Physics too easy
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Precision
How well a result can be determined. The consistency/agreement among individual measurements of the same quantity
Accuracy
Closeness of agreement between a measured value and a true/accepted value
Systematic error
Deviations of the mean value from the true value, with same sign and similar magnitude
random error
Deviations of the measured value from the mean value, with varying signs and magnitudes.
Distance
Total length travelled by a moving object irrespective of the direction of motion
Displacement
Displacement from a reference point O is the linear distance and direction of the object from O. The linear distance refers to the shortest distance from the initial to the final position of an object moved from one place to another.
speed
the rate of change of distance travelled by an object with respect to time.
velocity
the rate of change of displacement with respect to time
acceleration
the rate of change of velocity with respect to time
what is the gradient at a point of a displacement time graph?
Instantaneous velocity at that point
what is the gradient at a point of a velocity time graph?
Instantaneous acceleration at that point
What is the area under a velocity time graph?
The change in displacement
For vertical motion with air resistance, how does the time taken to travel upwards compare to the time taken to travel downwards?
Time taken to travel up is shorter than the time taken to travel down. (because weight and air resistance act in opposite direction when travelling down)
Normal contact force
net electrostatic repulsion between two surfaces that are in contact
Friction
force that resists the relative motion or the tendency for relative motion between two surfaces that are in contact
Contact force
vector sum of friction and normal contact force.
Tension
force exerted by one end of a string/rope which is being pulled taut. Tension is constant throughout the string and acts in both directions.
Mass
a measure of the inertia of a body
Weight
a measure of thegravitational pull on a body
Centre of gravity
the point at which the weight of the object appears to act.
Newton's first law of motion
A body stays at rest or continues to move with a constant speed in a straight line unless acted upon by a net external force
Linear momentum
the product of an object's mass and velocity
Newton's second law
The rate of change of linear momentum of a body is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on it and is in the direction of the resultant force.
Impulse
The impulse of a force is the product of the average force and the time interval over which it is applied
Impulse-momentum theorem
The total change in momentum of a particle during a time interval equals the impulse of the net force that acts on the particle during that interval.
Newton's third law
If body A exerts a force on body B, then body B will exert an equal and opposite force on body A.
Characteristics of an action-reaction pair
1) Equal in magnitude.
2) Opposite directino
3) Same type of force
4) acting on different bodies
Princeple of conservation of linear momentum
The total linear momentum of a system remains unchanged if no net external force acts on the system.
Head-on collosion
Directions of motion before and after the collision are along the same line of motion
Elastic collision
The relative speed of approach is equal to the relative speed of separation.
Hooke's law
States that the magnitude of force F exerted by a spring on a body attached to the spring is proportional to the extension x of the spring from its natural length provided the proportional limit of the spring is not exceeded.
Achimedes' Principle
For a body submerged or floating in a liquid, the upthrust acting on the body is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the weight of fluid displaced by the body
Translational equilibrium
The net external force acting on a body is zero
Moment of a force
The moment of a force about a point is the product of the (magnitude of the) force F and the perpendicular distance r from the line of action of the force to the point.
Rotational equilibrium
The net moment of the body about any point is zero
Principle of moments
For a body to be in rotational equilibrium, the sum of clockwise moments about any point equals the sum of anticlockwise moments about that same point.
Couple
A pair of forces which are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, whose lines of action do not coincide.
Torque of a couple
The product of the perpendicular distance between the lines of action of the forces and the magnitude of one of the forces.
Work done
The work done by a force on the body is defined as the product of the magnitude of the force F and the displacement s in the direction of the force.
Work done on F-s graph
Area under the F-s graph
work-energy theorem
The net work done on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object.
Gravitational potential energy
Energy stored in objects due to their relative position of the objects in the system.
Elastic potential energy
Energy stored in elastic objects as the result of their stretching or compression.
Principle of conservation of energy
Energy can be converted from one form to another but cannot be created or destroyed.
Power
Rate at which work is done
Efficiency
The ratio of the useful energy output to the total energy input or the useful power output to the power input.
Radian
1 radian is the angle subtended at the centre of the circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle.
Velocity-displacement relationship of SHM
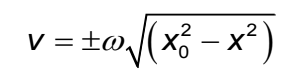
Definition of SHM
A periodic motion in which the acceleration of the body is directly proportional to the displacement from its equilibrium point and is always in the opposite direction to the displacement.
Light damping
The frequency remains constant, but the amplitude of the system decreases exponentially with time.
Critical damping
The system returns to the equilibrium position in the shortest possible time without oscillating at all.
Heavy damping
The oscillator takes a very long time to return to its equilibrium position.
Resonance
A phenomenon in which an oscillatory system responds with maximum amplitude to an external periodic driving force, when the frequency of the driving force equals the natural frequency of the driven system.
Transverse wave
A wave in which the points of disturbance oscillate about their equilibrium positions perpendicular to the direction of wave transfer or energy propagation.
Longitudinal wave
A wave in which the points of disturbance oscillate about their equilibrium position along the direction of wave travel or energy propagation.
Period of a wave
Time taken for a point on the wave to complete one oscillation cycle
Energy transmitted by a wave
The energy transmitted by a wave to a point is proportional to the square of the amplitude of the oscillator at that point.
Intensity of a wave
The intensity of a wave is the rate at which energy is transported by the wave, per unit area, across a surface perpendicular to the direction of propagation.
Plane polarisation
Polarisation is a phenomenon whereby vibrations in a transverse wave are restricted to only one direction in the plane normal to the direction of energy transfer.
Malus’ law
I = I0cos2θ
Principle of Superposition
When two or more waves of the same kind overlap, the resultant displacement at any point at any instant is given by the vector sum of the individual displacements that each individual wave would cause at that point at that instant.
Interference
The superposing or overlapping of two or more waves to give a resultant wave whose displacement is given by the principle of superposition, which states that displacement of the resultant wave at any point is the vector sum of the displacements of the individual waves at that point.
Constructive interference
Constructive interference occurs at a point when two waves meet in phase at that point. The resultant amplitude of the oscillation at that point is therefore a maximum.
Destructive interference
Destructive interference occurs at a point when two waves meet in antiphase. The resultant amplitude of the oscillation at that point is therefore a minimum.
Conditions for two waves to produce an interference pattern
The sources must be coherent, i.e. they must maintain a constant phase difference w.r.t. each other.
The sources must emit waves of roughly the same amplitude.
The waves must be unpolarised or have a common direction of polarisation.
Formulae for Young’s double slit and assumptions (conditions for constructive/destructive interference)

Formulae for Young’s double slit and assumptions (Positions of fringes)
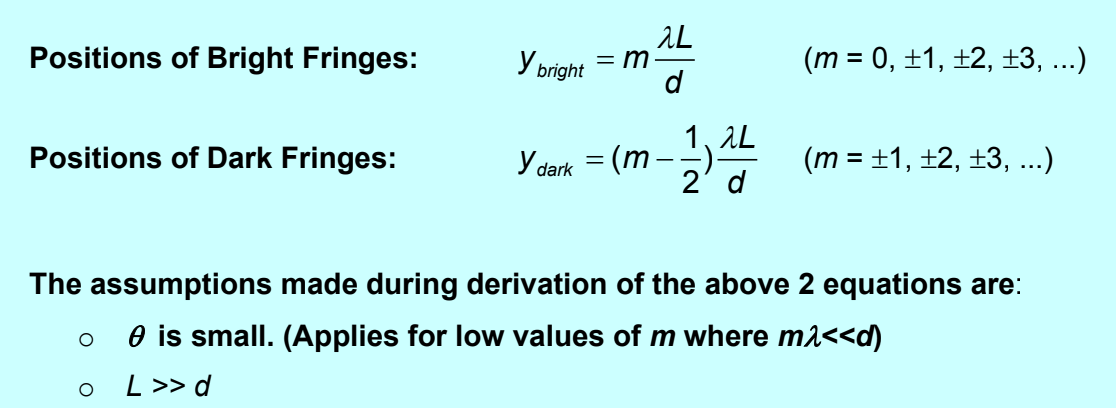
Formulae for Young’s double slit and assumptions (Fringe separation)
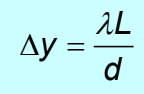
Conditions for constructive interference for a diffraction grating
Advantages of diffraction grating compared to double slit
Sharper fringes so that fringe positions are more precisely determined. Less uncertainty in measuring position of fringes and hence calculation of wavelength.
Angular displacements are large → lower percentage uncertainty in measuring angular displacement and hence lower uncertainty in calculation of wavelength.
Diffraction
The spreading of a wave into the geometrical shadow after passing through a slit or around an obstacle.
First minimum intensity of a single slit diffraction pattern
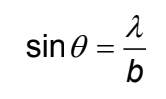
Rayleigh criterion
Two images are just resolved or distinguishable when the central maximum of one image coincides with the first minimum of the other image.
Stationary waves
When two identical waves of the same amplitude, frequency and speed but travelling in opposite directions are superposed together, the resultant wave obtained is called a stationary wave.
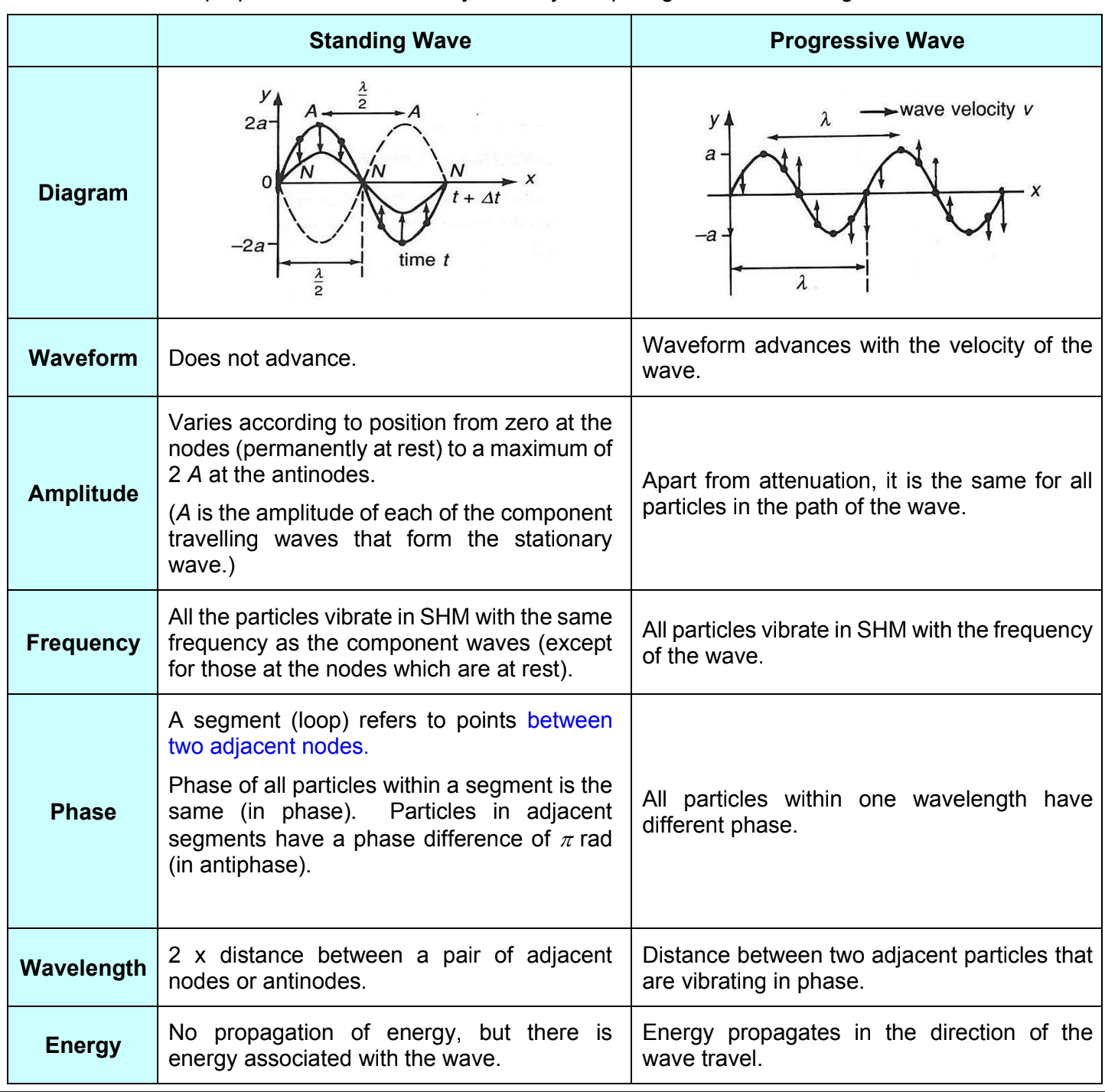
Differences between a stationary wave and a progressive wave
Heat
The transfer of energy between two objects due to a difference in temperature between them.
Specific heat capacity
The amount of energy per unit mass required to raise the temperature of the body by one unit.
Specific latent heat of fusion
The amount of energy per unit mass required to change a substance from solid to liquid without a change in temperature.
Specific latent heat of vapourisation
The amount of energy per unit mass required to change a substance from liquid to gas without a change in temperature.
Heat capacity
The amount of energy to be supplied to an object to produce a unit rise in its temperature.
Internal energy
The internal energy is the summation of microscopic kinetic energy due to random motion of the molecules and the microscopic potential energy due to the intermolecular forces.
First law of thermodynamics
The increase in the internal energy of a system is the sum of the heat supplied to the system and the work done on the system.
Electric field
An electric field is a region of space where a charge will experience an electric force.
Electric field strength
The electric field strength at a point is the electric force per unit positive charge acting on a small test charge placed at that point.
Coulomb’s Law
The magnitude of the electrical force acting etween two point charges is proportional to the product of the magnitude of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Electric potential energy
The electric potential energy of a system of charges is the work done by an external force in assembling the system where the charges were originally at infinity, without any change in the kinetic energy of the charges.
Electric potential
The electric potential at a point in an electric field is the work done per unit positive charge, by an external force, in bringing a small test charge from infinity to that point, without any change in KE.
Rules for drawing field lines
Number of field lines is proportional to the charge. e.g. q has 4 lines, then 2q has 8 lines.
Field lines point from higher potential to lower potential.
Field lines do not intersect.
Field lines are perpendicular to equipotential lines.
Define Coulomb (unit for electric charge)
The quantity of electric charge that pass through a given point in a circuit when a steady current of 1 A flows through that point for 1 second.
Why does a light bulb lights up almost instantaneously after the switch is closed despite the drift velocity is slow?
All mobile electrons in the circuit start drifting at the same time as the electric field is
established in the wire almost instantaneously.
The lamp lights up as soon as the mobile electrons already in the lamp filament begin to move which is much shorter than the time required for electrons to move from the battery to the charge.
Define emf
The electromotive force of a source is defined as the energy converted per unit electric charge to electrical energy in driving charge round a complete circuit.
Potential difference
The potential difference between two points in a circuit is defined as the energy converted per unit electric charge from electrical energy to other forms of energy when charge moved between the two points.
Resistance
The resistance of a device is the ratio of the potential difference across the device to the current flowing through the device.
Ohm’s Law
A steady current flowing through a metallic conductor is proportional to the potential difference across it, provided the temperature and other physical conditions are constant.
Kirchoff’s first Law
At a junction in a circuit, the current arriving equals the current leaving.
Kirchoff’s second Law
Round any closed circuit or loop, the algebraic sum of the e.m.f. is equal to the algebraic sum of the products of current and resistance.
Characteristics of diode
Only conducts electricity in 1 direction
Has a turn-on voltage