3.1.11 Electrode potentials and electrochemical cells
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Define electrochemical series
List of electrode potentials in numerical order
What is the IUPAC convention for writing half-equations?
Write them as reduction reactions
How can these be identified from an electrochemical series
Most powerful oxidising agent
Weakest oxidising agent
Most powerful reducing agent
Weakest reducing agent
Species on LHS with the most positive electrode potential
Species on LHS with the most negative electrode potential
Species on RHS with the most negative electrode potential
Species on RHS with the most positive electrode potential
How do you calculate the e.m.f of a cell?
Ecell= E⦵R - E⦵L= red - ox
Positive right red cat
For spontaneous electrochemical cells, the more positive half-equation goes right and this is reduction and occurs at the cathode.
The more positive half-equation also goes on the RHS in the spontaneous conventional representation
What are the charges of the electrodes?
Cathode = +ve electrode
Anode = -ve electrode
What are the standard conditions?
298K
All gaseous species at 100kPa
All aqueous species at 1 mol dm-3
How do you draw a standard hydrogen electrode?
Hydrogen gas at 1atm
1M HCl solution
Platinum electrode
298K
high-resistance voltmeter
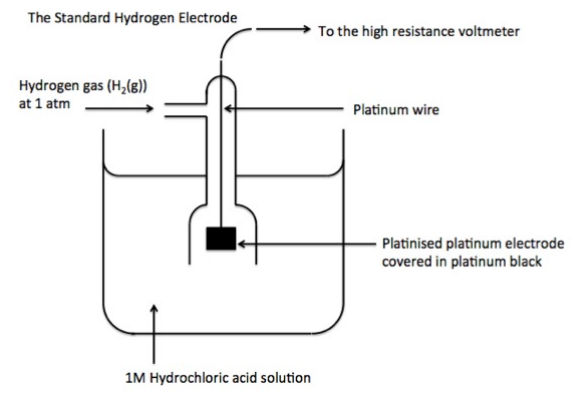
Why is the hydrogen electrode the reference electrode?
It is 0.00V by definition
How do you draw a cell?
solid metal or platinum electrode (Pt is inert so doesn’t create a potential difference, and is a conductor so allows the transfer of electrons)
salt bridge to provide an electrical connection from ions that are free to move and carry charge- usually KNO3 (unreactive as if a reaction occurs, there will be a change in the concentration, affecting the Ecell)
high-resistance voltmeter: doesn’t allow current to flow so allows emf to be measured
wire/ammeter: allows current to flow; Ecell eventually falls to 0.00 as the reactants are used up and the cell goes to equilibrium
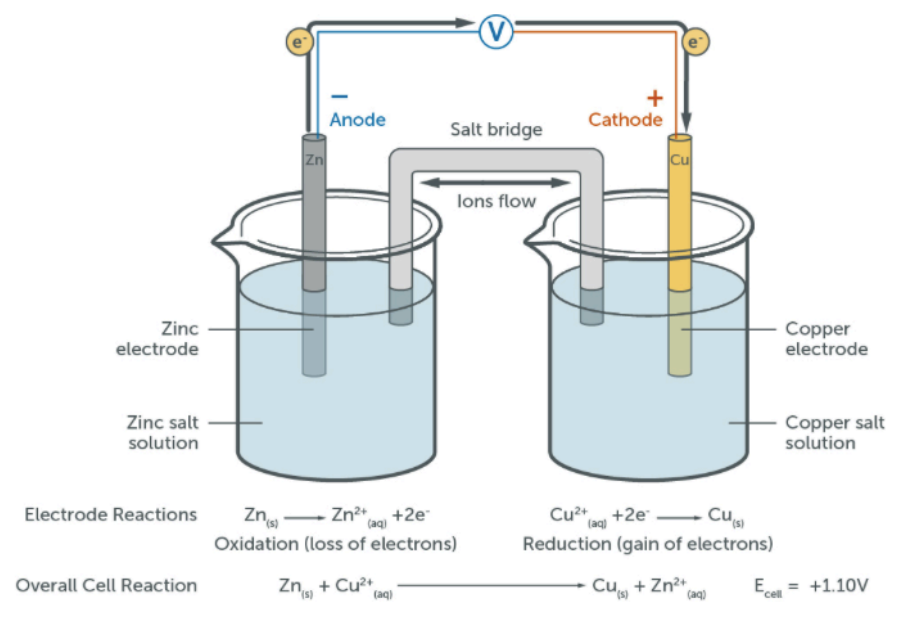
How do you write the conventional representation of a cell?
|| - salt bridge
right of salt bridge: positive terminal of voltmeter (half cell with more +ve electrode potential for a spontaneous reaction)
left of salt bridge: negative terminal of voltmeter (half cell with more -ve electrode potential for a spontaneous reaction) OR standard hydrogen electrode (always on LHS)
higher oxidation state goes next to salt bridge
| for phase change, comma for no phase change
What is a galvanic cell?
has a positive Ecell
cell is discharging: more positive E is reduced (cathode) and more negative E is oxidised (anode)
overall equation- flip more negative equation
the emf is determined when no current flows
the emf changes when electrodes are connected and voltmeter is replaced with a component that allows current to flow eg wire, bulb, ammeter; current flows so the concentration of the ions change and are no longer standard
What is an electrolytic cell?
-ve Ecell/ emf
cell is recharging: more positive E is oxidised and more negative E is reduced
overall equation occurs in the reverse direction- flip more positive equation
What is the effect on electrode potential if a change in concentration causes equilibrium of the right hand half cell to shift to the RHS?
More reduction occurs (less oxidation)
More electrons absorbed
Electrode becomes more positive
Electrode potential becomes more positive
What is the effect on electrode potential if a change in concentration causes equilibrium of the right hand half cell to shift to the LHS?
More oxidation occurs (less reduction)
More electrons released
Electrode becomes more negative
Electrode potential becomes more negative
Describe a non-rechargable electrochemical cell and its advantages and disadvantages
an irreversible cell that can’t be charged by electric current
reaction not reversible
Ecell changes over time and eventually falls to 0.00V as the reactants are used up and cell is at equilibrium
Advantages
cheaper initial cost
longer storage times
Disadvantages
cell can’t be reused (higher batter production which depletes supplies of materials used to make the battery so more mining, increases CO2 production as energy to extract the metal is generated from the burning of fossil fuels; disposal contributes to landfill problems, recycled separately to prevent pollution of the environment by toxic or dangerous substances and to make it easier to recycle valuable components)
may leak after a long period of use- dry cell specifically (Zn anode is oxidised/ used up)
Describe a rechargeable electrochemical cell and its advantages and disadvantages
a reversible cell that can be recharged by an electric current
reaction is reversible
Ecell changes over time and eventually falls to 0.00V as the reactants are used up
the cell can be recharged by changing the products back into reactants
Advantages
the cell can be reused (cheaper in the long run, supplies not depleted so less mining/ less energy required/ less CO2 released, fewer batteries go into landfill)
Disadvantages
battery may lose ability to maintain capacity over time
batteries must be recycled separately to prevent pollution of the environment by toxic or dangerous substances and to make it easier to recycle valuable components
What are the simplified electrode reactions in a lithium cell?
Positive electrode: Li+ + CoO2 + e- → Li+[CoO2]-
Negative electrode: Li → Li+ + e-
What do electrochemical cells use instead of a salt bridge?
A porous separator which allows ions to flow
Describe a fuel cell and its advantages and disadvantages
a cell where electricity is generated from the continuous oxidation of an external fuel source
overall reaction= combustion
hydrogen and oxygen supplied continuously (Ecell remains constant as long as H2 and O2 are constantly supplied)
Advantages
can be refuelled quickly compared to the time required to charge an electric battery
more efficient than combustion of hydrogen in an internal combustion engine and only produces H2O as the waste product/ does not produce CO2 (but CO2 is produced to make hydrogen: CH4 + 2H2O → 4H2 + CO2)
Disadvantages
hydrogen is more expensive than petrol
refuelling is difficult as fewer fuel stations sell hydrogen gas
hydrogen is explosive so heavy and strong material needed for its storage
hydrogen may need to be made using an energy source that is not ‘carbon neutral’ (however can use carbon neutral method eg electrolysis of water, generate the electricity using a method that doesn’t produce CO2 eg solar, wind, geothermal, tidal)
What are the electrode reactions in an alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
Positive: O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e– → 4OH– (aq)
Negative: 4H2O(l) + 4e– → 4OH– (aq) + 2H2(g)
Overall: O2(g) + 2H2(g) —> 2H2O(l)
What are the electrode reactions in an acidic hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell? Why is the voltage the same for alkaline and acidic?
Positive: O2(g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e- → 2H2O(l)
Negative: 4H+(aq) + 4e- → 2H2(g)
Overall: O2(g) + 2H2(g) —> 2H2O(l)
The overall reaction is the same