B cell differentiation, maturation and activity
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
week 4 clinical immunology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
B cell maturation
B cells are central to adaptive humoral immune system
produce antigen-specific immunoglobulin (Ig) or ABs, directed against invasive pathogens
early B cell development and commitment to the B cell lineage occurs in the foetal liver prenatally
B cells differentiate from haemapoietic stem cell (HSC) in bone marrow throughout life
1 bill B cells produced each day
B = bursa
B cell maturation overview
antigen-independent maturation phase
antigen-dependent maturation phase
antigen-independent maturation phase
immunocompetent B cells expressing membrane IgM and IgD are generated in the bone marrow
10% of potential B cells reach maturity and exit bone marrow
antigen-dependent maturation phase
naive B cells in the periphery die within a few days unless they encounter soluble protein antigen and activated Th cells
activated B cells proliferate within secondary lymphoid organs
B cells with high-affinity mlg differentiate into plasma ells and memory B cells
may express different isotypes bc of class switching
progenitor B cells (pro B cell): earliest distinctive B-lineage cell
expresses a transmembrane tyrosine phosphatase called CD45R
bone marrow stromal cells are required for maturation of pro-B cells into precursor B cells
pro-B cells bind to stromal cells via VCAM-1 on the stromal cell and VLA-4 on the pro-B cell
binding of c-kit (receptor) omn the pro-B cell to stem cell factor (SCF) on the stromal cell, triggers a signal, mediated by tyrosine kinase activity of c-kit → expression of IL-7 receptors
IL-7 released from the stromal cell then binds to IL-7 receptors, inducing pro-B cell to mature into pre-B cell
stromal cell role
form specific adhesive contacts with the developing lymphocytes by interactions between cell adhesion molecules and their ligands
provide soluble and membrane bound cytokines and chemokines that control lymphocyte differentiation and proliferation
Ig-gene rearragement produces immature B cells
progenitor B cells rearrange their immunoglobulin genes
assemble and expression of functional antigen-receptor gene
recombination activating genes (RAG 1 ) and RAG2 are expressed in developing B cells
required for rearrangement of antigen receptor genes
allelic exclusion: B cells rearrange one gene locus at a time
Ig heavy and light chain genes of only one parental chromosome are expressed per cell
ensures that B cells possess a single antigenic specificity
allele selected for rearrangement is chosen randomly
expressed Ig may contain one maternal and one paternal chain or both chains may derive from only one parent
only B and T cells exhibit allelic exclusion
gene rearrangement in B cell development
early pro B cells: heavy chain gene rearrangement is inititated with D to JH rearrangements
no functional μ protein is expressed, although transcription occurs
late pro-B cells: VH to DJH rearrangement occurs on one chromosome first
if no functional H chain produced, VH to DJH rearrangement occurs on second chromosome
productive heavy chain gene: μ chains are expressed together with 2 other chains: λ5 and Vpre5
Igα and Igβ signal to halt heavy chain gene rearrangement: drives the transition to the large pre B stage by inducing proliferation
gene rearrangement in B cell development cont.
progeny of large pre B cells stop dividing and become small pre-B cells, in which light chain gene rearrangements commence
Vκ-Jκ occurs first, and if unsuccessful, Vλ to Jλ rearrangement occurs next
successful light chain gene rearrangement results in production of a light chain that binds the μ chain to form complete IgM molecule
expressed together with Igα and Igβ at the cell surface
pre-B receptor: important checkpoint
tests for successful production of a complete heavy chain
test takes place in the absence of light chains
signals the transition from pro-B cell to the pre B cell stage
pre-B cell receptor initiates signalling through spontaneous dimerization
surrogate protein chains, VpreB (orange) and λ5 contain unique amino-terminal regions that are not present in other immunoglobulin like domains
dimerizarion generates signalling from the pre-B cell receptor that is dependent on the presence of the ITAM-containing signalling chains Igα and Igβ
signalling inhibits RAG-1 and RAG-2 expression and causes proliferation of the large pre-B cell
large pre-B cells transitions to small pre-B cell
cell division expands large pre-B cell population with successful in-frame joins
RAG proteins now cause the rearrangement of the light chain locus
developing B cells fail to assemble a complete surface immunoglobulin undergo apoptosis in the bone marrow and are eliminated from the B cell pool
immature B cells carry an intact IgM molecule
IgM: rearranged light chain paired with a μ chain
antigen receptor is tested for reactivity to self-antigens (autoreactivity)
elimination of autoreactive B cells ensures that B cell population will be tolerant of self antigens
central tolerance
B cells leaving the bone marrow require additional maturation steps that take place in peripheral lymphoid organs
central tolerance: B cell development
immature B cells without self reaction migrate from bone marrow to peripheral lymphoid tissues
they may become mature recirculating B cells bearing both IgM and IgD on their surface
if developing BCRs recognise self-molecules, these receptors are deleted from the repertoire
B cells either undergo receptor editing to eliminate autoreactivity or undergo apoptosis, resulting in clonal deletion
immature B cells that bind soluble self-antigens able to cross-link the BCR are rendered unresponsive to the antigen
bear little surface IgM
migrate to periphery where they express IgD but remain anergic
immature B cells whose antigen is inaccessible to them, or which bind monovalent or soluble self antigens with low affinity don’t receive any signal and mature normally
potentially self-reactive cells however are clonally ignorant as their ligand is present but unable to activate them
3 major mature B cell populations
follicular B-2 cells circulate secondary lymphoid organs
if antigens stimulate a response, B-2 cells migrate to border of B/T cell boundary and interact with stimulated T cells
B cell activation
plasma cells: terminal differentitation of a B cell
from germinal centre or the memory B cell population, antigen specific B cells will proliferate (in presence of the antigen) and become plasmablasts and then plasma cells
short term plasma cells are in spleen/lymph node
long lived plasma cells are in bone marrow and secrete ABs into bloodstream
B cell receptor (BCR)
antigen binding receptor
membrane bound immunoglobulin associated with one disulphide-liked Igα-Igβ heterodimer contains the immunoglobulin-fold structure and cytoplasmic tails that are longer than those of mlg signal transduction
B cell co-receptor
amplifies the activating signal transmitted through the BCR
complex of 3 cell membrane molecules: TAPA-1 (CD81), CR2 (CD21) and CD19
binding of the CR2 component to complement-derived C3d that has coated antigen captured by mlg results in the phosphorylation of CD19
the Src family tyrosine kinase Lyn binds to phosphorylated CD19
resulting activated Lyn and Fyn can trigger the signal-transduction pathways that begin with phospholipase C
initial stages of B cell activation
BCR crosslinking causes interaction of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) with Src tyrosine kinases (Fyn, Blk and Lck) and kinase activation
activated kinases phosphorylate tyrosine residues on the cytoplasmic tails of the Igα/Igβ heterodimer. creating docking sites for Syk kinase which is also activated
B cell activation mechanisms
B cells recognise soluble or cell-bound epitopes directly through their BCRs
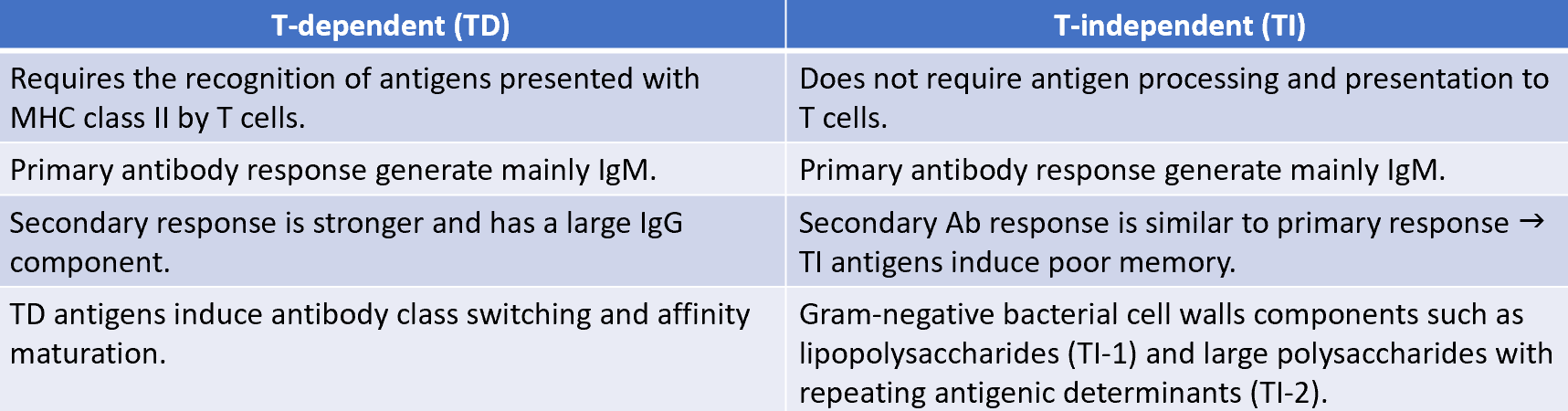
steps in B cell activation by TD antigens
antigen cross linkage of immunoglobulin induces signal-1 which leads to increased expression of class II MHC and co-stimulatory B7 on B cell
TH cell recognises antigen-class II MHC on B cell membrane and activates TH cell with co-stimulatory signal
expresses CD40L, then provides signal-2 with CD40 and CD40L interaction
B7-CD38 interactions provide co-stimulation to the TH cell
steps in B cell activation by TD antigens (cont)
B cell expresses receptors for various cytokines including:
IL-4
IL-5
IL-6
IFN-γ
TGF- α
the humoral response
activation leads to production of secreted ABs of various isotypes (differ in their ability to mediate specific effector functions)
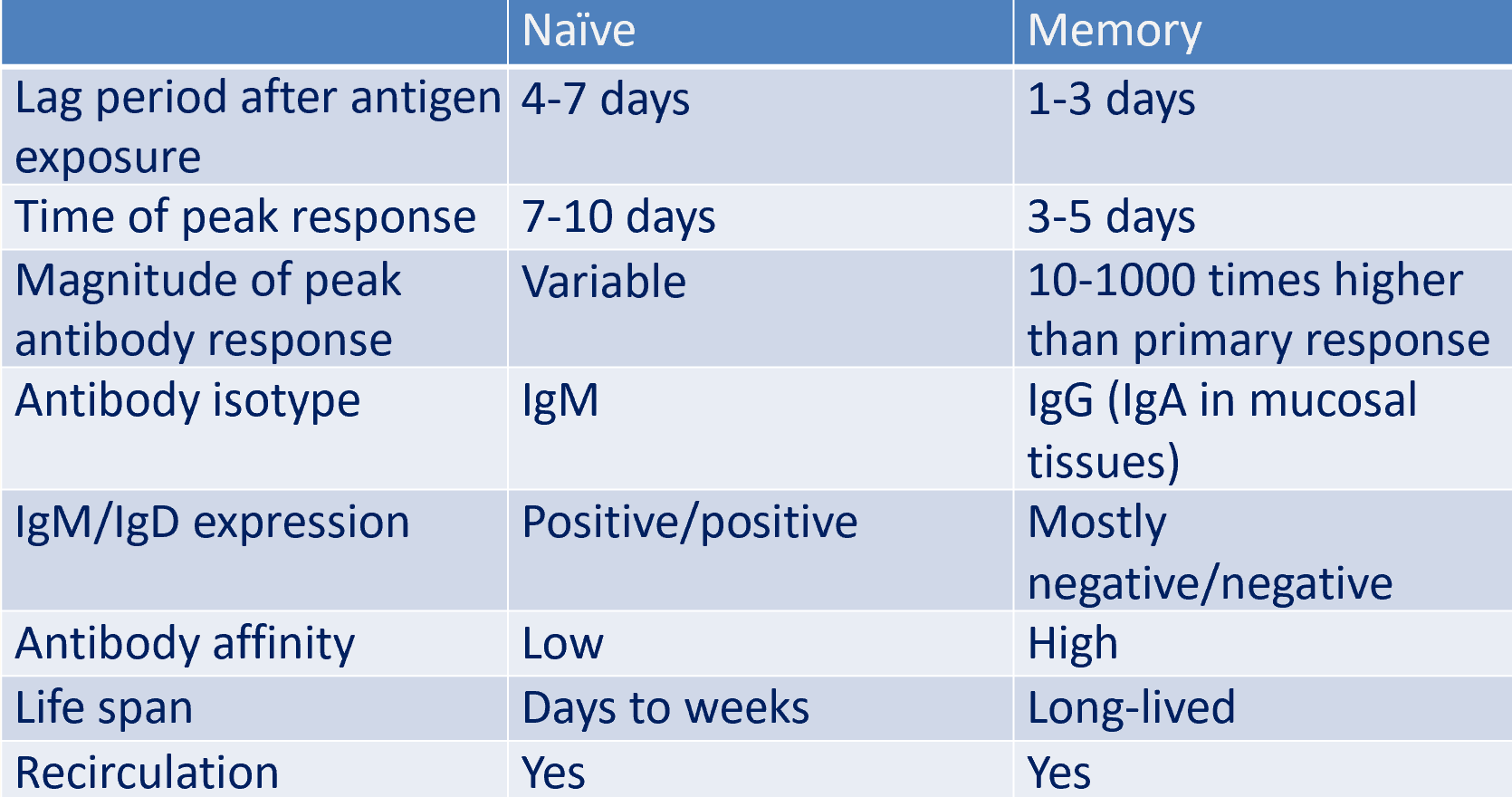
naive lymphocytes (primary response) vs memory lympho
AB functions in humoral response
neutralisation: ABs neutralise bacterial toxins (diphtheria, tetanus) and prevent adherence of microorganisms to their target cells (eg IgA in the gut)
opsonisation: ABs bind to antogens and enhance phagocytosis
activation of complement (classical pathway): leads to bacterial lysis
mediate AB-dependent cellular cytotoxicity: by macrophages and NK cells
agglutination: ABs clump bacteria leading to phagocytosis
primary response vs. secondary
primary response:
rapid production of IgM
slightly delayed IgG response due to class switching
secondary response:
produces small amounts of IgM initially, larger amounts of IgG with some IgA and IgE
ABs are made by memory B cells that were generated in the primary response and have already switched from IgM to another isotype
memory B cells express more MHC class II molecules and the co-stimulatory ligand B7.1 than naive B cells
helps memory B cells acquire and present antigen more effectively to TFH cells
characterised by a more vigorous and earlier generation of plasma cells than in the primary response
primary B cells vs. secondary B cells
selective Ig A deficiency
most common humoral AB deficiency
50-80% are asymptomatic
recurrent sinopulmonary infections arae the most frequent manifestations
may have severe malabsorption (chronic diarrhea)
isolated low IgA level
increased risk of autoimmune disorders
Bruton’s X-linked agammaglobulinaemia
results from defected BTSK gene (encodes tyrosine kinase)
no B cells
child will be clinically well for first 6 months of life
recurrent upper/lower respiratory tract infections (RTIs) with encapsulated bacteria
sepsis, meningitis, skin infections
paucity of lymphoid tissue (tossils, adenoids)
markedly decreased IgG, IgA, IgM
treatment: IVIG, antibiotics
common variable immunodeficiency
B cells don’t differentiate into plasma cells
recurrent sinopulmonary infections
low IgG, IgA, IgM
treatment: IVIG (IV immunoglobulin G)
associated with autoimmune disease, lymphoma
lymphocyte recirculation routes
an individual lymphocyte may make a complete circuit from the blood to the tissues and lymph and back again (as often as 1-2 times a day)
lymphocytes migrate from the blood into lymph nodes through specialiased areas in postcapillary venules called high-endothelial venules (HEVs)
cell adhesion molcules (CAMs)
HEVs express variety of cell-adhesion molecules (membrane proteins)
facilitate lymphocyte extravasation
CAMs expressed either:
constitutively
induced by cytokines during inflammation
vascular addressins (VAs) distributed in a tissue-specific manner and direct the extravasation of different populations or recirculating lymphocytes to a particule lymphoid organ
CAM expression controls lymphocyte movement through tissues
4 families of adhesion molecules:
selectins: bind to sialic acid residues on mucins
mucins: heavily glycosylated proteins on cell surface that contain sialic acid residues which bind to selectins
integrins: heterodimers consisting of a common β chain and a unique α chain
integrins bind to ICAMs
ICAMs (intracellular adhesion molecule): members of immunoglobulin family
extravasation
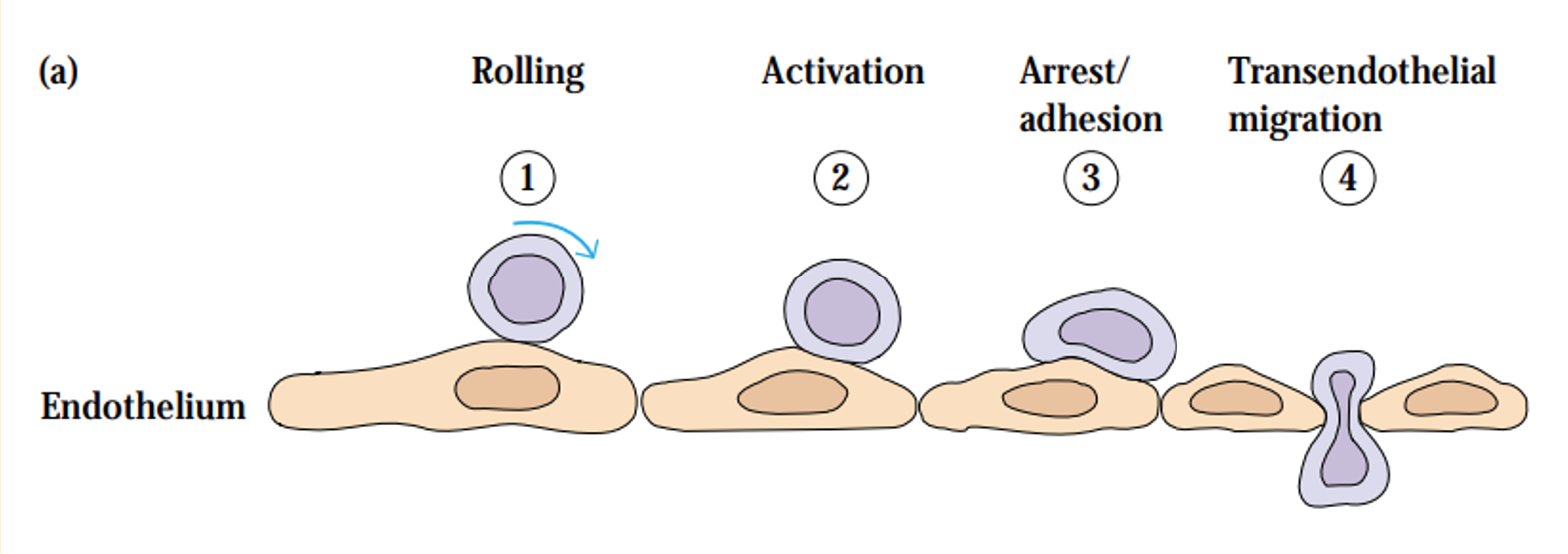
homing receptors direct trafficking of lymphocytes
naive lymphocytes attach to HEVs via L-selectin (homing receptor) and adhesion molecules such as GlyCAM-1 and CD34 on HEVs
antigen-specific lymphocytes undergo rapid proliferation and differentiation
effector and memory cells that are generated by this process leave the lymphoid tissue and recirculate
effector and memory lymphocytes adopt different trafficking patterns
effector cells home to regions of infection: by recognising inflamed vascular endothelium and chemoattractant molecules generated during inflammatory response
memory lymphocytes home selectively to the type of tissue in which they first encountered the antigen
express different different combinations of cell-adhesion molecules to enter sites of inflammation