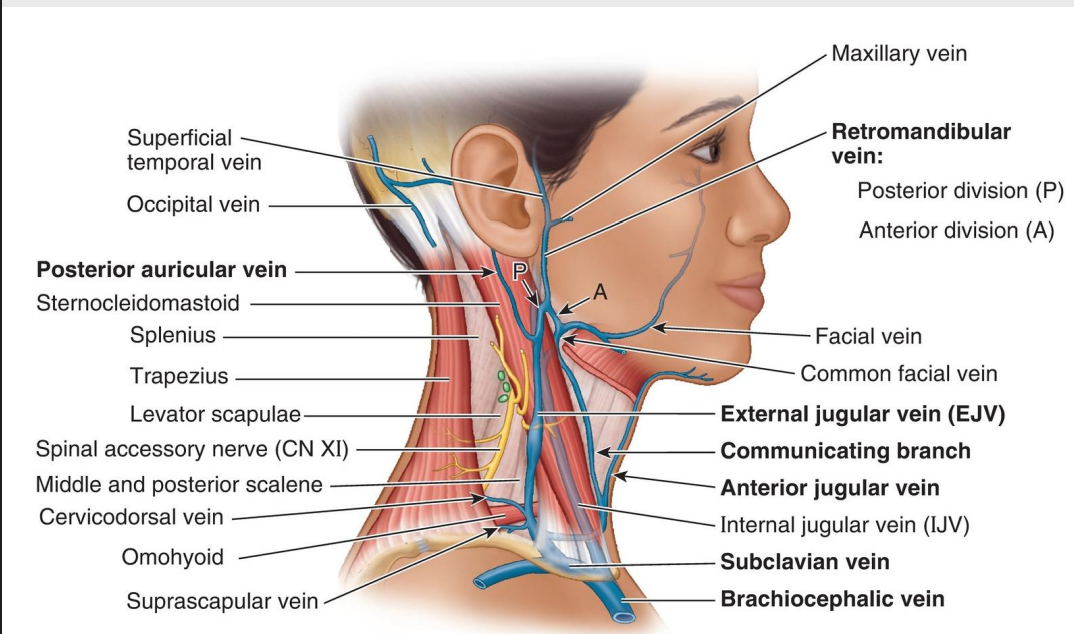
Name the Structure (1) [Posterior Triangle]
External Jugular vein
Communicating Branch
Anterior Jugular v. [front part of neck]
Internal jugular v. [split by SCM]
Subclavian v.
Brachiocephalic v.
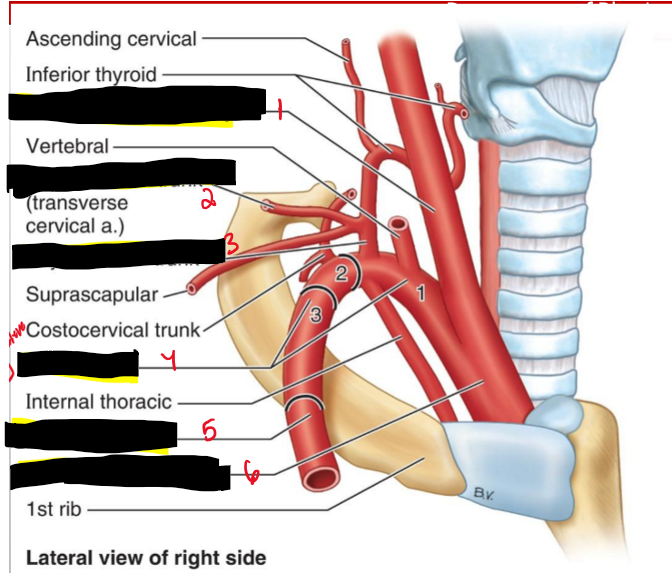
Name the Structures. (2)
Common carotid a.
Cervicodorsal trunk
Thyrocervical trunk
Subclavian [3 parts]
Axillary a.
Brachiocephalic trunk
What are the nerves of the posterior triangle?
Spinal accessory n.
Cervical plexus
Brachial plexus
Name the Structure (3)
Spinal accessory n [CN XI]
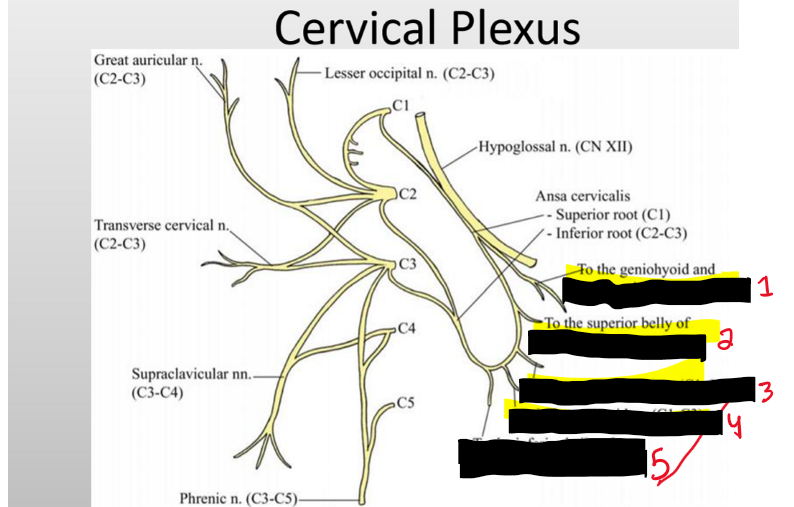
Name the structure. (4)
Thyrohyoid (C1)
superior belly Omohyoid (C1)
Sternothyroid (C1-C3)
Sternohyoid (C1-C3)
Inferior belly omohyoid (C2-C3)
What are the muscles of the posterior triangle?
• Splenius capitis • Levator scapulae • Posterior scalene • Middle scalene • Anterior scalene • Omohyoid
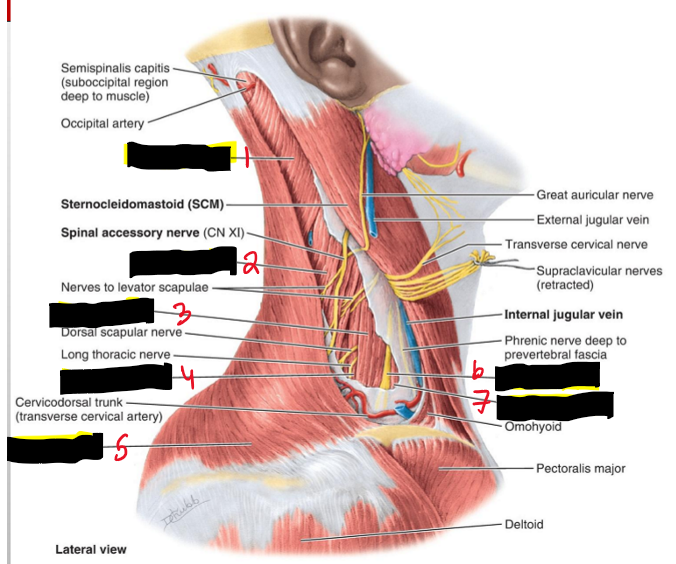
Name the Structures. (5)
Splenius capitis
Levator scapulae
Middle scalene
Posterior scalene
Trapezius
Brachial plexus
Anterior scalene
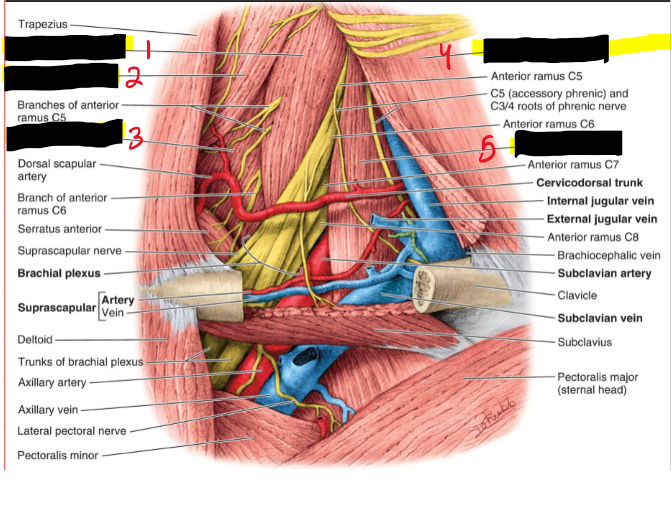
Name the Structures (6)
Middle scalene
Levator scapulae
Posterior scalene
SCM
Anterior scalene
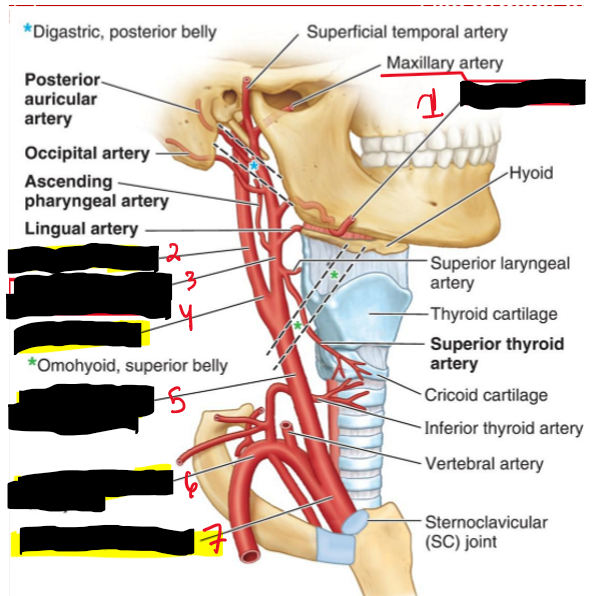
Name the structures. (7)
Facial a.
internal carotid
External carotid
Carotid sinus
Right common carotid a.
Right subclavian
Brachiocephalic trunk
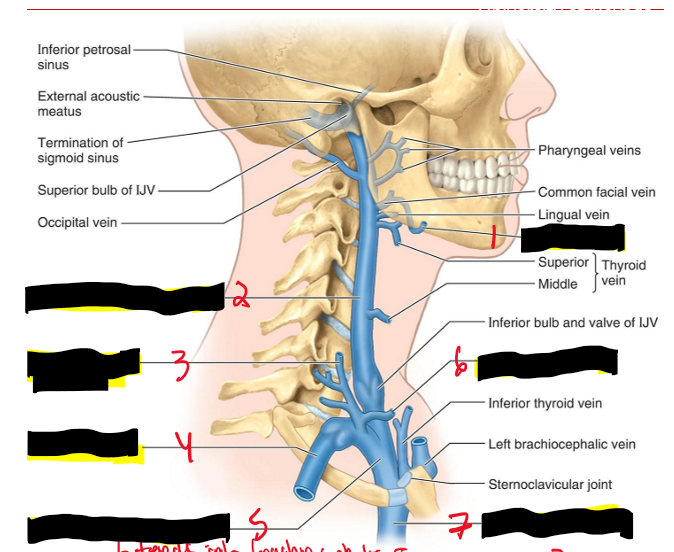
Name the structures. (8)
Facial v.
Internal jugular v.
External jugular v.
Subclavian v.
Right brachiocephalic v.
Anterior jugular v.
Superior vena cava
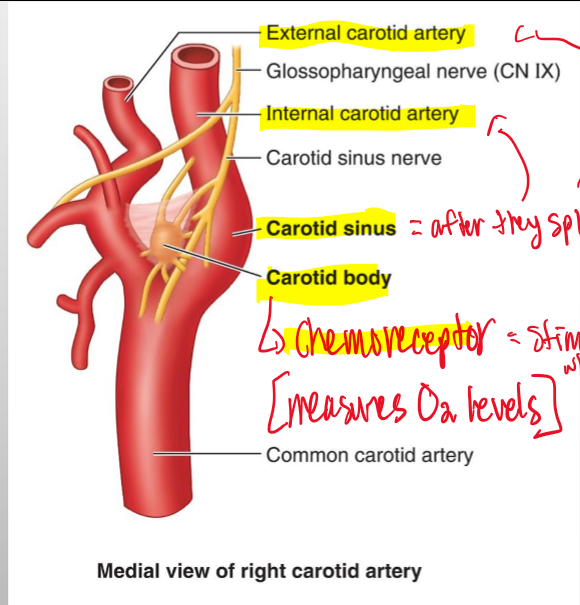
The coratid sinus of the anterior triangle rides with what major a.?
Internal coratid a.
The carotid sinus is also known as what and what does it do?
Baroreceptor = a pressure receptor that reacts to changes in BLOOD PRESSURE
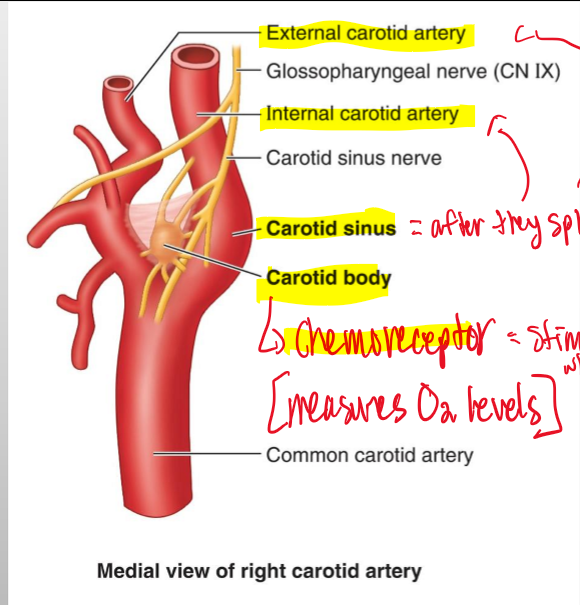
The coratid sinus is also known as what and what does it do?
Chemoreceptors= maintains proper oxygen and CO2 in the body, which control BLOOD PRESSURE
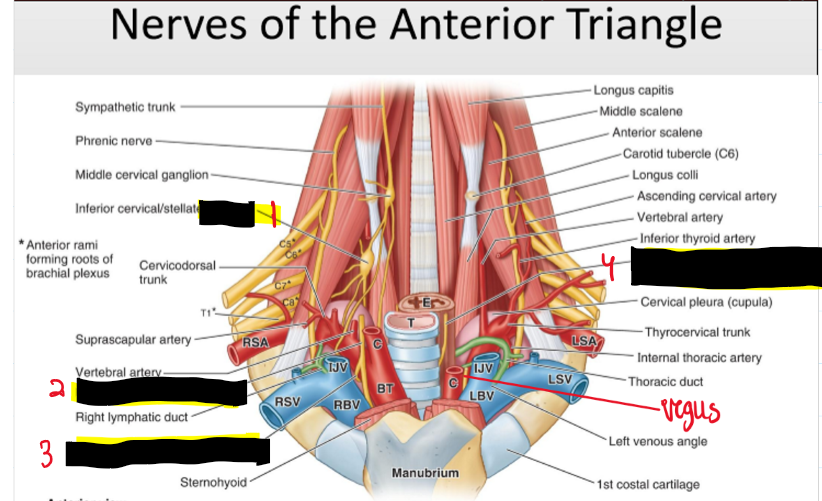
Name the structures. (9)
Ganglion
Right vagus n. [CN X]
Right recurrent laryngeal n.
Left recurrent laryngeal n. in tracheo-esophageal groove
What are nerves of the cervical plexus?
• Cervical Plexus • Vagus – Recurrent laryngeal nerves • Sympathetic Chain
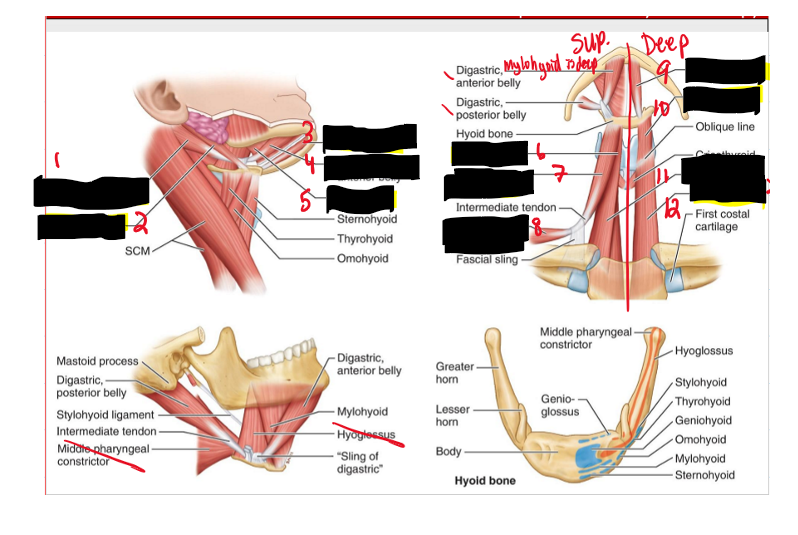
Name the structure. (10)
Digastric posterior belly
Stylohyoid
Geniohyoid
Digastric anterior belly
Mylohyoid
What are muscles of the anterior triangle?
• Mylohyoid • Geniohyoid • Stylohyoid • Digastric • Sternohyoid • Omohyoid • Sternothyroid • Thyrohyoid
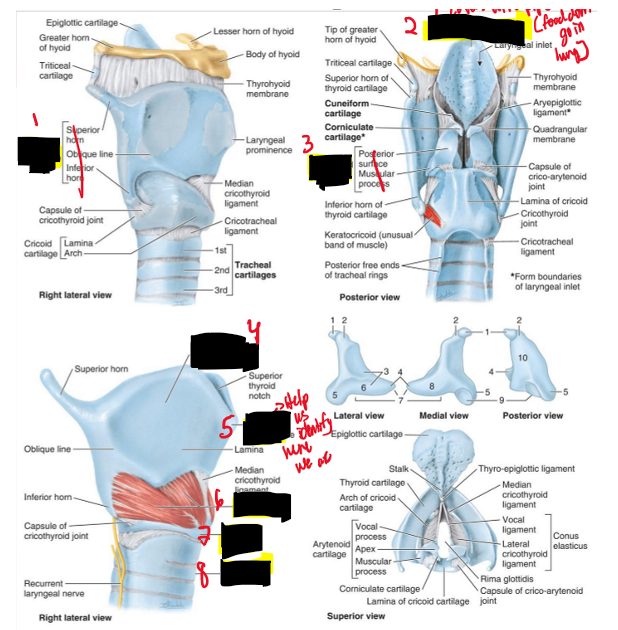
Name the structure (11)
Thyroid cartilage
Epiglottic cartilage
Arytenoid cartilage
Thyroid cartilage
Laryngeal Prominence
Cricothyroid
Cricoid cartilage
Trachea
What are other important structures of the anterior triangle?
Larynx and Pharynx
What is the function of the larynx (voice box)?
Part of the respiratory system designed for vocalizing.
What structures make up the larynx?
Series of cartilages with attached muscles, ligaments, and fibroelastic membranes.
Where does the larynx open into?
A: The oropharynx.
Q: Where is the larynx located relative to the laryngopharynx?
A: Anterior to the laryngopharynx.
Q: What are the cartilages of the larynx?
A: Thyroid, cricoid, arytenoid, epiglottic, and tracheal.
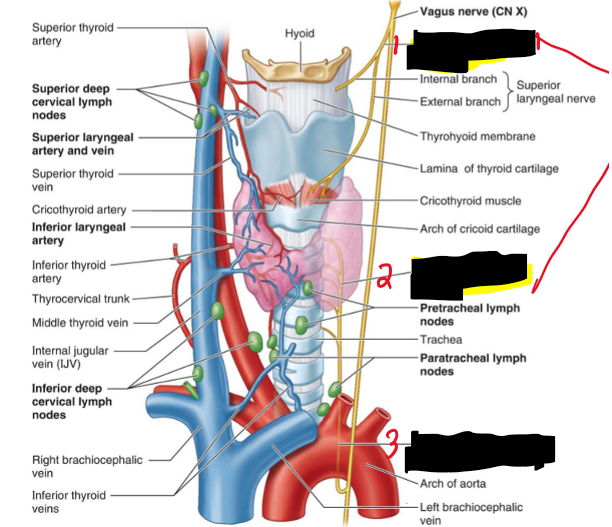
Name the structure. (12)
Superior laryngeal n.
Inferior laryngeal n.
Left recurrent laryngeal n.
What is the function of laryngeal muscles in the inlet of the larynx?
Prevent food from entering.
What is the function of laryngeal muscles that act on the space between the vocal cords?
Open and close the space between the vocal cords.
What is the function of laryngeal muscles that act on the vocal cords themselves?
Tense and relax the vocal cords.
How do changes in vocal cord position affect sound?
They affect pitch and sound production.
What artery supplies the larynx from the superior thyroid artery?
Superior laryngeal artery.
: What artery supplies the larynx from the inferior thyroid artery?
Inferior laryngeal artery.
What nerve provides sensory innervation superior to the vocal folds?
Superior laryngeal nerve.
What nerve provides sensory innervation inferior to the vocal folds?
Recurrent laryngeal nerve.
What nerves provide motor innervation to the larynx?
Superior laryngeal nerve and recurrent laryngeal nerve.
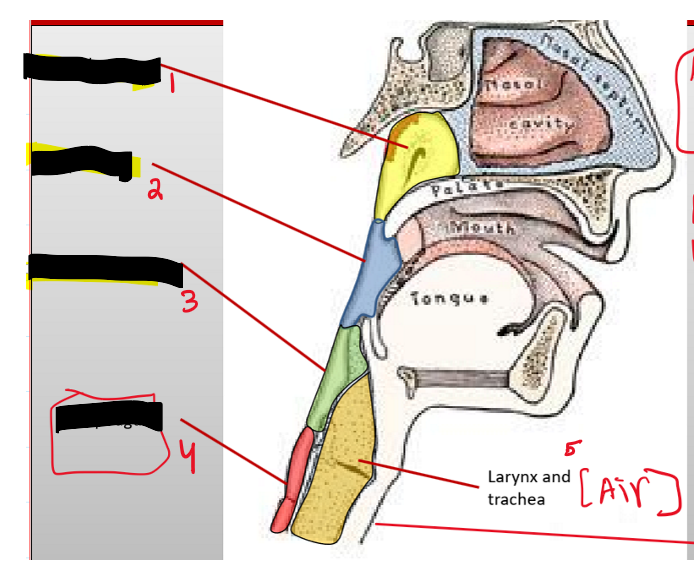
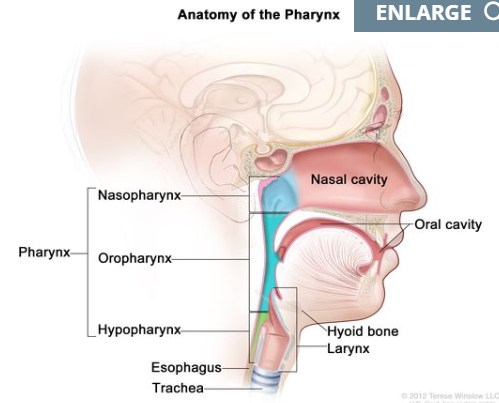
Name the structures (13)
Nasopharynx
Oropharynx
Laryngopharynx
If you damage these 2 nerves and they made you struggle to speak what are they?
Superior laryngeal and Inferior laryngeal nn.
The Pharynx serve 2 very important roles and they are?
Air passage - is always open except during swallowing
– Food passage - to swallow food, one must hold their breath
What are the 3 sections of the pharynx?
– Nasopharynx – Oropharynx – Laryngopharynx
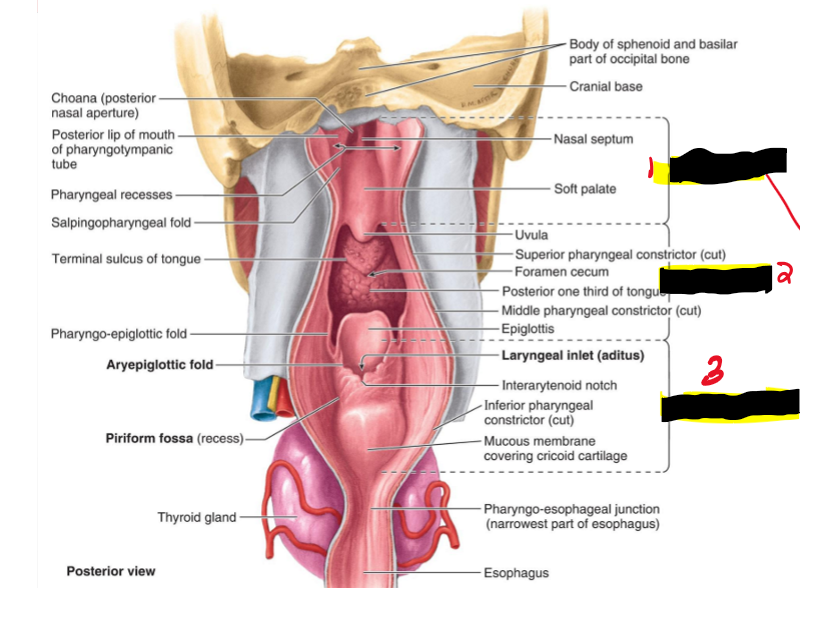
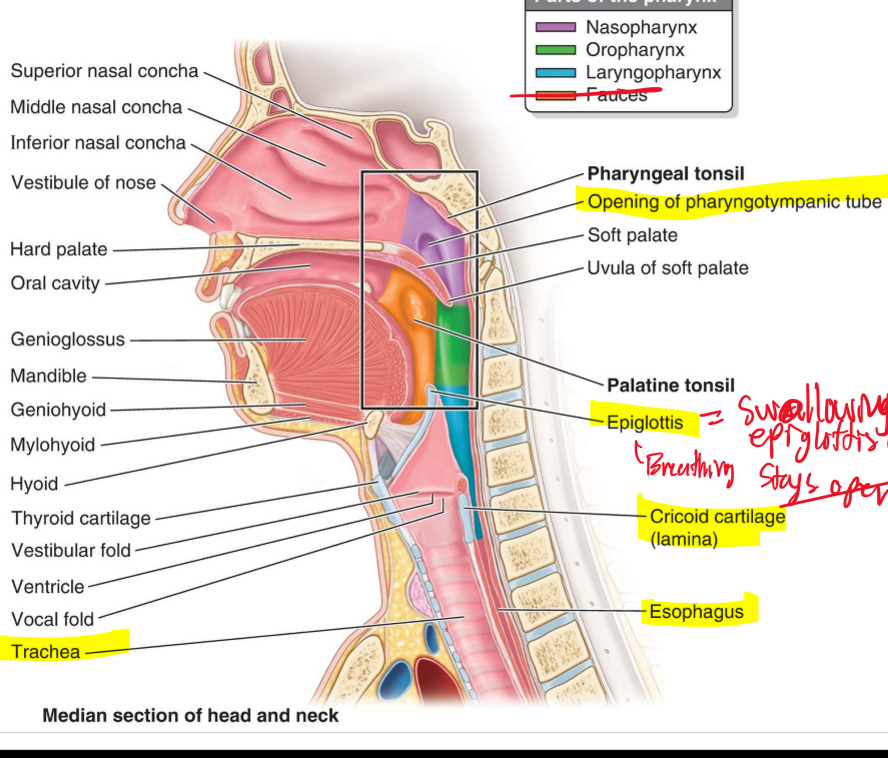
Name the structues. (14)
Nasopharynx
Oropharynx
Laryngopharynx
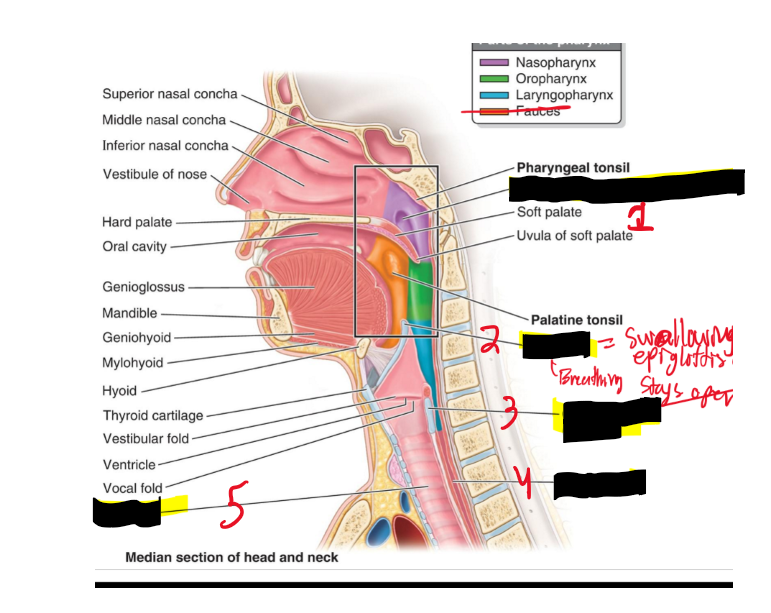
Name the structures. (15)
Opening of pharyngotympanic tube
Epiglottis
Cricoid cartilage [lamina]
What is the purpose of the epiglottis?
When swallowing it closes on top of the cricoid cartilage to prevent food going into the trachea.
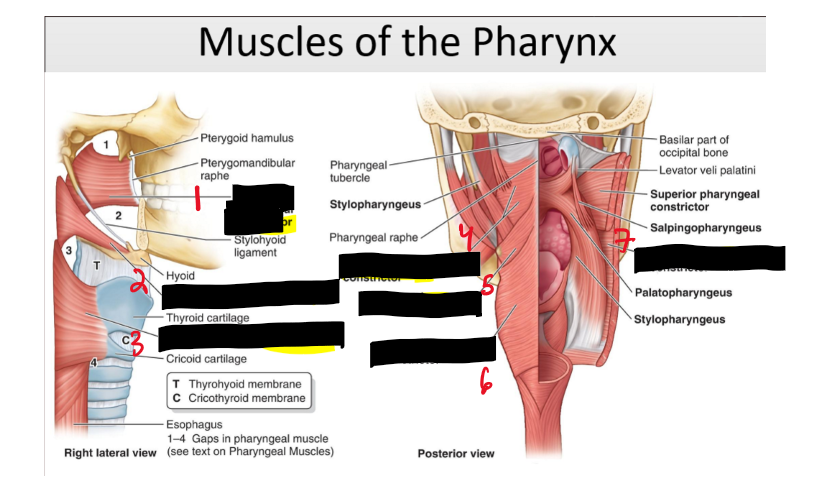
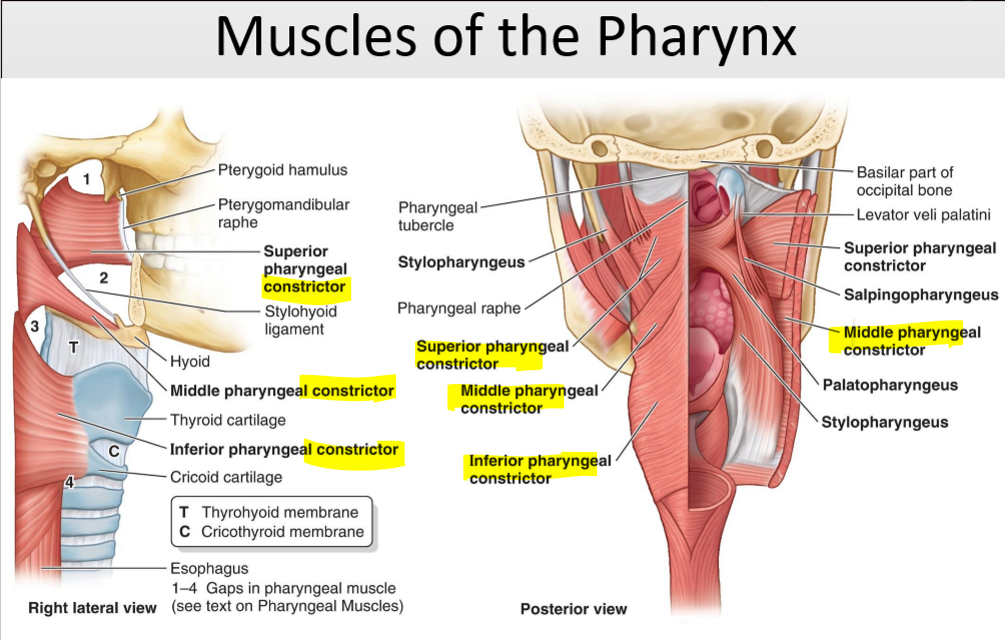
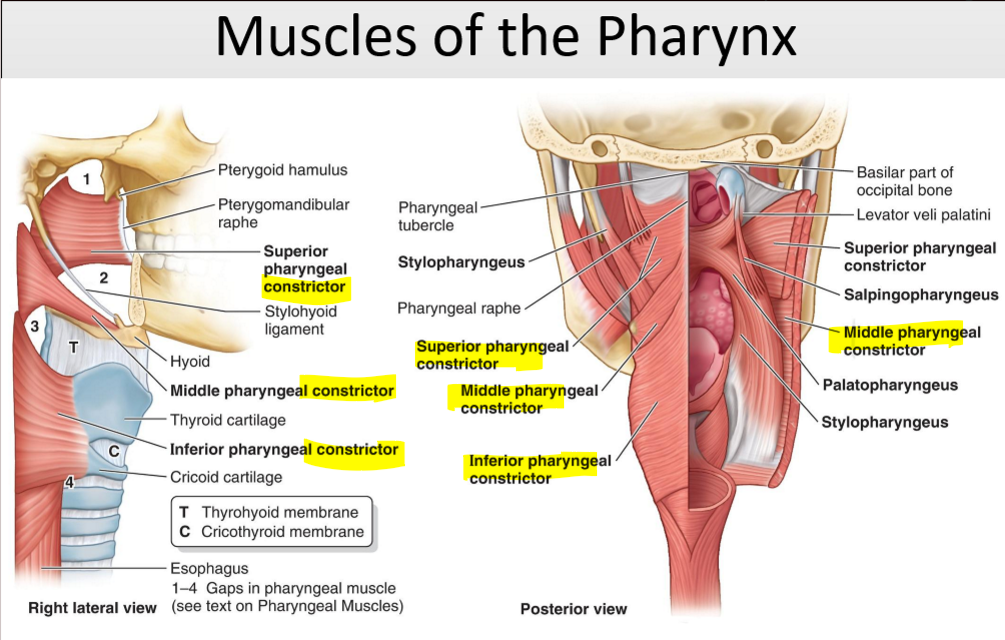
Name the structure. (16)
Superior Pharyngeal constrictor
Middle Pharyngeal constrictor
Inferior Pharyngeal constrictor
Superior
Middle
Inferior
Middle
What are the three pharyngeal constrictor muscles?
Superior, middle, and inferior constrictors.
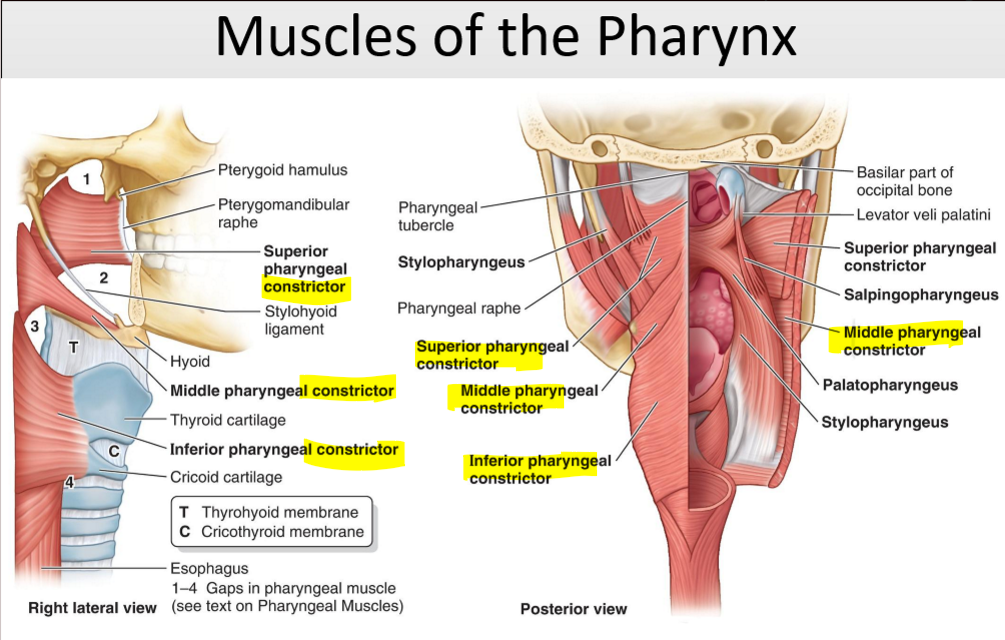
What is the function of the pharyngeal constrictor muscles?
Constrict the pharynx and propel food to the esophagus.
What is the function of the pharyngeus muscles?
Elevate the pharynx and larynx during swallowing.
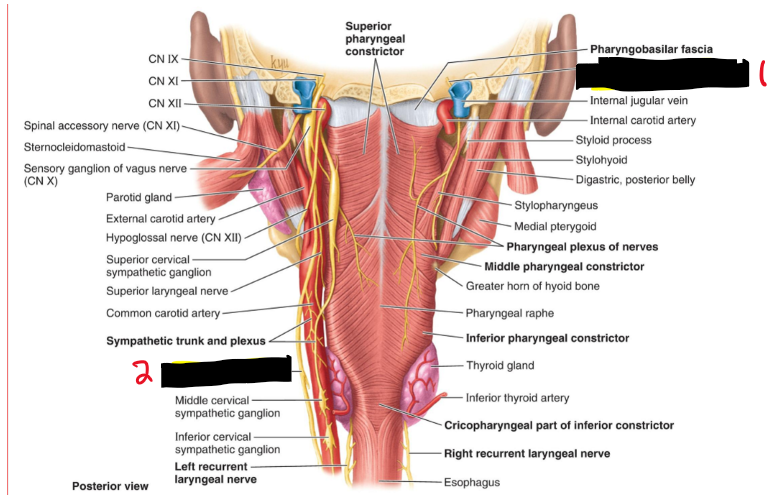
Name the structure. (17)
Glossopharyngeal n.
Vagus n [CN X]
What nerve provides motor innervation to the pharynx via the pharyngeal plexus?
Vagus nerve (CN X).
What nerve provides sensory innervation to the pharynx via the pharyngeal plexus?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).
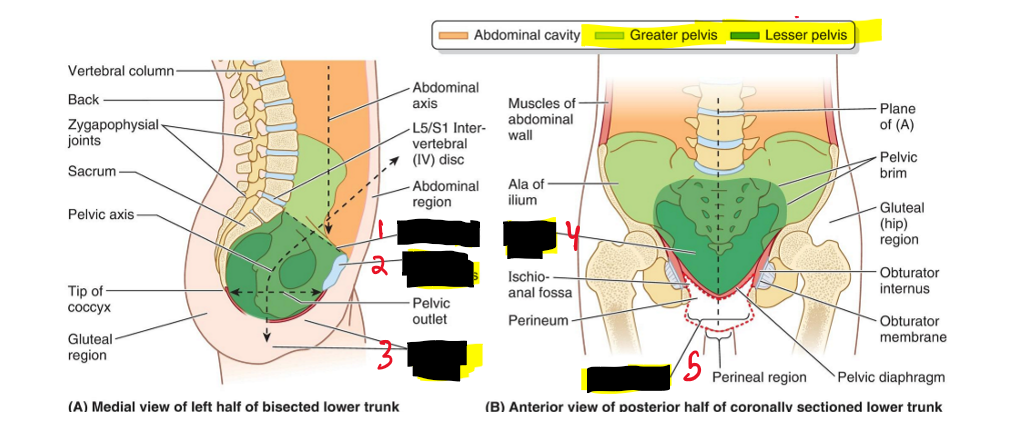
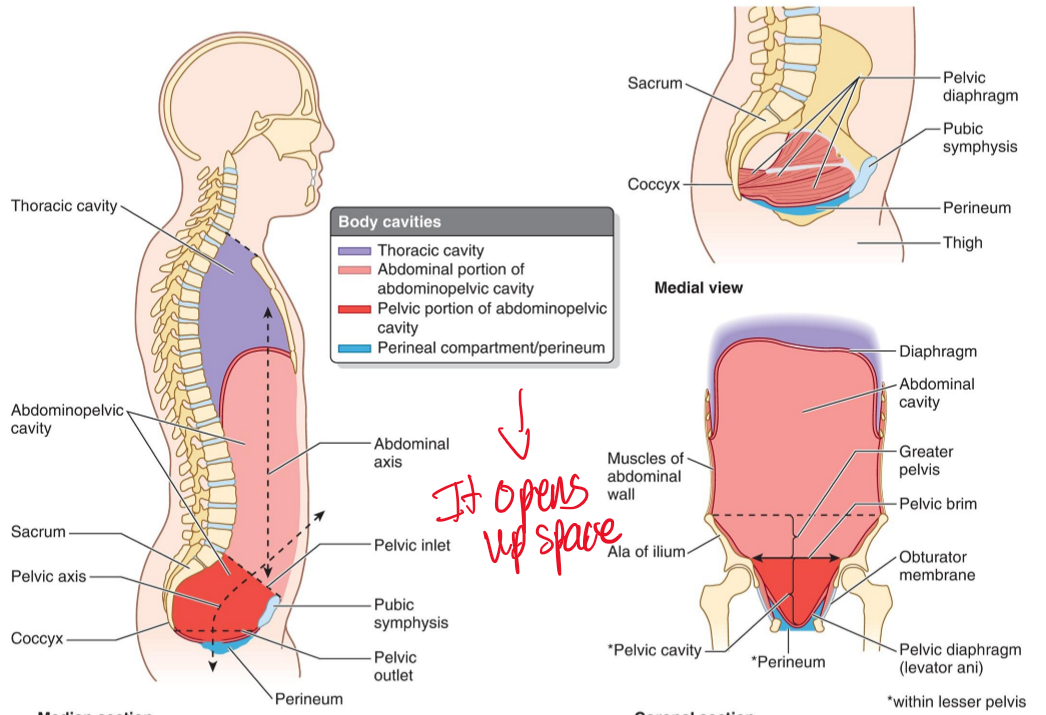
Name the structures. (18)
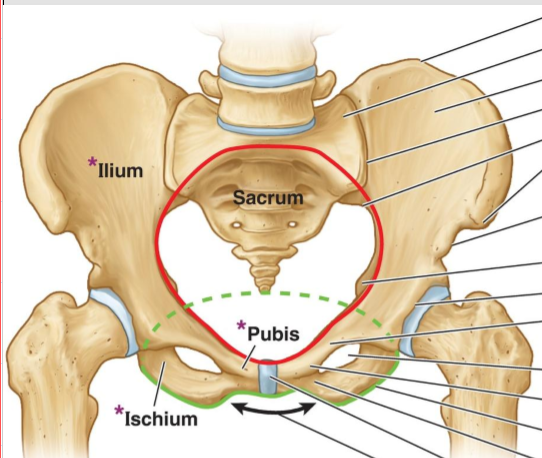
Pelvic inlet
Pubic symphysis
Perineal region
Pelvic cavity
Pelvic outlet
How is a bolus of food moved from the oral cavity to the oral pharynx?
By the tongue after mastication.
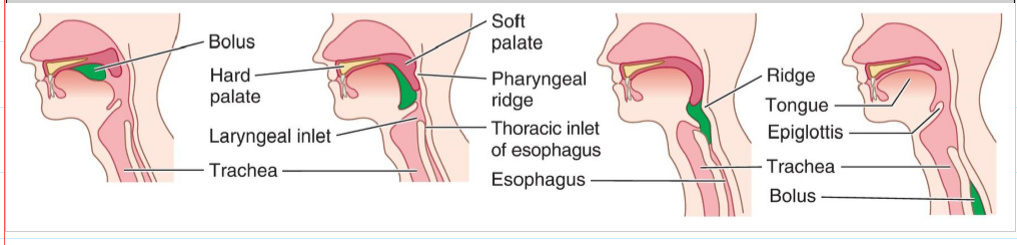
How is the nasopharynx protected during swallowing?
Muscular contraction of the soft palate prevents food from entering the nasal cavity.
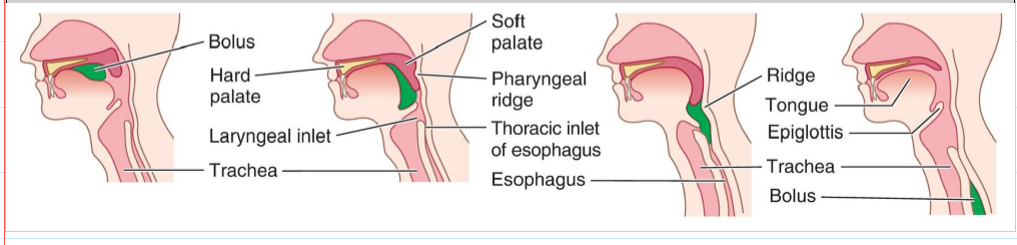
What is the function of the inlet constrictors of the larynx during swallowing?
Prevent the bolus from entering the trachea (prevent aspiration).
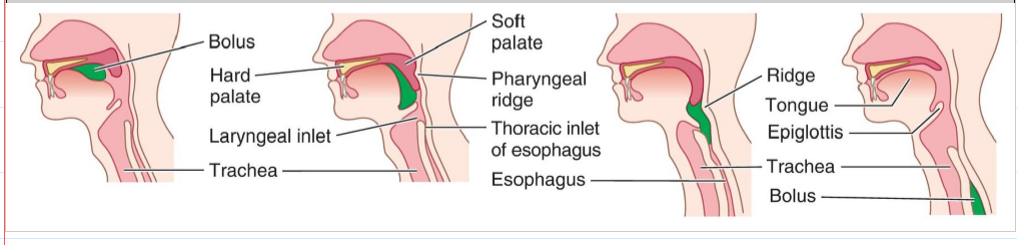
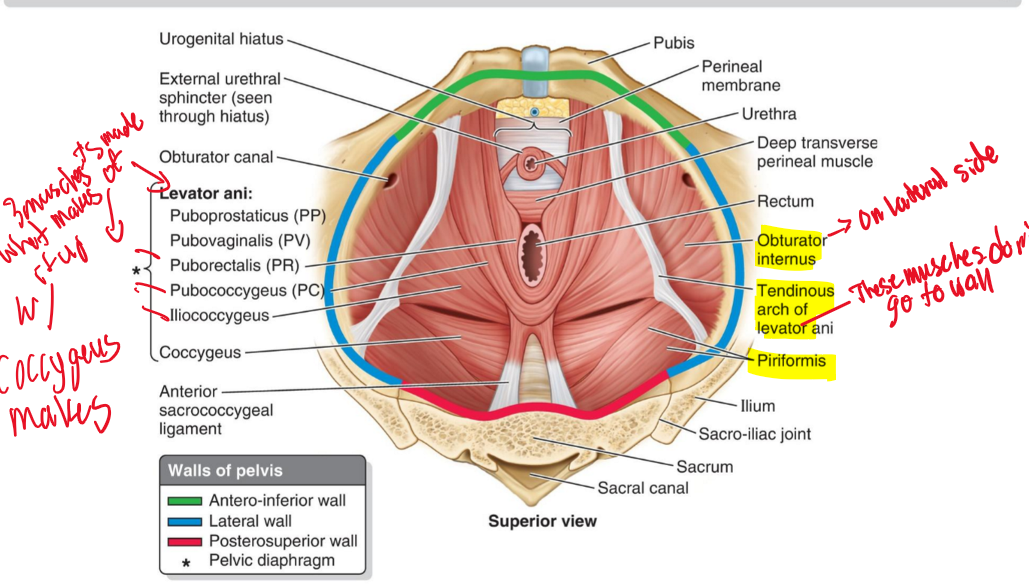
Name the structure. (19)
Obturator internus
Tendinous arch of levator ani
Piriformis
The greater pelvic relates to what?
wider part of ilium
The lesser pelvic relates to what?
inside the pelvic.
What is the pelvic opening?
Superior opening and is consider the pelvic floor
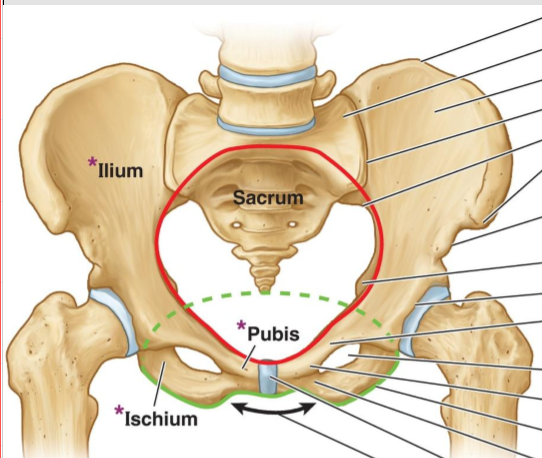
What is the pelvic outlet?
Closed by the pelvic diaphragm and is considered outside of pelvic floor
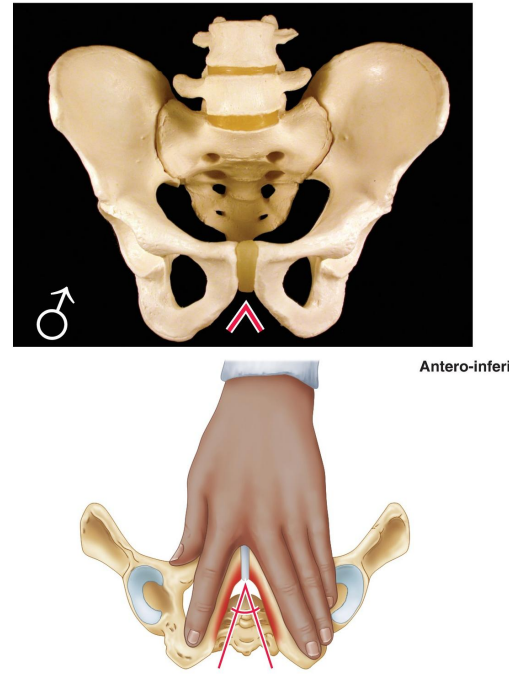
How is the general structure of the male pelvis described?
Thick and heavy.
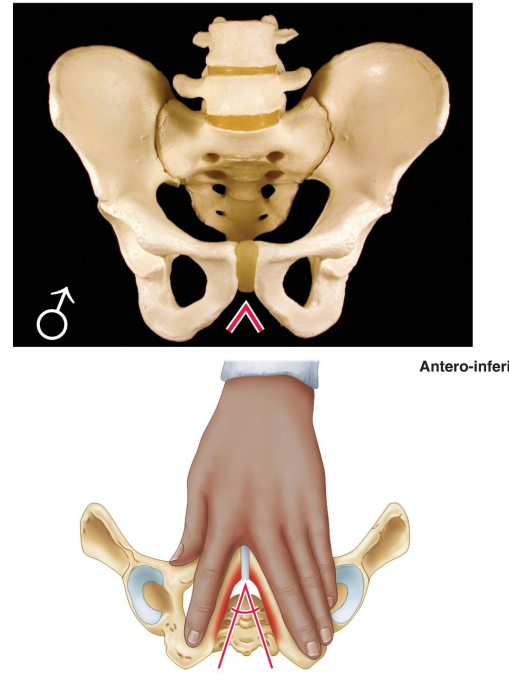
Describe the greater pelvis (false pelvis) in males.
Deep.
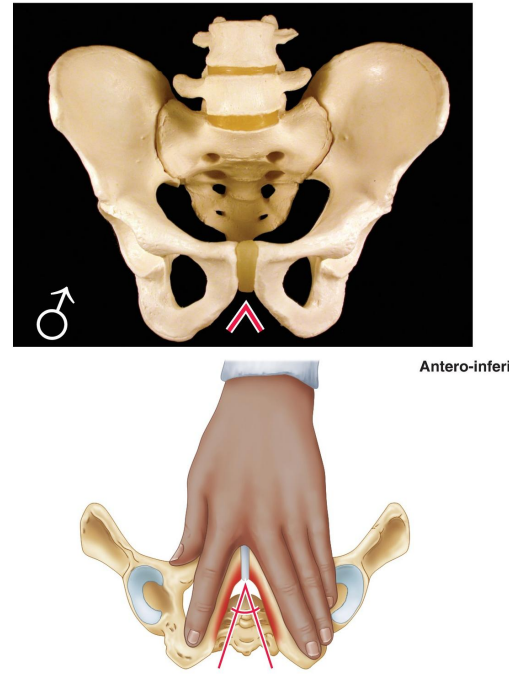
Describe the lesser pelvis (true pelvis) in males.
Narrow and deep.
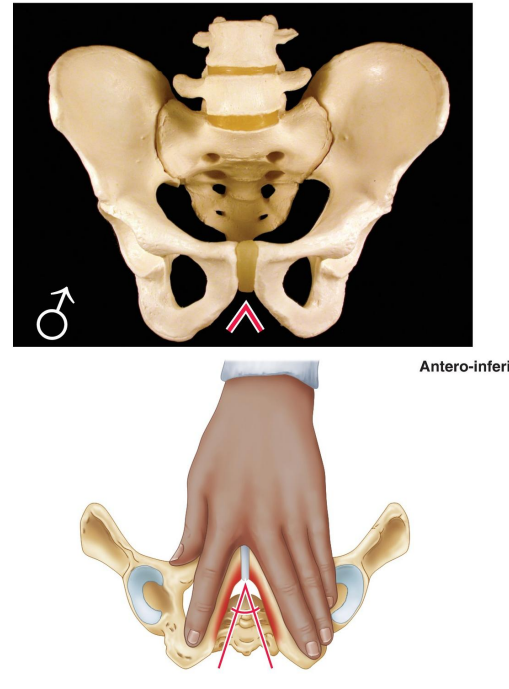
What is the shape of the male pelvic inlet?
Heart shaped.
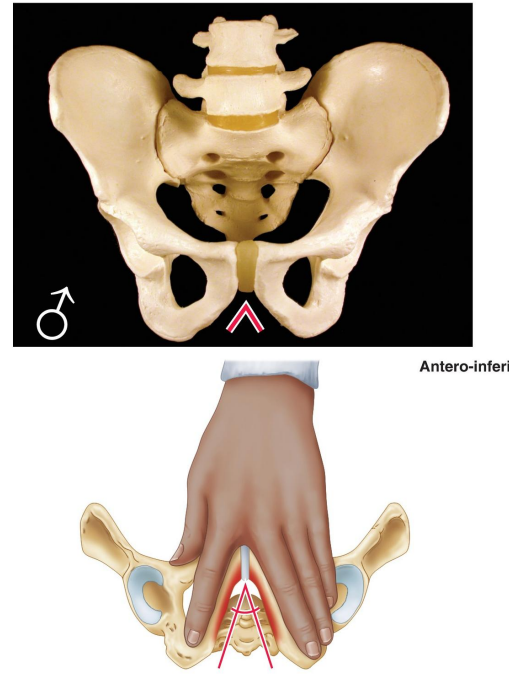
How is the male pelvic outlet described?
Small.
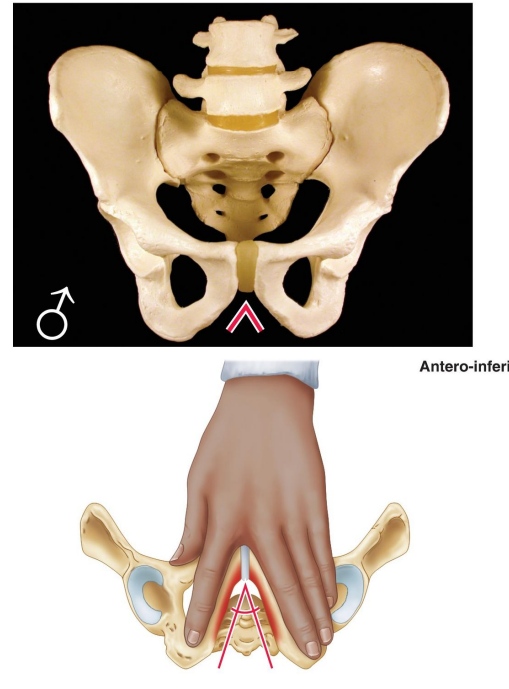
What is the angle of the male pubic arch?
Narrow, less than 70°.
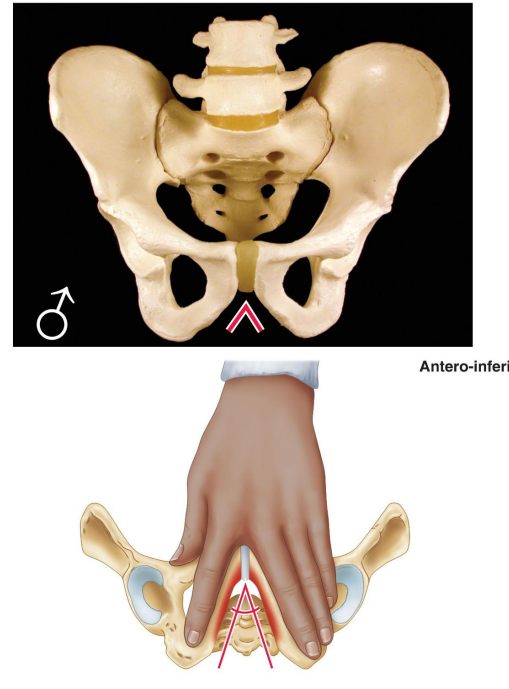
What is the shape of the male obturator foramen?
Round.
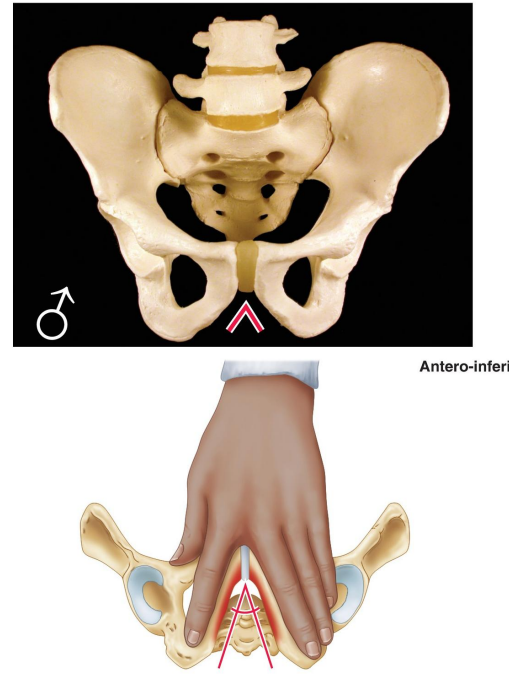
How is the male acetabulum described?
Large.
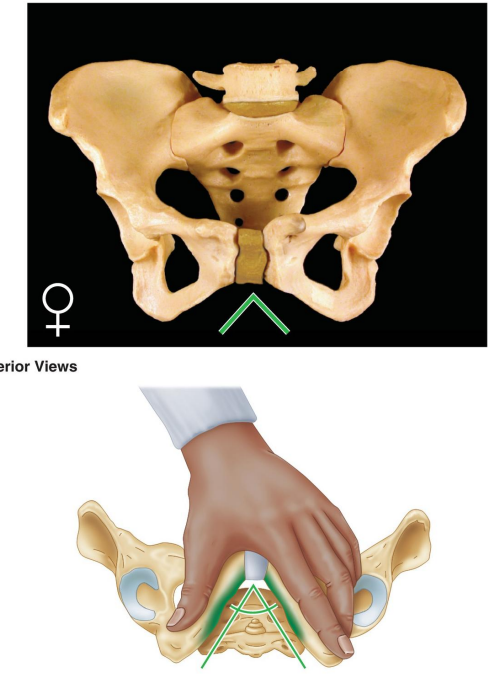
: How is the general structure of the female pelvis described?
Thin and light.
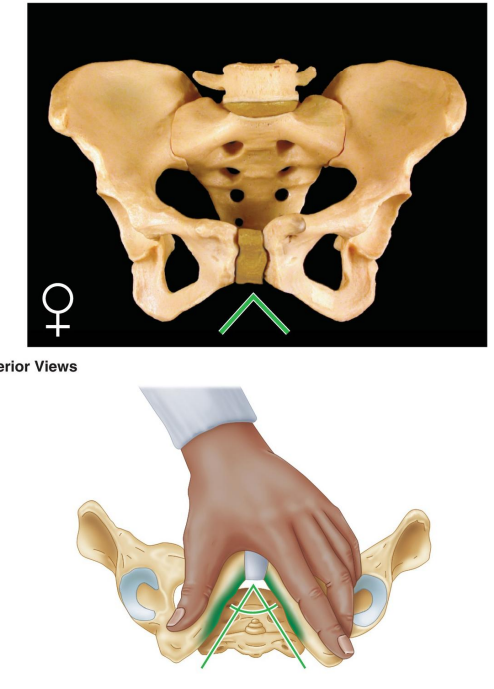
Describe the greater pelvis (false pelvis) in females.
Shallow.
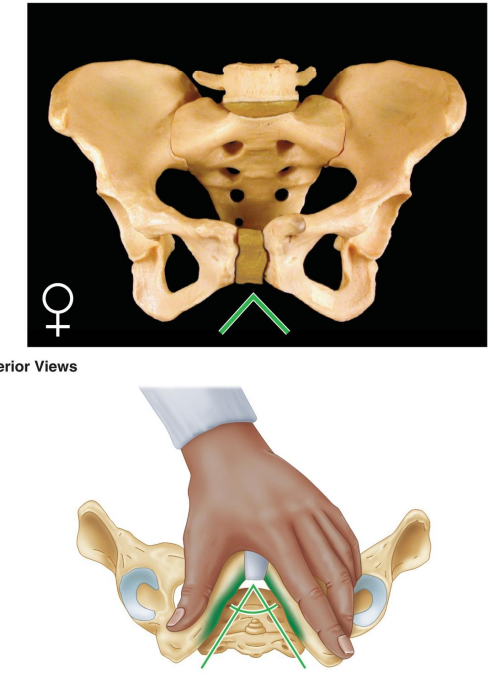
Describe the lesser pelvis (true pelvis) in females.
Wide and shallow.
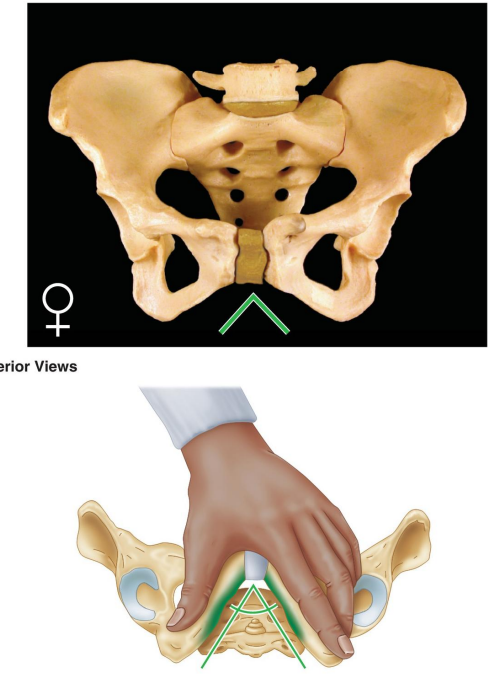
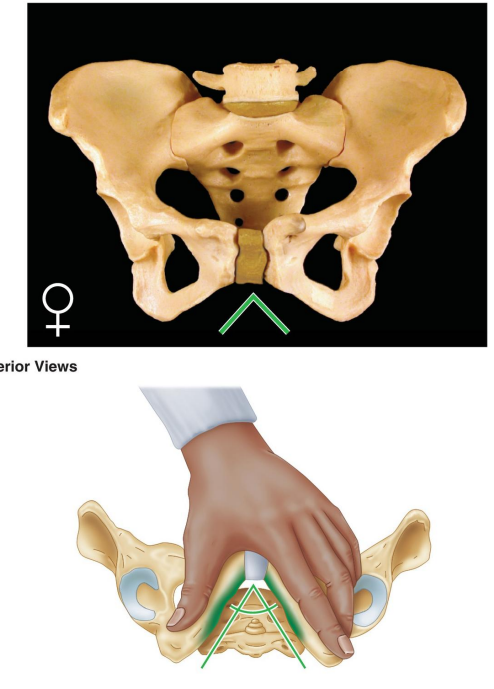
What is the shape of the female pelvic inlet?
Oval and rounded.
How is the female pelvic outlet described?
Large.
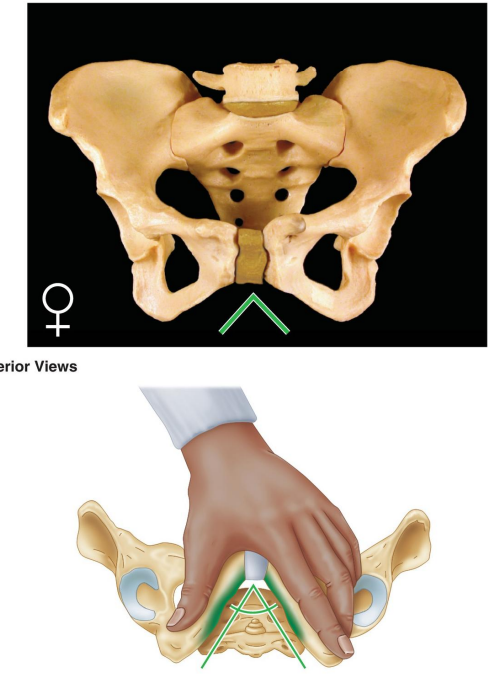
What is the angle of the female pubic arch?
Wide, greater than 80°.
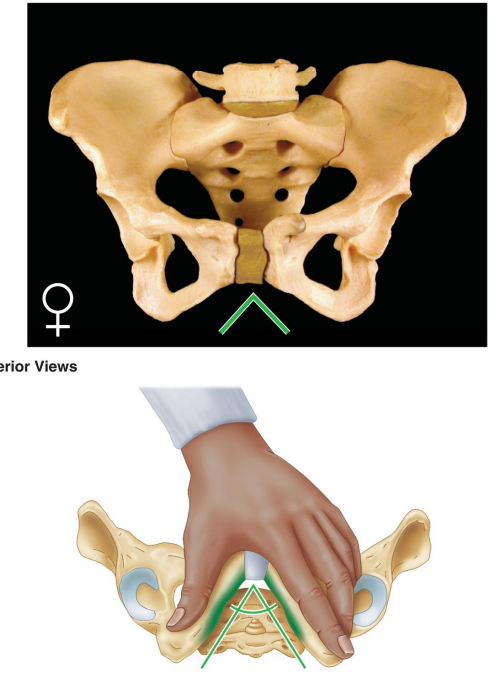
What is the shape of the female obturator foramen?
Oval.
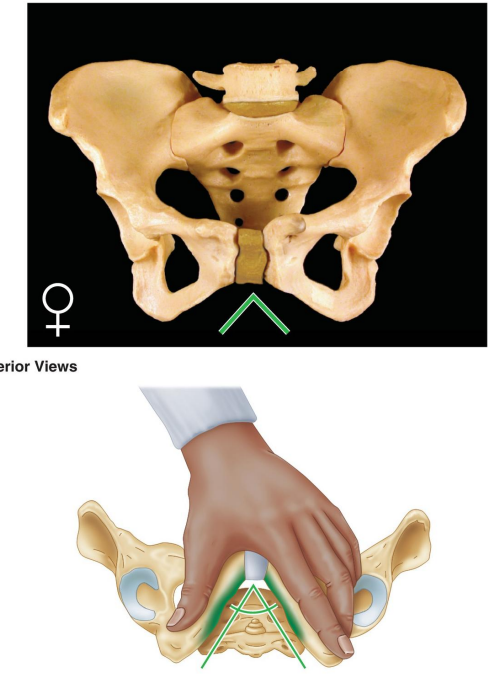
How is the female acetabulum described?
Small.
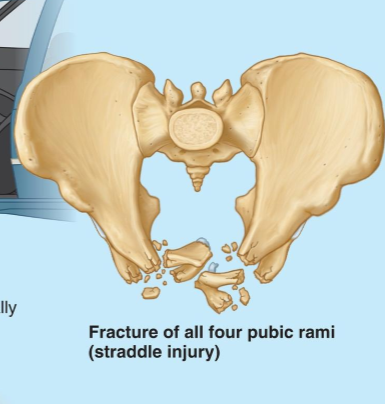
What kind of injury is this
(CALLED A STRADDLE INJURY) This happens most of the time in a car accident when the individual is not wearing a seatbelt
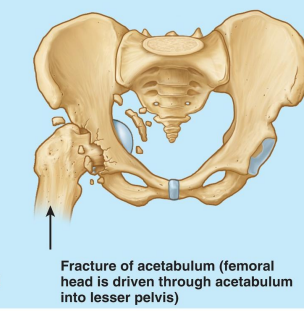
What kind of injury is this?
Fracture of the acetabulum when the head of the femur fractures through the acetabulum into the lesser pelvis
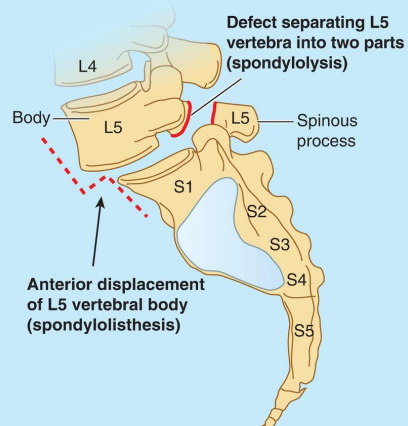
What injury is this?
Anterior displacement of L5 vertebral body (spondylolisthesis)
What forms the pelvic floor?
The funnel-shaped pelvic diaphragm.
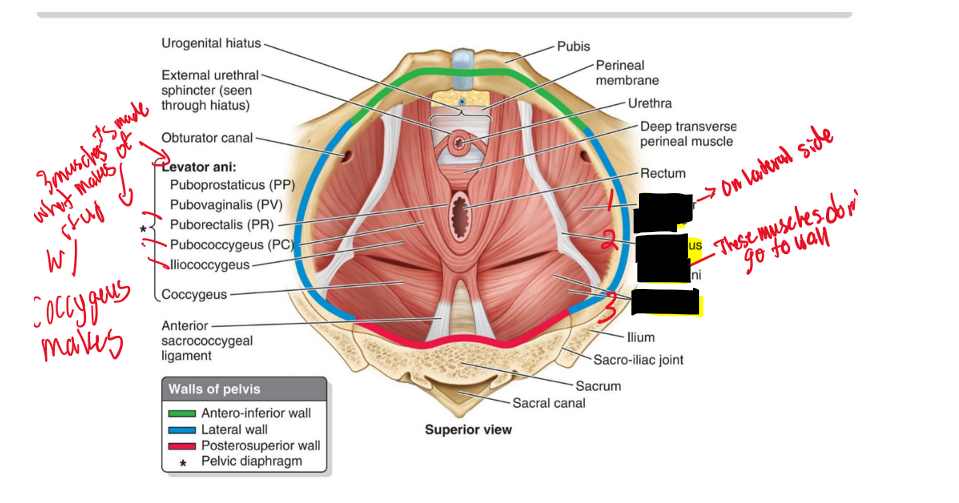
What muscles make up the pelvic diaphragm?
Levator ani and coccygeus.
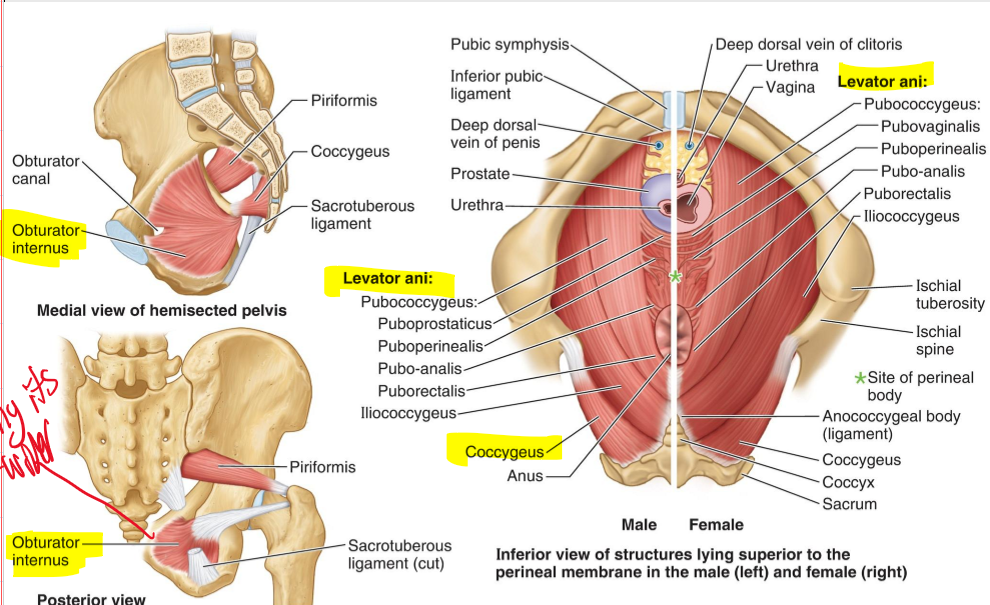
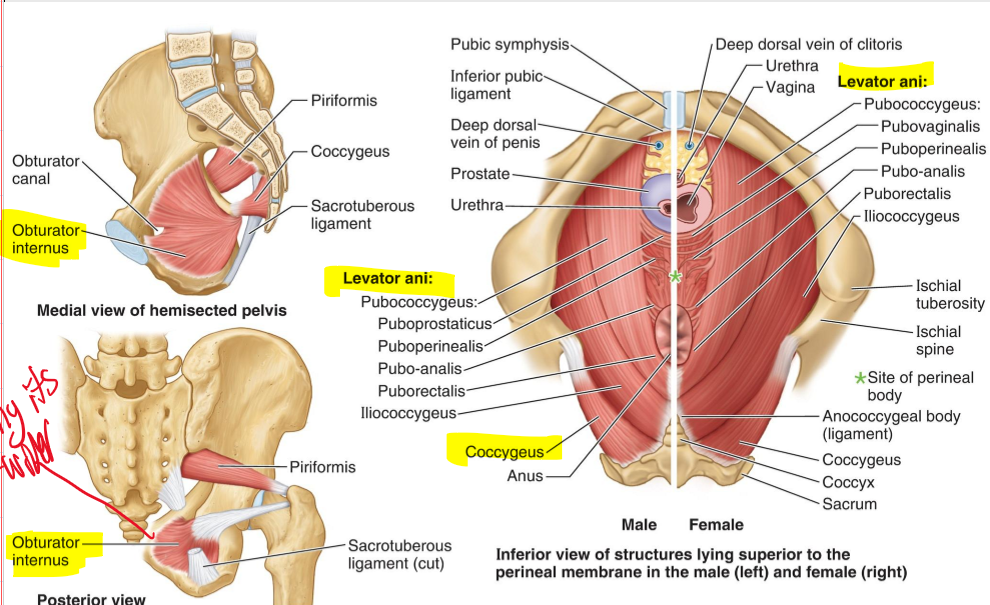
From where to where does the pelvic diaphragm stretch anteriorly to posteriorly?
From the pubis to the coccyx.
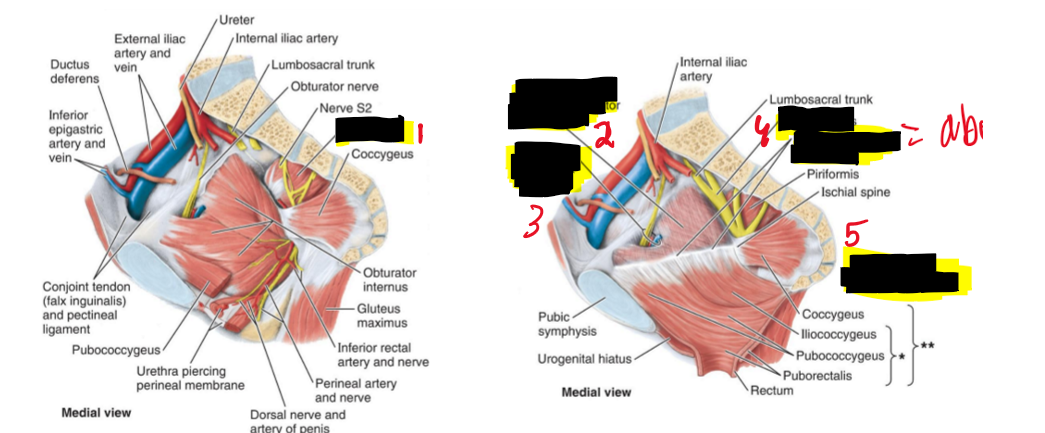
Name the structure.
Piriformis
Obturator fascia covering obturator internus
Obturator nerve and vessels
Sacral plexus
Tendinous arch of levator ani
Levator ani and Pelvic diaphragm
Pubococcygeus + Iliococcygeus=
Levator Ani (LA)
Male: Puborectalis(PR)+ Puboprostaticus (PP)= Pubococcygeus (PC)
Pubococcygeus (PC)
Female: Puborectalis (PR) + Pubovaginalis (PV)=
Pubococcygeus
Levator ani (LA) + Coccygeus (C)=
Pelvic diaphragm (PD)
What is the most important muscle group in the pelvic floor?
Levator ani
What muscles compose the levator ani?
Pubococcygeus, puborectalis, and iliococcygeus.
What action does the levator ani perform?
Forms a muscular sling supporting abdominopelvic viscera and holds pelvic viscera in position. [important to have these muscles because there are no bones to support this area]
How does the levator ani assist in abdominal compression?
Helps compress the abdominopelvic cavity during coughing, sneezing, vomiting, etc.
Which nerve is traditionally said to innervate the pelvic floor?
Pudendal nerve and its branches.
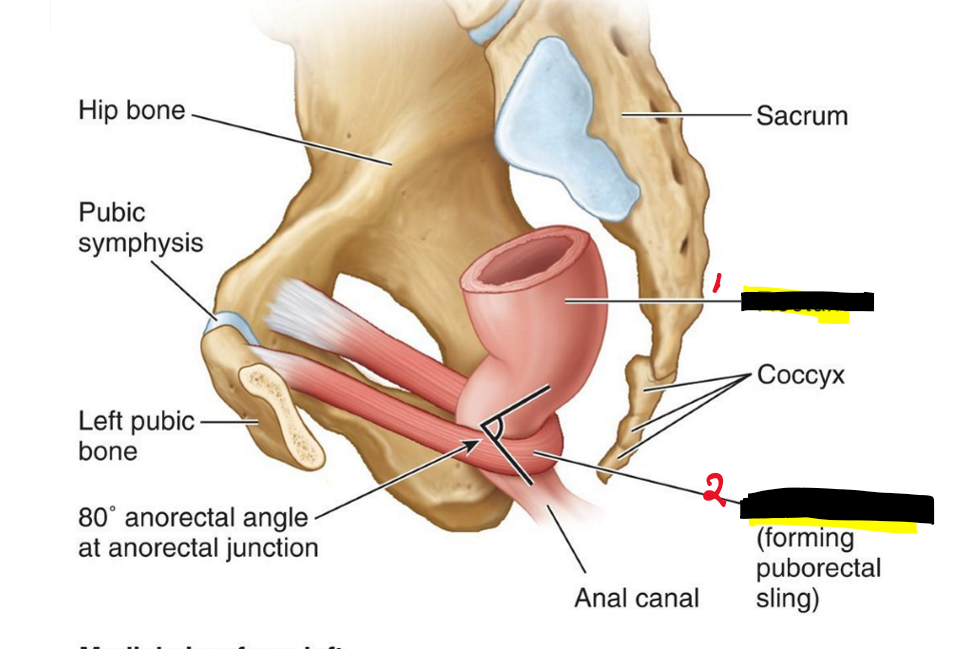
Name the structures. (21)
Rectum
Puborectalis(form the sling)
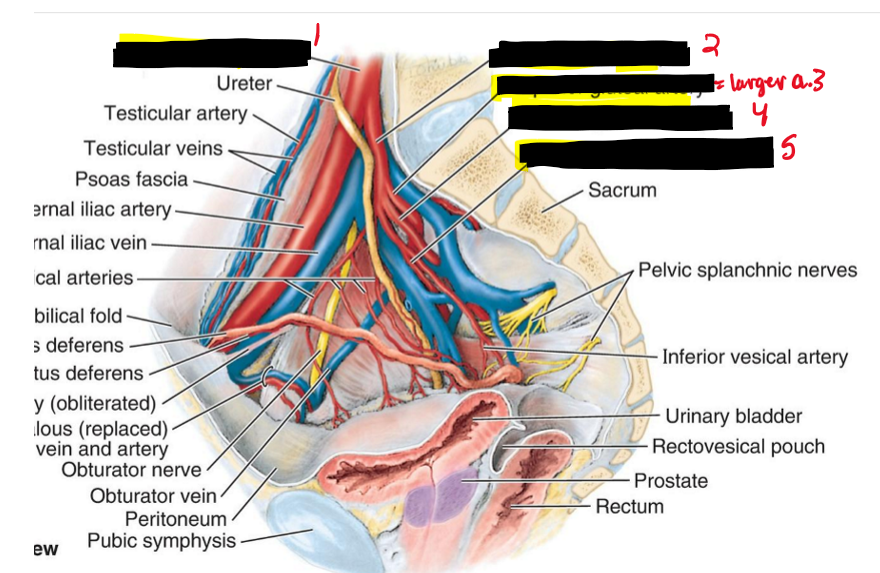
Name the structure (22)
Common iliac a.
Internal iliac a.
Superior gluteal a.
Inferior gluteal a.
Internal pudendal a.
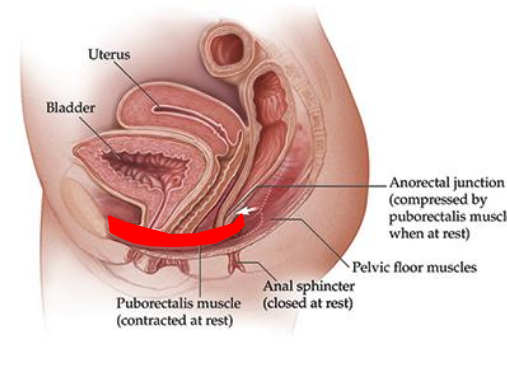
At rest is the puborectalis muscles contracted or relaxed?
Contracted at rest!!
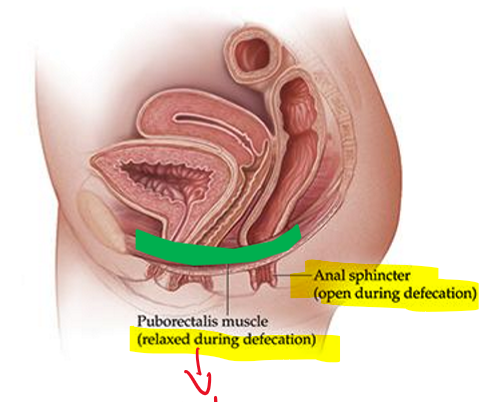
During defecation is the puborectalis muscles contracted or relaxed?
It is relaxed which allows the sphincter to be open!
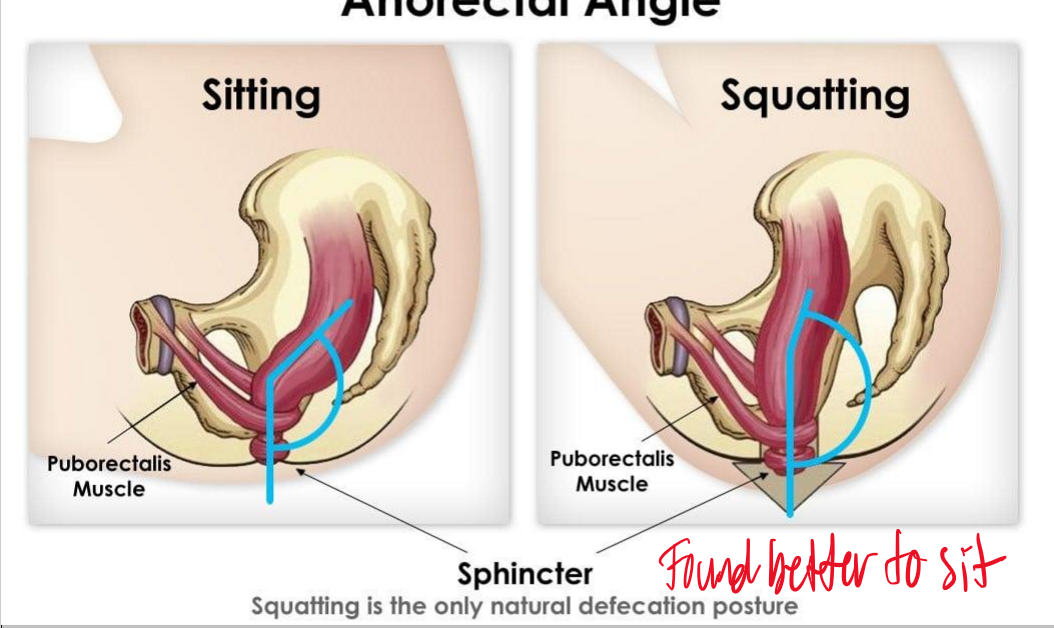
When defecating is it found better to sit or squat and why?
It is better to squat because the sphincter is in a natural angle
How does the pelvic floor function during inhalation?
Pelvic floor muscles loosen to increase pelvic floor space while the diaphragm contracts downward.
What artery is the main supplier to the pelvic region?
Internal iliac a.