Micro Chapter 7: Bacterial and Archaeal Growth
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
How long can bacterial biomasses survive and where?
100 million years and in extreme environments
Binary Fission
Occurs after genome replication, half of replicated genome is placed in half the elongated cell and then a septum is formed
Other forms of reproduction
Budding, multiple fission (progeny stays in parent until mature), and spore formation (uninucleoid) dispersed by filamentous fungi
3 Phases of Bacterial Cell Cycles
1) Growth phase
2) Chromosome replication and segregation phase
3) Cytokinesis
Bacterial division different from eukaryotic
1) Chromosome rep and partitioning occur concurrently
2) Initial cytokinesis occurs before genome rep is complete
3) Start new rep before cytokinesis is finished
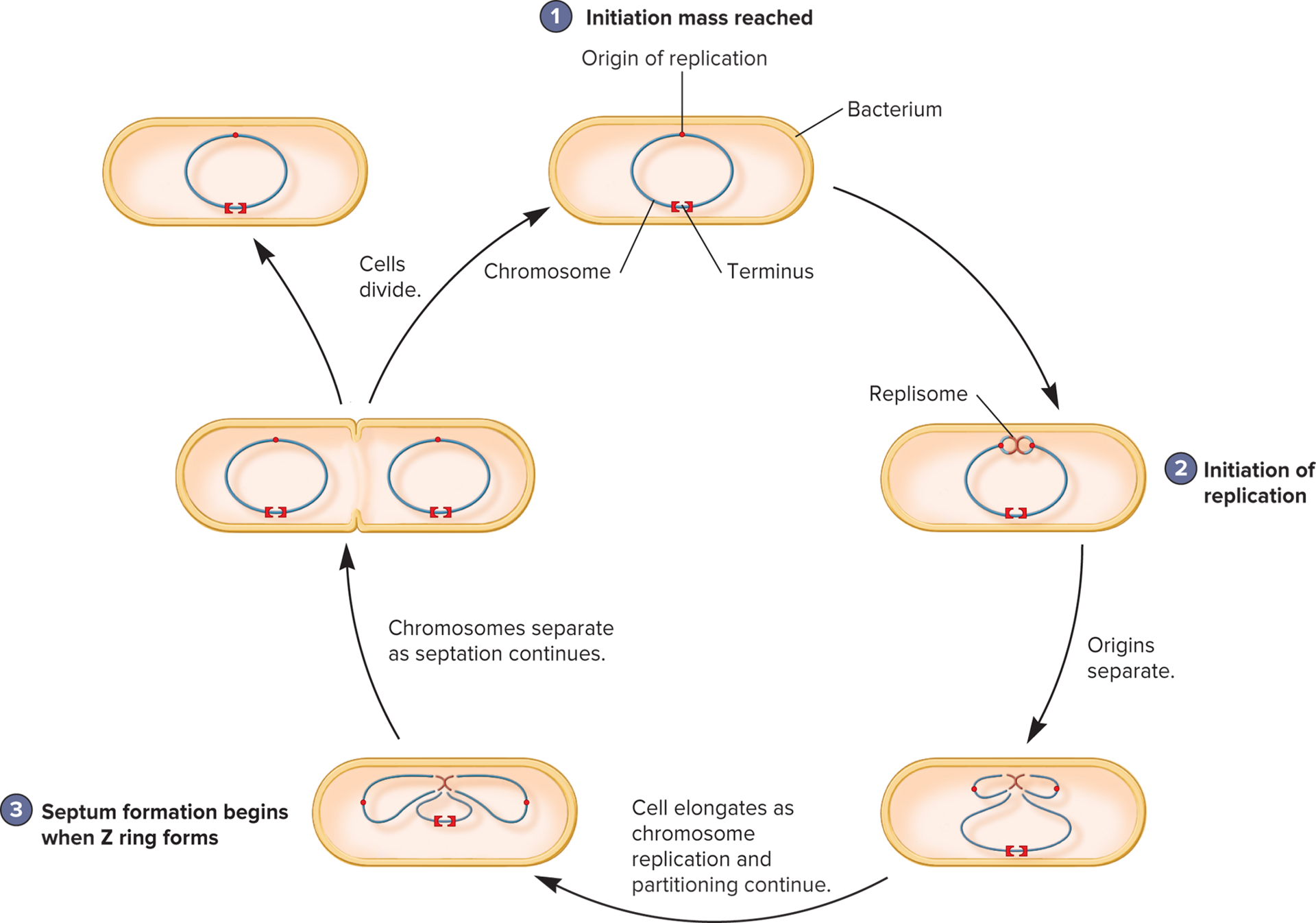
Origin of Replication
where rep begins on the chromosome
Terminus
where rep stops
Replisome
DNA synthesizing complex
C. crescentus
1 daughter cell is a swarmer cell with a flagella, 1 daughter cell is a stalked cell to adhere to surfaces (chromosome rep only in stalked cell stage)
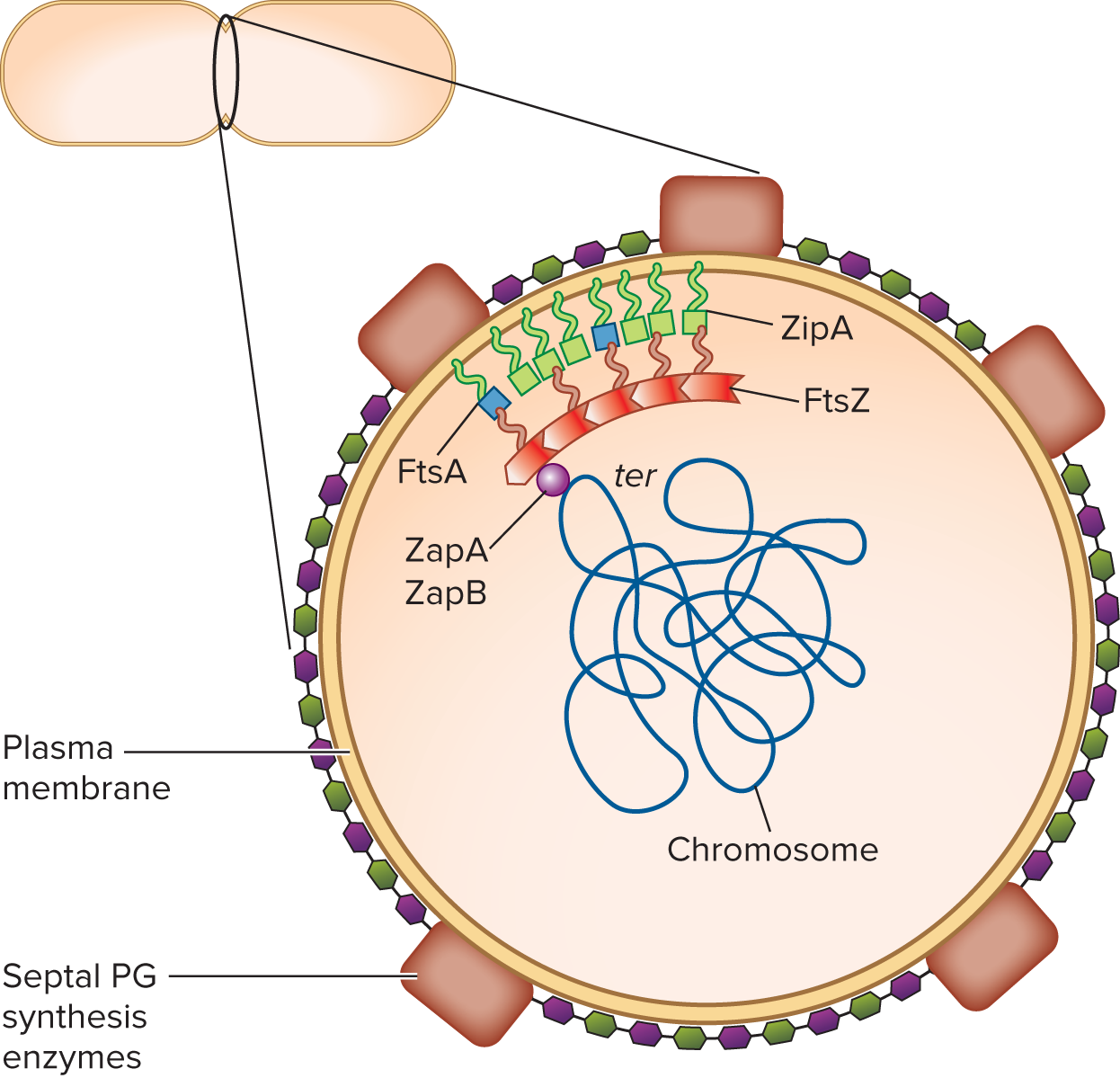
Cytokinesis Steps
1) Site selection for septum formation
2) Z ring polar formation of cytoskeletal protein FtsZ
3) PG synthesis machinery assembly
4) Septum formation
Cytokinesis in E. coli
1) Initiate rep
2) Separate origins
3) Z ring formation
4) Chromo separate
5) Cell divide
FtsZ
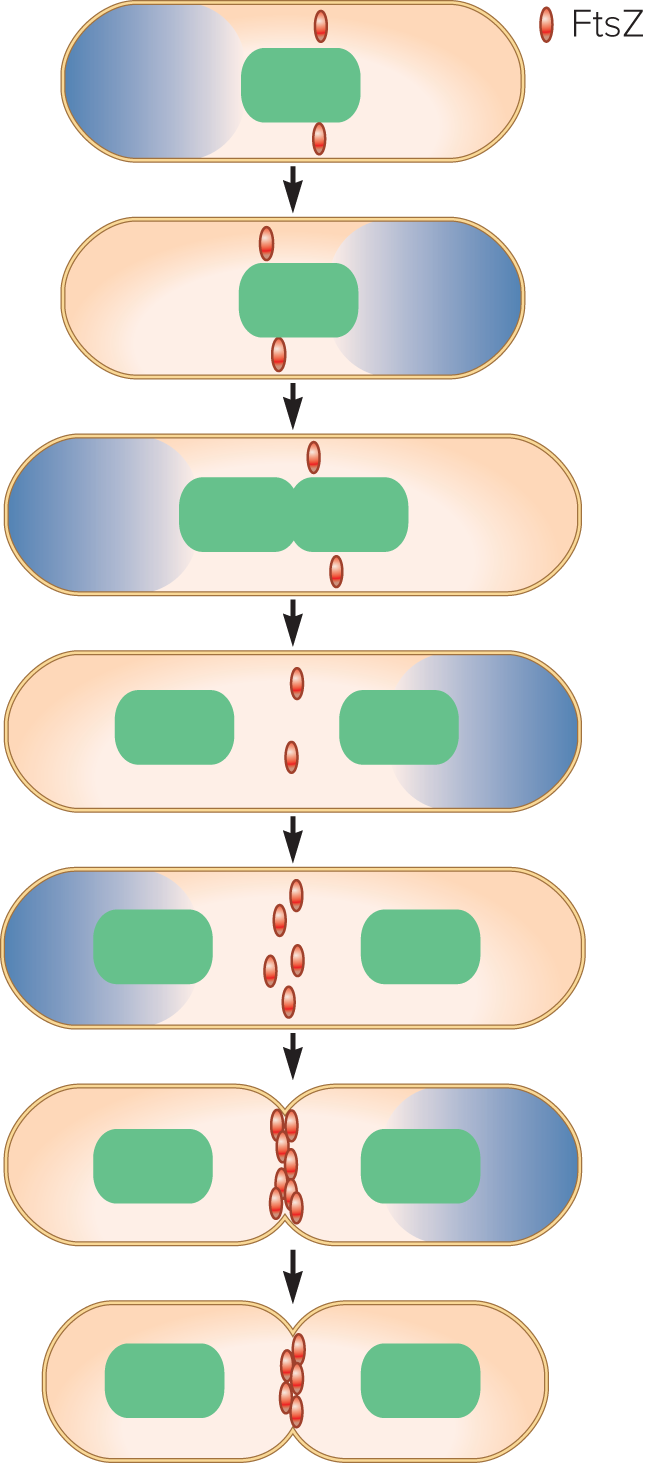
protein goes to future division site to form Z ring
Z ring
clump of FtsZ filaments at the mid cell, move inside membrane by treadmilling
Min System
place FtsZ proteins around the cell by preventing polymer formation in the wrong places
Cell Growth
1) increase in size of single cell
2) increase in number of cells
Helicobacter pylori
changes from helical shape to straight rods depending on environmentand is known to cause stomach ulcers and gastritis.
Turgor pressure
cell wall sacculus prevents swelling and bursting, PG prevents lysis
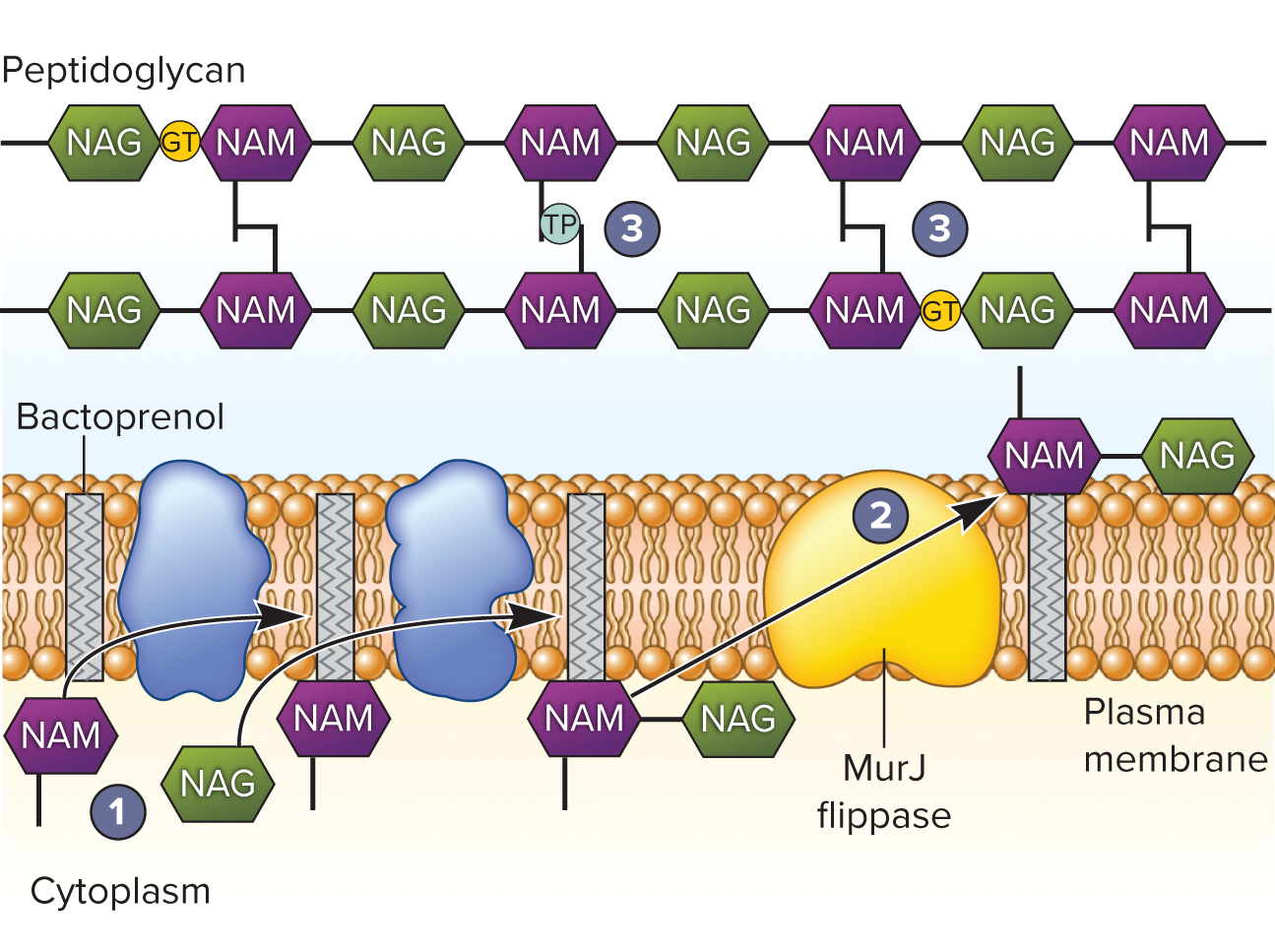
PG Synthesis
1) NAG NAM made in cytoplasm and attached to lipid carrier (bactoprenol) in plasma membrane
2) Carrier sent across membrane by MurJ (flippase)
3) NAG NAM pentapeptide unit placed in PG strand by glycotransferases (Gtases)
4) Strands crosslinked by transpeptidase (Tpases)
Divisome
complex of 30+ proteins that catalyzes PG remodeling to split the sacculus
Elongasome
Synthesize PG during cell growth made of MreB
Used in rod shaped cell wall formation
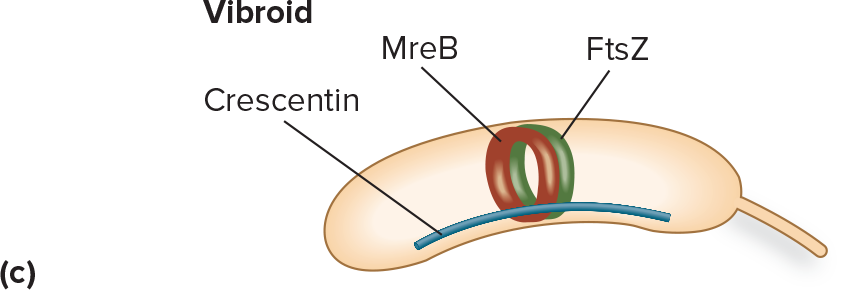
divisome, elongasome, MreB
Used in curved/spirochete cell wall formation
crescentin, flagella, spiroplasm
Crescentin
causes asymmetric cell wall growth to make a curved shape
Spiroplasma
lacks a cell wall, uses contractile cytoplasmic fibrils to make a spiral shape
Sulfolobus spp
Has 3 origins of replication and daughter cells remain unseparated (G2)
SegA
archaeal protein that forms filaments and helps segregate chromosomes
SegB
archaeal protein that binds DNA and enhances filament formation
Archaeal comparison to bacteria and eukaryotes
Chromosome segregation similar to bacteria
Cytokinesis similar to eukaryotes
Z ring in archaea
New S layer, no PG
Population growth of binary fission
log10 of the # of viable cells vs incubation time
Lag phase
cells not yet multiplying, synthesizing new components
Exponential phase
cells grow and divaide at their max rate
Stationary phase
growth ceases and curve is horzontal, cells dying, cells reproducing
Death phase
number of viable cells decreases as nutrient deprivation and toxic wastes rises
Long term stationary phase
cell population remains constant, waves of genetic variants
Generation or Doubling Time
cell population doubles,1/k
Growth rate constant (k)
number of generations per unit of time (n/t)
Osmophiles
adapted to hypertonic environments
Halophiles
adapted to high salt conditions (are osmophiles)
Salt in mode
keep salt in cytoplasm to be hypertonic
Salt out mode
keep salt out of cytoplasm by importing solutes (sucrose, glycerol, amino acids)
Compatible Solutes
protect cell from osmolarity changes, sucrose, glycerol, amino acid (proline, glutamic acid), choline, betaines
Water Activity (aw)
measure of water in environment (1/100 relative humidity of the solution)
Distilled water=1
Milk=0.97
Saturated salt solution=0.75
Dried fruit=0.5
Osmotolerant
grow best at high aw, Staphylococcus aureus, Zygosaccharomyces rouxii
Xerotolerant
tolerate high solute concentration
pH equation
pH=-log[H]=log(1/[H])
Acidophiles
grow best pH 0-5.5
Neutrophiles
grow best pH 5.5-8
Alkaliphiles
grow best pH 8-11.5
Range of temperature for microbes
-15 C to 113 C
Psychrophiles
grow well at 0C, optimum growth 15C, maximum 20C
Psychrotolerants
grow at 0C, maximum 35C
Mesophiles
Optimal growth 20-45C, minimum 15-20C, maximum 45C
Thermophiles
Optimal 55-65C, minimum 45C, maximum 85C
Hyperthermophiles
Optimal 85-100C, minimum 55C
Cardinal Temperatures
minimum, optimum, maximum growth temperatures
Obligate aerobes
Only grow in presence of O2
Microaerophile
Low levels of O2 for growth, 2-10%, damaged by atmospheric O2 (20%)
Facultative anaerobes
Do not require O2 for growth, but grow better in presence of O2
Aerotolerant anaerobes
grow equally well whether or not O2 is present
Obligate anaerobes
Cannot tolerate O2, will die if exposed unless live with facultative anaerobes that use up O2, ex: porphyromonas gingivalis
Barotolerant
survive increased pressure
Plezophilic
require high pressure for growth
Ionizing Radiation
Short wavelengths and high energy damage microbes, break H bonds, destroys rings, polymerizes some molecules, oxidizes proteins
Low level=mutation
High level=lethal
UV radiation
lethal at 260 nm, destroys DNA repair processes
Eutrophic
Nutrient rich environment, microbes dont live here
Oligotrophic environment
low level of nutrients, microbes live here
Viable but not curable (VBNC)
cells unable to grow under certain conditions, can resume growth in normal conditions
Persisters
remain alive despite antibiotics, low ATP levels
Growth arrest
not actively dividing or dead
E coli growth arrest molecules
RpoS (enzymes for starvation) and ppGpp (regulatory network), Dps (protects DNA), chaperones (protect protein denaturation)
Biofilms
slime encased microbial communities
Percent of bacteria living in biofilms
40-80%
Extracellular polymeric substances
include polysaccharides, proteins, glycoproteins, glycolipids, and DNA that makes up biofilm matrix
Quorum sensing
assess size of population to assure minimum number of cells needed
ex: Vibrio fischeri biofilm in light organ of fish
Autoinducer
diffusible chemical signals produced by bacteria in response to changes in the population density and to communicate, gram negative
Autoinducing peptides
gram positive cell communication, transferring genes, uptake DNA
Culture media classification
1) Chemical composition
2) Physical nature
3) Function
Defined medium
Ingredients that can be measured
Complex medium
Ingredients that cant be measured
Agar
solidifying agent, D-galactose, 3,6-anhydro-L-galactose, D-glucuronic acid from red algae
Supportive media
grow a variety of microbes, soy and broth
Enriched media
contains blood to encourage fastidious microbes
Selective media
particular microbes can grow
Differential media
show difference between groups of microbes
Segei Winogradsky and Martinus Beijerinck
Enrichment culture techniques
1) suitable microbial source
2) Nutrients to exclude
3) Environmental conditions
Methods for isolation
1) Streak plates
2) Spread plates
3) Pour plates
Culturomics
many media types and many conditions to isolate new microbes
Diffusion chambers
enclosure within natural habitat that diffuses in nutrients
Co culturing
presence of a different species to survive
Direct counts
use microscope in a counting chamber
Membrane filtration
aquatic samples stained
Flow cytometer
laser detects each cell and counts
Viable counting methods
1) membrane filtration to agar plate
2) Viable air samples by suction
3) Viable contact of plating surfaces
Dry weight measurement
cells washed and centrifuged and taken the mass of
Spectrophotometry
measures turbidity of sample
Total protein or nitrogen analysis
measures cell mass by analyzing cell contents
Chemostats
add essential nutrients at the same rate that media with microbes is being removed, lower dilution
Turbidostats
measure turbidity of culture in which media is continuously added, higher dilution
Define microbial growth.
Microbial growth is the increase in the number of cells in a population.