Unit 4: Reproduction
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
sprem cells that are not chosen by the egg are
have their heads cut off
sperm is _____ to the egg
attracted to the egg by chemoattractants that the egg secretes
genotypic sex
sex chromosomes
XX or XY
gonadal sex
having testis vs ovaries
where gametes are stored
phenotypic sex
if something upstream goes wrong
DSD
differences in in sex development
ex: being intersex, which can involve having XXX, XYY, or just a single chromosome
so you can be insensitive to male hormones and have atypical testes or be XX but receive male hormones leading to ambiguous genitalia
mammalian sex determination
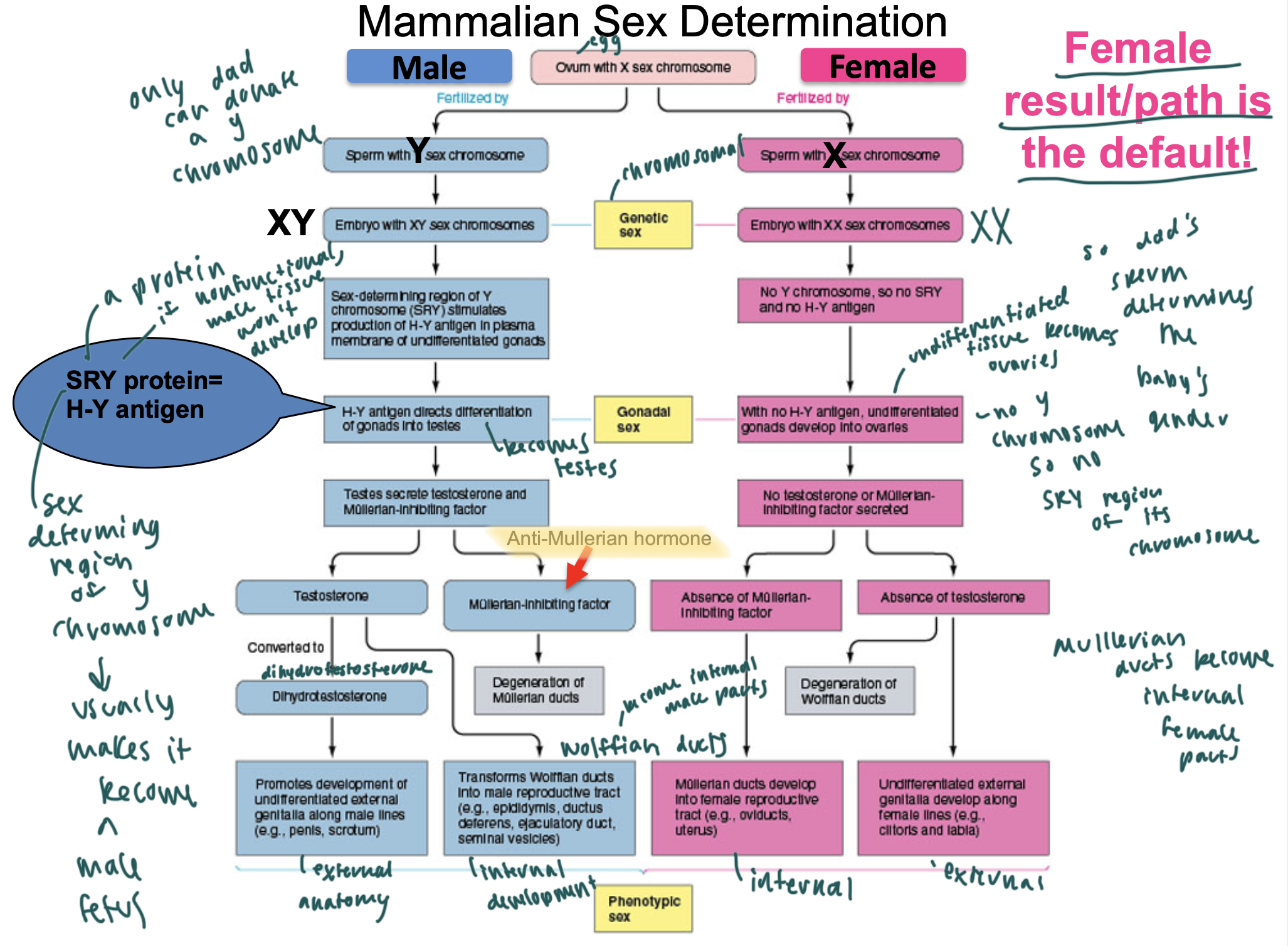
SRY protein
a protein that is sex-determining and stimulates production of the H-Y antigen, leading to differentiation of gonads into testes (so male parts)
so makes the fetus a male fetus (default is for the fetus to become female)
anti-mullerian hormone
aka mullerian-inhibiting factor
causes degeneration of the mullerian ducts (which create female parts normally)
testesterone
causes the wolffan ducts to become the epididymus, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, seminal vesicles
so the internal male parts develop from the wolffan ducts
dihydrotestesterone
DHT
promotes development of male external anatomy
so penis, scrotum
what happens if the SRY protein is nonfunctional?
then male tissue will not develop
mullerian ducts when developed cause
development of internal female parts
oviducts, uterus
absence of testosterone causes ____ in development of a fetus
degeneration of the wolffan ducts, s female external parts develop instead
clitoris
labia
what determines the baby’s gender
the sperm since it either adds a X or a Y to the preexisting X
what happens if the fetus lacks the H-Y antigen
the previously undifferentiated gonads will develop into the overies
female is the default
gender
genetic sex is determined by
the chromosomes
either XX or XY
undifferentiated gonads develop into
ovaries
everyone is ____ at conception
identical
so has a bipotential stage
since the cell lacks differentiated sex organs here and doesn’t differentiate until about 7 weeks
if there is a problem with the anti-mullerian hormone, then
you could have both mullerian ducts and wolffan ducts
sex differentiation

if you are “6 weeks pregnant” you have only missed your period for
2 weeks
so the fetus has only actually existed for 4 weeks
male sex differentiation
starts if you have an XY chromosome with a functional SRY protein
so functional SRY protein causes gonads to develop into the testes
leydig cells: secretes T, causing development of the wolffian ducts, causing development of male external genitalia
sertoli cells: secretes anti-mullerian hormone, causing regression of mullerian duct, so you don’t develop internal female anatomy
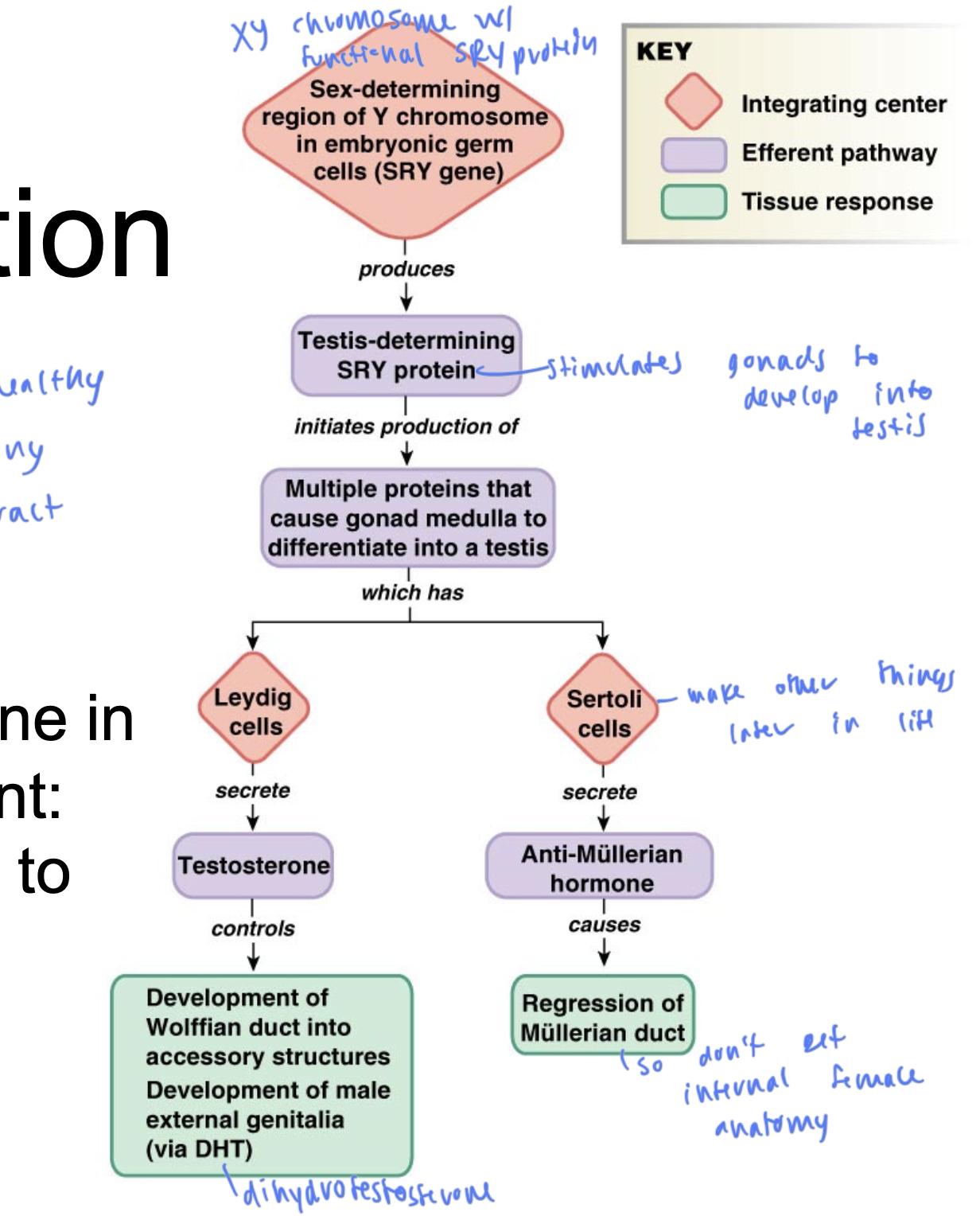
higher T corresponds to higher
sex drive
evolution wants males to have
large numbers of gametes that are healthy and can live for a bit in the female reproductive tract
sperm is produced in the
testes
sperm need to be at a temp
about 3º C lower than body temp
male anatomy
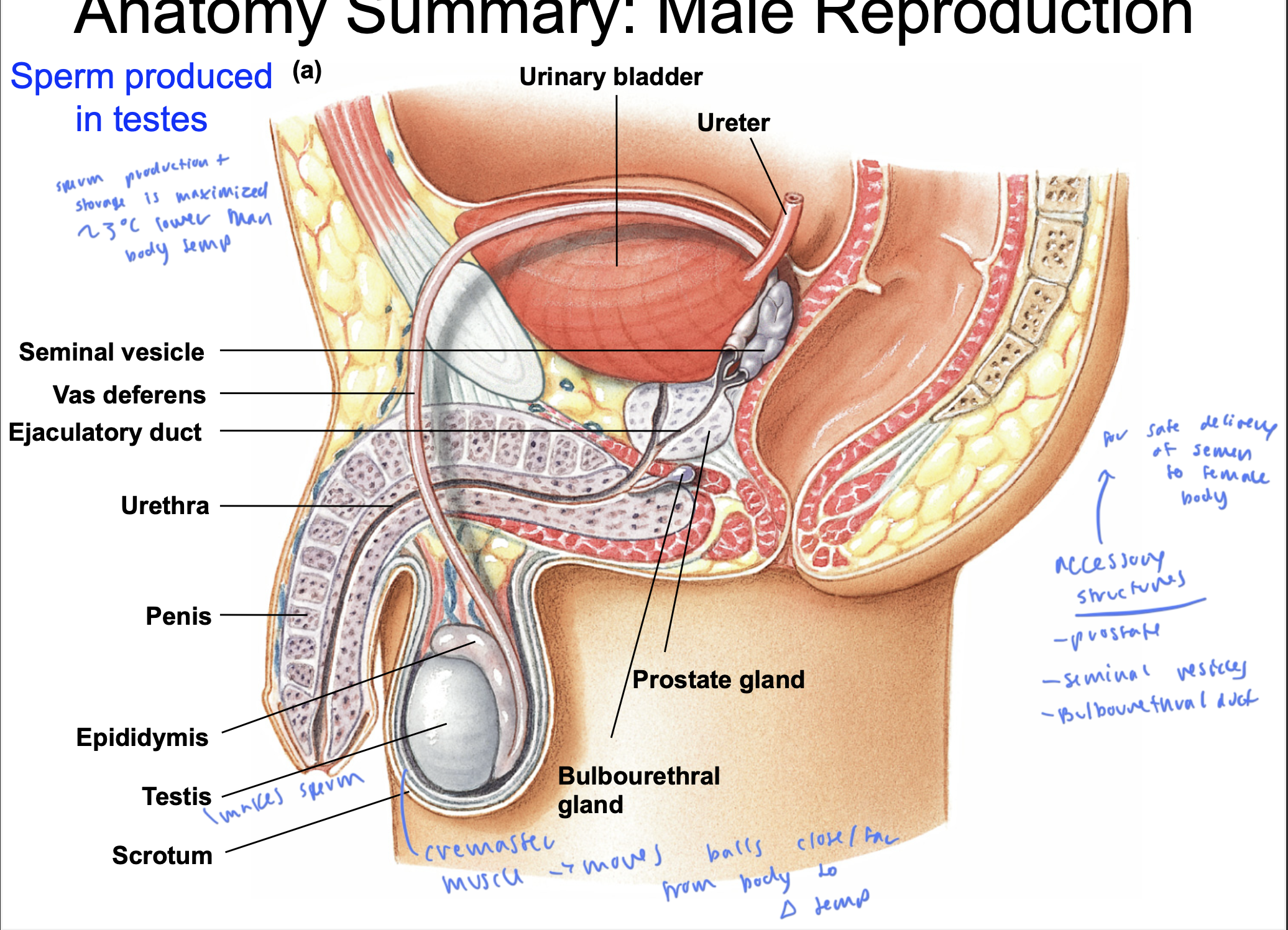
accessory structures of male anatomy
prostate
seminal vesicles
Bulbouerthral duct
as help the semen get delivered safl;y to the female party
cremaster muscle
moves the testes closer and farther from the body to regulate theor temp
testes make
sperm
where are the gametes from a male?
in the sperm
there is a spike in ____ after ejaculation in males
vasopressin
which helps bring the fluid volume back up after you lost some
sperm can live for _____ in the vagina
5 days
so need nourishment from fructose and vitamins to last until then
vasectomy
vas deferens is clamped or snipped off so sperm cannot enter semen
so semen has everything else besides the sperm that it would normally have
zinc in semen
has an unknown function, but is possibly associated with fertility
enzymes help the sperm
clot then liquify so it can swim to the egg
peristaltic contractions on semen
helps aid in sperm transport
peristaltic contractions in women help
induce contractions
sperm is developed in the
seminiferous tubules
mucus in sperm is developed
in the bulbourethral glands
water in semen is developed in
all the accessory glands
nutrients for sperm are developed
in
seminal vesicles
prostate
seminal vesicles
epididymis
enzymes for semen are from
seminal vesicles and the prostate
prostaglandins that induce peristaltic contractions to aid in sperm transport are generated in the
seminal vesicles
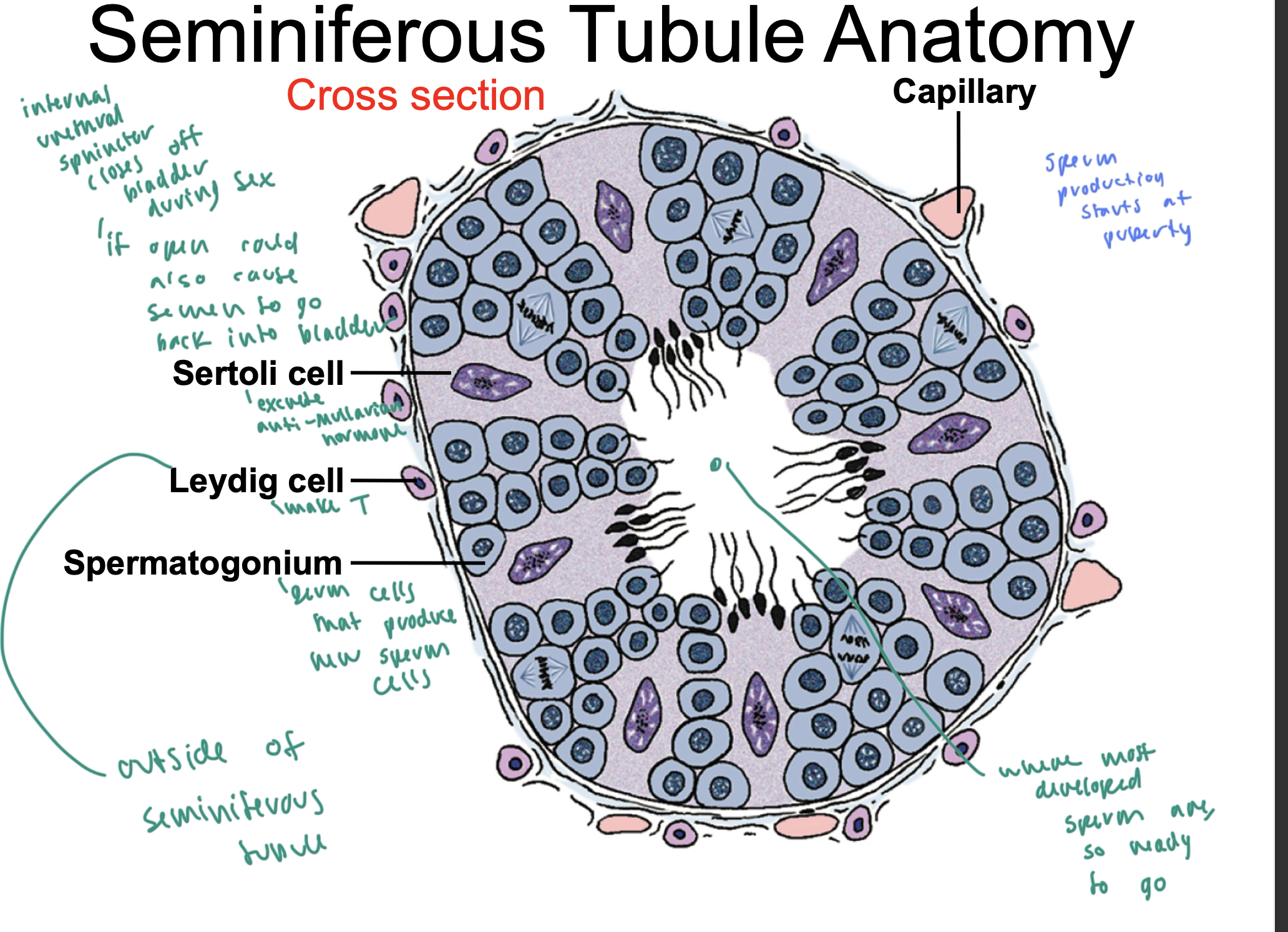
testes anatomy
coiled tubes are the seminiferous tubules, which make sperm
they then merge into the epididymis, which then merges into the vas deferens
the seminiferous tubules have both sertoli cells and spermatogonia
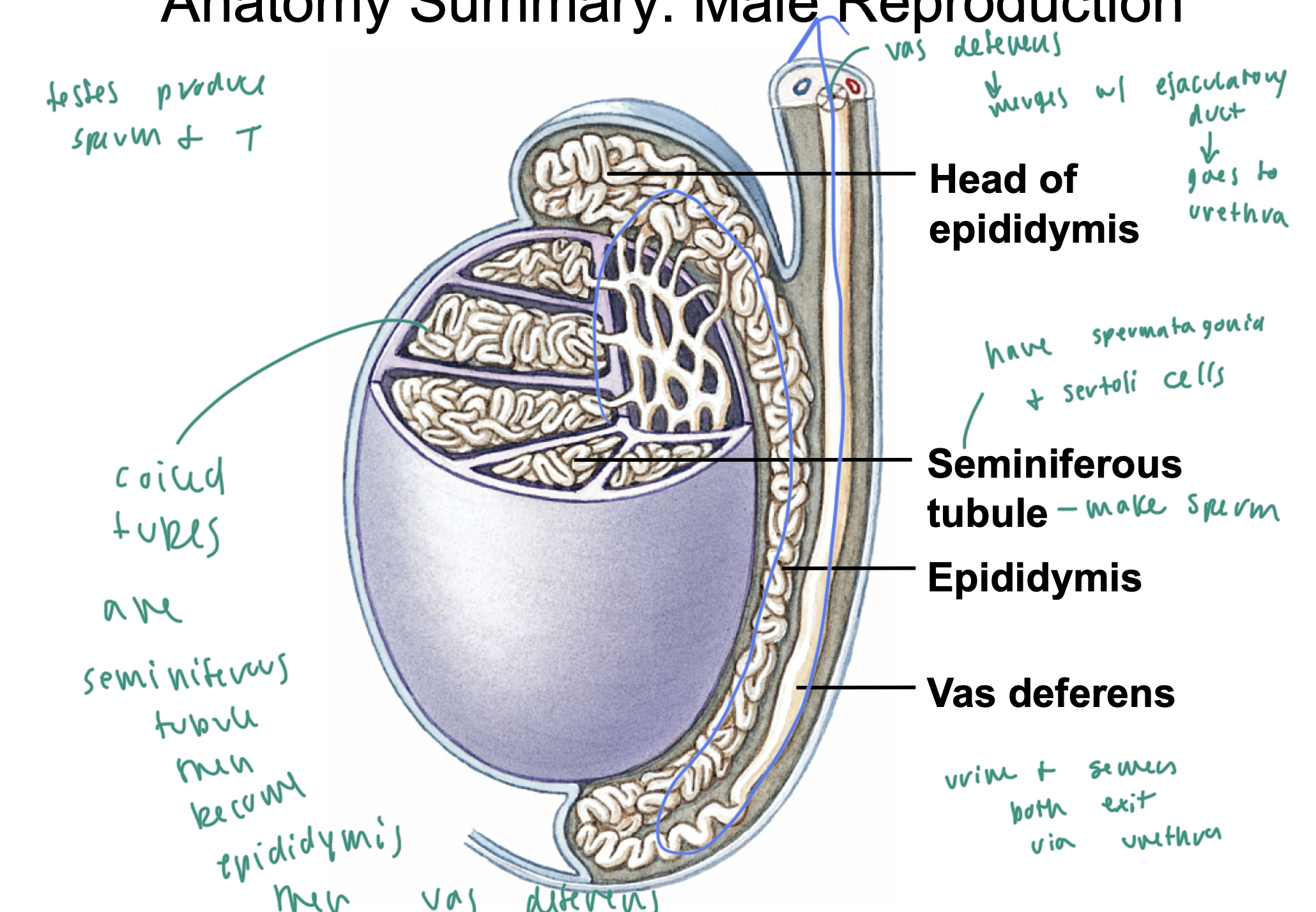
urine and semen both exit via
the urethra
the vas deferens merges with
the ejaculatory duct
seminiferous tubule anatomy
leydigs cells are on the exterior of the tubule: make T
sertoli cells are in the middle part of the tubule: excrete anti-mullerian hormone
spermatogonium cells cluster in the tubule and produce new sperm cells
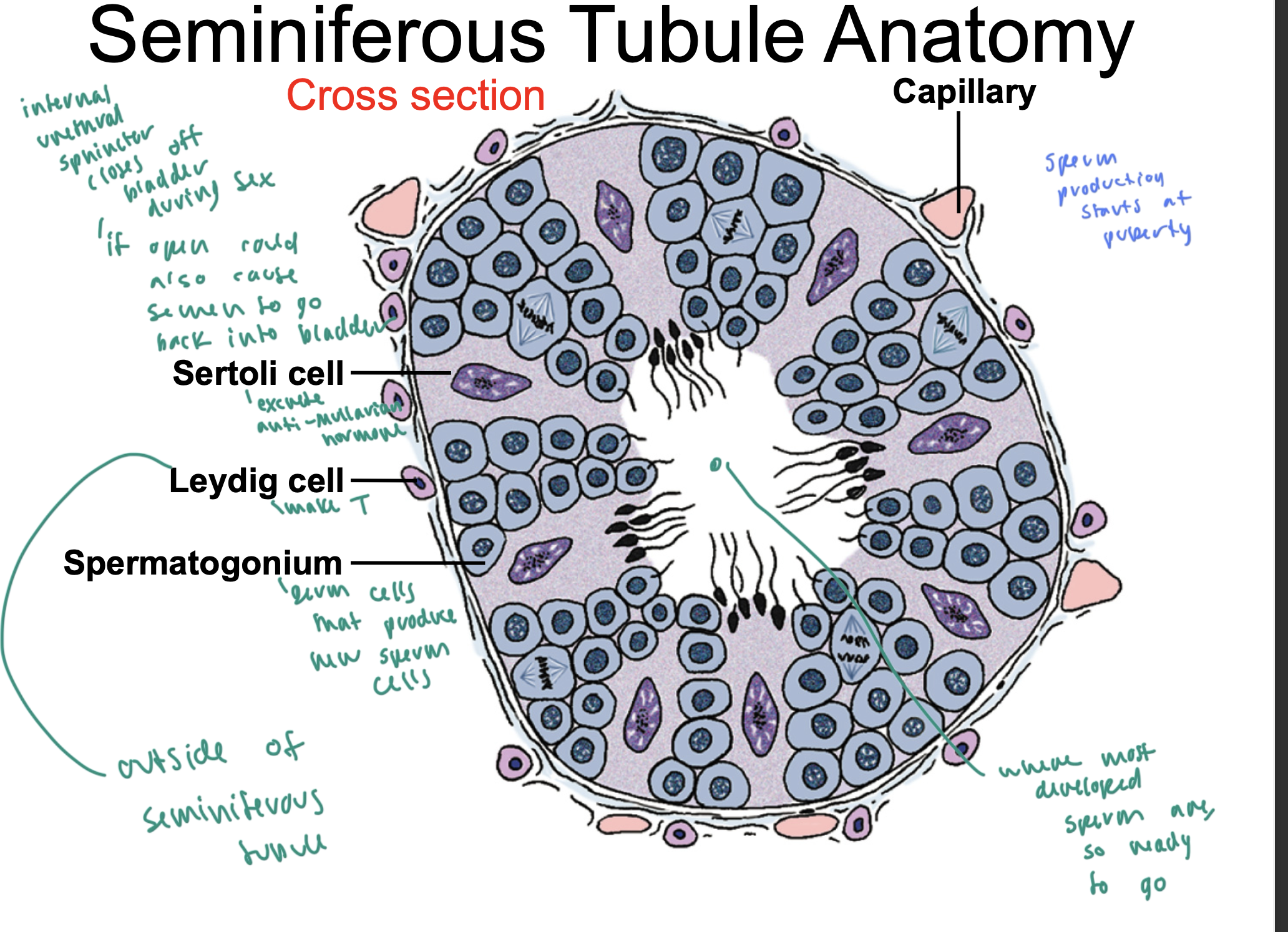
____ close the bladder off during sex
internal urethral spincter
sperm production starts at
puberty
once sperm is in the ____ of the seminiferous tubule, it is ready to go
middle of the tubule
GnRH
gonadotropin releasing hormone
comes from the hypo
causes release of LH and FSH
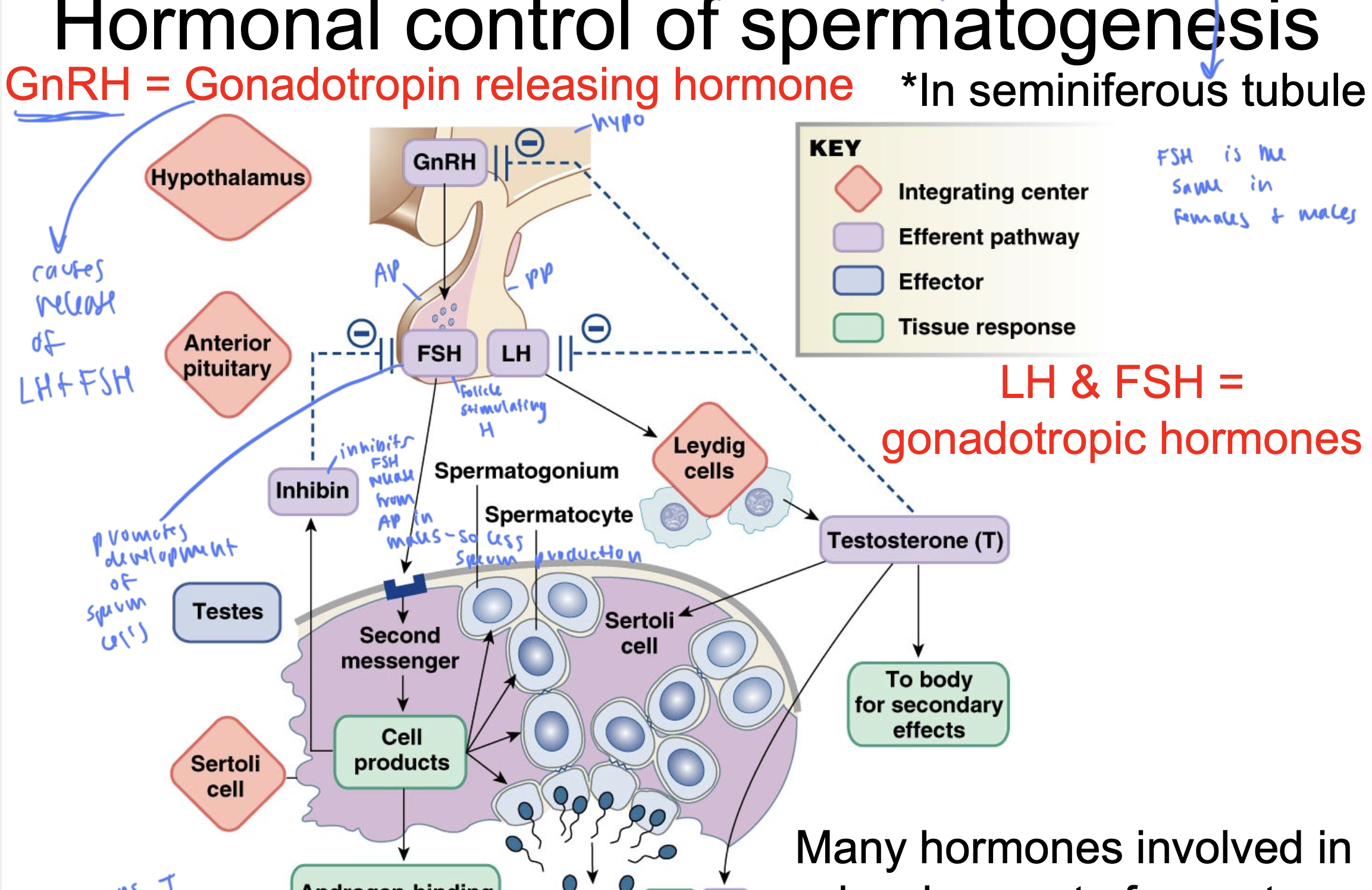
FSH
follicle stimulating hormone
released from AP
stimulates the production of sperm within the testicles by acting on Sertoli cells
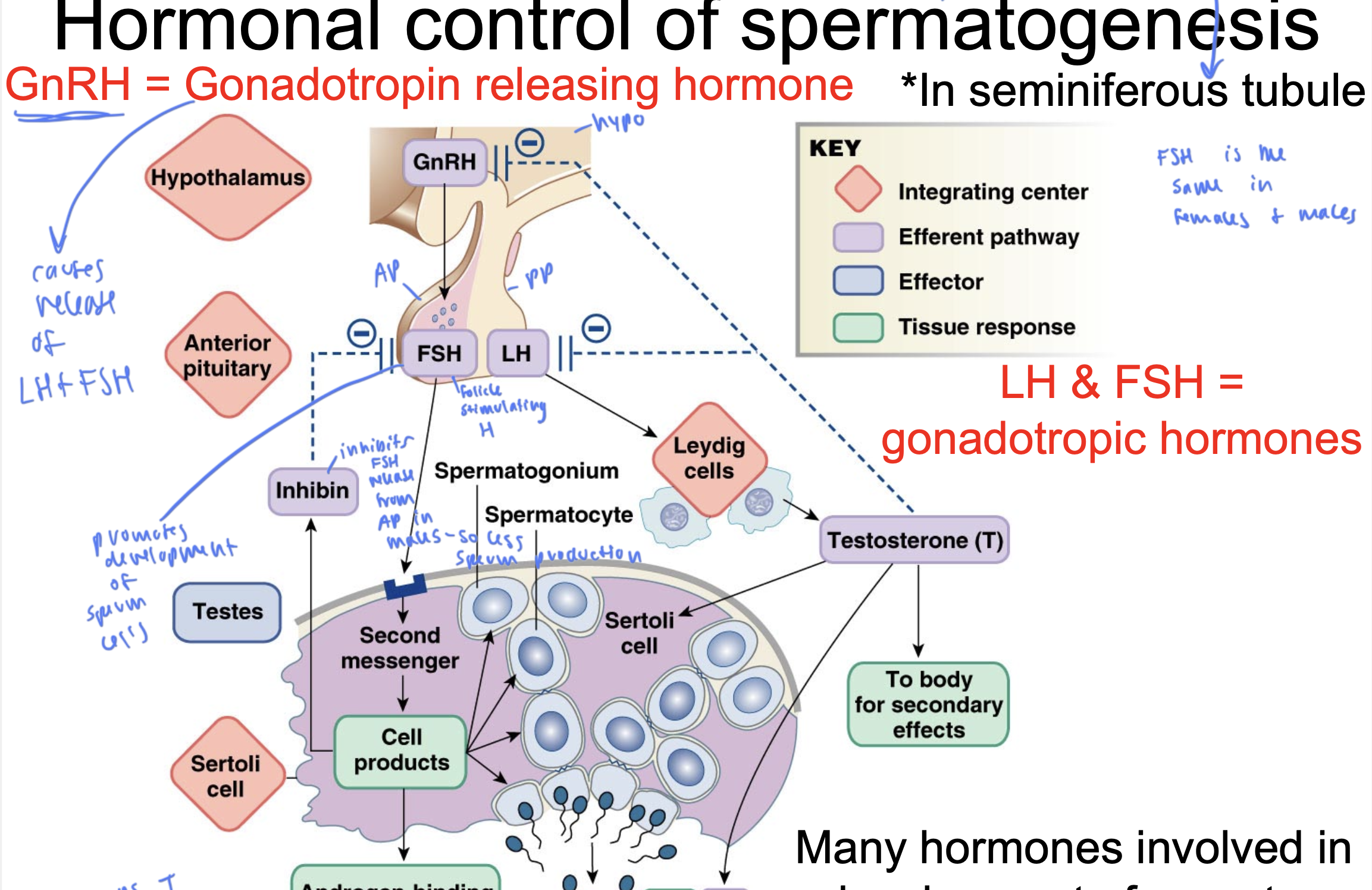
LH
luteinizing hormone
released from PP
causes leydig cells to secrete T
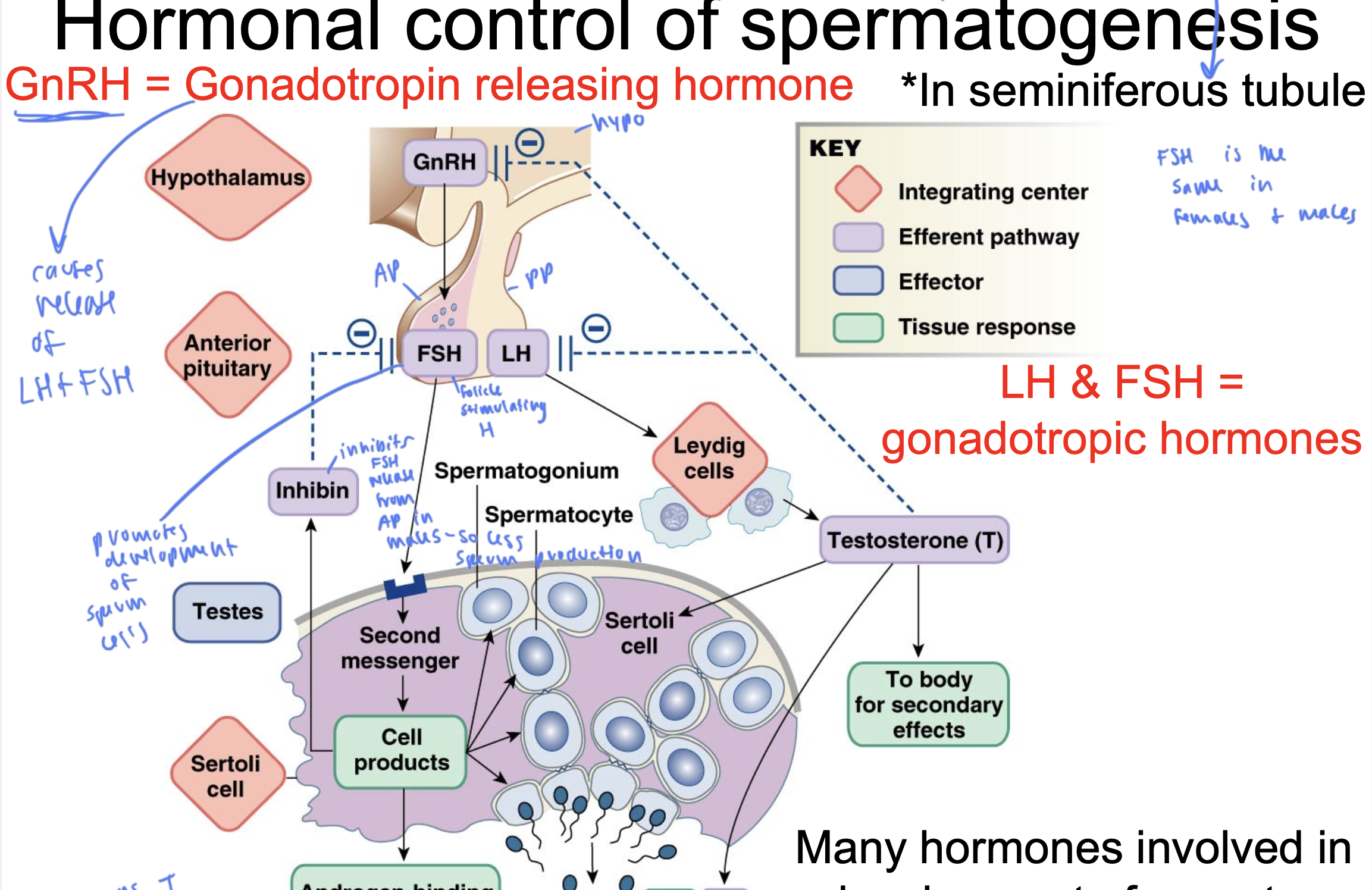
gonadotropic hormones
LH and FSH
FSH is the same
in males and females
inhibin
inhibits FSH release from AP in males, so causes less sperm
ABP
androgen-binding protein
keeps T in tubules instead of exiting since T is lipid soluble
FSH
promotes development of sperm cells
T comes from ____ and gets released to ____
come from leydig cells and gets released to sertoli cells and to the body for secondary effects
anabolic steroids
mimic T to help incr muscle mass
decr the affects that T would normally have, and can cause infertility since sertoli cells are not stimulated and the sperm don’t develop correctly
also makes the testicles shrink
normal testes are egg sized and w steroids are grape sized
male sex act
thoughts of sex/ visual/physical stimuli trigger IC in brain
descending sensory pathway stimulates parasympathetic pathway
para causes penile arterioles to vasodilate, causing an erection
tactile stimuli in penis cause sensory neuron to trigger IC in spinal cord, which affects brain IC
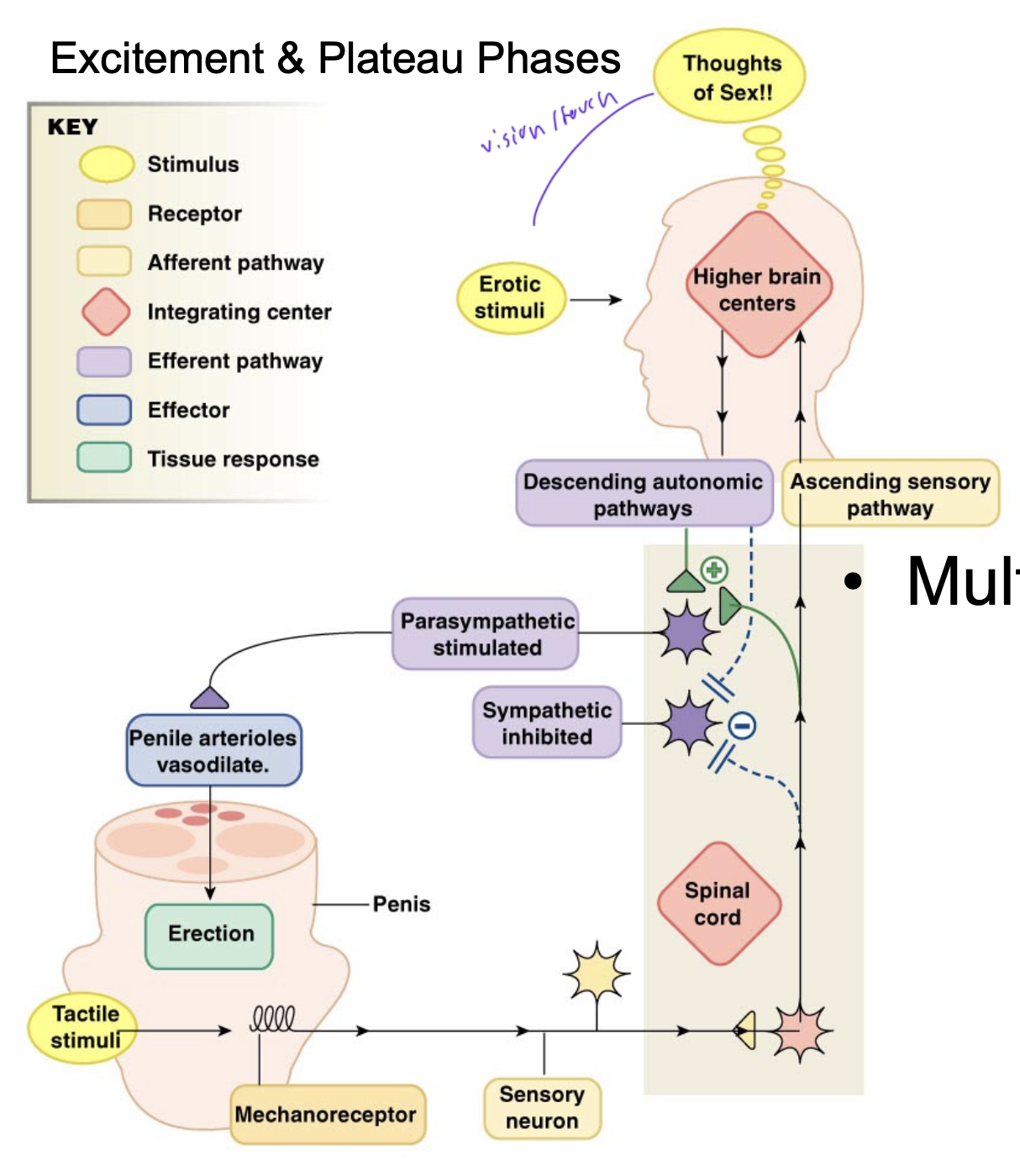
male sex stimuli comes from
various sources
thoughts of sex
physical stimuli in penis
since IC in spinal cord, a spinal cord injury can impact erection
to promote an erection, you want to stimulate the ____ response and inhibit the ____ response
promote para and inhibit sympathetic
this is why stress and cardio problems can impede erections and make it hard to maintain them
how alcohol affects erections
alcohol decr vasopressin, so you get dehydrated and can impede erections
penis anatomy
corpus cavernosum: 2 large parts inside shaft of penis where 90% of blood for the erection is
aka the body containing cavern
corpus spongiosum: soft spongey thing surrounding urethra and tightens to help ejaculate come out more forcefully

during an erection, you experience ____ which keeps the blood in the penis
veno-occlusion
erections are based mostly on
hydrostatic pressure
pressure of blood maintained in the penis
3 steps of male sex act
excitement
plateau (maintaining erection)
orgasm/ejaculation (largely involves spinal cord, and during this, sympathetic response takes over)
speed of ejaculate
10-20 mph
parasympathetic control of vasodiation in penis
parasympathetic stimulation causes NANC (nonadrenergic-noncholinergic nerve cells) cells to release NO
NO causes guanylate cyclase to product cGMP
cGMP promotes relaxation of smooth muscles, allowing for vasodilation of penis
PDE a phosphodieterase converts cGMP back to GTP to maintain vasodilation of the cycle
what happens if the arteries of the penis do not dilate enough?
you have erectile dysfunction
could occur due to atherosclerosis
NO in women causes
incr blood flow to clitoris
post nut clarity
due to spike in prolactin after ejaculation
____ drops right after ejaculation in men
dopamine
it is easier for ___ to orgasm multiple times in a row because
easier for women
because their T incr after orgasm, while it decr for men after ejaculation (so they have time to regenerate sperm)
estrogen upregulates the effects of
oxytocin
oxytocin spikes when
women orgasm
viagra
prolongs the effects of NO by eliminating PDE so CGMP never decomposes to GTP and you can maintain an erection by promoting prolonged vasodilation
only effects PDE5 and PDE6 a little bit
6 is used in cone cells in retina, so you have slightly blue vision when you take viagra
bipotential tissue turns into either
vulva or penis and scrotum
you rbody has ___ diff PDEs
11
penis has PDE5 and retina has 6
why would an erection longer than 4 hours become medically emergent?
since the blood has been in your penis for so long that it is super low in oxygen and the penis cells will start to die
called priapism
female internal reproductive anatomy
most of these parts came from mullerian duct development
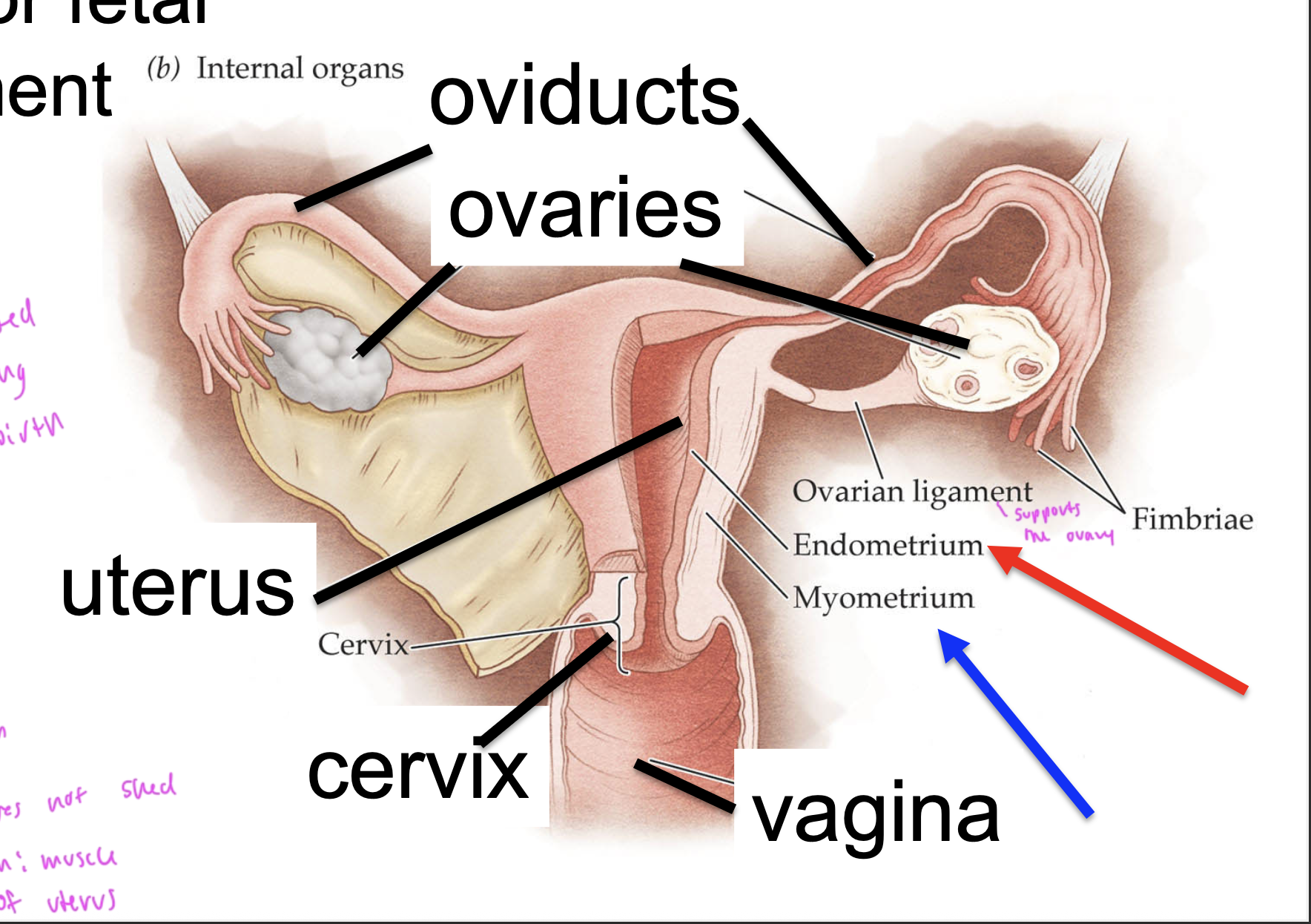
ovarian ligament supports
the ovary
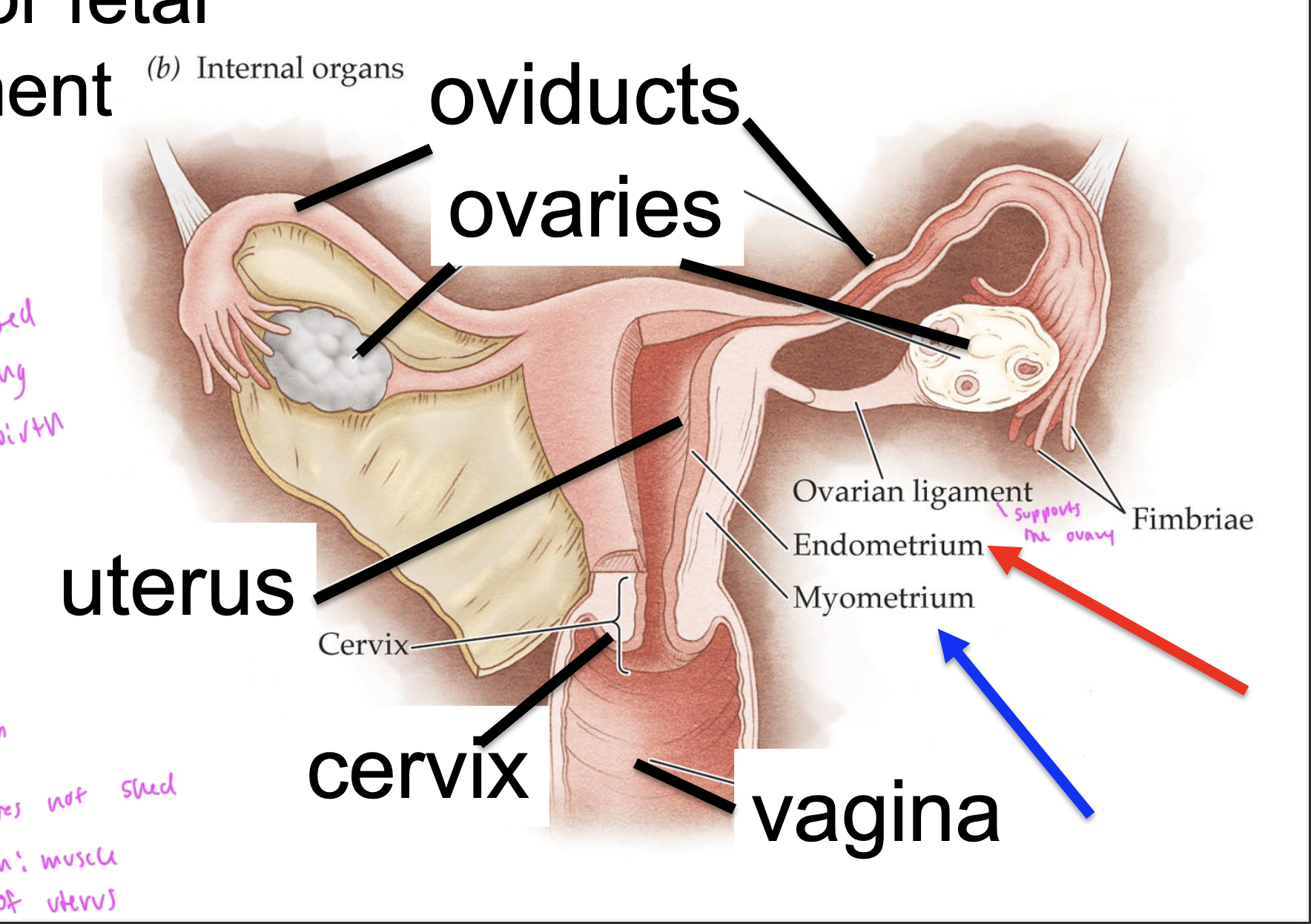
the cervix is usually
closed
except during childbirth
endometrium
the epithelial layer of cells that sloughs off during menstruation
myometrium
muscle in the uterus, does NOT get shed like the endometrium does
menstrual cycle
follicular phase in ovaries: the follicle develops, stimulated by FSH
ovulation occurs and an egg is released (lasts 15 min to 1 hr)
luteal phase in ovaries: corpus luteum produces estrogen, progesterone, inhibin
menstrual phase in the uterus occurs during the follicular phase of the ovaries
then proliferative phase builds the endometrium back up
during secretory phase of the uterus, the endometrium is fully developed with lush lining, ready to support pregnancy
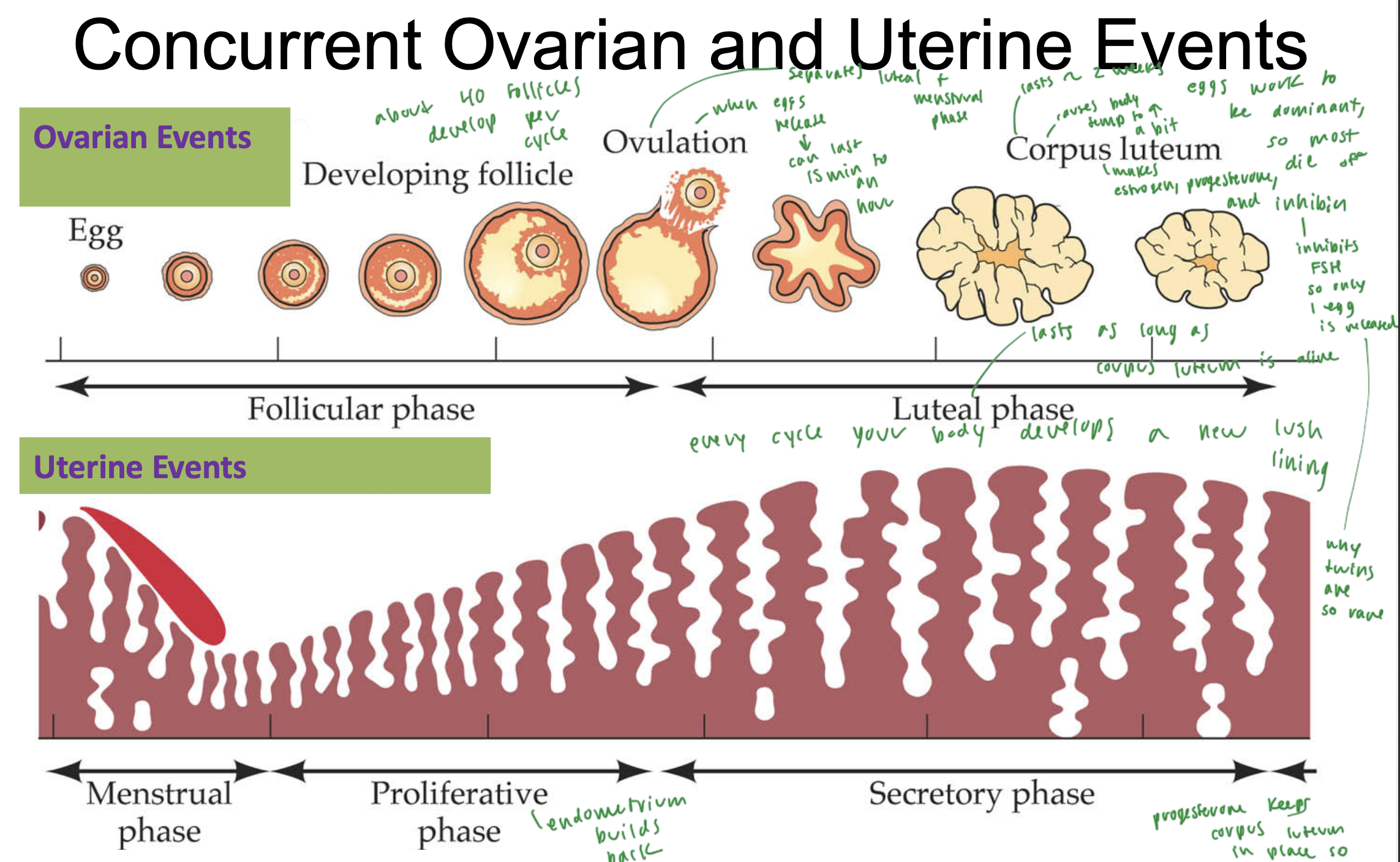
corpus luteum
develops during the luteal phase of the ovaries, while the endometrium builds back up in the uterus
causes body temp to incr a bit
produces estrogen, progesterone, and inhibin
inhibin inhibits FSH
this phase lasts about 2 weeks
every cycle, your body develops a new
lush lining
eggs work to be
dominant, and all the other eggs die off
what separates the follicular phase and the luteal phase?
ovulation
why are twins so rare?
since you usually just release 1 egg during your cycle
but about 40 total follicles develop, just all the eggs don’t survive
LH
luteinizing hormone
helps release an egg, so spikes before ovulation
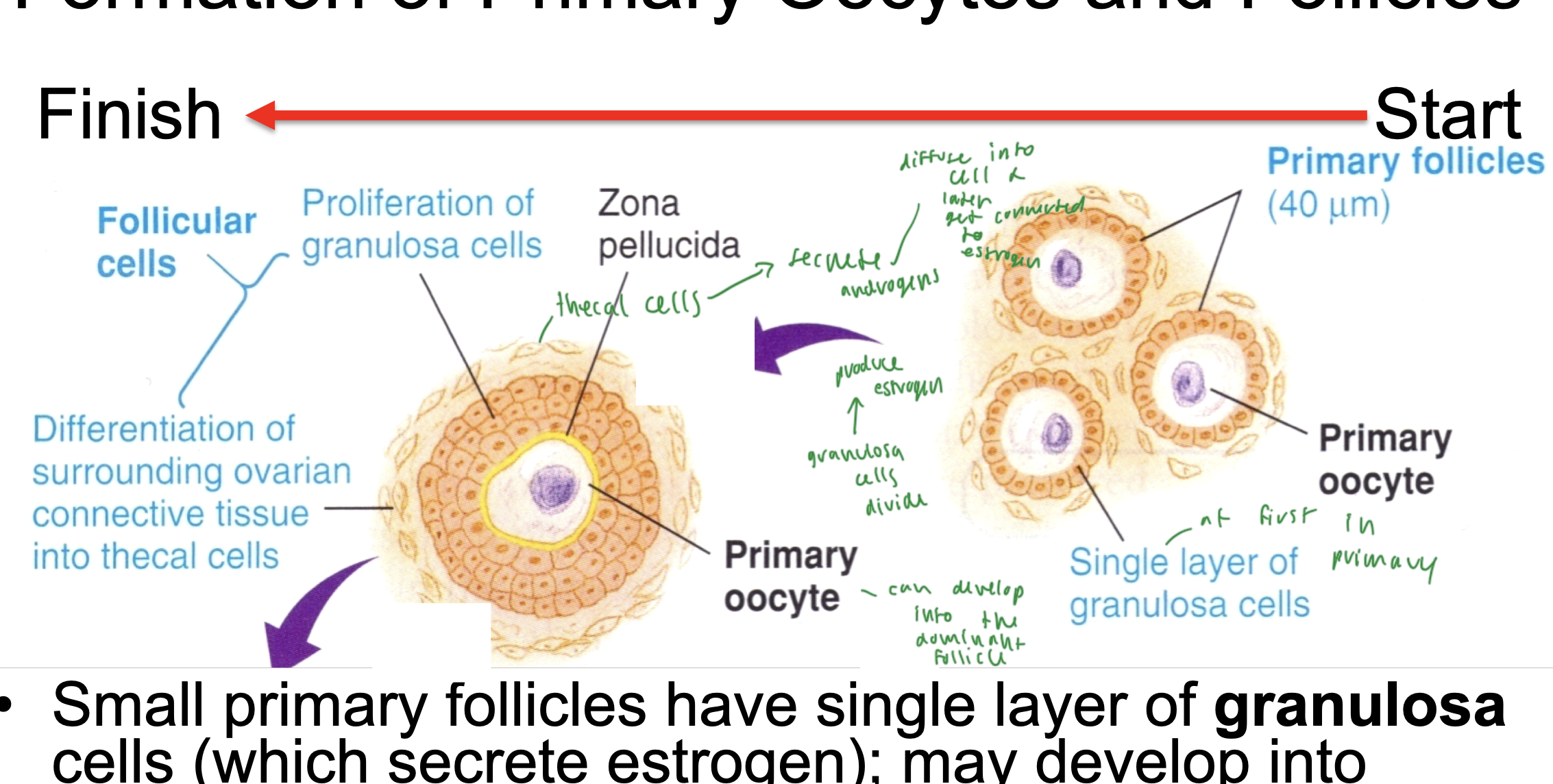
development of a follicle steps
a primary oocyte has just a single layer of granulosa cells (which secrete estrogen)
as the oocyte develops, the granulosa cells divide, and therefore can produce more and more estrogen
granulosa cells proliferate and grow into the peripheral cells, which become the thecal cells
thecal cells on the surface of the oocyte secret androgens, which turn into estrogen later
this primary oocyte can develop into the dominant follicle
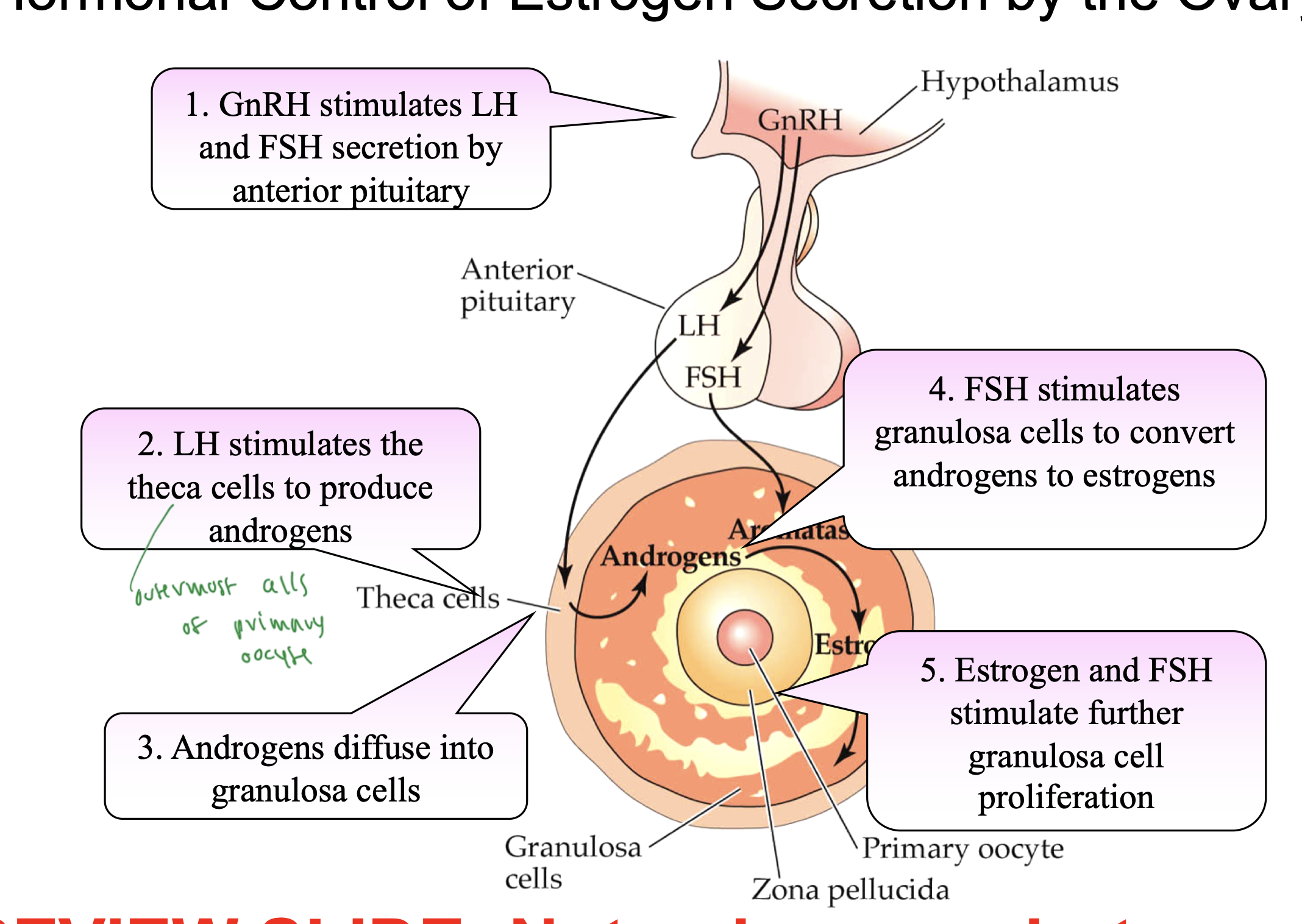
all hormones released in a woman
hypo sceretes GnRH
GnRH stimulates secretion of LH and FSH by AP
LH stimulates thecal cells to produce androgens, which convert to estrogen
FSH stimulates granulosa cells to convert androgens to estrogens
estrogen and FSH further stimulate granulosa cell proliferation in the follicle
___% of eggs undergo atresia
99
so only less than 1% actually becomes the dominant oocyte and all others dies
difference in male vs female gametes
women are born with all the eggs they will ever have but men produce thousands of sperm each day