Science revision
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
What is a force?
A force is a push or pull that acts on an object due to interaction with another object.
What are forces measured in?
Forces are measured in newtons (N).
What are the two main categories of force?
Contact and non-contact.
What is the difference between a scalar quantity and a vector quantity?
A scalar quantity has magnitude only, while a vector quantity has both magnitude and direction.
Define “contact force”
A contact force is a type of force that acts between two objects that are physically touching each other, such as friction, tension, and normal force.
Define “non-contact force”
A non-contact force is a type of force that acts on an object without physical contact, such as gravitational, electromagnetic, and nuclear forces.
What is upthrust?
Upthrust is the upward force exerted by a fluid on an object immersed in it, counteracting the weight of the object and causing it to float or rise.
Define “reaction force”
A reaction force is a force that occurs in response to an action force, as described by Newton's third law of motion; it acts in the opposite direction to the action force and is equal in magnitude.
What happens if an object is not strong enough to give the reaction force required to lift or support an object?
The object will not be able to support the weight and will fail under the load, resulting in a collapse or deformation.
What device is commonly used to measure forces?
A force meter.
In what direction does air resistance occur?
Air resistance occurs in the opposite direction to the motion of an object moving through the air, acting to slow it down.
What are three key structures in the lungs?
Trachea, bronchi and alveoli.
True or false: the heart pumps blood around the body in a single circulatory system.
False; it is a double circulatory system.
Which ventricle pumps to where?
The right ventricle pumps to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps to the body.
Aerobic respiration = ?
Anaerobic respiration = ?
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
Glucose → Lactic Acid
What are the two types of drug and what do they do?
Medicinal and recreational drugs; medicinal treats illness, recreational used for pleasure.
What are the energy stores?
Magnetic (magnets), thermal (heat; also “internal), chemical (stored in atoms), kinetic (movement), electrostatic (contrasting charges), elastic (something stretched), gravitational (something lifted), nuclear (split/fused atoms releasing energy)
What are the energy pathways?
Mechanical, electrical, by heating, radiation
Work done = ?
Force (N) x distance (m)
Distance (m) / time (s)
Ke = ?
½ mass(kg) x velocity (m/s) squared
GPE = ?
Mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg) x height (m)
Power = ? (2x)
Energy transferred (J) divided by time (s)
Current (A) x Potential Difference (V)
What is the difference between A.C and D.C?
Alternating current switches direction, direct current does not.
What type of current is mains electricity, what is its frequency, and what is its voltage?
Direct current, 50Hz, 230V
What colours are what wires in a plug and what do they do?
Brown = live; carries the current
Blue = neutral; completes the circuit
Green/yellow = earth; carries current safely if circuit breaks
What do plants and animals compete for?
Plants = light, water, minerals + space
Animals = food, territory + mates
What are examples of evidence for evolution?
Fossil record, development of antibiotic resistance, DNA comparisons, comparative anatomy and embryology.
Give examples for the three types of adaptations.
Structural = cactus spines
Behavioural = penguin huddle
Physiological = antifreeze icefish blood
Define sustainability
Providing for now without harming future generations or their ability to do so.
Characteristics of the three rock types.
Igneous = formed by cooling magma, made of randomly interlocking crystals (intrusive big extrusive small)
Metamorphic = crystals squashed into layers
Sedimentary = different sized grains, often with pores between them
What makes up the atmosphere?
78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% other mixed gasses
What are the steps of the water treatment cycle?
Sedimentation
Filtration
Chlorination
Fluoridation
What does LCA stand for, what is it and what are its stages?
A life cycle assessment; an analysis of the environmental impact of a product.
Extraction of raw materials
Manufacture
Use
Disposal
What are the three “r’s”
Re-use, recycle, replace
What is weight and what is its equation?
The force acting on an object due to gravity exerted on it by a massive object.
Weight (N) = Mass (kg) x GFS (N/kg)
For elastic objects force is directly proportional to what?
Extension.
EPE = ?
½ Spring constant (N/m) x extension (m) squared
What is the center of mass?
The point representing the mean position of all mass in the object.
What is a moment and what is its equation?
A moment is the turning force of an object on a fixed “pivot”
Force (N) x perpendicular distance (m)
Why would an object float or sink?
If the upthrust and weight were balanced or unbalanced.
Pressure = ?
Force (N) / Area (m squared)
Describe the difference between a pure substance and a mixture.
Pure substances contain one type of substance and have a sharp melting point, whereas mixtures are made up of multiple different substances and melt/boil over a range of temperatures.
What is an emulsifier and describe its shape.
A substance that allows two immiscible substances to mix; one hydrophilic end (head) and one hydrophobic end (tail)
Gas test positive results for:
Hydrogen
Oxygen
CO2
Chlorine
Water
Squeaky pop
Put-out splint relights
Limewater goes from clear to cloudy
Bleaches blue litmus paper
Blue cobalt chloride paper turns pink
True or false: in chromotography, the more soluble a substance is the less it moves up the paper
False it moves more
Colours of ion burning:
Strontium
Copper
Sodium
Potassium
Lithium
Calcium
Red
Green
Orange
Lilac
Crimson-red
Orange-red
What is a precipitate and what colour are those produced by:
Iron (II)
Iron (III)
Copper
Calcium
Magnesium
Green
Brown
Blue
White
White
What is a halide and what colour is the precipitate of a silver ion and a:
Chloride ion
Bromide ion
Iodide ion
White
Cream
Yellow
What is the product of a carbonate reacting with a dilute acid?
Carbon Dioxide
What happens when a sulphate reacts with barium chloride?
A white precipitate is formed
If a sound has a high amplitude and a low frequency, describe the sound.
Loud and low pitched.
What is frequency?
The amount of sound waves a second.
What is the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves?
Transverse waves go in straight lines, longitudinal waves “wobble” or oscillate.
What is the highest and lowest frequency an average human can hear?
20Hz - 20000Hz
What do quieter, louder, higher and lower sounds look like on an oscilliope graph?
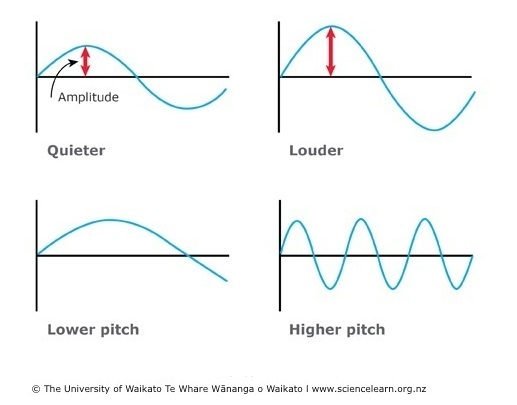
True or false?
Light is a transverse wave.
Light can travel through a vacuum.
Light is not reflect-able and refract-able
True
True
False
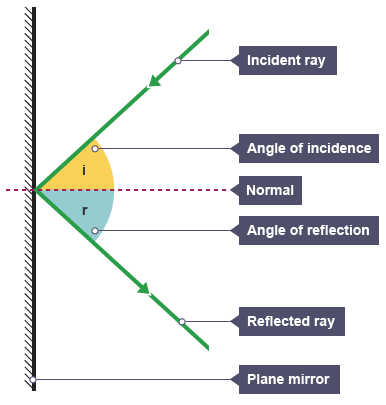
Label the parts of a ray diagram.
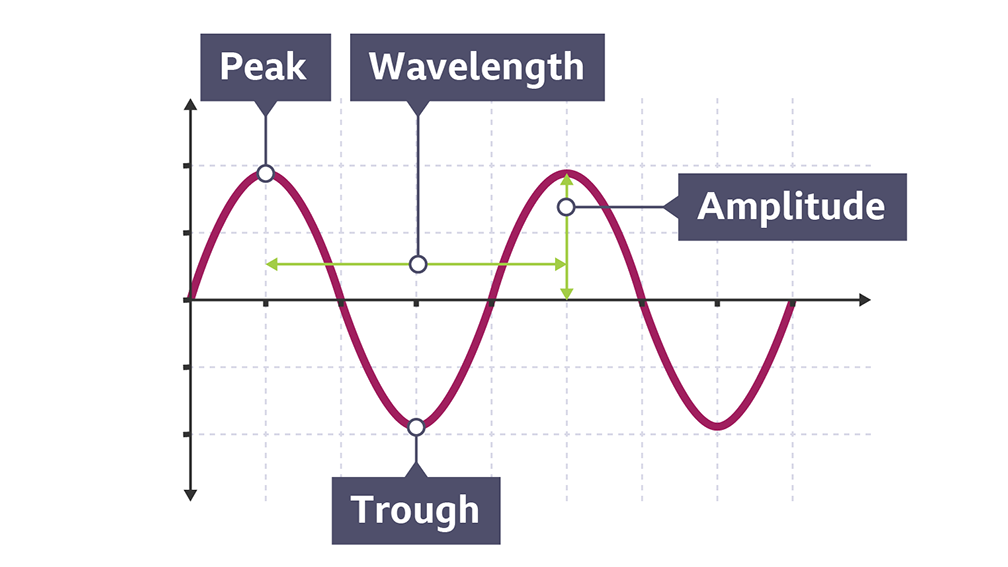
Label the different parts of a transverse wave diagram.
Describe the particle models of the different states of matter.
Solid = organised in a grid and so close the only possible movement is vibration.
Liquid = jumbled up and capable of flowing over each other but always touching.
Gas = very far apart and whizzing around.
Describe the ways of separating:
Insoluble solid from liquid
Soluble solid from its solution.
Liquid from its solution.
Filtration: pour mixed solid and liquid through filter paper, solid left in paper liquid let through into beaker.
Evaporation: put solution in evaporation basin over flame. Liquid dissolves, leaving crystallised solids.
Distillation: put solution in boiling flask and connect it via condenser to a beaker. Liquid with lower boiling point will evaporate and distill into beaker leaving behind liquid with higher melting point.
Who produced the first practical periodic table and how did he organise it?
Dmitri Mendeleev, by chemical and physical properties.
What are the horizontal and vertical rows of the periodic table called?
Horizontal = periods
Vertical = groups
How is the periodic table ordered?
In order of increasing atomic number
How many elements are there on the periodic table?
118
What do the left and right sides of the periodic table contain?
Left = metals
Right = non-metals
What do groups on the periodic table have in common?
Chemical and physical properties.
What are the key properties of transition metals?
They conduct heat and electricity, are shiny and are malleable.
What is the only liquid transition metal?
Mercury.
What are physical and chemical characteristics of alkali metals?
Physical: They are soft, have a low melting point, and have low density.
Chemical: They are highly reactive and produce hydrogen and an alkaline solution when they react with water.
What are the physical characteristics of non-metals?
Poor conductors, weak and brittle, dull in appearance.
What is an acid, what is a base, and what is an alkali?
An acid is a substance with a ph below 7, a base is a substance that neutralises an acid, and an alkali is a soluble base.
Acid + alkali = ?
Acid + alkali → salt + water
How can you detect acids and alkalis?
Acids are sour and turn blue litmus paper red, whereas alkalis taste bitter and turn red litmus paper blue.
What would be produced if calcium reacted with sulphuric acid?
Calcium + sulphuric acid → Calcium Sulfate + water.
Metal carbonate + acid → ?
Metal carbonate + acid → Salt + water + carbon dioxide.
Define chemical energy and give two examples of places it is stored.
The energy store in the bonds of chemical compounds, such as in batteries or in our muscles.
True or false? Chemical reactions make new chemicals.
True.
What happens to atoms in a chemical reaction, and how can you tell if a chemical reaction is happening/has happened?
They rearrange but do not add or subtract.
Large temperature change, colour change, or effervescence (fizzing).
What happens to energy in a chemical reaction?
It is transferred to or from the surroundings.
What is the difference between an endothermic and exothermic reaction?
Endothermic reactions take in heat energy, whereas exothermic reactions give out energy; usually as heat but not necessarily.
What is the structure of the earth?
Crust, mantle, inner core, outer core
Explain convection currents in the earth's mantle
Hot material from next to the core rises, shunting material out the way above it. This displaced material cools and sinks, then gets heated by the core etc.
What are the characteristics of different parts of the earth's structure?
Crust: thin plates of rock, called tectonic plates, floating on the mantle
Mantle: semi-molten rock that shifts slowly
Outer core: liquid iron and nickel, makes earth's magnetic field, very dense and hot.
Inner core: solid iron and nickel, extremely dense and hot
What is the difference between planets and comets orbit
Planets are circular, comets are more oval.
Order the planets
Mercury, venus, earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
Define satellite
An object orbiting a planet or a star
What are the two types of satellite? Give an example for each
Artificial: ISS
Natural: The moon
Describe climate change
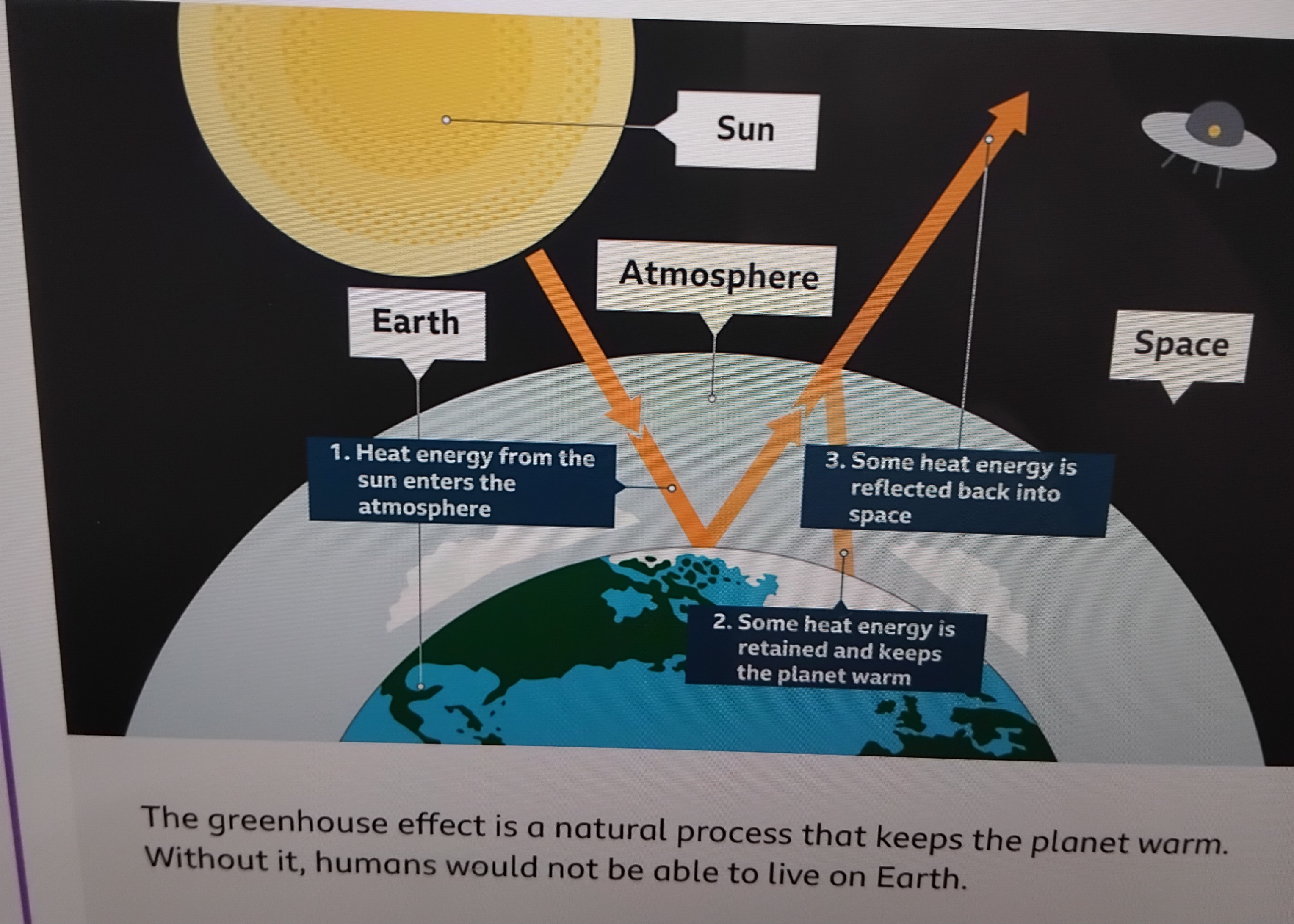
Define mitigation
When people take steps to reduce the severity of something
How much have global temperatures increased over the past 100 years?
1 degree Celsius
What are cells?
The building blocks of life
What do plant and animal cells have in common? What are their differences?
They both have: cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, cytoplasm
Only plant cells have: vacuole, cell wall, chloroplasts
What are the adaptions of root hair cells
Large surface area to increase water intake
Describe the structure of a leaf
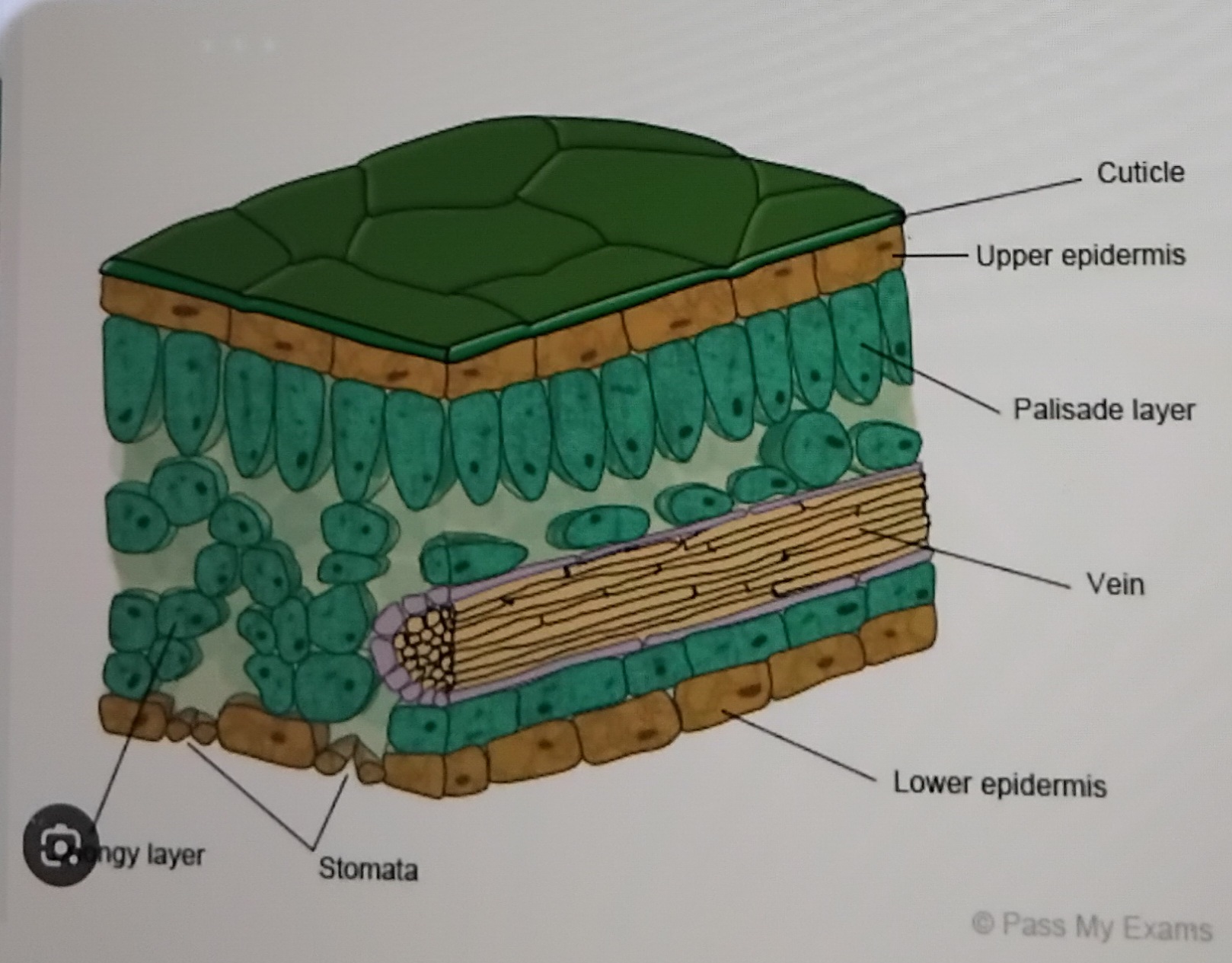
What do xylem do
They carry water up the plant, and are stiff to keep it upright
What do phloem do
Carry sugary water with the help of companion cells with lots of mitochondria
What is the function of a vacuole
It contains cell sap and keeps the cell firm
What is cytoplasm mainly made of
Water
Describe the process of breathing or ventilation
As the intercostal muscles and diaphragm contract, the volume of the chest cavity increases, sucking air in through the nose and mouth, through the bronchi and bronchioles, before undergoing gas exchange.
Define digestion
The breaking down of food and other useful substances