anatomy unit 5: muscular system notes (w/o major muscles)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
muscle
Soft Tissue that contains protein filaments that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell.
functions of muscular system
Producing Force and Movement
Maintaining Posture
Stabilizing Joints
Generating Heat
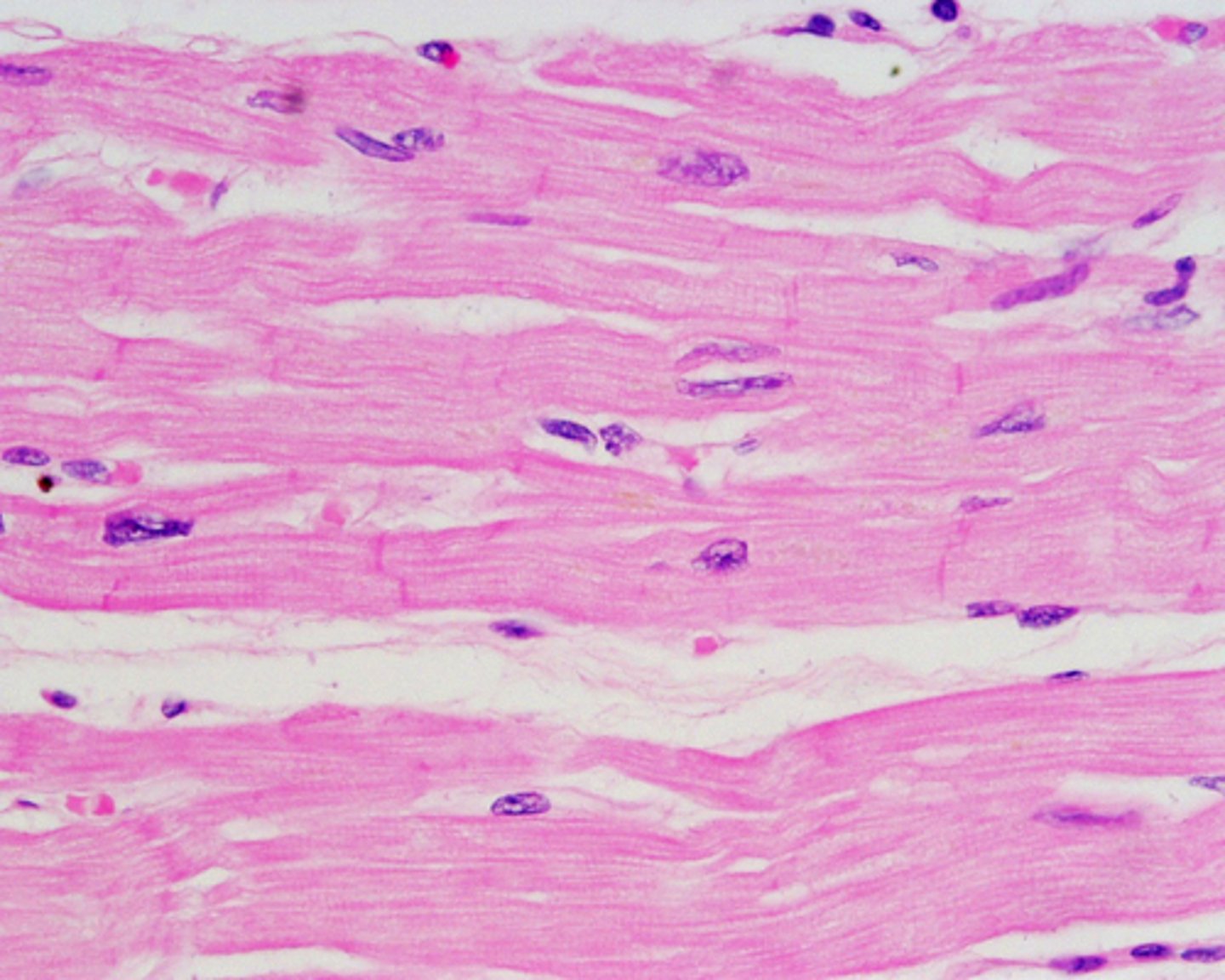
cardiac muscle
muscle that has striations, One nucleus, Branching cell shape, and Intercalated Disks
Functions: Involuntary Movement of Heart
smooth muscle
Found in Walls of Hollow Organs. No striations, One nucleus, Spindle-shaped cells
Function: Involuntary movement (propels substances along a pathway)
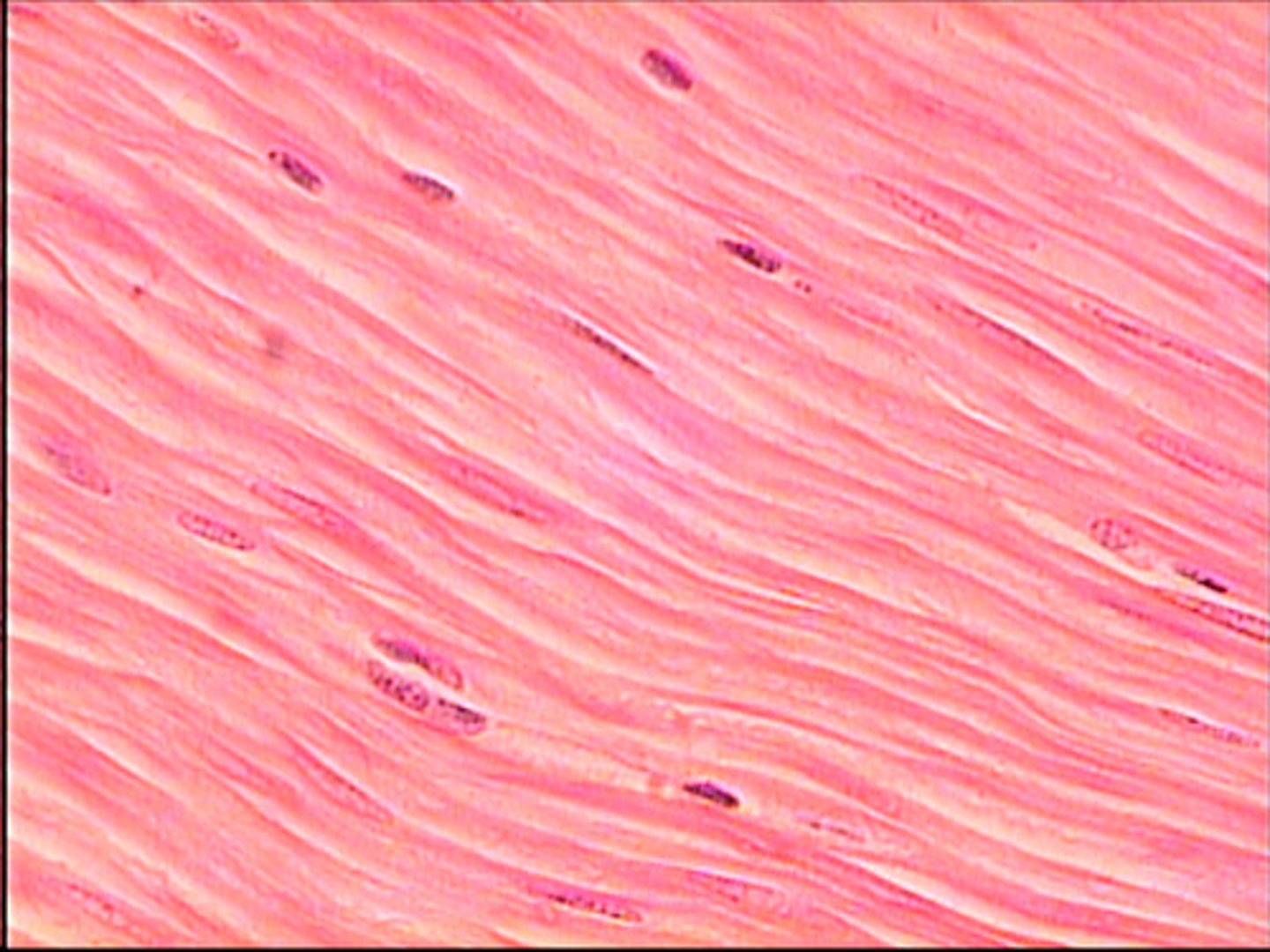
skeletal muscle
Found attached to the skeleton
Features: Striations, Many nuclei, Long cylindrical cells
Functions: Voluntary movement
tendon
dense regular connective tissue that attaches a muscle to bone
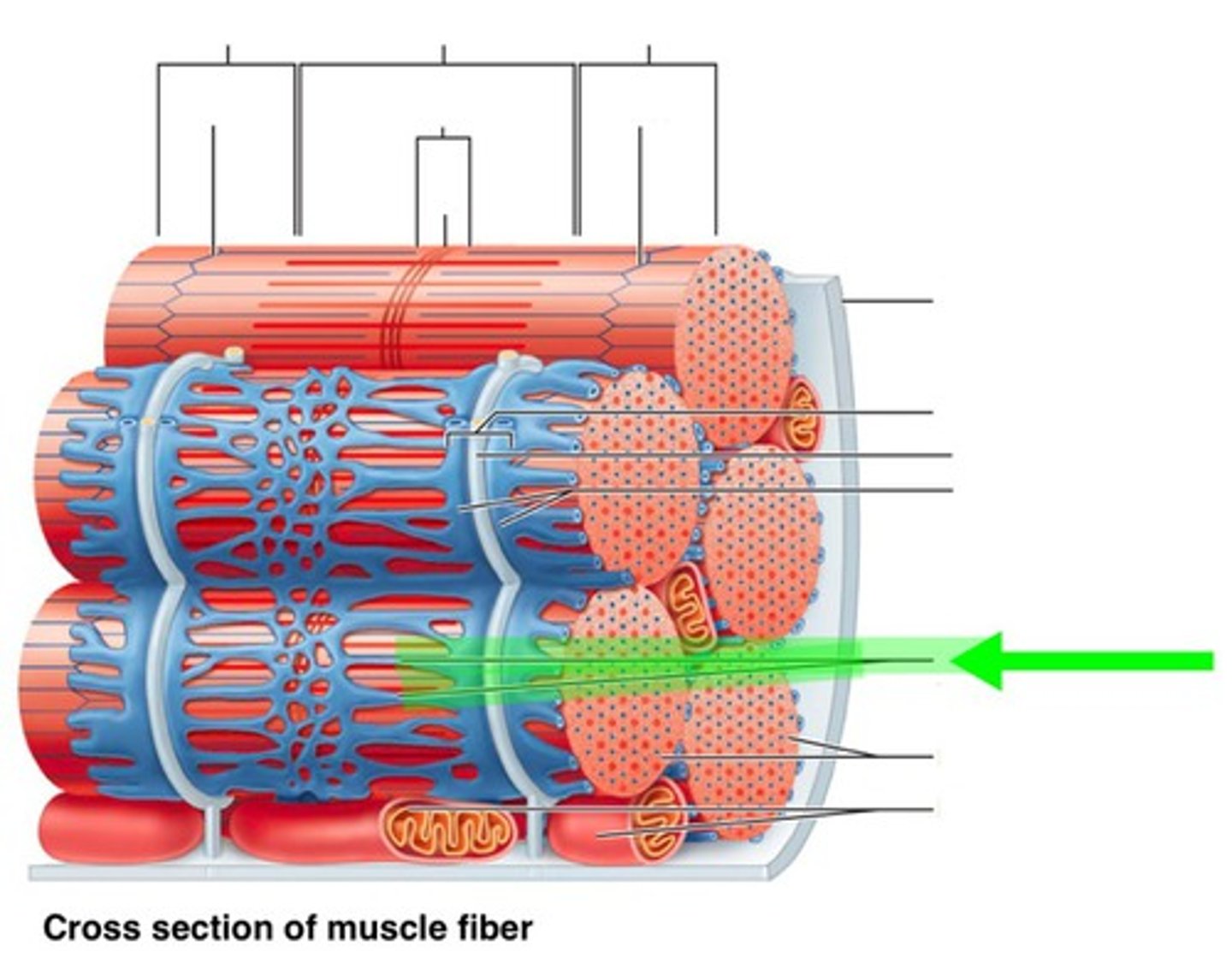
Epimysium
connective tissue layer that surrounds an entire muscle
Muscle Bundle
a collection of muscle fibers
Perimysium
connective tissue layer that surrounds a muscle bundle
Muscle Fiber
muscle cell
Endomysium
connective tissue layer that surrounds a muscle cell/fiber
Sarcolemma
the plasma membrane of a muscle cell.
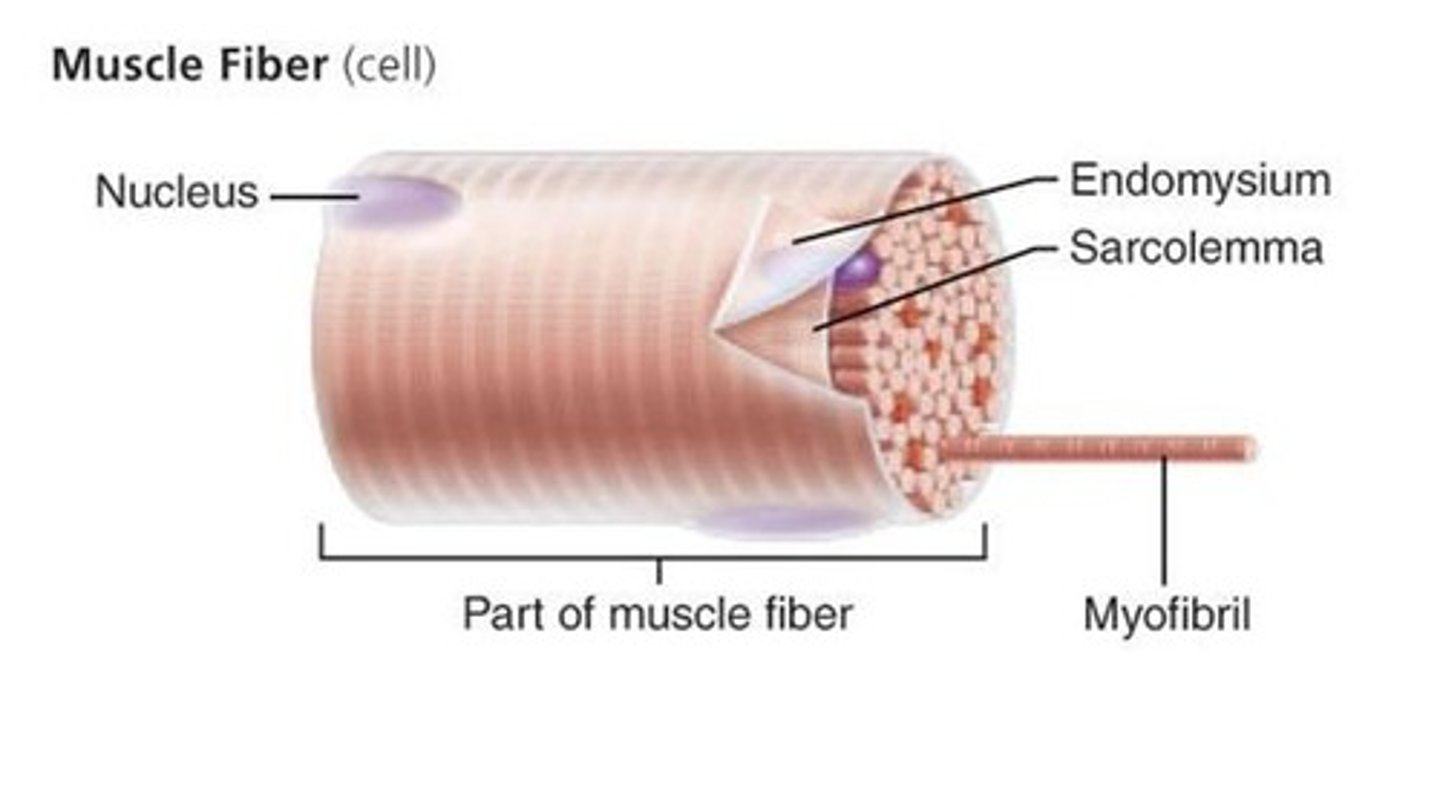
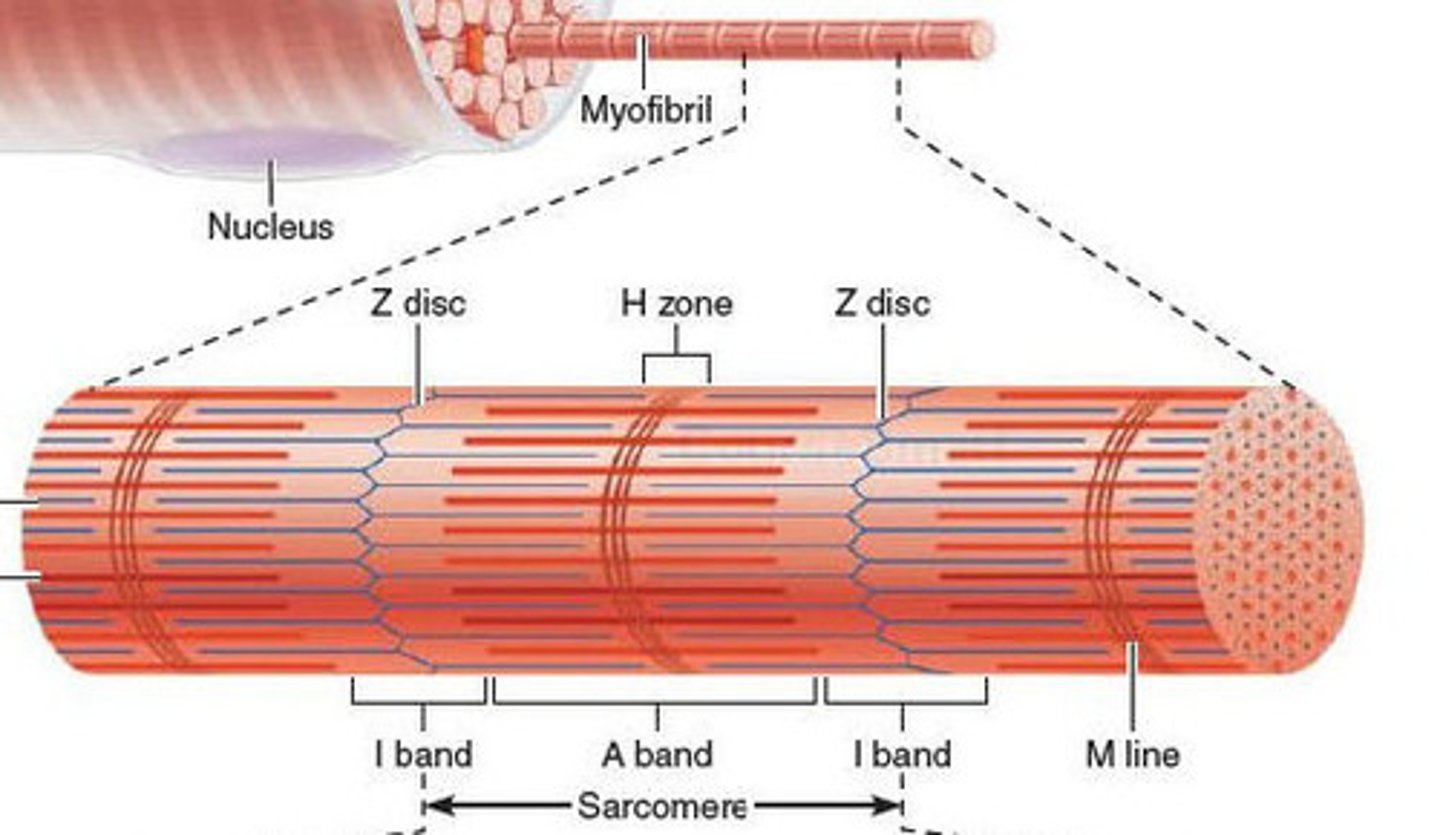
myofibril
Long ribbon-like organelles, which nearly fill the entire cell. Responsible for contractions.
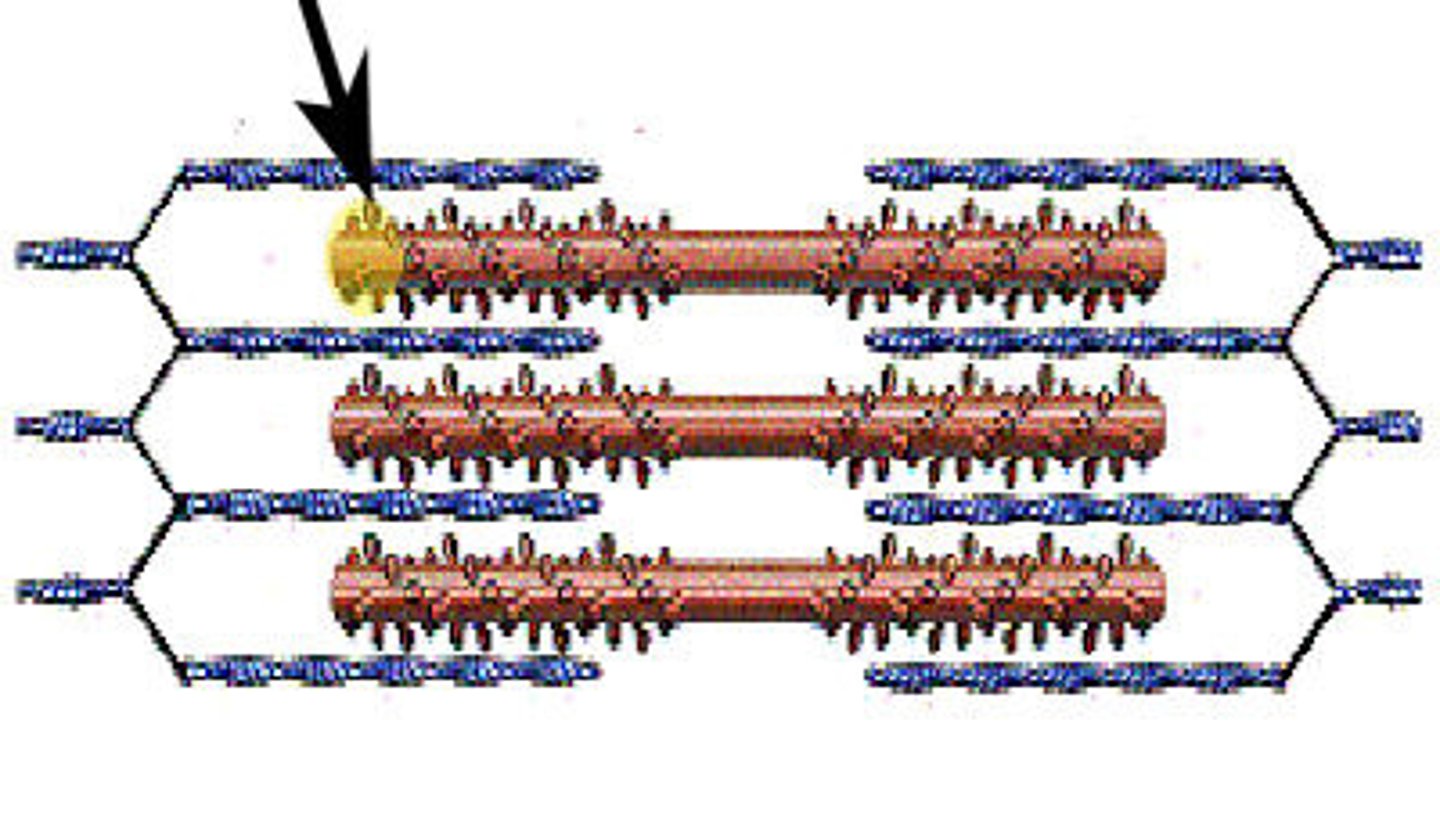
Sarcomeres
a section of the myofibril. Tiny contractile units, which are lined up and make up the myofibril.
Myofilaments
Thin threadlike proteins within the sarcomere.
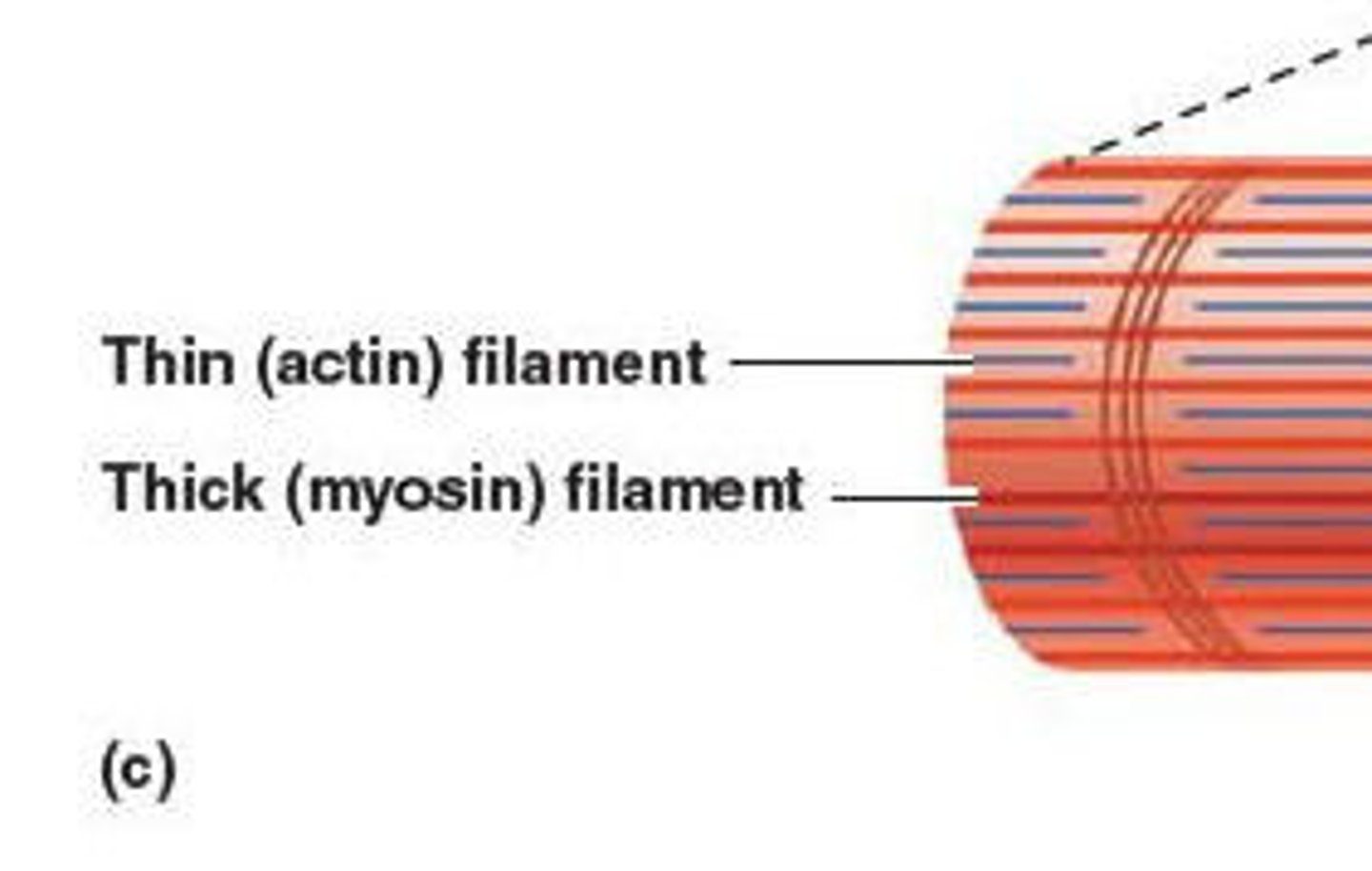
Thick filaments
or myosin filaments, are made mostly of bundled molecules of the protein myosin.
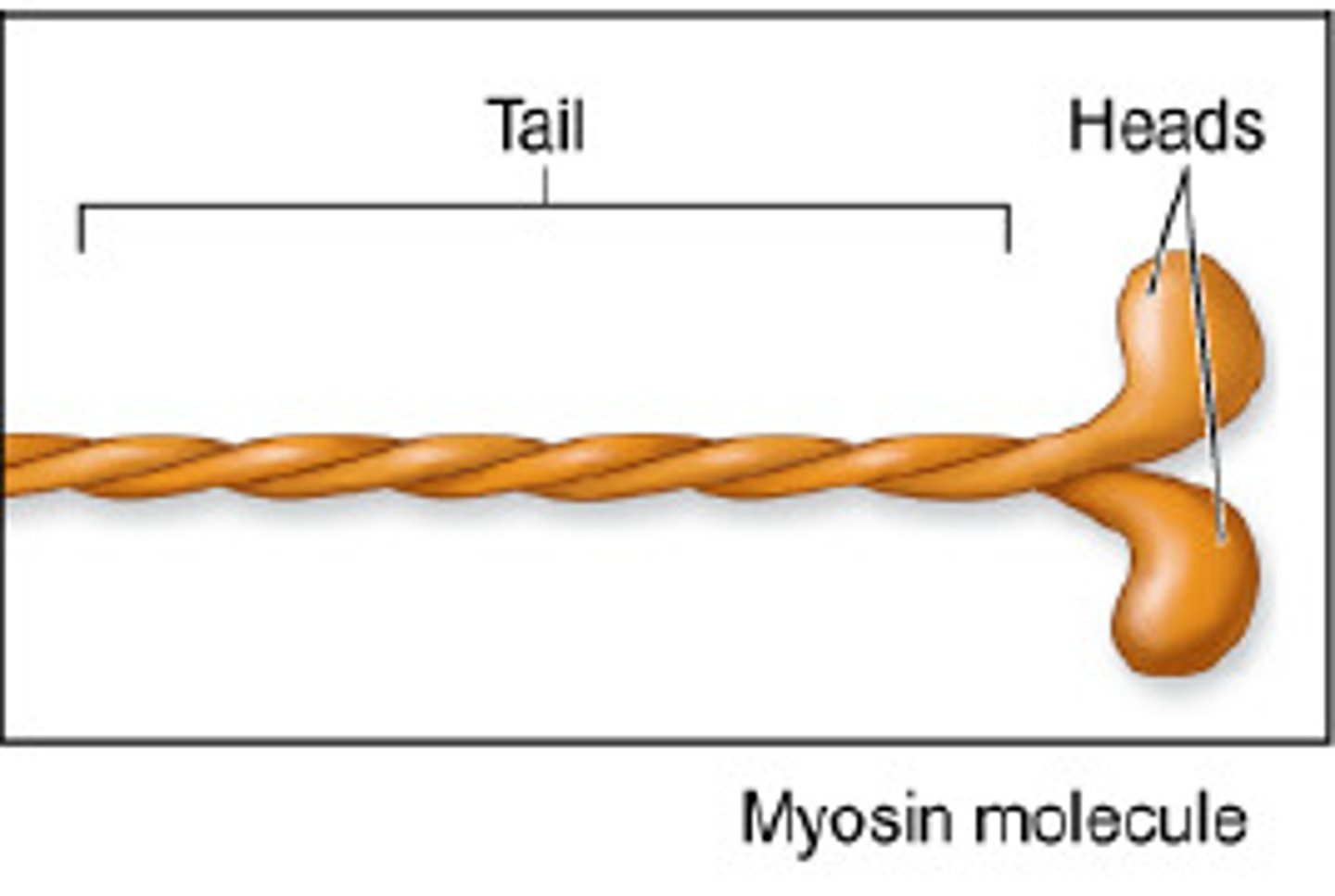
Myosin
one of the principal contractile proteins.
Cross bridges
Small projections or myosin heads. (On thick filaments) Also called myosin heads.
Thin filaments
composed of actin.
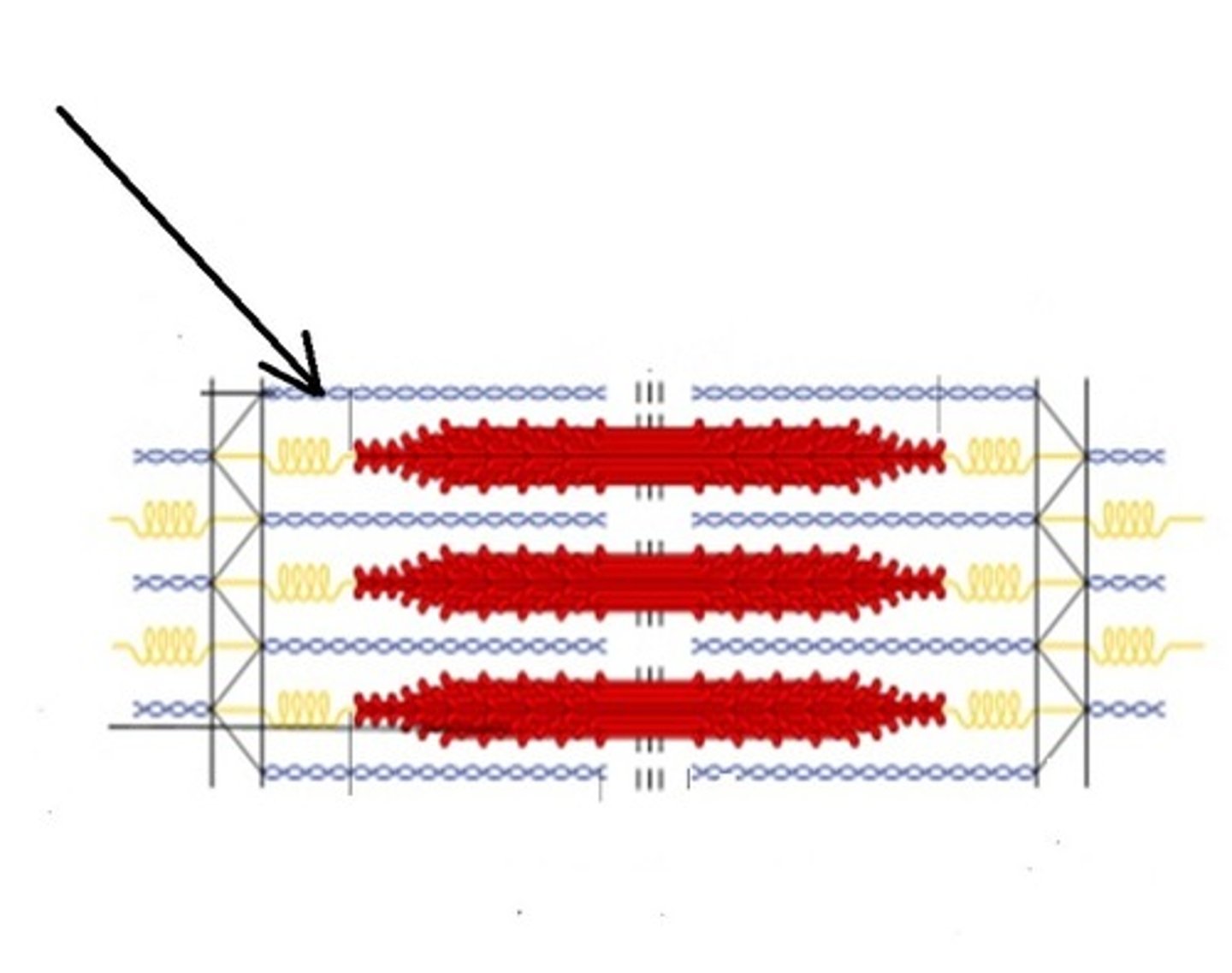
Actin
one of the principal contractile proteins.
Z-disk
structural element, fiber that holds the sarcomere together
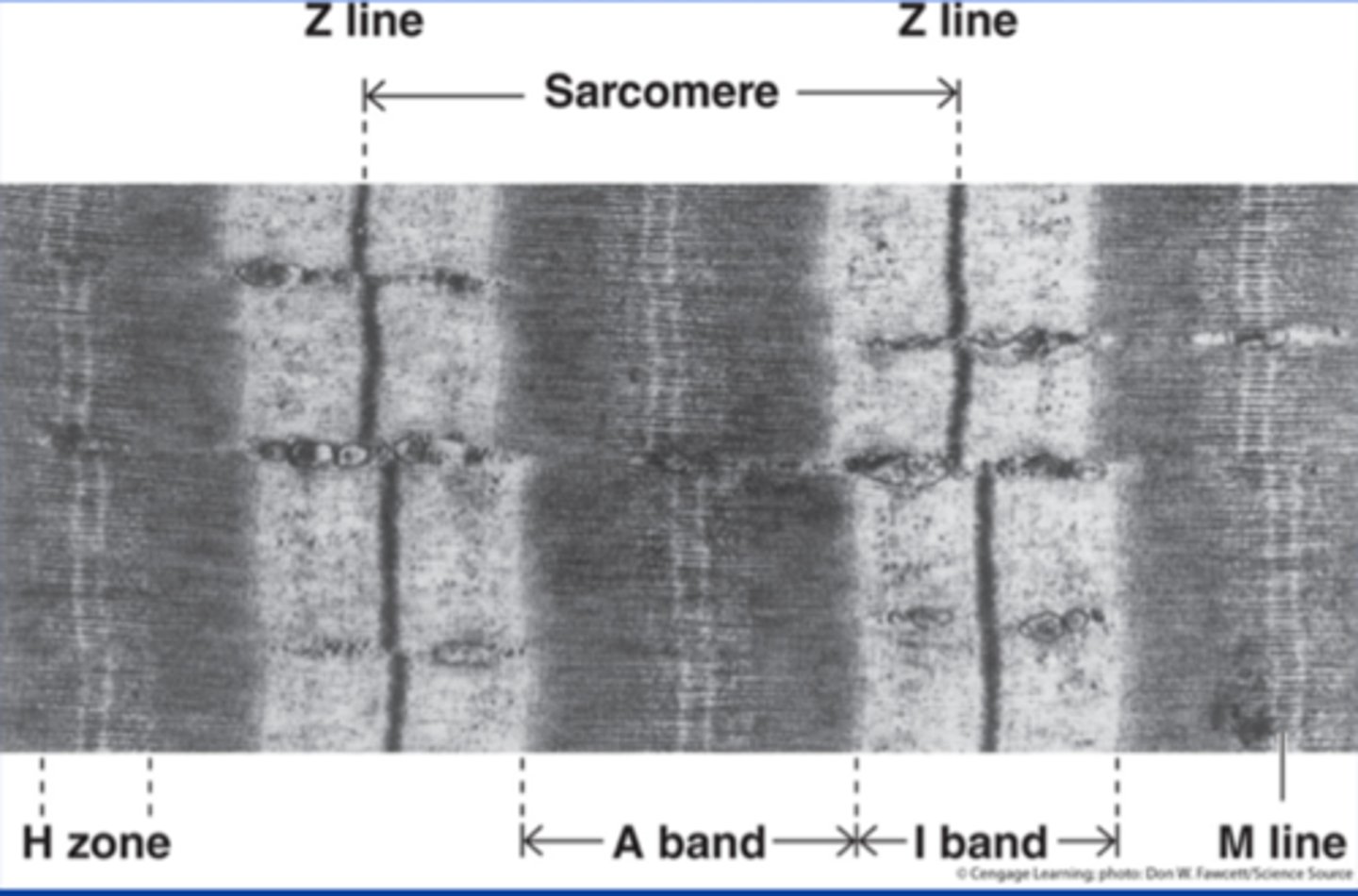
H-zone
space in the middle of the sarcomere where thin filaments are absent, this disappears during a contraction
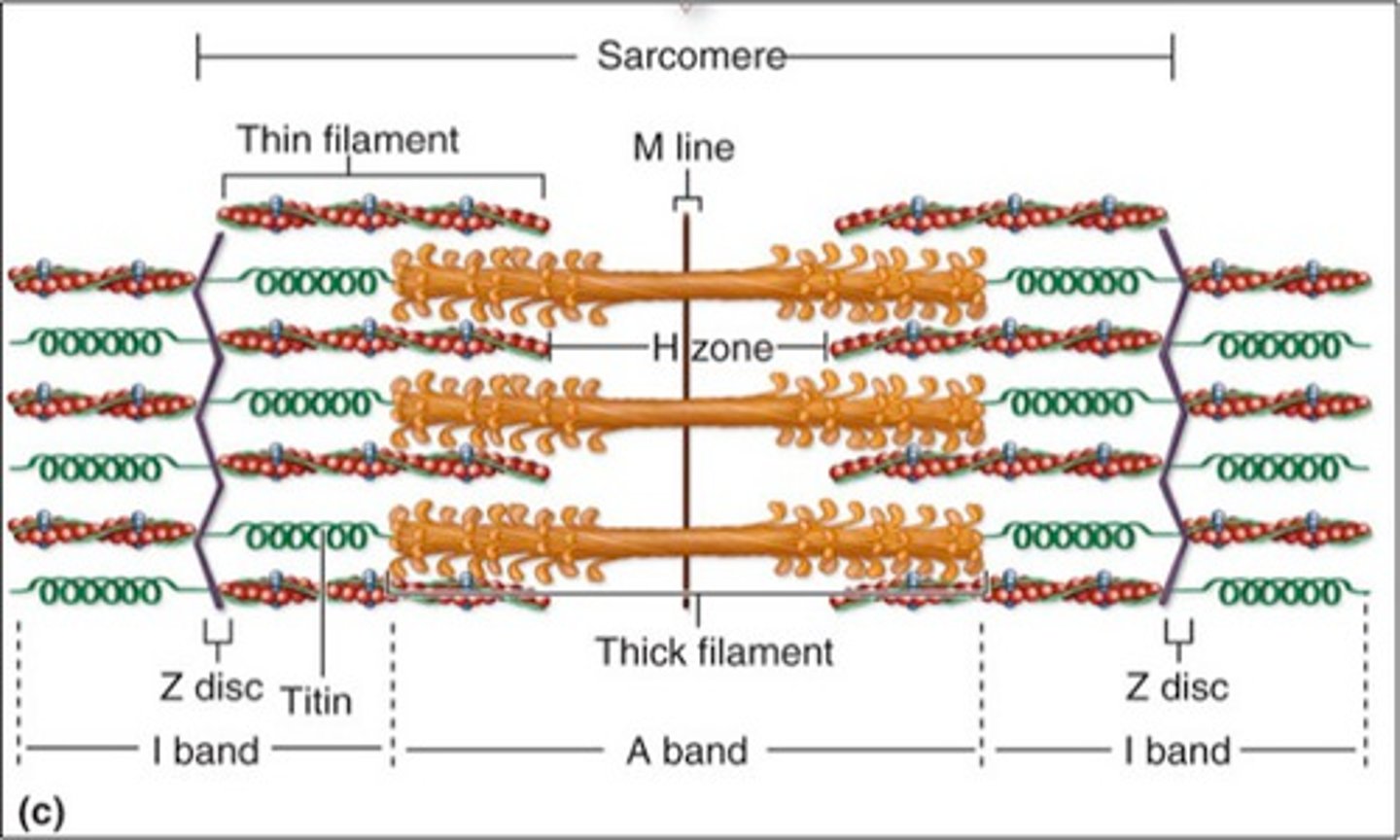
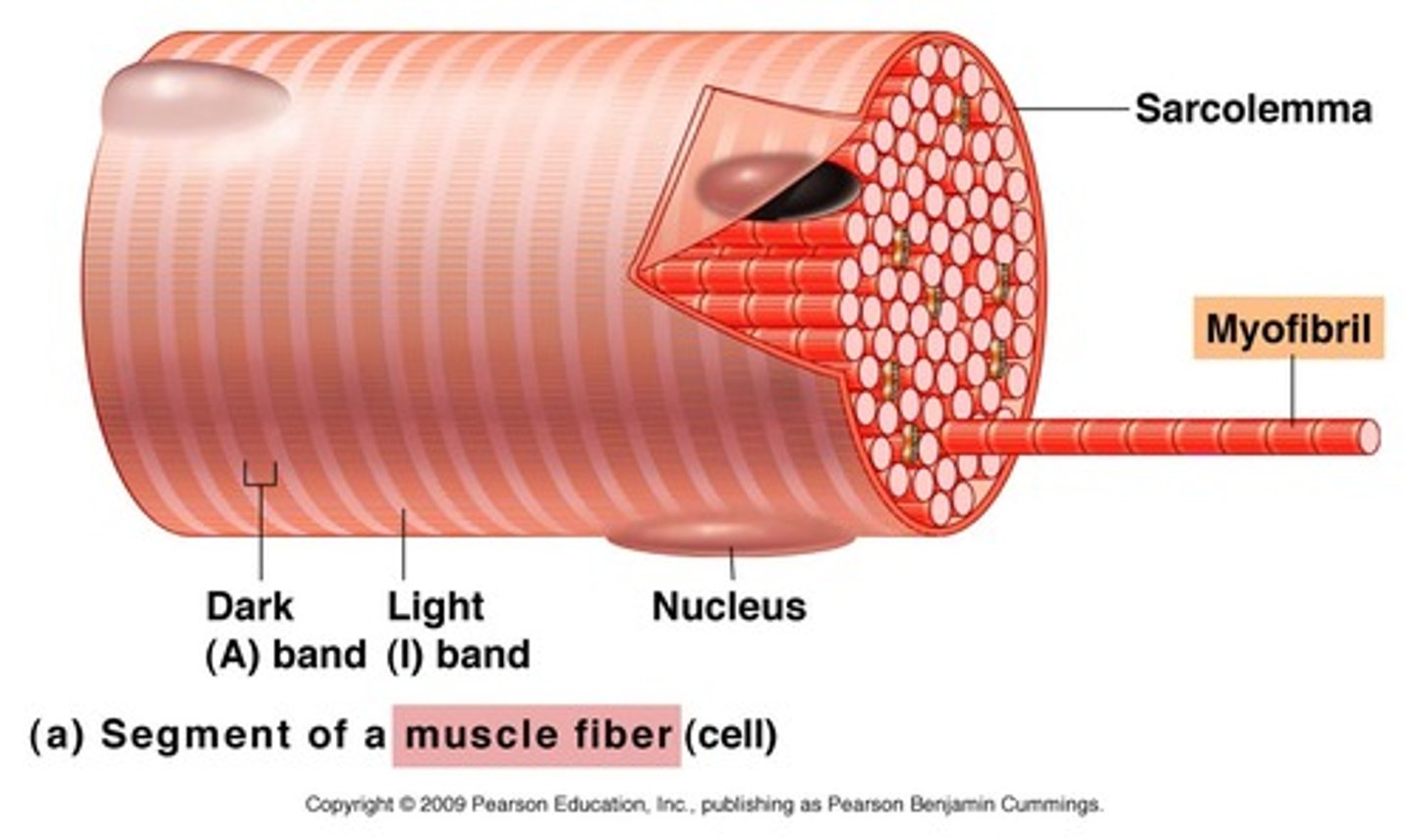
A-Band
dark region on the electron micrograph
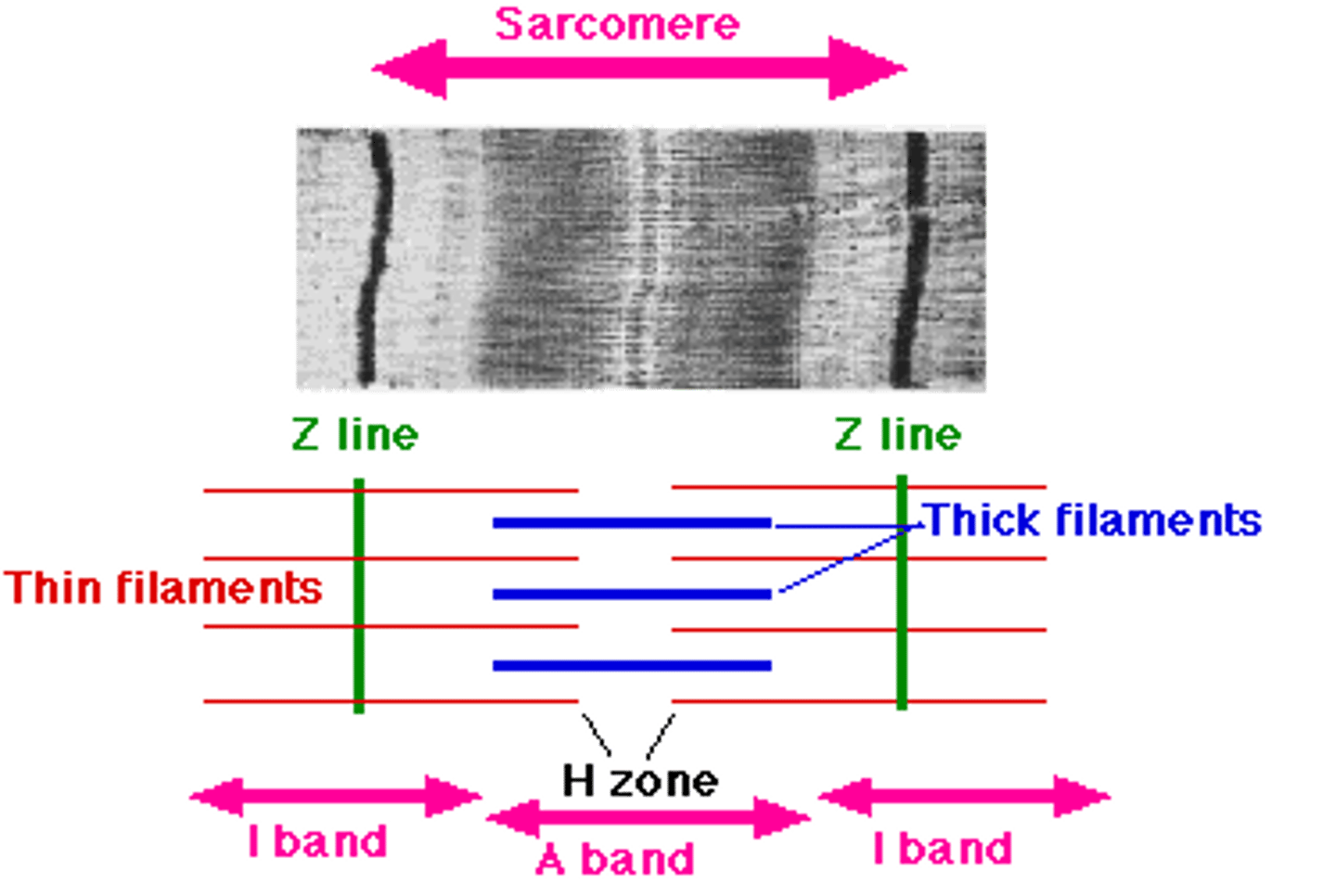
I-band
lighter region on the electron micrograph
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
a specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
The interconnecting tubules and sacs of the SR surround each and every myofibril.
The major role: to store calcium and to release it on demand when the muscle fiber is stimulated to contract. (Calcium provides the final "go" signal for contraction.)
The Sliding Filament Theory
theory that actin filaments slide toward each other during muscle contraction, while the myosin filaments are still
steps:
1. Muscle fibers are activated by the nervous system, and an action potential begins.
2. Calcium ions are released from the SR.
3. Calcium ions bind to the regulatory proteins on the thin filaments, exposing the binding site to the Myosin Heads.
4. The Myosin Heads (cross bridges) attach to the myosin binding sites on the thin filaments.
5. Energized by ATP, each Myosin Head attaches and detaches several times during a contraction.
6. When the action potential ends, the calcium ions are reabsorbed by the SR and the Myosin Heads can no longer attach to the binding sites; everything slides back into place.
nerve impulses
electrical signals transmitted by neurons that are required for skeletal muscles to contract
Motor Unit
One neuron and all of muscle cells it stimulates.
Neuromuscular junction
the region where a motor neuron comes into close contact with a skeletal muscle.
Synaptic cleft
the fluid-filled space at a synapse between neurons
Neurotransmitter
chemical released by neurons that may, upon binding to receptors stimulate or inhibit them.
Acetylcholine
a chemical transmitter (signal) released by nerve endings that enables muscle action
Action potential
an electrical event occurring when a stimulus of sufficient intensity is applied to a neuron or muscle cell.
Aerobic/endurance exercise
exercise that will result in stronger, more flexible muscles with greater resistance to fatigue. Does not cause muscles to increase in size.
Resistance/isometric
exercise that will result in larger muscle cells, also increases the amount of connective tissue that reinforces the muscle. Muscles increase in size.
muscle atrophy
lack of muscle activity; reduces muscle size, tone, and power
aerobic exercise effect on the body
Blood supply increases to muscles
Individual muscle cells form more mitochondria
Muscle cells store more oxygen
Overall body metabolism becomes more efficient
Digestion improves
Neuromuscular coordination increases
Skeleton become stronger
Heart enlarges
Fat deposits are cleared from blood vessels
Lungs become more efficient
resistance/isometric effect on body
Increases muscle cell size
Muscle cells make more contractile filaments
Increases amount of connective tissue around muscle
Muscle fatigue
is the decline in ability of a muscle to generate force.
neural fatigue
a reduced ability to generate force caused by a diminished signal from the nervous system to the muscle
metabolic fatigue
fatigue when there is reduced ability of the muscle fiber to contract; thought to happen due to insufficient oxygen that leads to lactic acid, but evidence now suggests its from insufficient amounts of ions in the immediate area, so the muscles run low on their supply of ions.
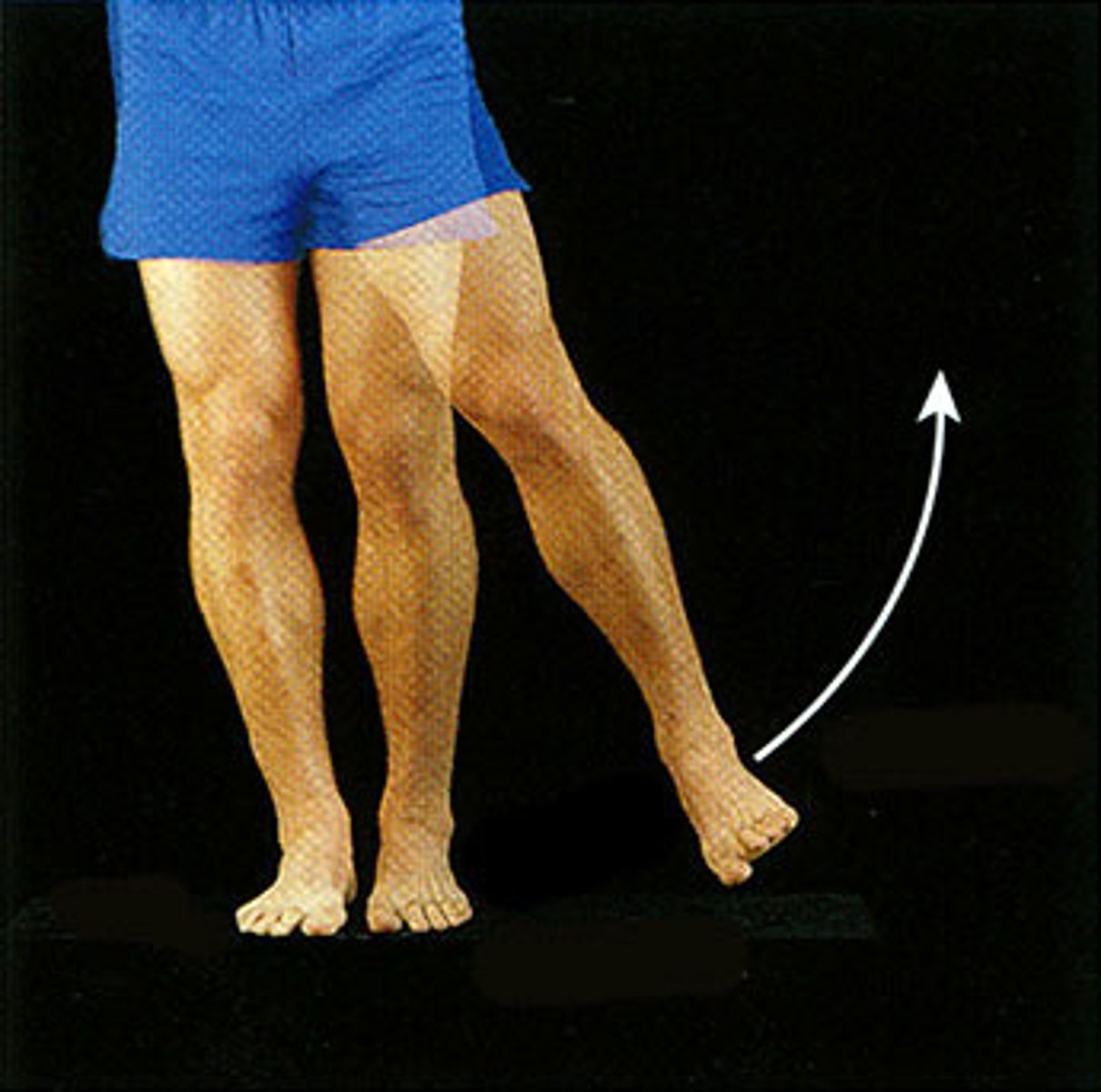
Abduction
moving limb away from midline
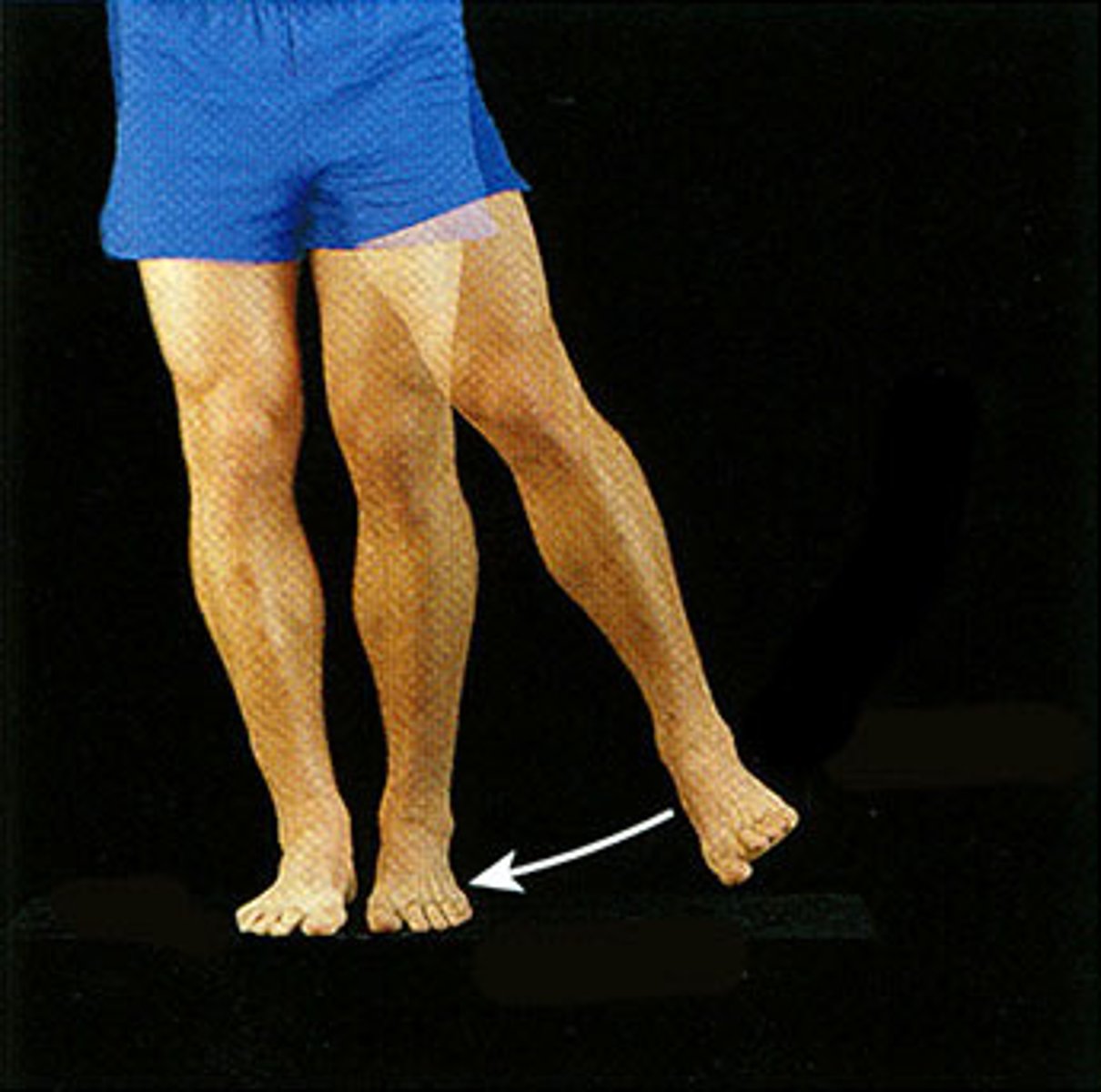
Adduction
moving limb towards midline
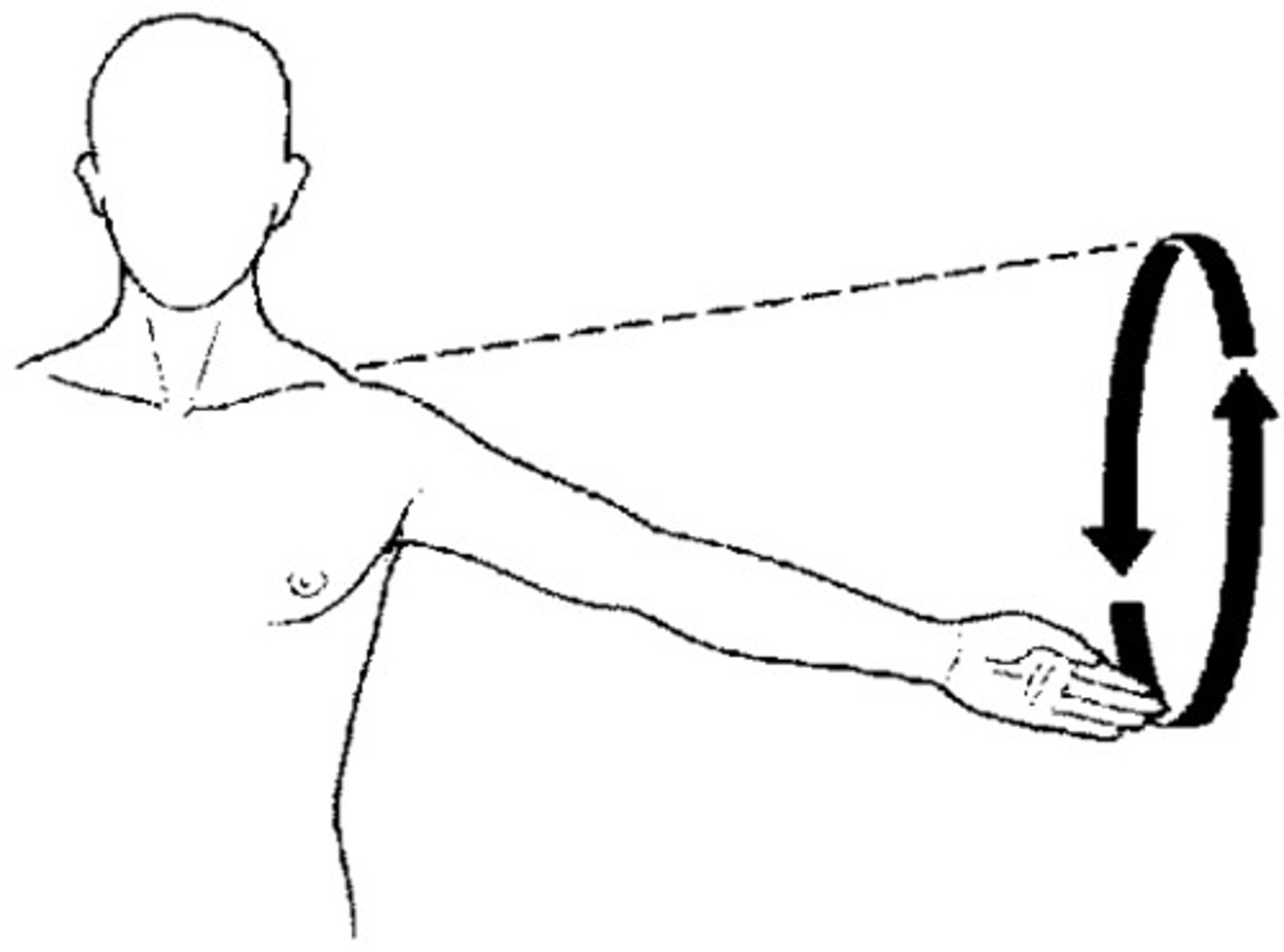
Circumduction
moving a limb in a circular motion
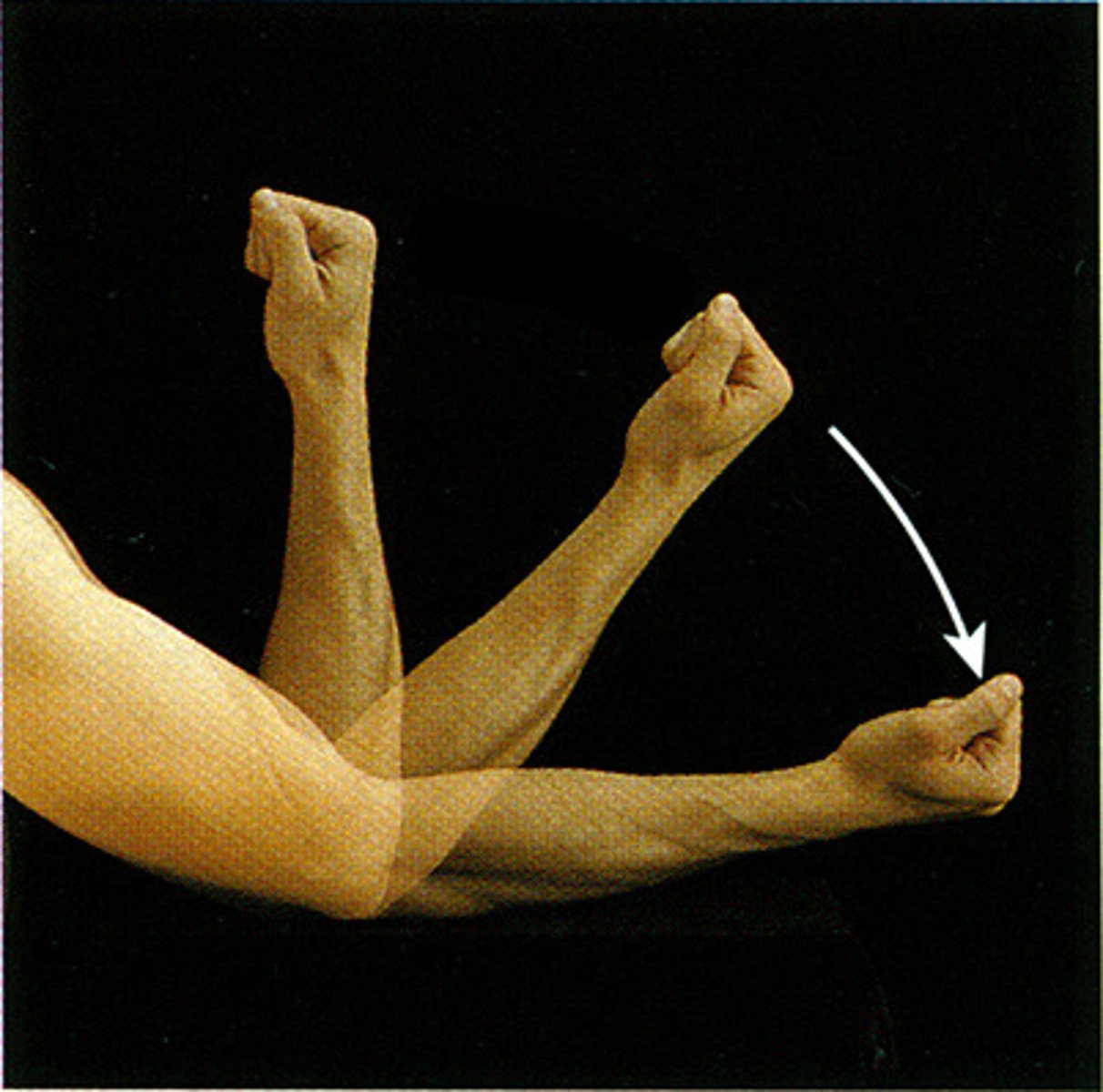
Flexion-
decreasing the angle of a limb (bending)
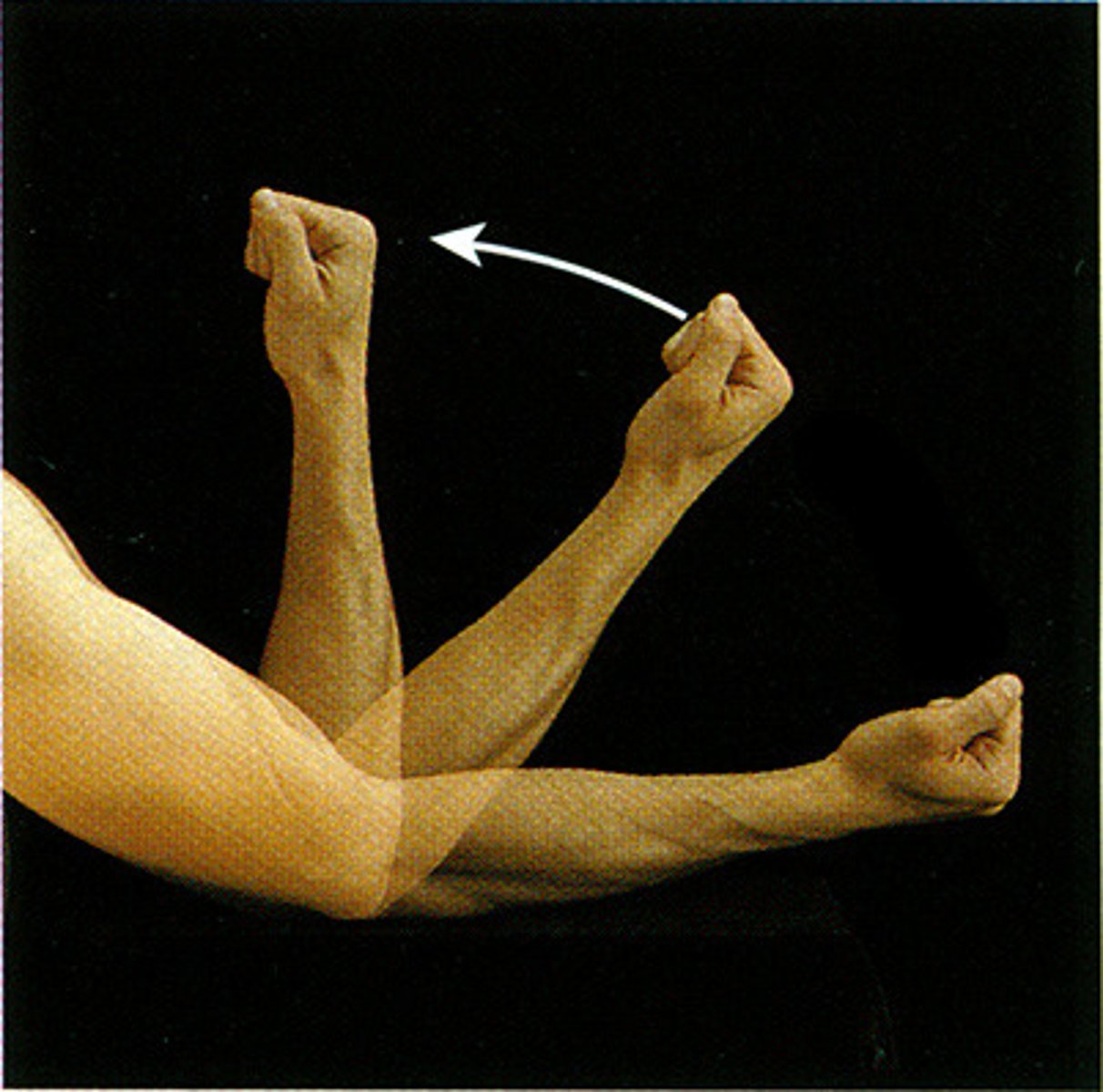
Extension
increasing the angle of a limb (straightening)
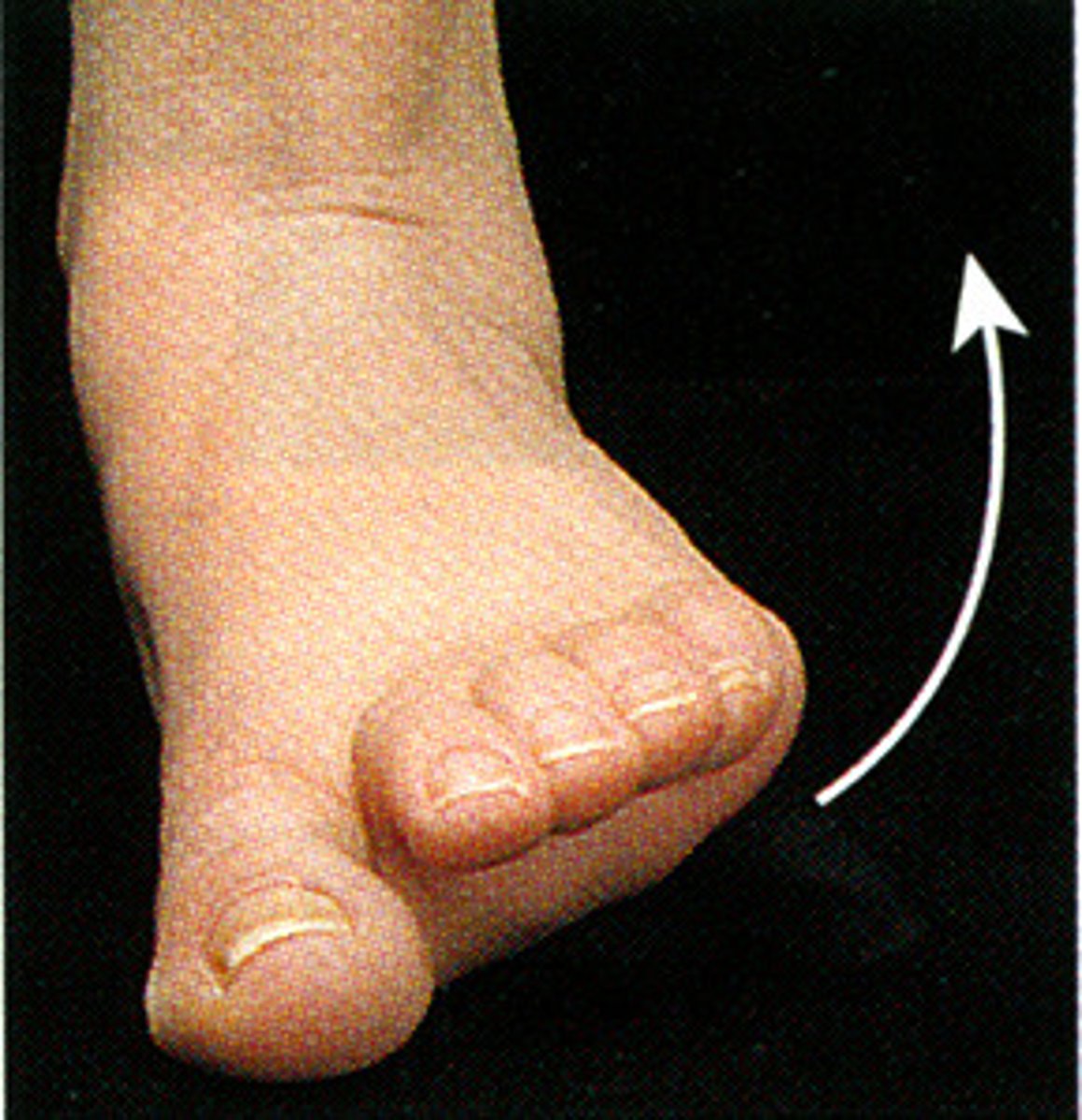
Eversion
twisting limb laterally (away from midline)
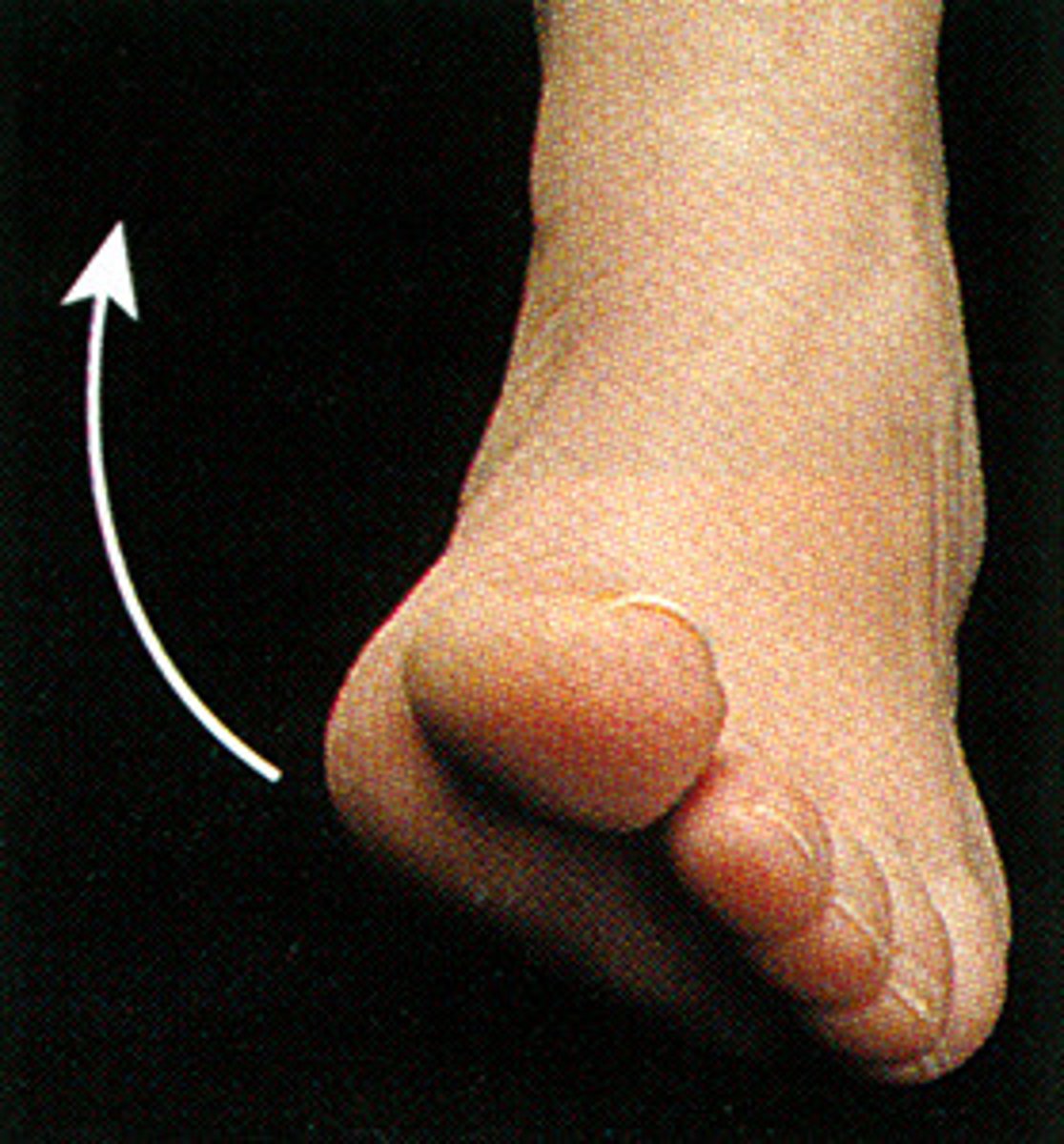
Inversion
twisting limb medially (towards midline)
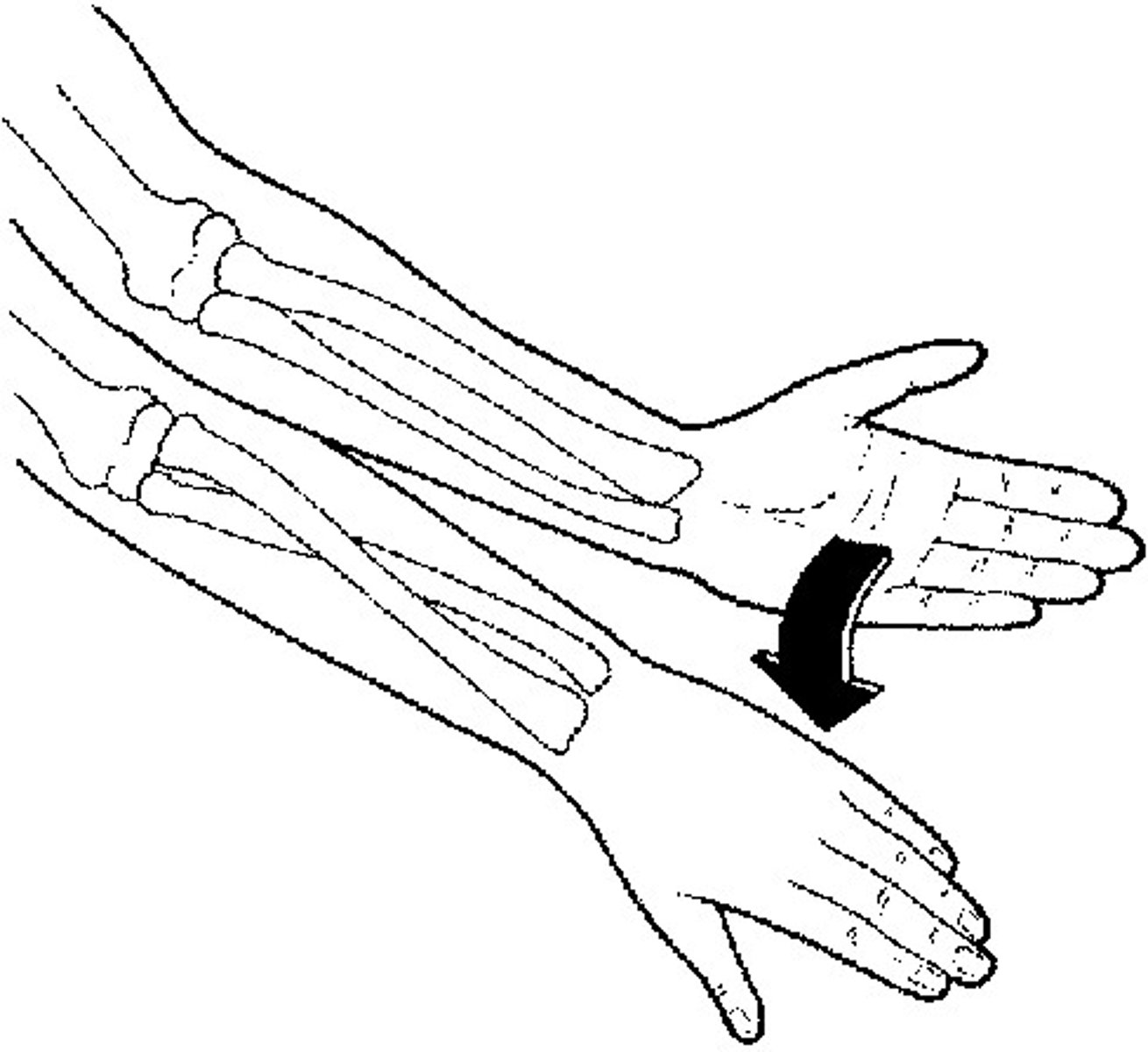
Pronation
a limb is turned down (palms faced down; weight on foot is turned inwards)
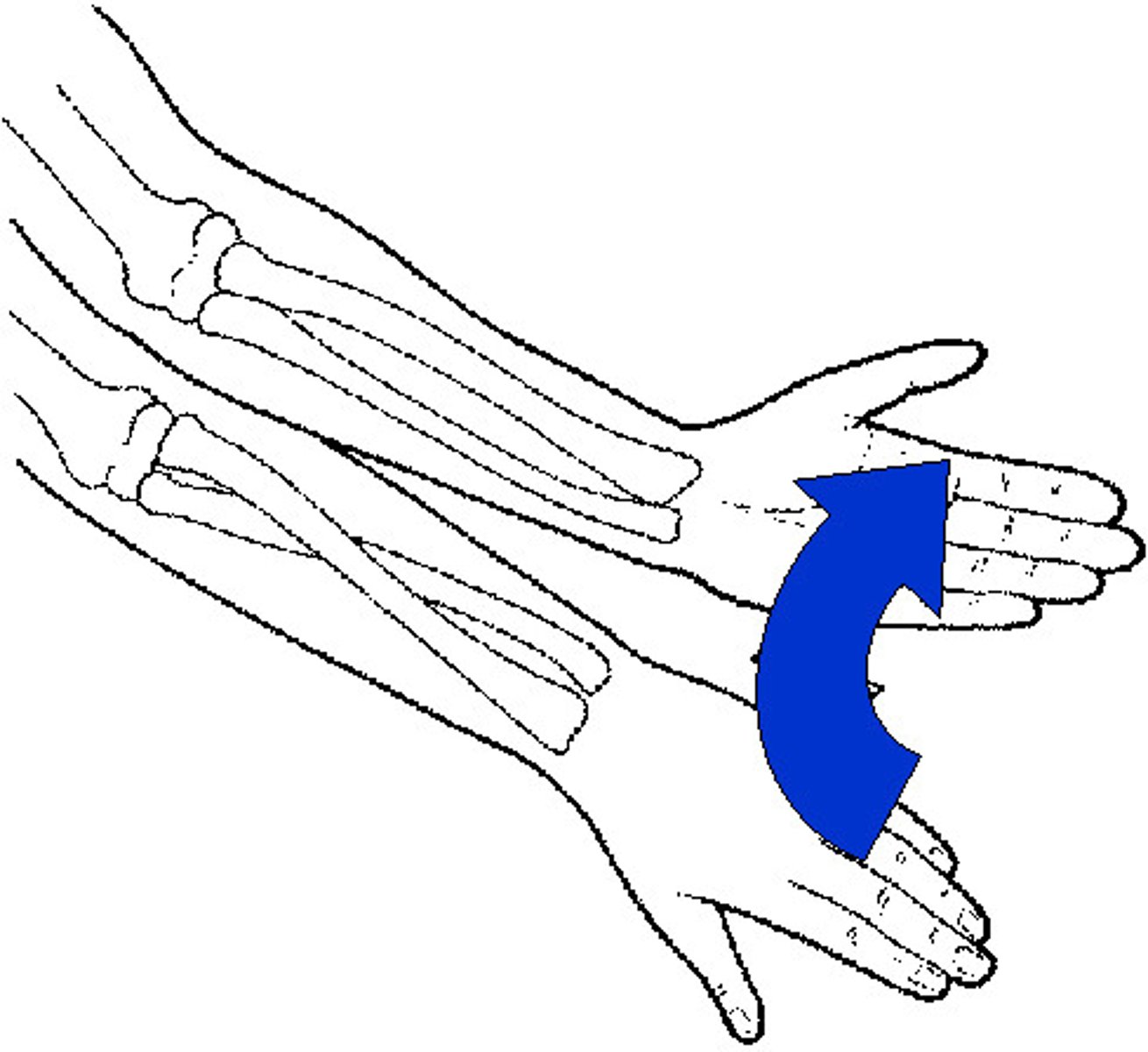
Supination
a limb is turned up (palms faced up; weight on foot is turned outwards)
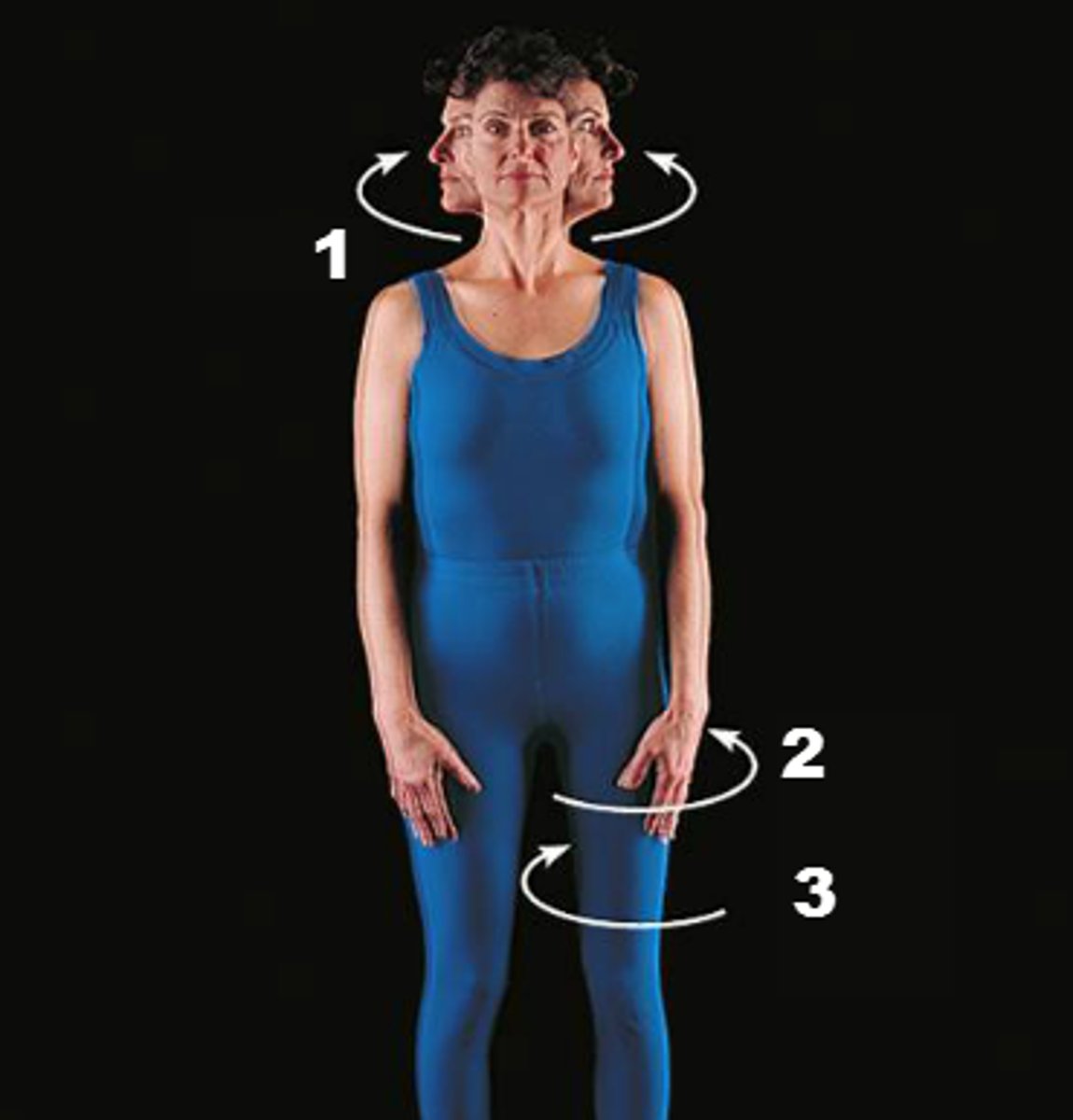
Rotation
twisting a limb around a pivot point (similar to circumduction, but it does not have to be a full circle)
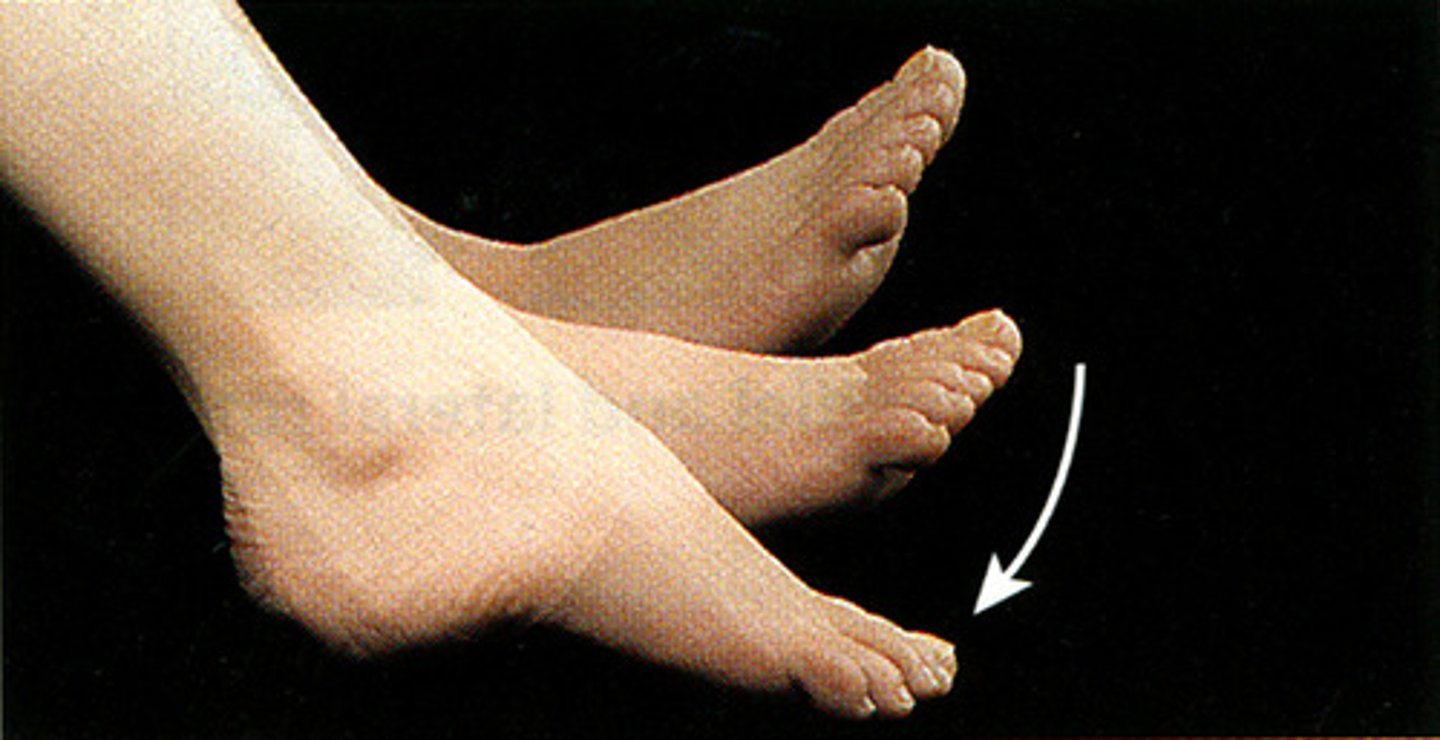
Plantar flexion
movement of the foot when it is bent at the ankle away from the body (point toes)
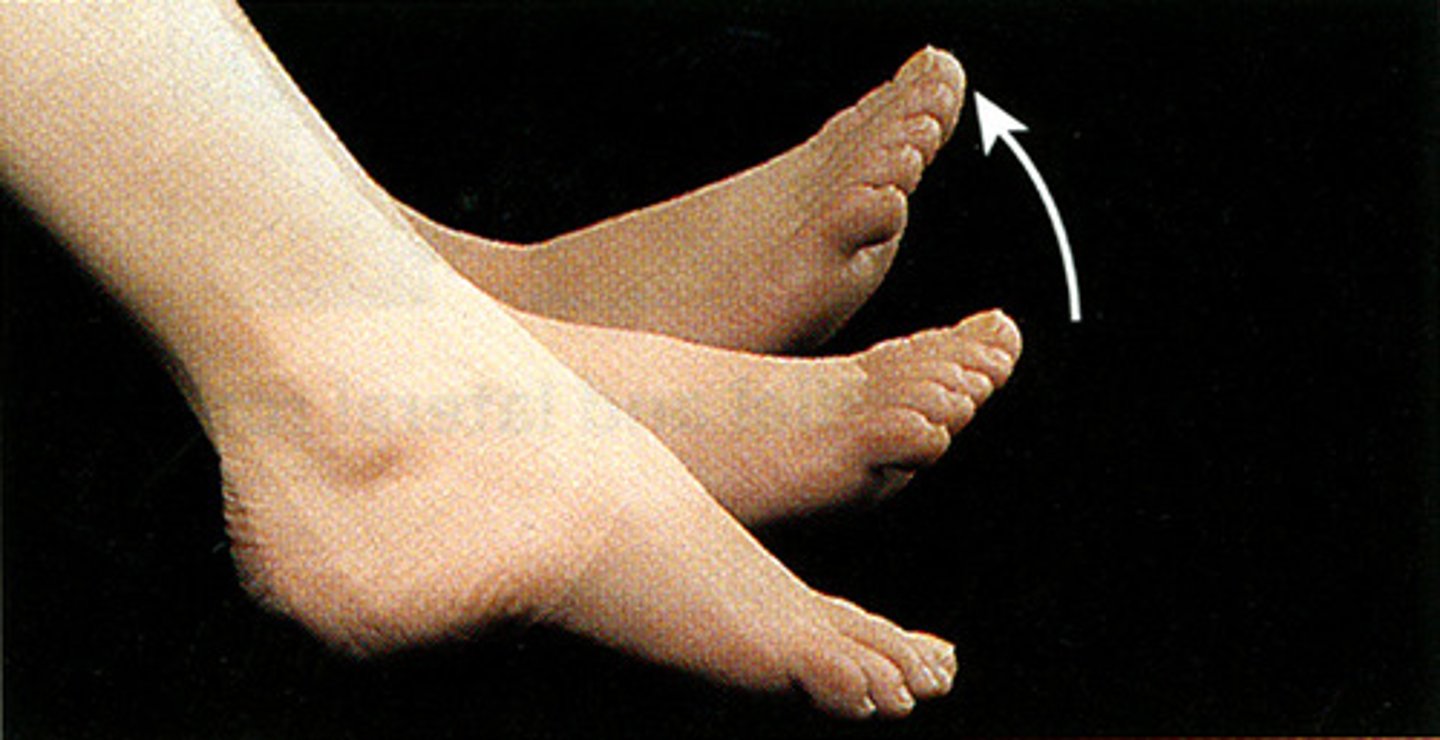
Dorsiflexion
raising the foot upwards towards the shin (flex toes)
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
aka Lou Gehrig's disease; is a progressive neurodegenerative disease. The spinal cord and brain harden/ scar, motor neurons stop working and the muscle wastes away. The cause is unknown.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
autoimmune disease, where the immune system is attacking the protective coating around neurons leading to harden/scarring of the neurons. Motor neurons stop working and the muscle wastes away.
Muscular Dystrophy
a genetic disorder, symptoms appear during childhood. Abnormal genes lead to muscular deterioration.
Myasthenia gravis
autoimmune disease, where the immune system attacks the acetylcholine receptor sites. This makes is hard to for the nervous system to properly communicate with the muscles, leading to poor control over muscle function.
Myopathy
a genetic disorder and a group of diseases where the muscle fibers do not contract as they should. this can affect any muscle type: smooth, cardiac, or skeletal.