Exam 2- Secondary Growth/Roots
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
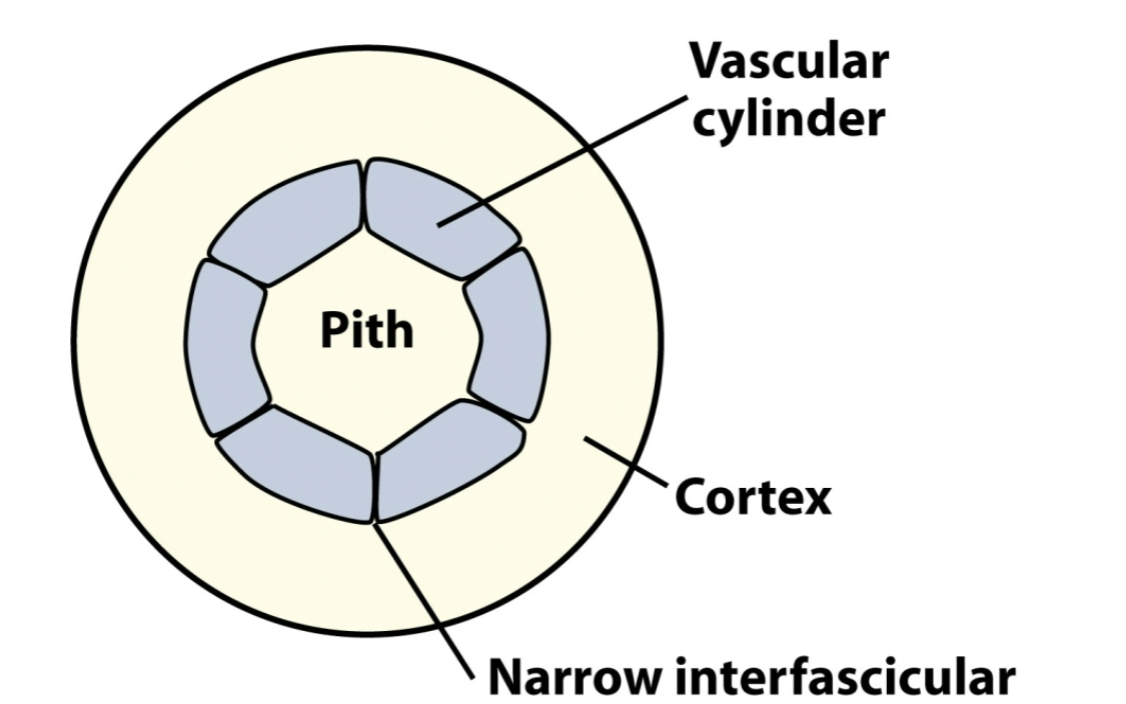
continuous cylinder
common in dicots/gymnosperms
narrow interfasicular regions
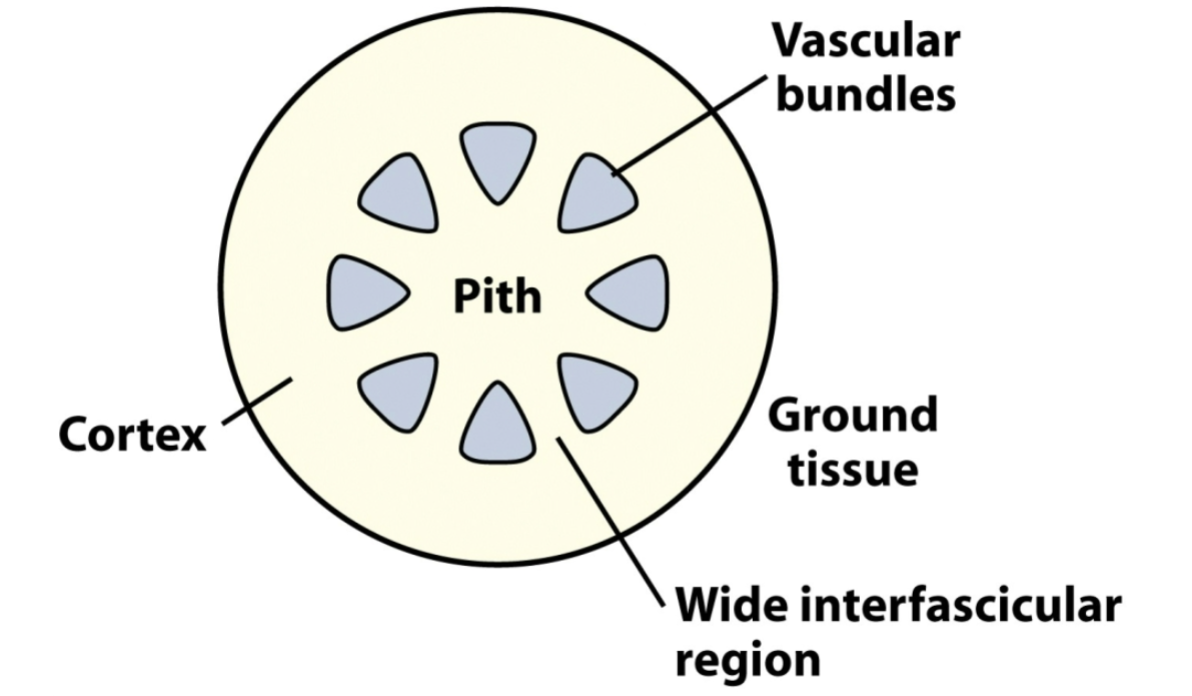
discrete bundles
wide interfasicular region
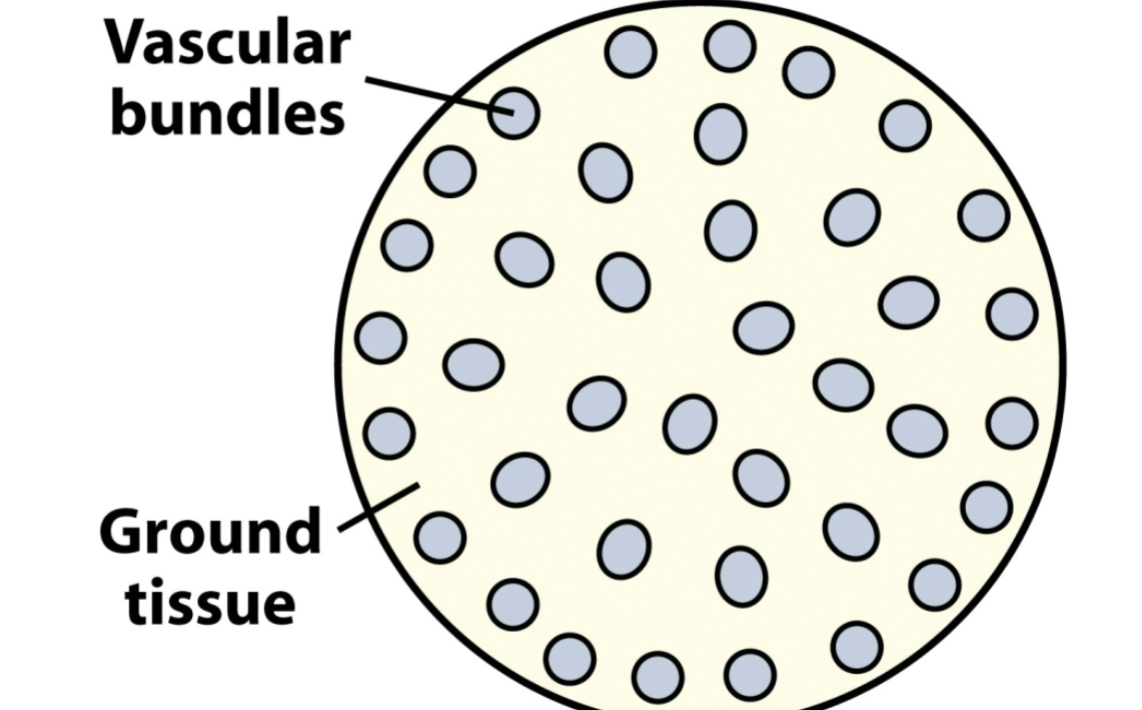
scattered bundles
randomly scattered vascular bundles, no discrete pith or cortex
common in monocots
tend to be higher in concentration near the epidermis
Open vascular bundle
bundle sheath is present, but there is a gap, doesn’t form a complete ring around bundle
mostly eudicots
closed vascular bundle
is surrounded by a bundle sheath
stomata
exist in stems
become lenticels
Leaf gap
space in developing plant near the axillary bud
appears as if there is no vasculature, but the vascualture actually moves around the axillary bud
not broken, just moved
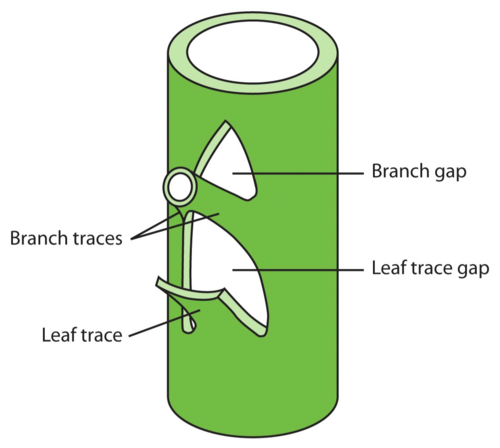
branch traces
protrude for space for the vasculature to grow as the axillary bud grows/matures
refers to the veins diverging from the stem
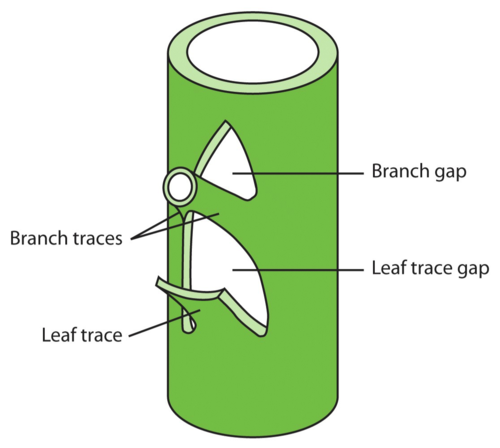
leaf trace
the vein that enters the leaf on a stem
stem trace
two exist at each leaf gap
unite above the leaf gap
Proximal-distal
distance from stem
adaxial
upper surface of leaf (usually)
abaxial
lower surface of leaf (usually)
Alternate phyllotaxy
1 leaf is formed at a time
includes spiral/helical and distichous
spiral/helical
alternate leaf (1 at a time)
arranged in a circle around the stem
arranged 137 degrees apart to avoid 1 leaf shading another
in a short stem, arrangement is usually called a whorl
ex- sunflower
arranged as far away from another as possible, trying to position so all leaves get equal sun access
distichous
alternate (1 leaf at a time)
arranged in a circle 180 degrees apart
opposite sides of stem
opposite leaves
2 leaves formed at a time
decussate
a type of opposite leaf (2 leaves at a time)
180 degrees apart from one another, as it makes new pairs, the meristem rotates 90 degrees
whorled leaves
3 leaves formed at a time
3 or more leaves attached at the the same point
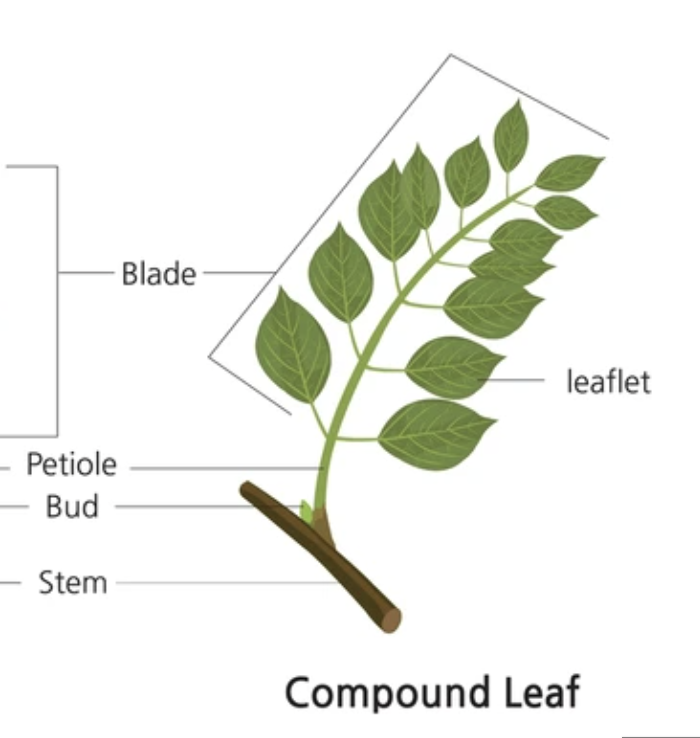
Simple leaves
1 unit, 1 margin
a single leaf, undivided blade
can have lobes
compound leaves
nondivided leaflets
blade consists of multiple leaflets, leaflets have no axillary bud at base
double compound leaves
each leaflet is divided into smaller “leaves”
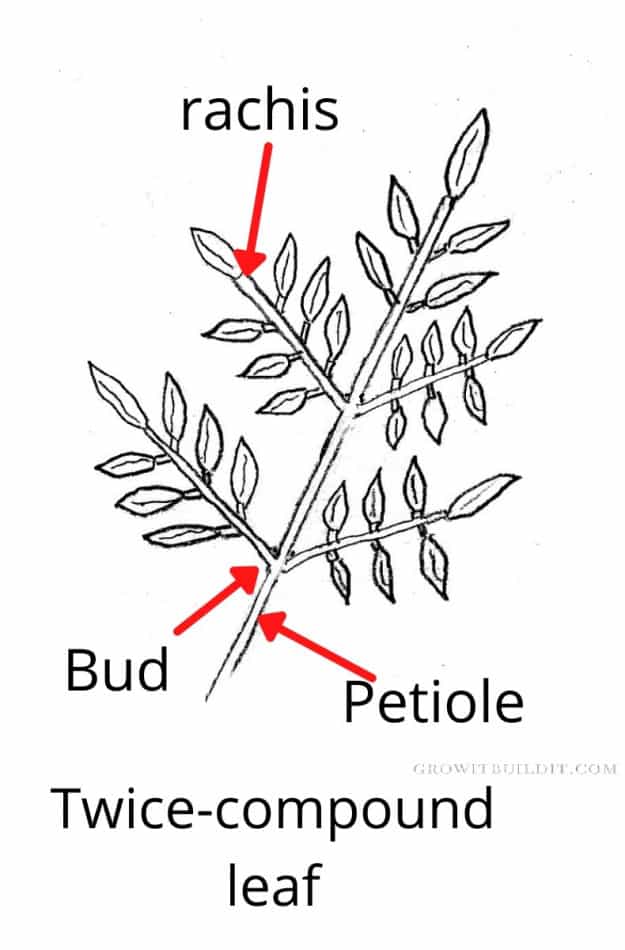
Compound leaf types
palmate
pinnate
palmate leaves
compound leaves
leaflets arise from a common point
pinnate leaves
leaflets arise from several locations along the axis
Abscission zone
located at the base of the leaf, composed of smaller cells
has a protective layer that eventually covers the stem and creates a new covering to cover the wound site/abscission site
protective layer usually occurs on side closest to stem, sometimes makes a second protective layer on the side that will fall
after abscission, area is heavily lignified and leaves a scar
Kranz anatomy
a specific arrangement of leaf cells present in C4 photosynthetic plants
typical of monocots/grasses, but not all monocots/grasses are c4
consists of a bundle sheath and a ring of mesophyll cells that surround the bundle sheath
1:2:2:1 architecture (bundle sheath, mesophyll, bundle sheath)
C4 photosynthesis
c4 plants use a different pathway for fixing co2
they have a higher concentration of co2, so rubisco only/mainly fixes co2 instead of o2 (rubisco can accidentally fix o2 and that is not great)
Bulliform cells
only form on adaxial size
typical of monocots, but not all
large and full of water
when full of water, turgor pressure causes leaves to lay flat for maximum photosynthesis
when not enough water is present, the bulliform cells lose turgor pressure and fold the leaf in on itself to prevent the sun frying the leaves
Intercalary meristem
common in grasses
meristems found between differentiated tissue
allow for continued growth of leaves and stems in monocots
located at the base of the internote, leaf sheath, and blade
stomatal crypts
sunken in cavities where stomata are housed in some plants
prevent water loss by trapping hot water vapor
characteristic of plants in arid environments
lots of trichomes in the crypt to help trap that water
laticifers
specialized cells, long and stringlike
can be 1 long cell or many smaller cells joined together
present throughout the plant, running from root to shoot
usually located near the phloem
produce latex
can be branched(horizontally connected to other laticifers) or unbranched
evolved independently in multiple lineages
articulated laticifer
composed of multiple cells that have been fused together
their cell walls are either completely intact (non anastomosing) or partially dissolved (anastomosing)
ex - rubber tree and poppy
non articulated laticifers
compose of one elongated cell, no separation
ex - cannabis
Latex
primarily a defensive mechanism against pathogens/threats
contain peptidases, osmotins, chitinases, and germin like molecules
lithocyst
located in the epidermis
forms a crystal called a cystolith
function as a light refraction mechanism, a way to direct light into photosynthetic cells
taproot
dicots
larger and longer than all other roots
form first
fibrous roots
monocots
many small roots
hypocotyl
segment of plant between the root and the cotyledons
mucigel
carb based polymer that is hydrophilic
gel that protects the root tip from being damaged
located from below root cap to the zone of differentiation
root cap
zone that covers the root apical meristem for protection
cells are shed from the root cap into the mucigel during development
quiescence center
located in the root apical meristem
divides slowly to maintain the quiesence center/ram
once cells are pushed to peripheral zone, they then rapidly divide
casparian strip
restrict the movement of water through a root
act as a filter to what can access/enter vasculature
located in the endodermis
Gravity sensing in the root cap
occurs in root cap collumella cells
orientation of amyloplast determines directional growth
will follow gravity (ex- all amyloplasts fall to the bottom with gravity, causing the root to grow downwards)
root hairs
single celled protrusions that increase the surface area for water, air, etc.
grow int eh zone of differentiation
form from trichoblasts - originate from epidermis
atrichoblasts
non root hair forming cells
lateral roots
originate from the pericycle
side roots, smaller than the taproot in eudicots
adventitious roots
roots derived from non root tissue
usually from a node, which is called a nodal root
ex- maize brace roots
maize brace roots
adventitious root
produced from the stem nodes sequentially throughout development
form the major framework of the mature root system
critical to sustain water and nutrient uptake as the plant matures
under drought conditions, have to grow into and through the surface soil, which can become very dry
rhizobia
nitrogen fixing symbiont in legumes
find the plant by producing a nod signal
the plant makes flavinoids
Rhizobium recognize the flavinoids
infect plant via roothairs
frankia
nitrogen fixing symbiont in non legumes
nitrogen fixing symbionts (rhizobia/frankia)
take nitrogen in the atmosphere and convert it into a bioavailable form that the plant can use
leghemoglobin
bacterial nitrogenase enzyme complex
sensitive to oxygen
presence of leghemogloblin in root nodules provides low oxygen environment suitable for nitrogenase activity
indeterminate nodule
no known end
branched
determinate nodule
known end
mycorrhizal fungi
genera of fungi that form symbiotic relationships with plants
dramatically expand access to moisture and nutrients from the soil
in return, the plant feeds the fungi with sugars and organic substances
ectomycorrhizae
go around plant cells, forming a hartig net between cells
never enter plant cells
common in temeprate trees
arbuscular mycorrhizae
enter in the plant
goes through the cell wall and forces plant to form a membrane around the haustorium
never technically enters the cell, only the cell wall
non woody plants
fasicular
formed from differentiated procambium
separates the primary xylem and phloem
interfasicular
between fasicles (bundles)
formed from the pith
fusiform initial
longer, vertically oriented
produce the axial system of secondary vascular tissues
ray initial
smaller, square/circle shaped
form the radial system of secondary vascular tissue
composed of parenchyma cells that conduct food substance from the secondary phloem to the secondary xylem and water from the secondary xylem to the secondary phloem
can also store starch, lipid, proteins, and tannins
extend horizontally through the secondary xylem and phloem
dilated phloem ray
wedge shaped phloem that grows to fill empty space
due to the shape of the stem/root being a circle, the outside part is larger than the inner part, leading to more space or gaps that needed to be filled
heartwood
non conducting portion of xylem
older in age
closer to pith
secondary compound storage
darker in color
Resin ducts
found in some gymnosperms
intercellular spaces lined with thin walled parenchyma cells
the parenchyma cells secrete resin into the space where it serves as a defense against pathogens
Sapwood
functional xylem, more recently formed
has less sap, resin, etc.
usually lighter in color
conductive
Tight knots
living, no dead zone
branch is integrated into wood
loose knot
dead zone that forms around the branch
Knots
result of branches that were buried in the growing stem
can be tight (living) or loose (dead)
Uniserate
one column of ray initials
multiserrate
multiple columns of rays
Ring porous
large variation in xylem size
earliest forming vessels are larger
later formed vessels are smaller
diffuse
less variation in xylem size
hardwood
angiosperms/deciduous
softwood
gymnosperms/confiers
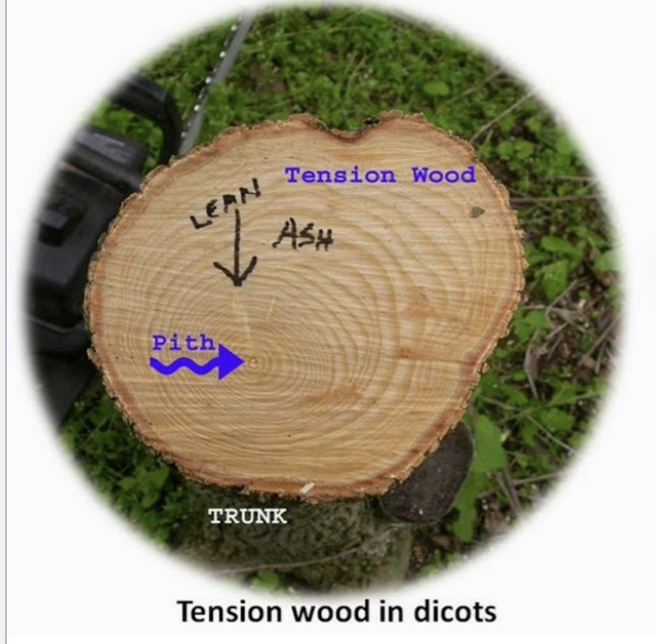
tension wood
tilted hardwood stem is pulled upright again by tension wood
forms in the newly developed growth rings - asymmetrical stem cross section
new growth occurs above to pull the wood back into place

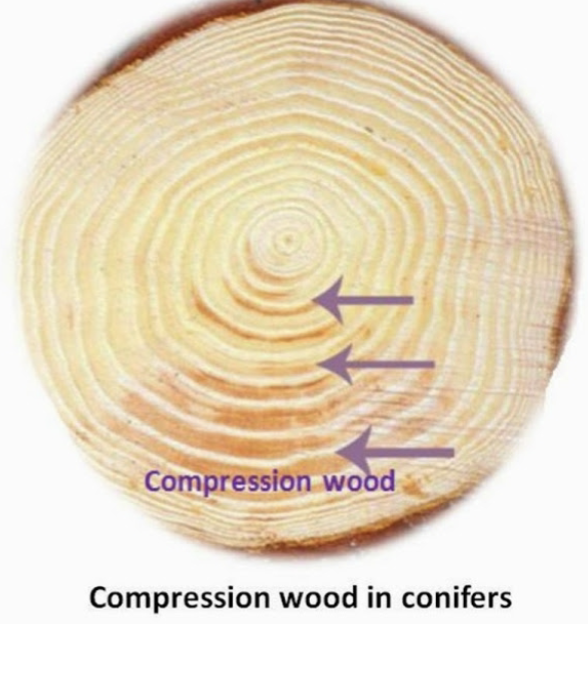
compression wood
grows below the pith to push the wood up into place
softwoods
cystolith
crystal like structure in the lithocyst
acts like a disco ball, refracting light further into the mesophyll
Paper about xylem velocity
Main focus: looks at sieve tube relation to flow regulation, higher conductivity is not associated with higher velocity and that the temporal development of the callouses show that small sieve plates can be plugged in minutes but larger pores need additional support to be plugged
Method: SEM and NMR flow imaging (magnetic resonance imaging) to measure flow rate
Phloem Size
Main focus: after 90 microns in diameter, the cell wall size for the parenchyma phloem transfer cell is increased, depends plant to plant and environment. Why more plants don’t have thicker phloem: carbon resource
Arabidopsis phloem parenchyma transfer cells paper
Main focus: More towards the apex of the leaf and smaller veins had more ingrowths, classified ingrowths into 5 classes based on ingrowth amount, more correlation with sieve
Trichomes in arid perennial species
Main point: glandular trichome secretions protect against herbivory, non glandular broken down to make gelatinous substance that coats developing organs for protection and preventing degradation
Methods: SEM, TEM, light microscopy, histochemical tests
lavender paper
Main point: peltate trichomes produce most compounds, capitate trichomes were on petals, more glandular trichomes on bottom of leaves
submerged vs aerial leaf paper
main point: both leaves differ developmentally and morphologically
arsenic and amf paper
main point: different levels of arsenic and different mycorrhizae species, G. clarum was the best at taking up arsenic, does not hyperaccumulate, amf takes up arsenic instead of phosphate, causing cell wall collapse and lipid formations. As arsenic levels increased, more severe collapsing and more lipid formations occured
methods: TEM, light microscopy, SEM