Ch.17 Aromatic Compounds
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
-cyclic
-resonance
-conjugated
-4n + 2pi electrons (Huckel's rule)
-coplanar
aromatic requirements
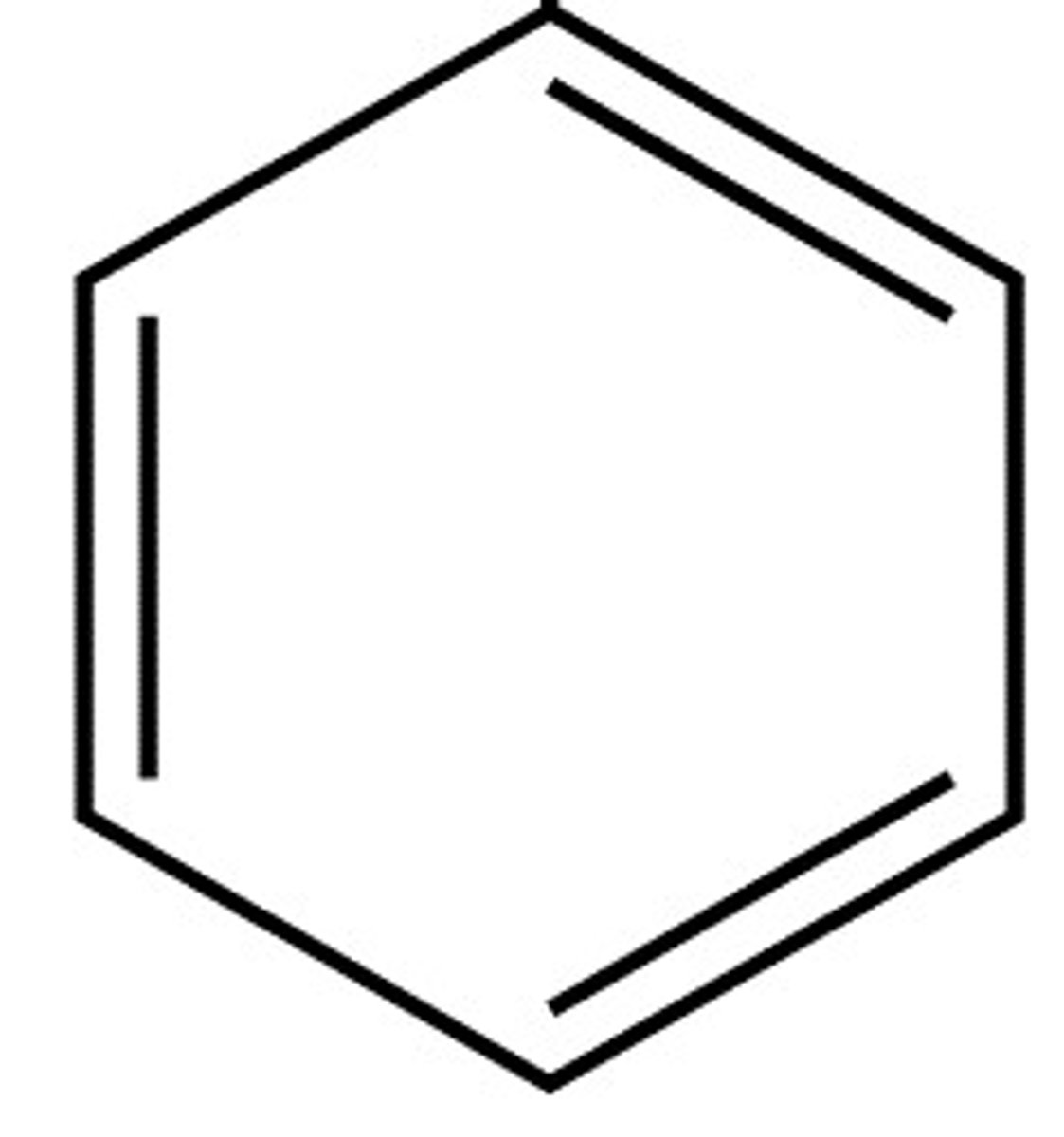
antiaromatic
contain 4n electrons (4,8,12,etc)

weak base- N has resonance
strong base- N doesn't participate in resonance
How do you know if nitrogen in a weak or strong base in an aromatic compound?
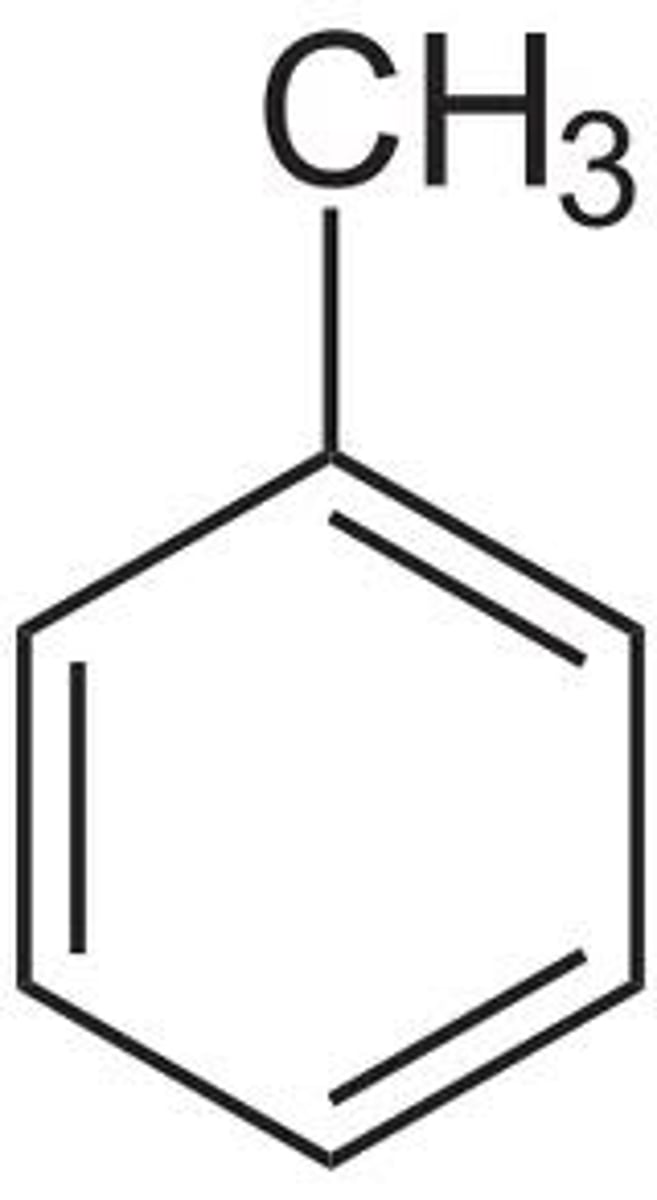
toluene
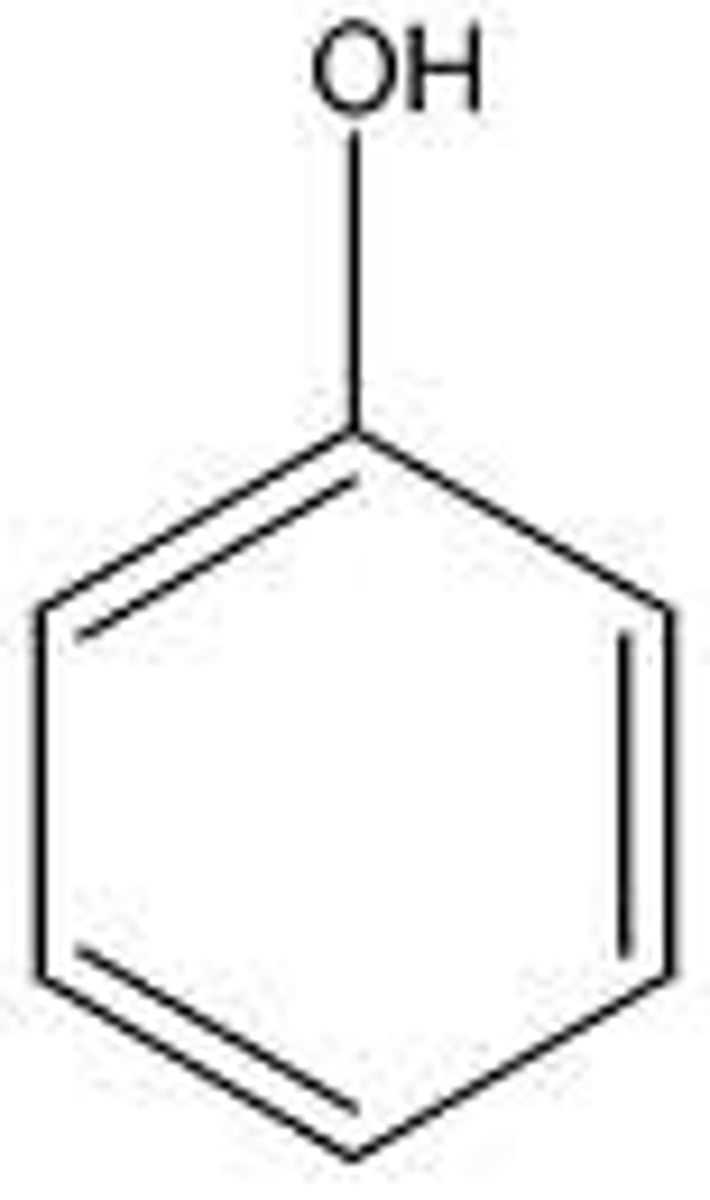
phenol
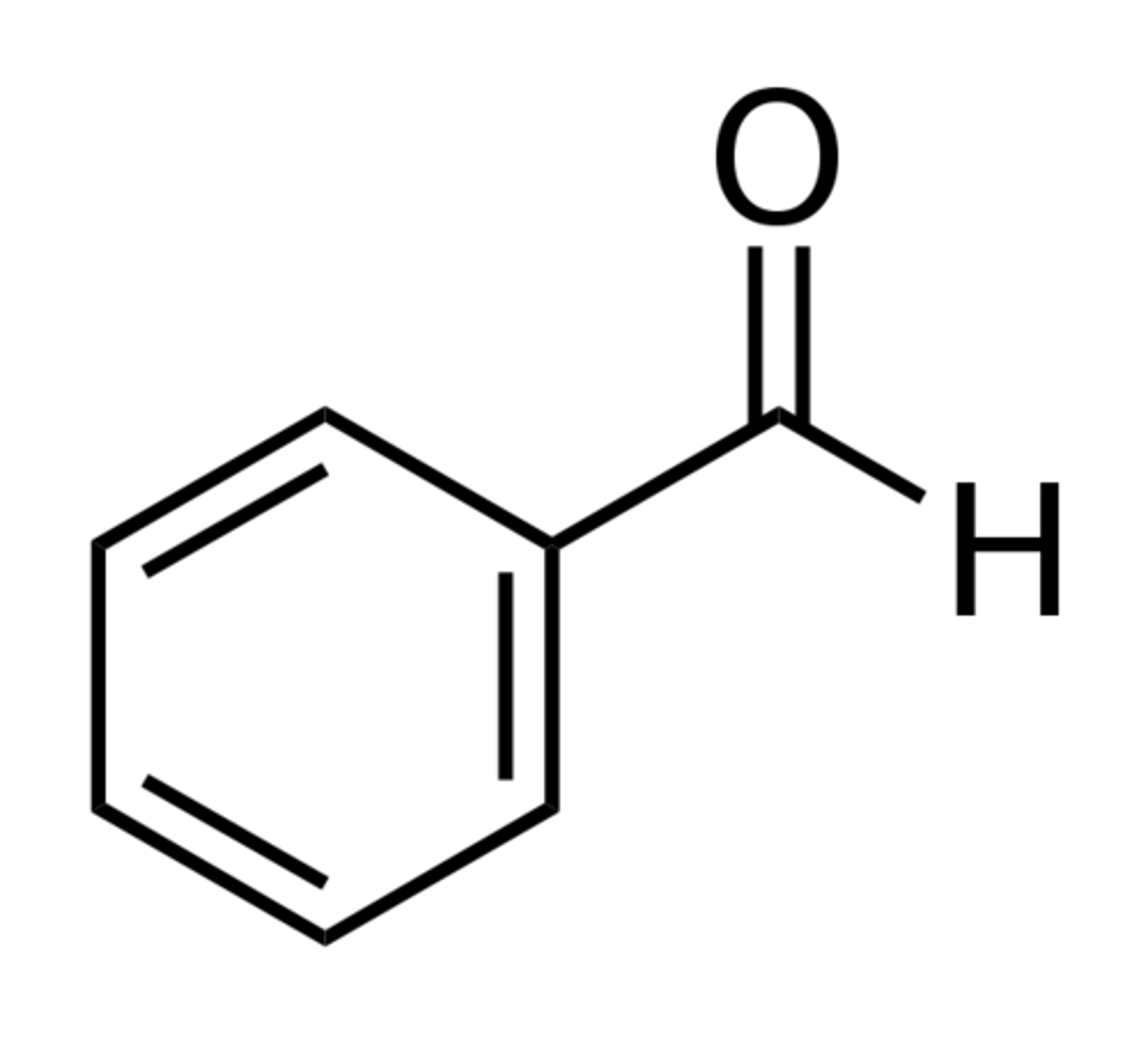
anisole
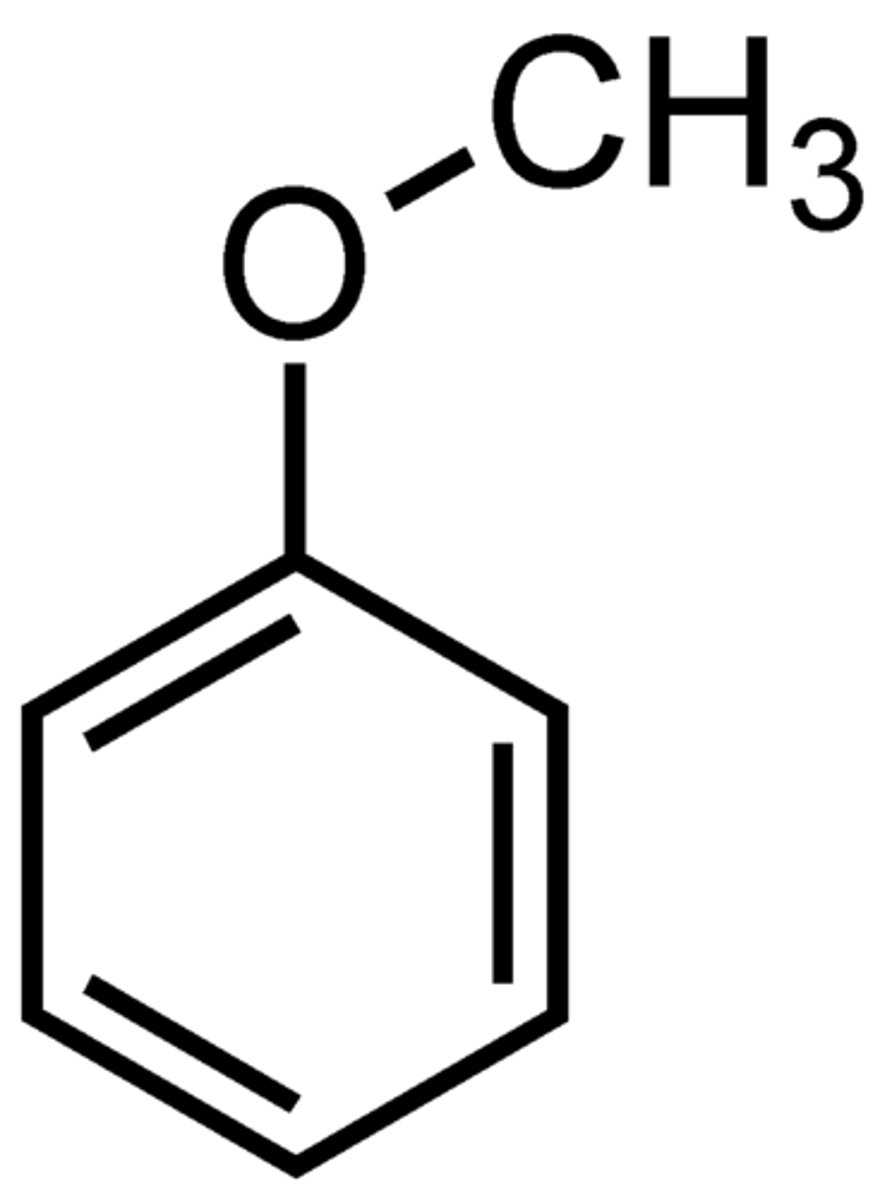
aniline
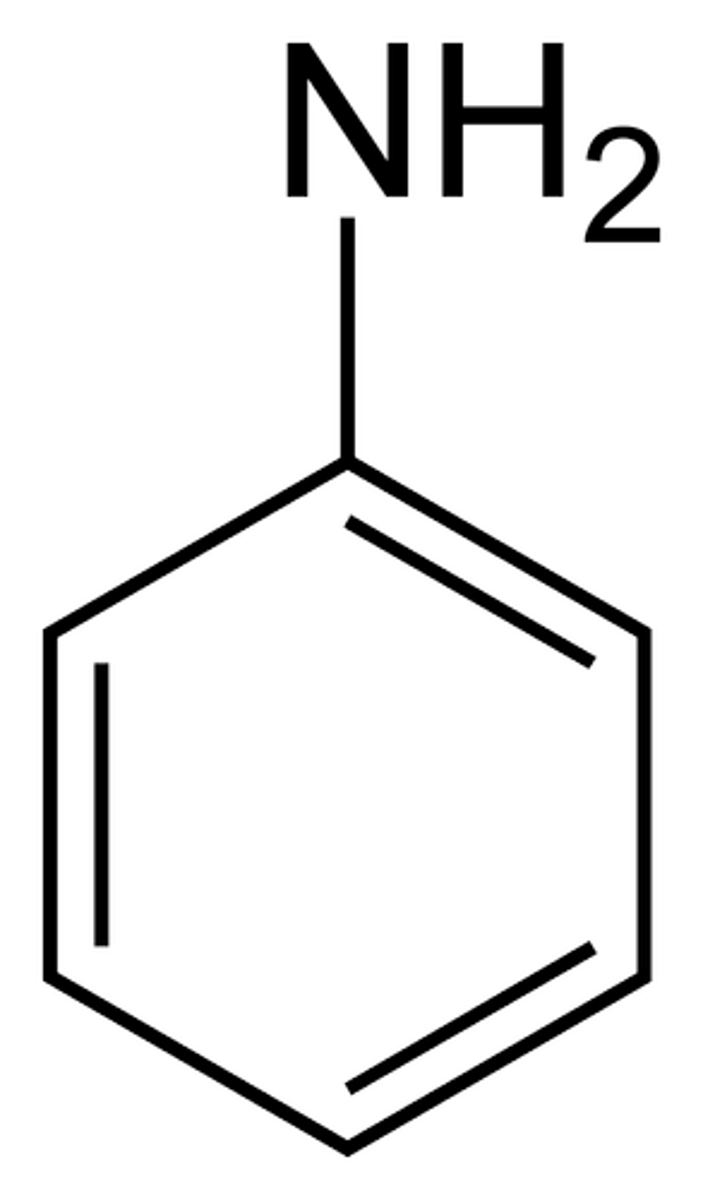
benzoic acid
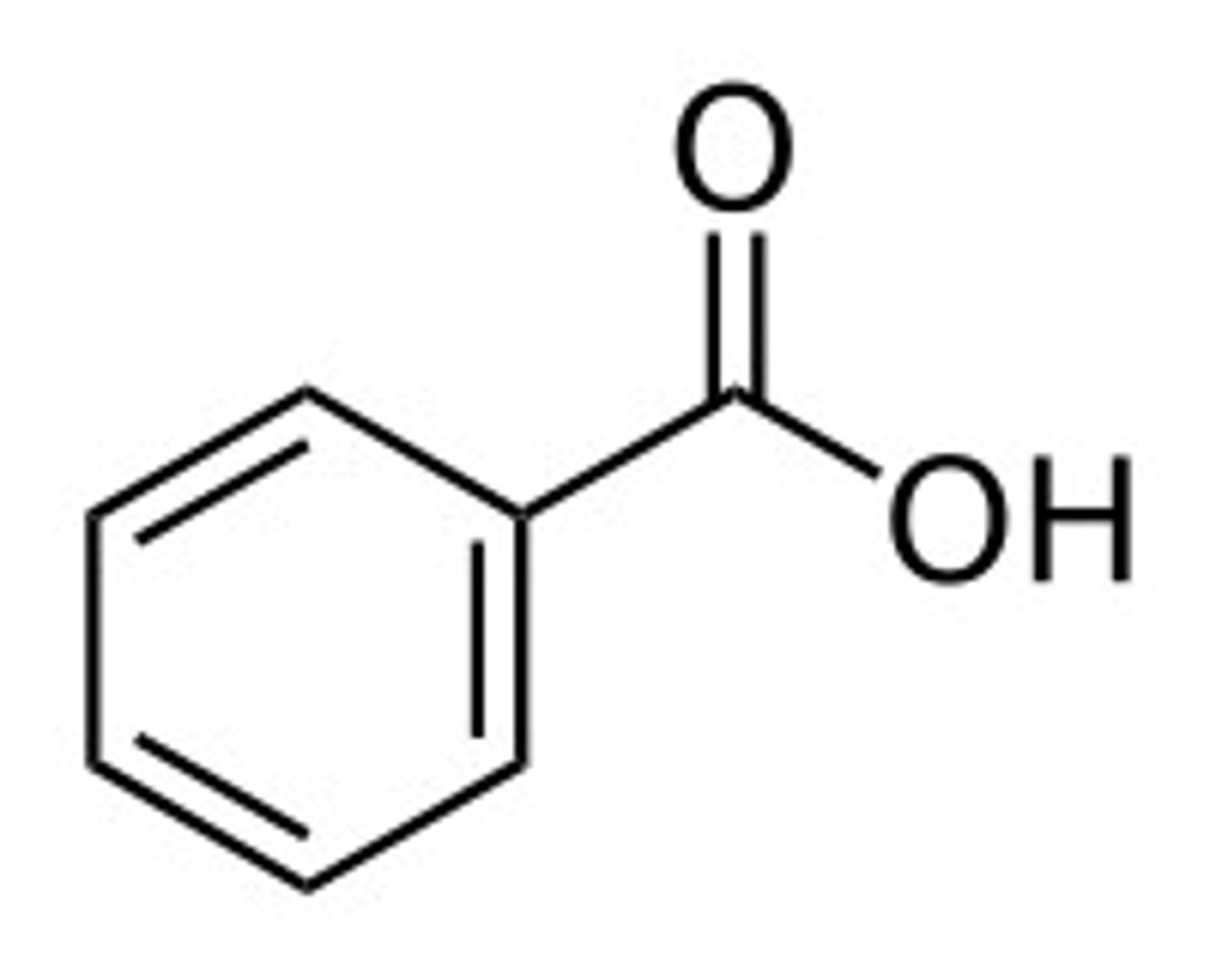
benzaldehyde
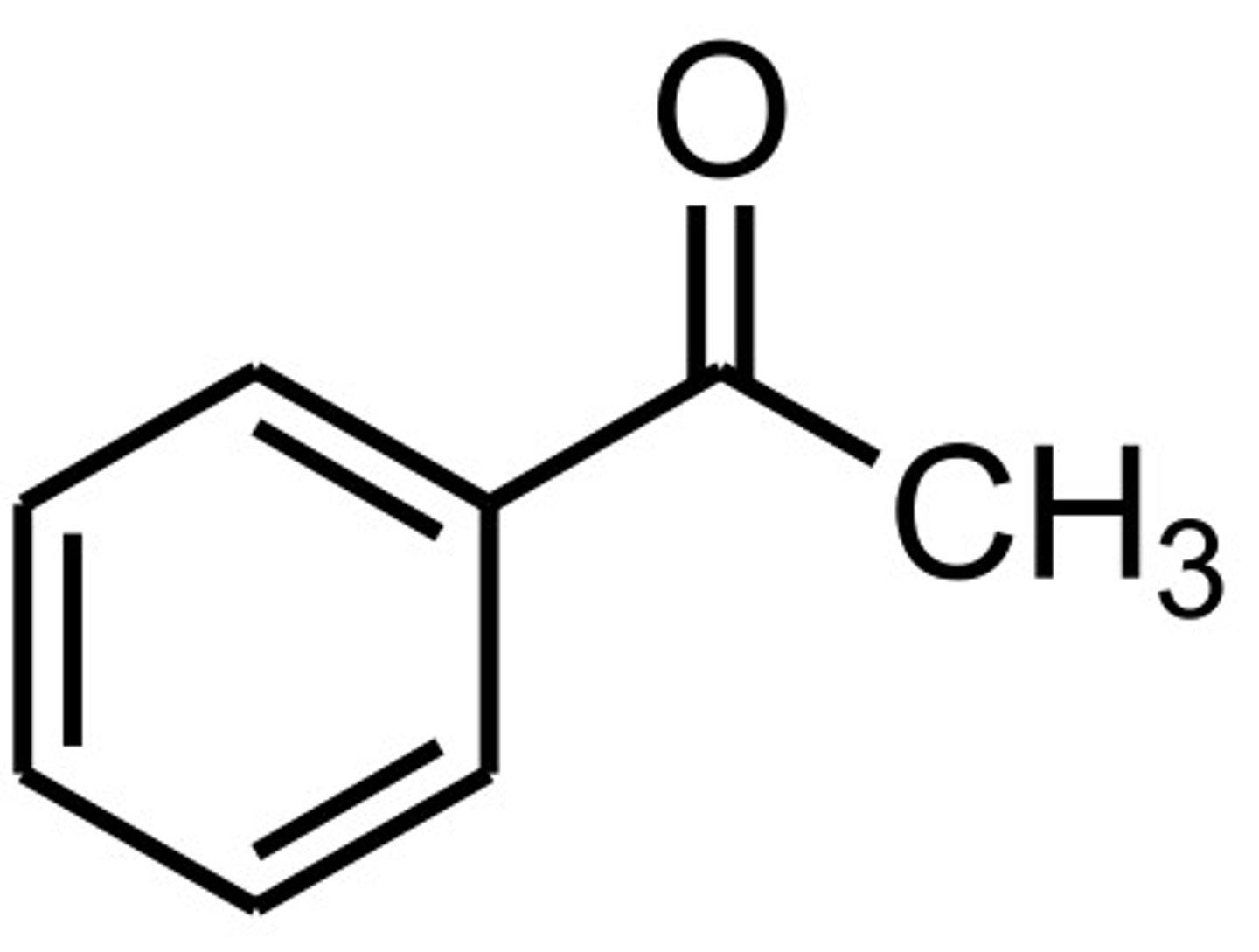
acetophenone
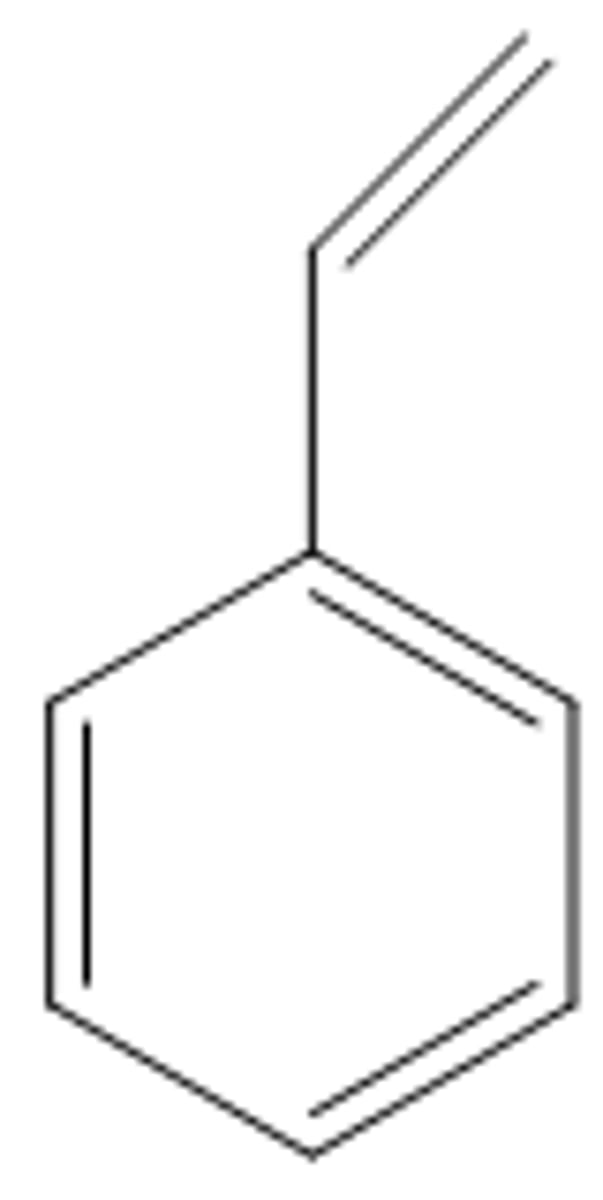
styrene
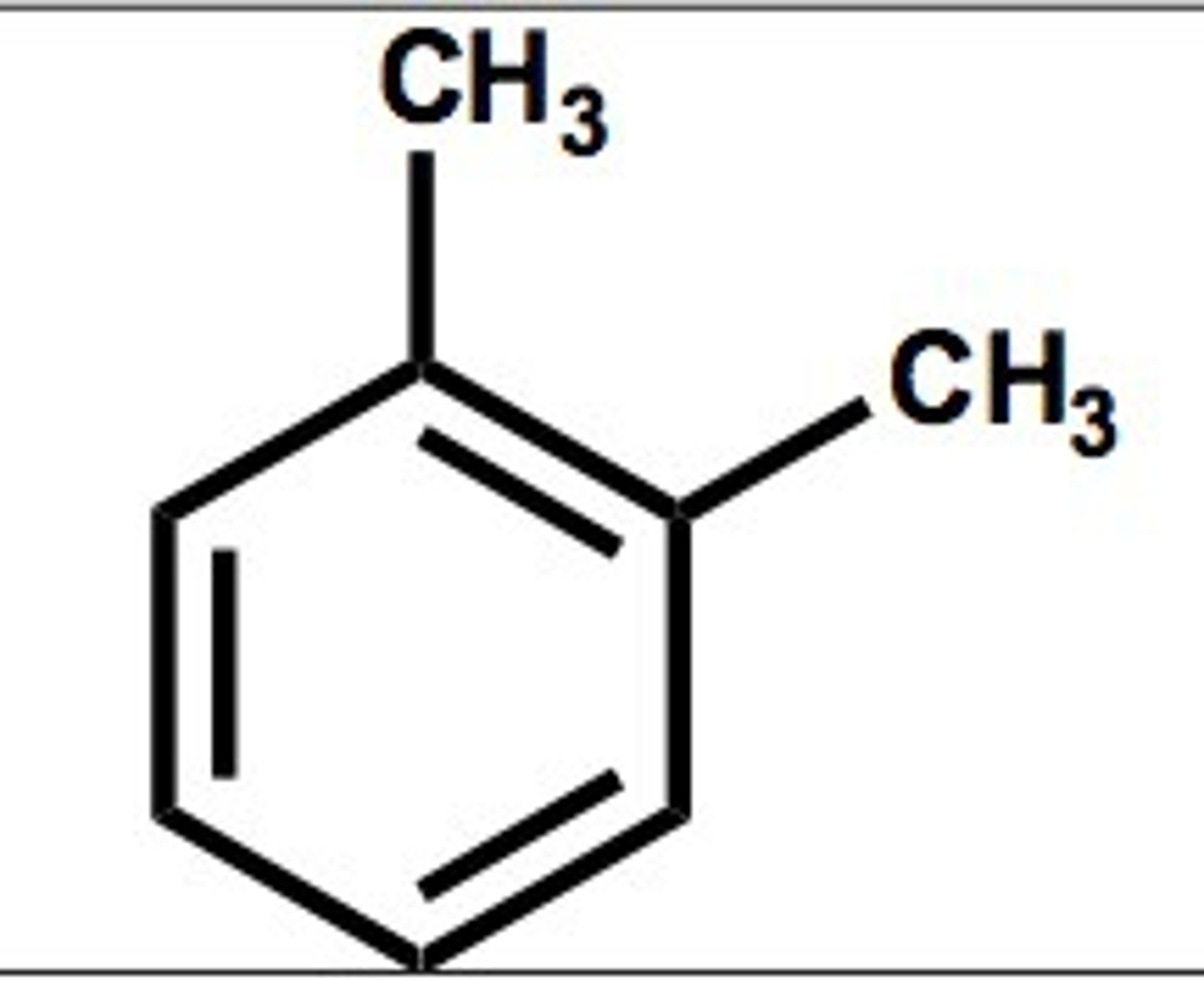
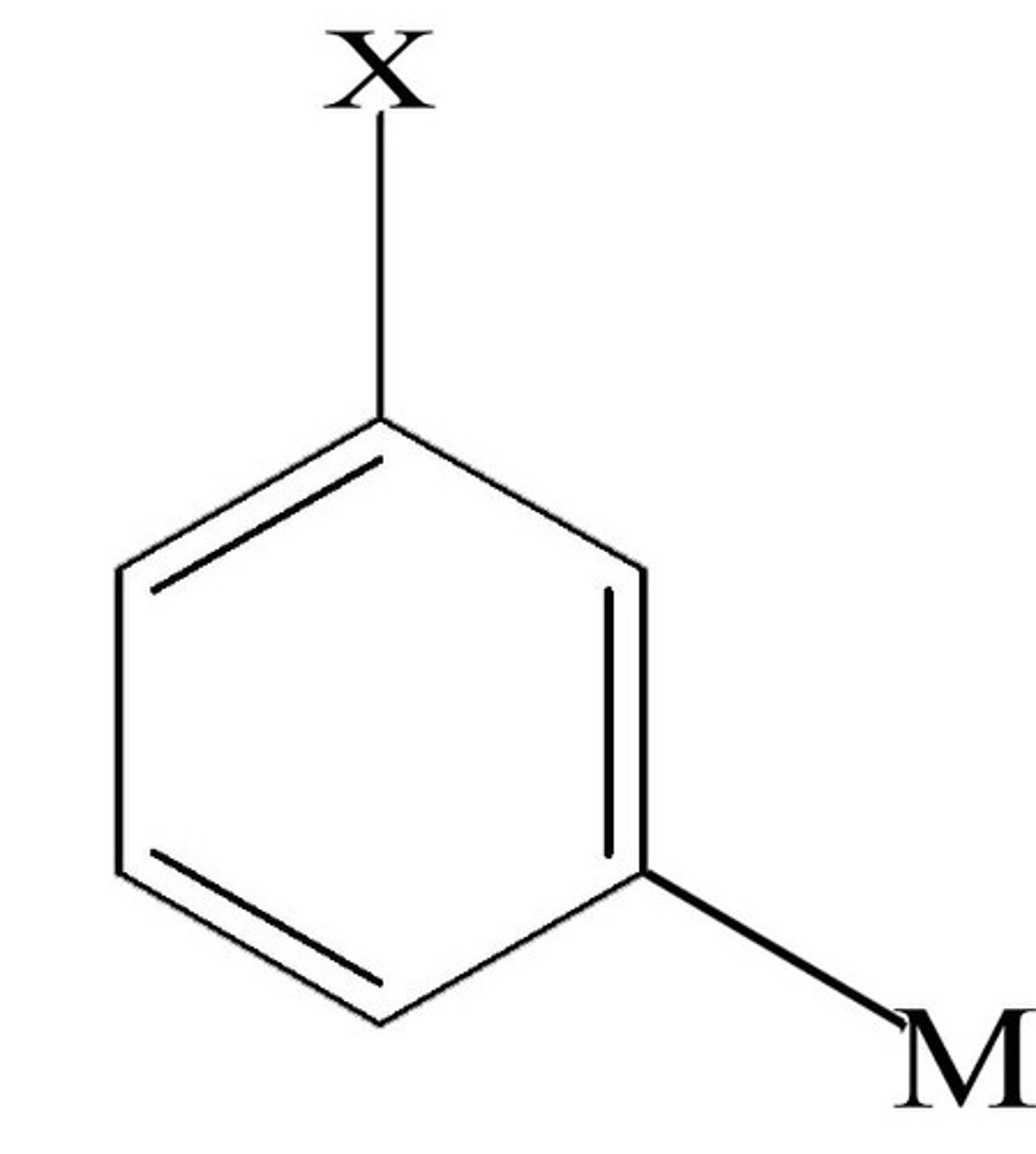
ortho (o)
next to each other
para (p)
opposite side
meta (m)
two groups separated by a carbon
heterocyclic
ring shaped carbon chain which has to have at least one atom that isn't carbon in the ring
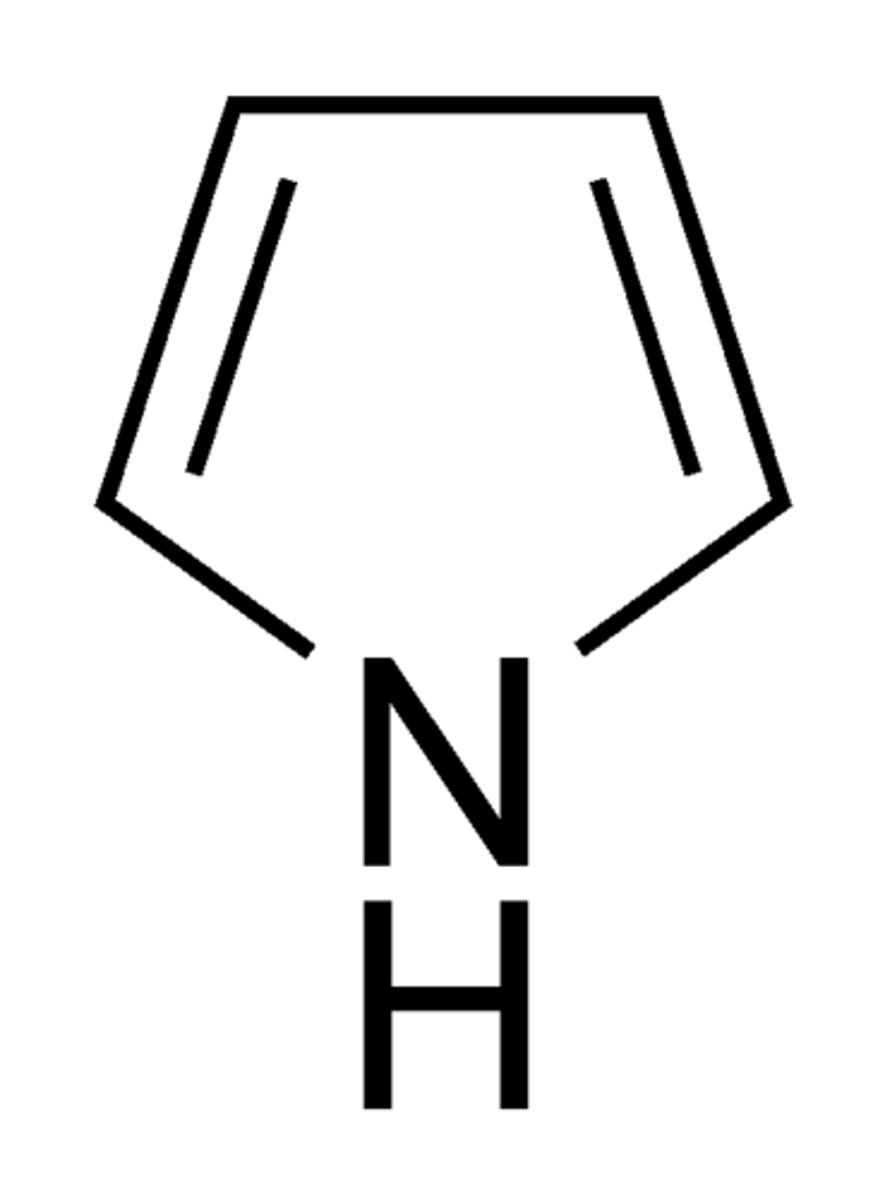
pyrrole
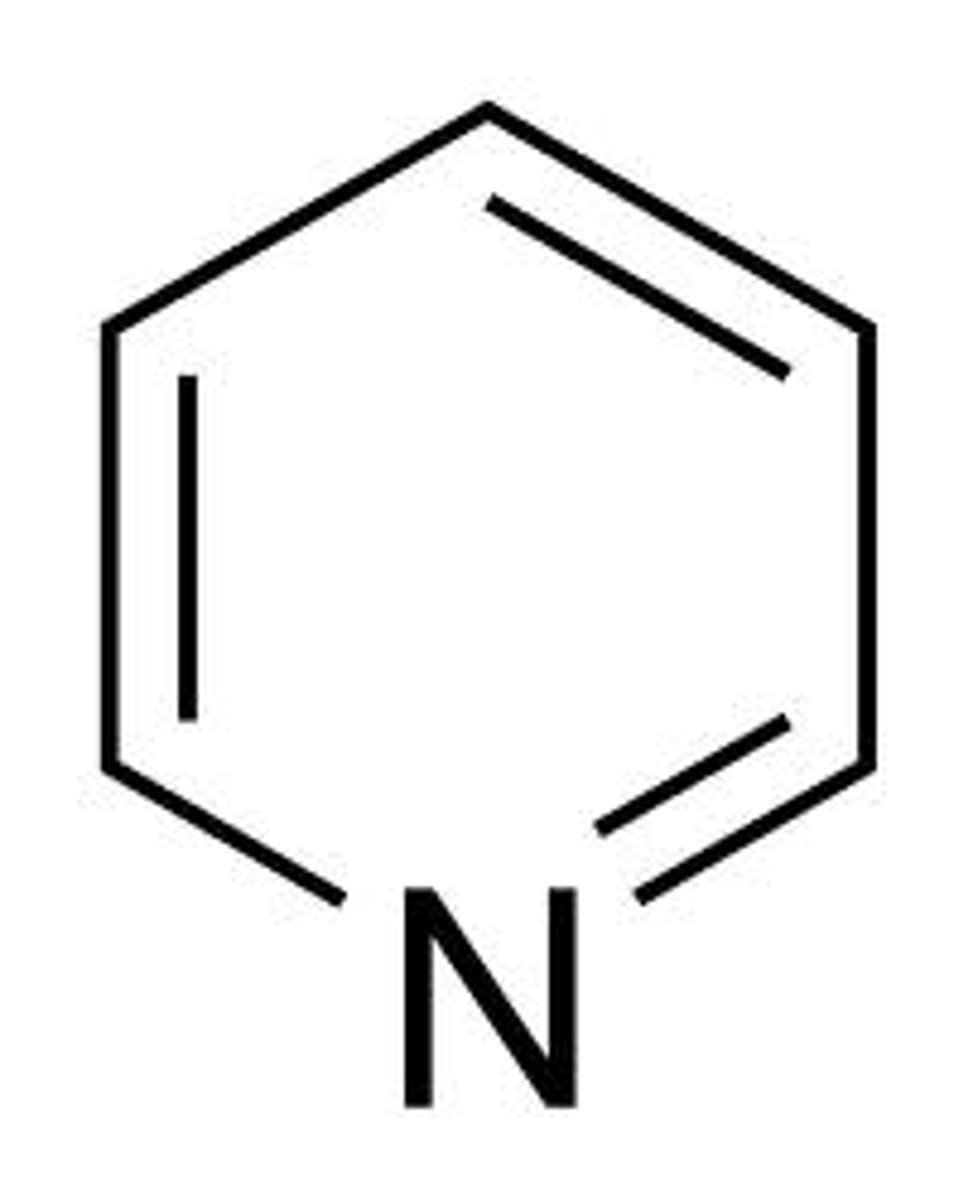
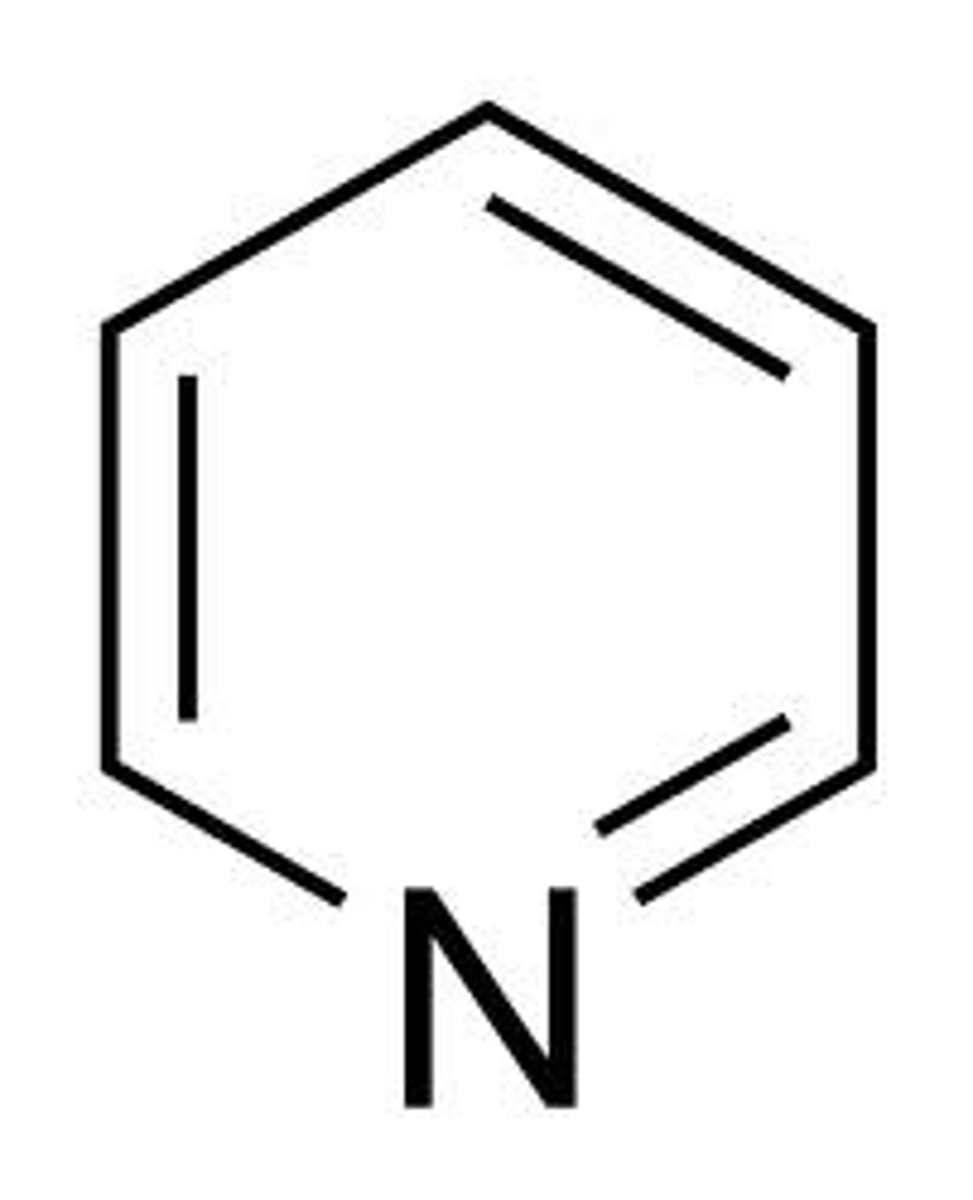
pyridine
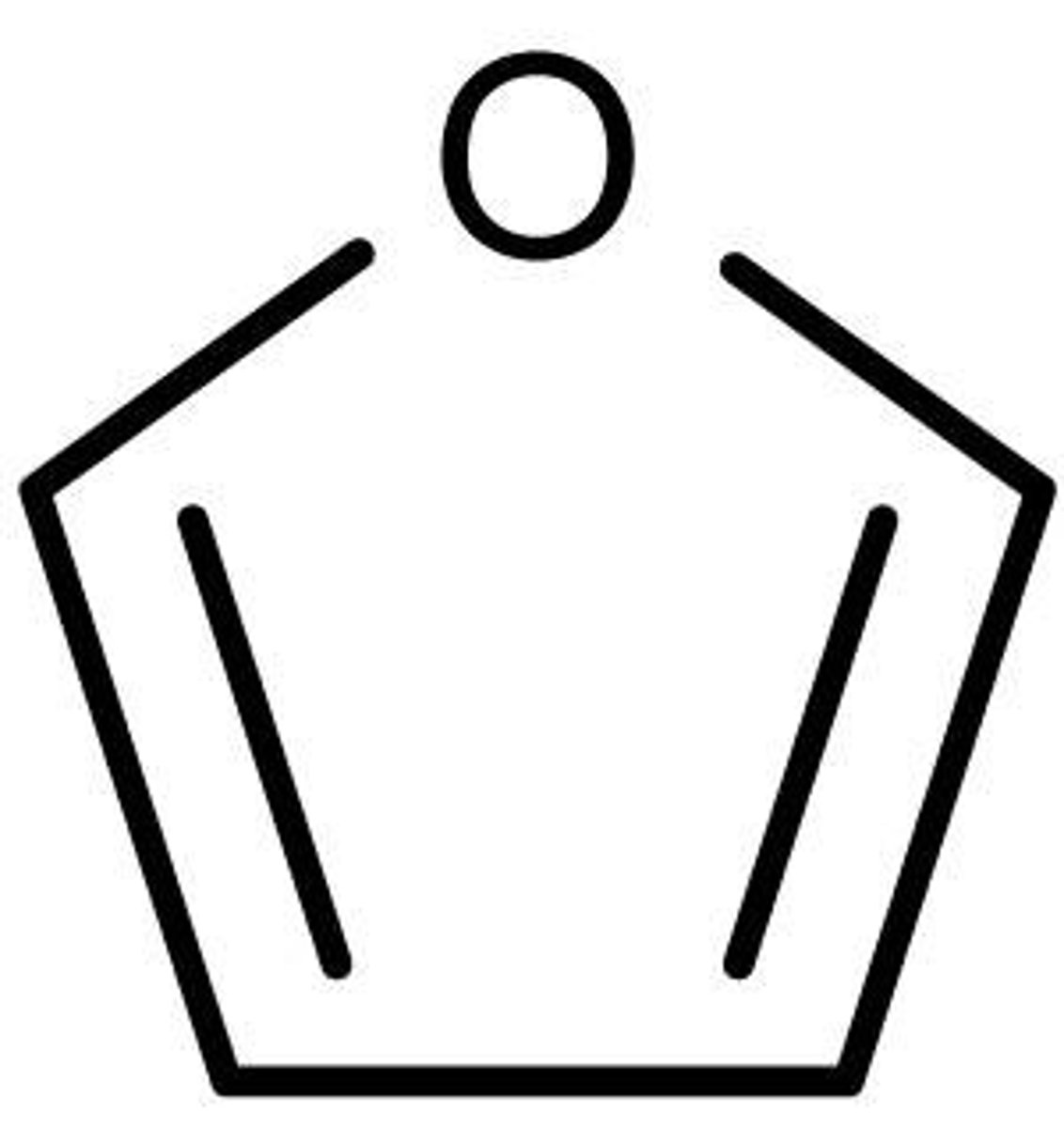
furan
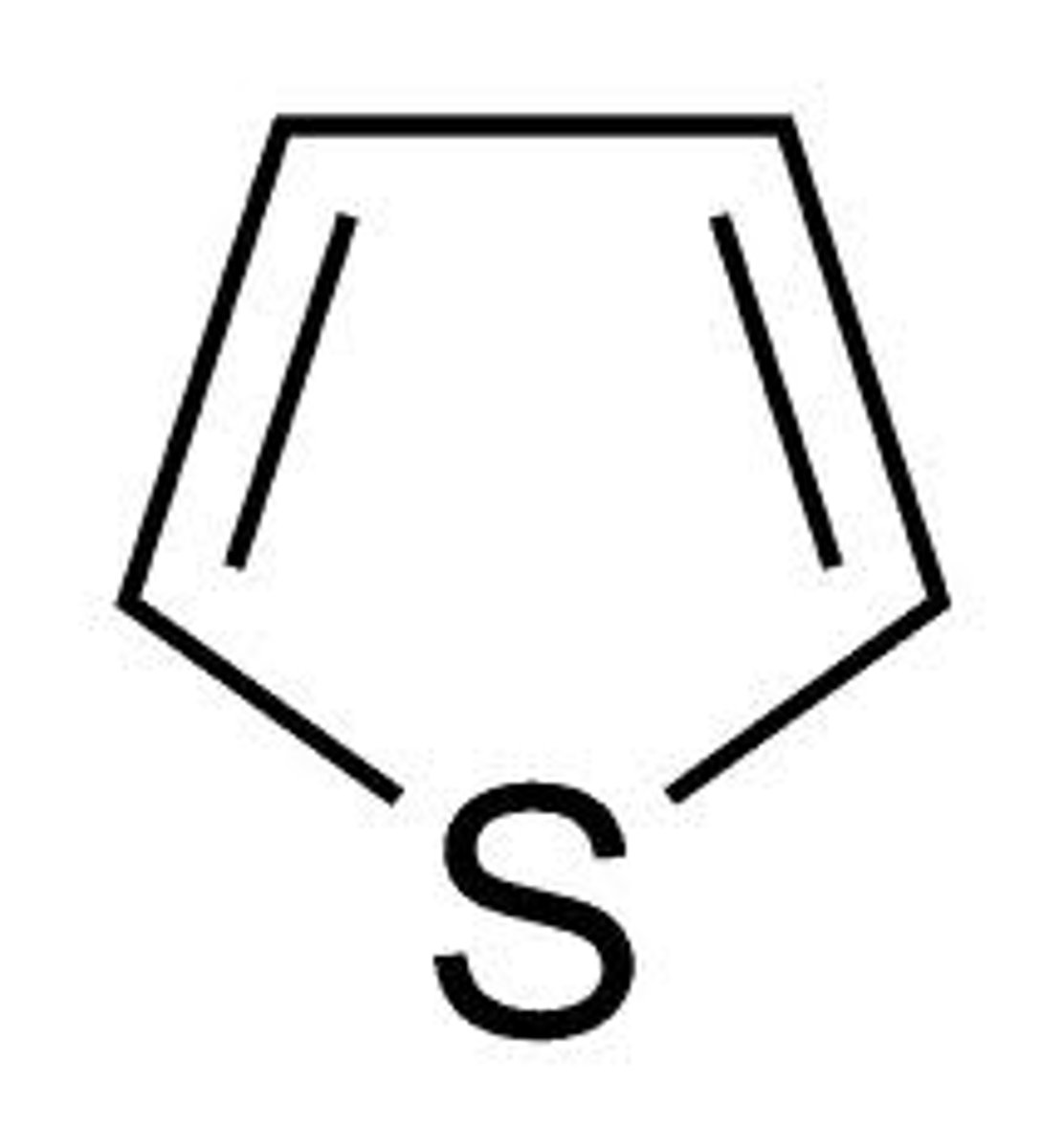
thiophene
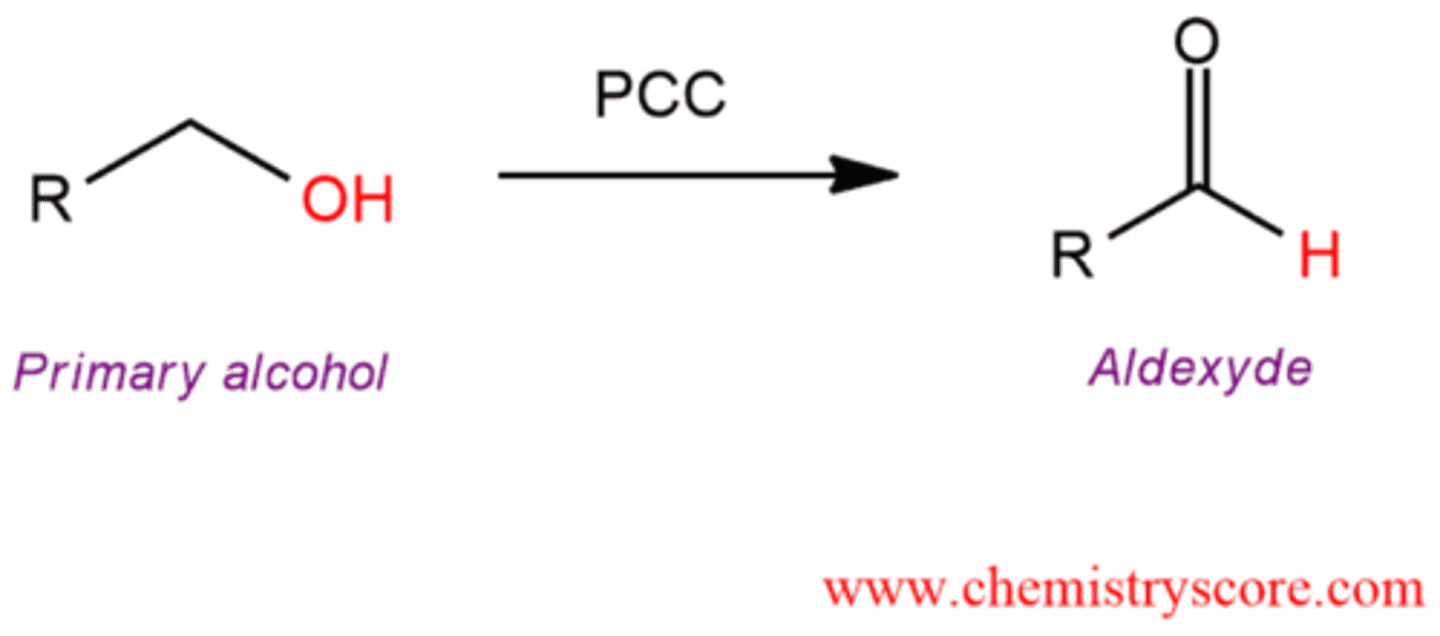
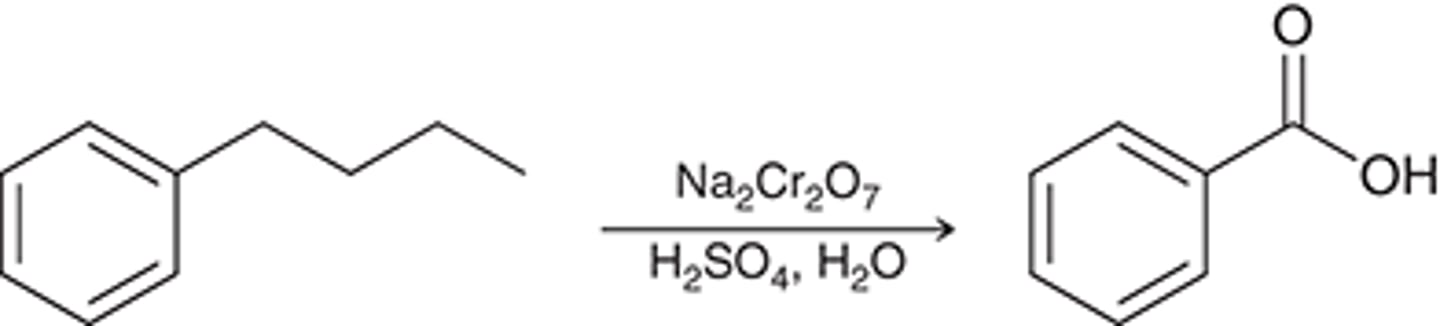
oxidation
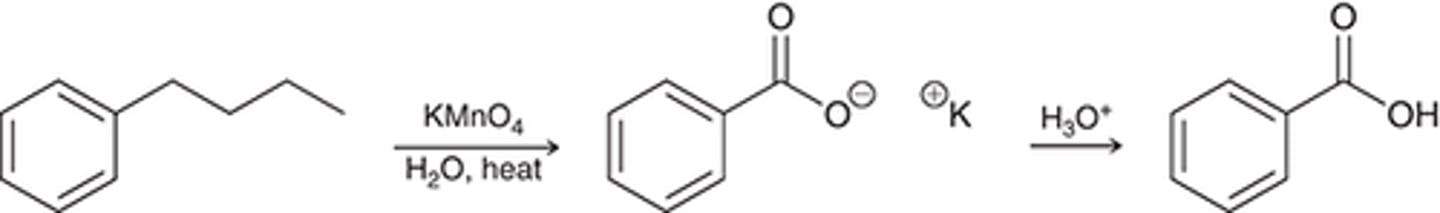
oxidation 2nd reagent
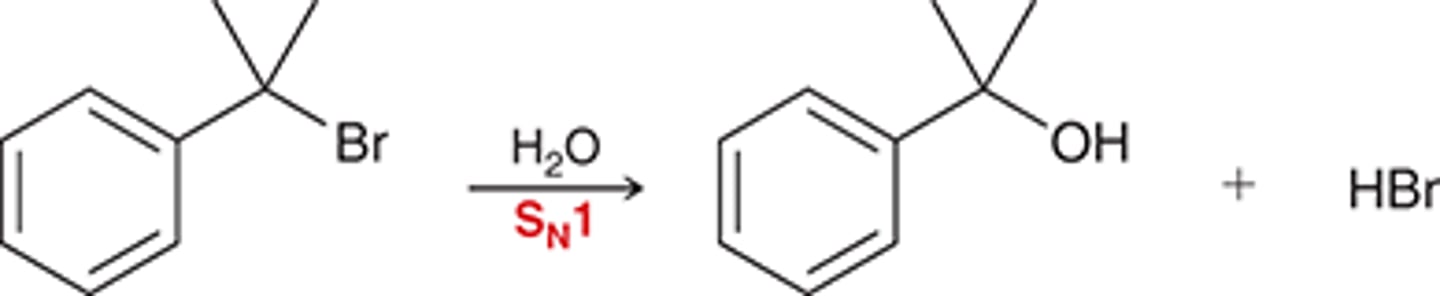
substitution SN1
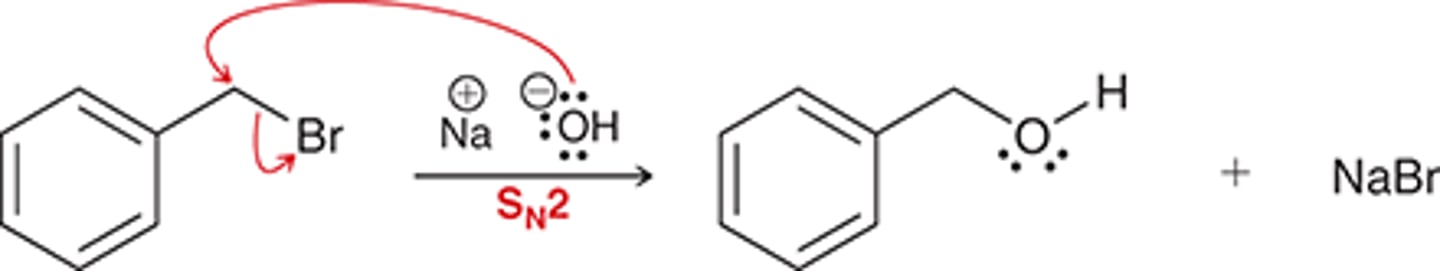
substitution SN2
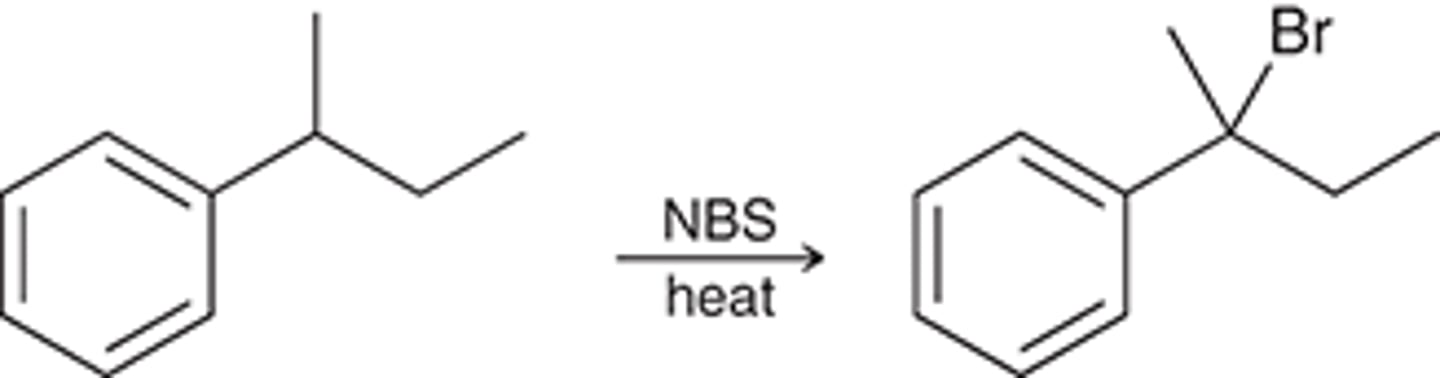
free radical bromination
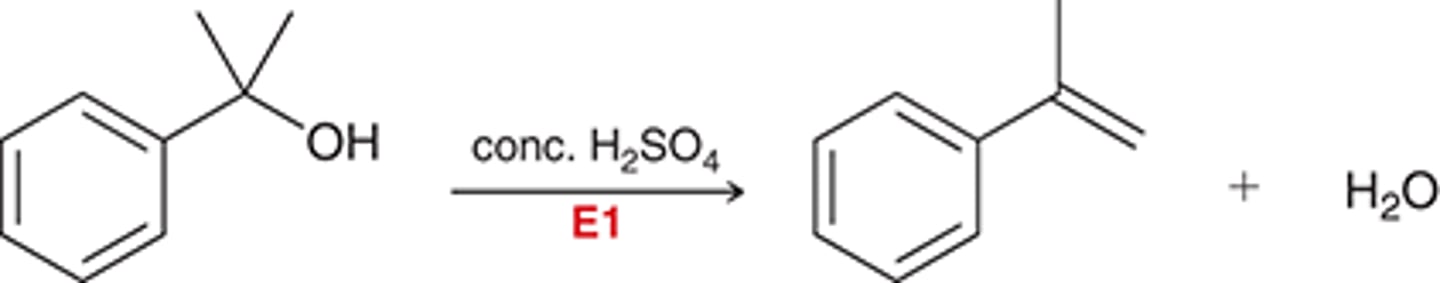
elimination E1
elimination E2
or:
DBU
tbuOK
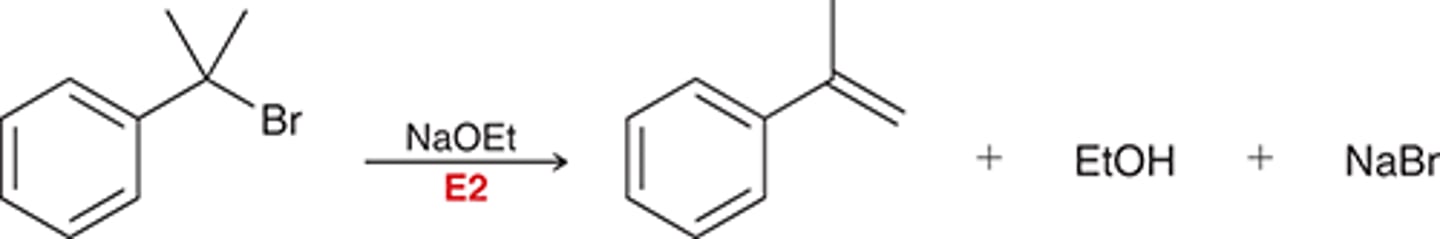
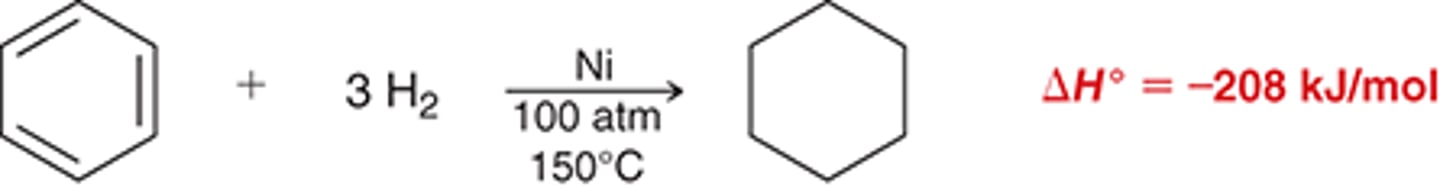
catalytic hydrogenation
must have high temp + pressure because aromatics are very stable
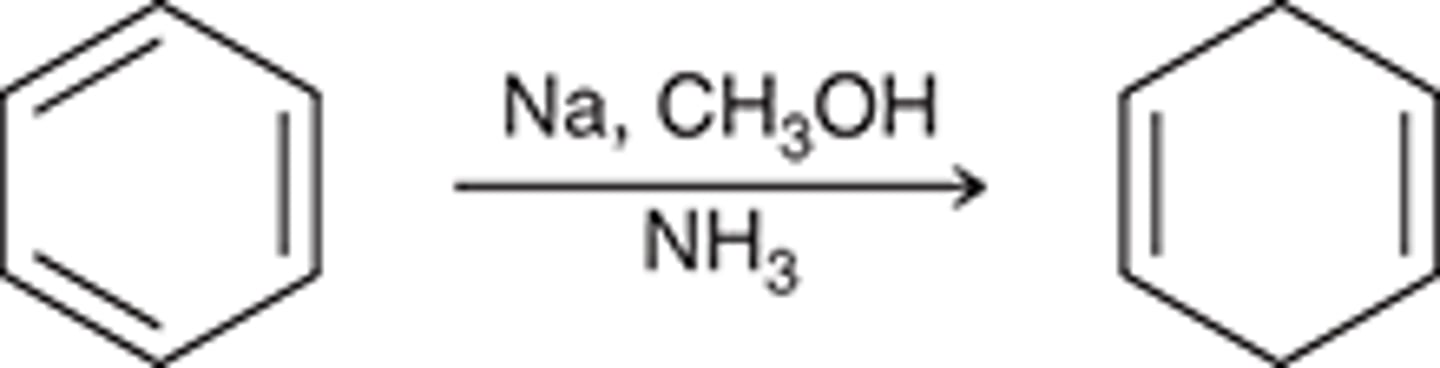
birch reduction
hydrogen, oxygen
oxygen, hydrogen
reduction gains ____________ and loses ________________
oxidation gains ______________ and loses ____________
benzylic position
any carbon atom attached directly to a benzene ring (must have at least 1 hydrogen)
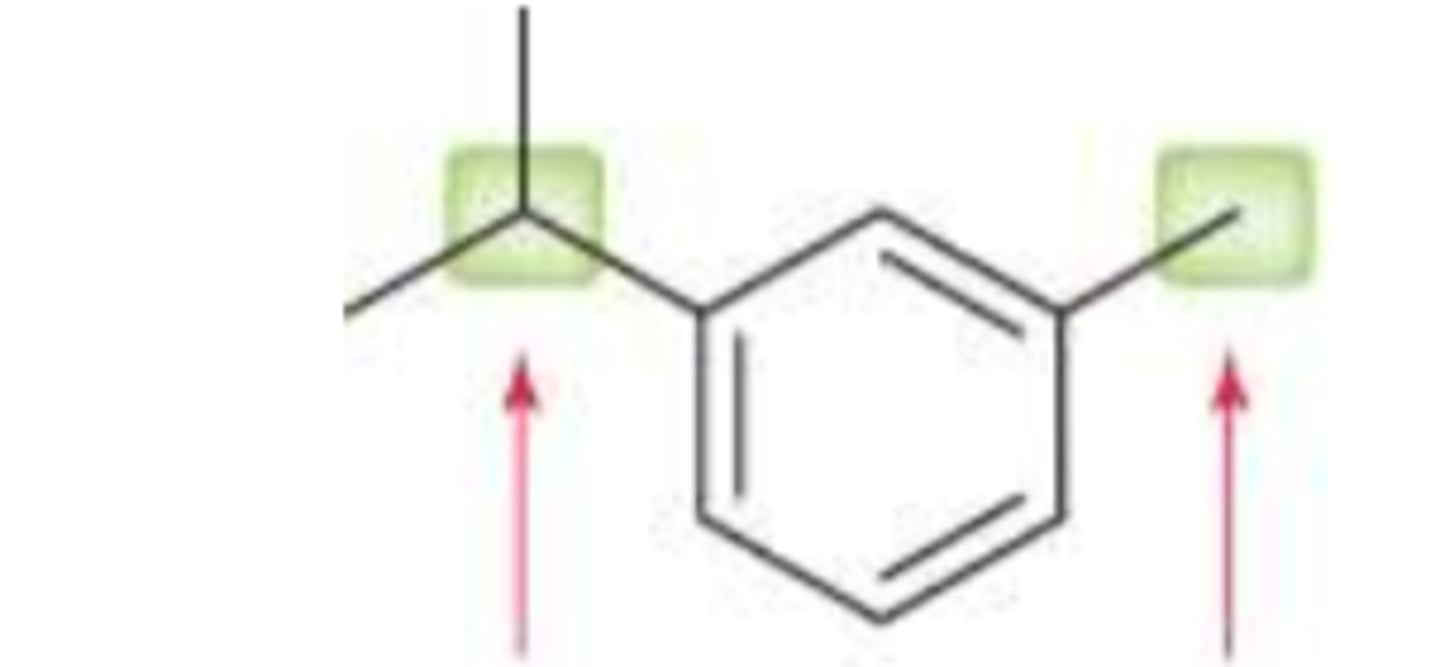
ortho and para are more stable then meta
which is more stable: ortho, para, or meta?
sp3
NBS can only react on carbons that are _______
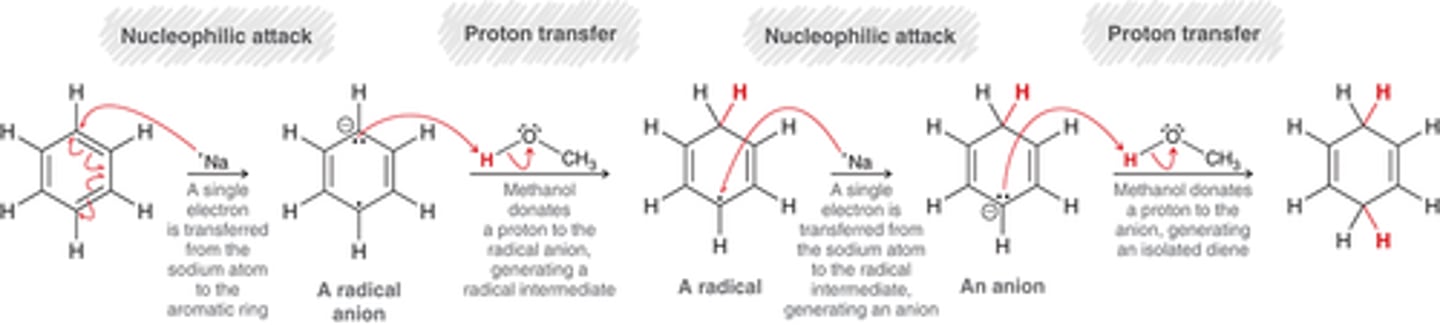
birch reduction mechanism
electron donating group (EDG)
An atom or group that release electron density to neighboring atoms from itself
toluene, phenol, anisole, aniline
EDG examples
electron withdrawing group (EWG)
a group or atom that has the ability to draw electron density toward itself and away from other adjacent atoms
benzoic acid, benzaldehyde, acetophenone
EWG examples
halogen
Aromatic substitution cannot take place if there's a ___________ attached
PCC