Therapies & interventions for neurodevelopmental conditions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Neurodevelopmental conditions
What we know so far:
Causes – genetic, environmental, unknown
Prevalence can be influenced by numerous factors
Different profiles
Strengths
Weaknesses
Assessed using standardised tests & experimental designs
Interventions
William’s syndrome - strengths
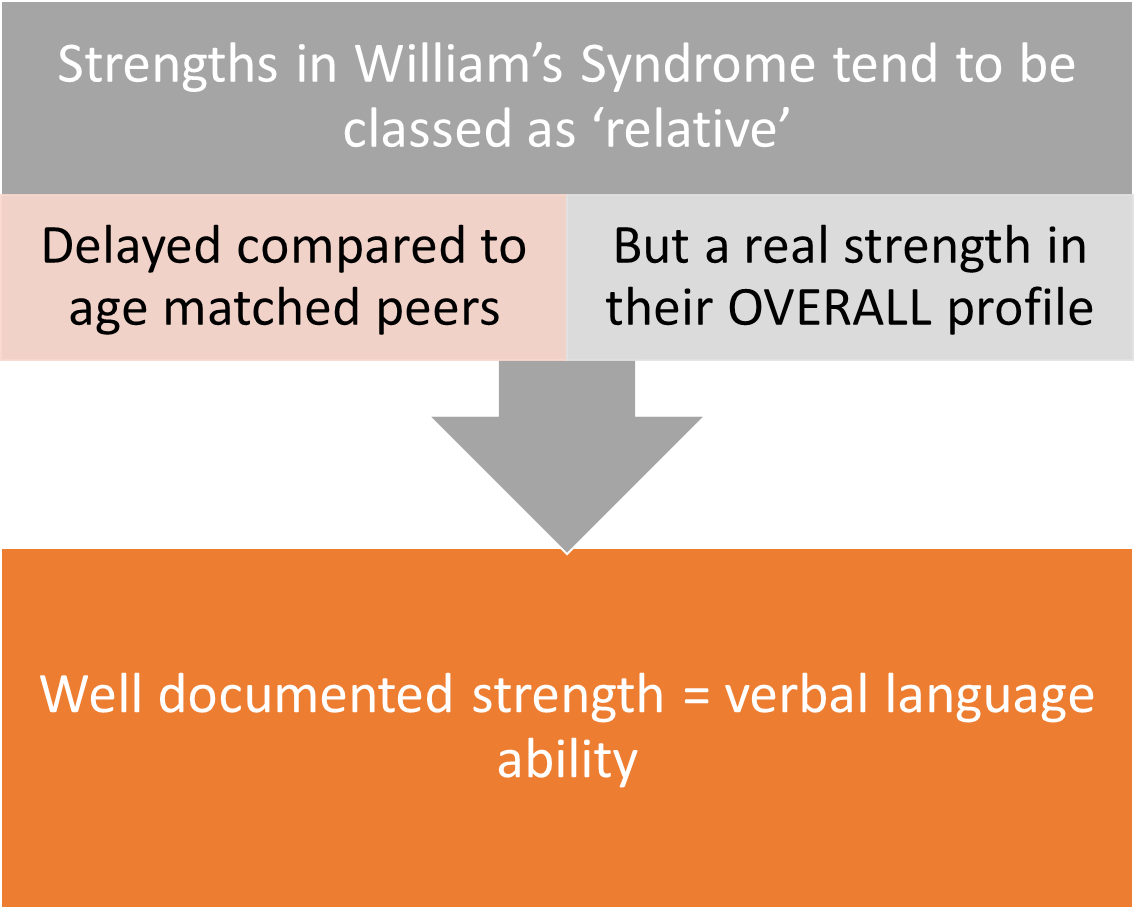
Relative strengths:
Speech production
Fluency
Syntax
Grammar
Difficulties in pragmatics (understanding intended meanng of words)
Williams syndrome - weaknesses
Executive function
Numerous studies suggesting that individuals with William’s syndrome experience difficulties across several executive functions including
inhibitory control
planning
workign memory
Visuospatial abilities
eg. as measure by the WISC (standardised IQ test)
Autism - potential strengths
Excellent attention to detail & pattern recognition
Strong systemising abilities = heightened attention to detail and advanced capabilities in pattern recognition
Superior visual serarch skills are consistently reported
Shirama, Kato & Kashino (2017) used two visual search tasks and increased the level of difficulty of each task:
Conjunction search
Feature search
Regardless of the difficulty of the task autistic individuals outperformed neurotypical individuals on every task
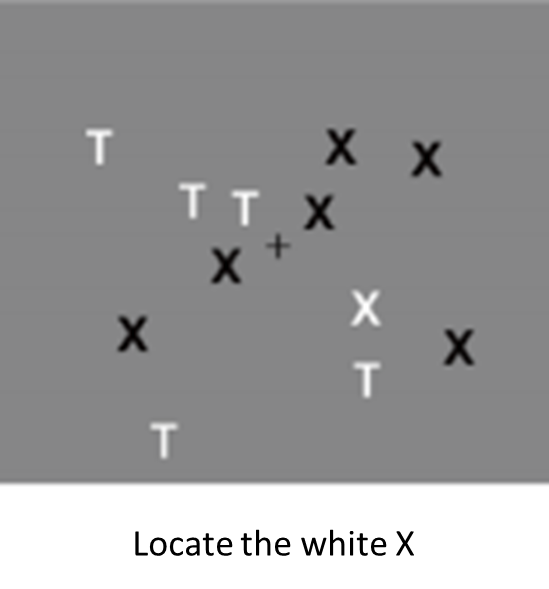
Visual search task real ligfe application
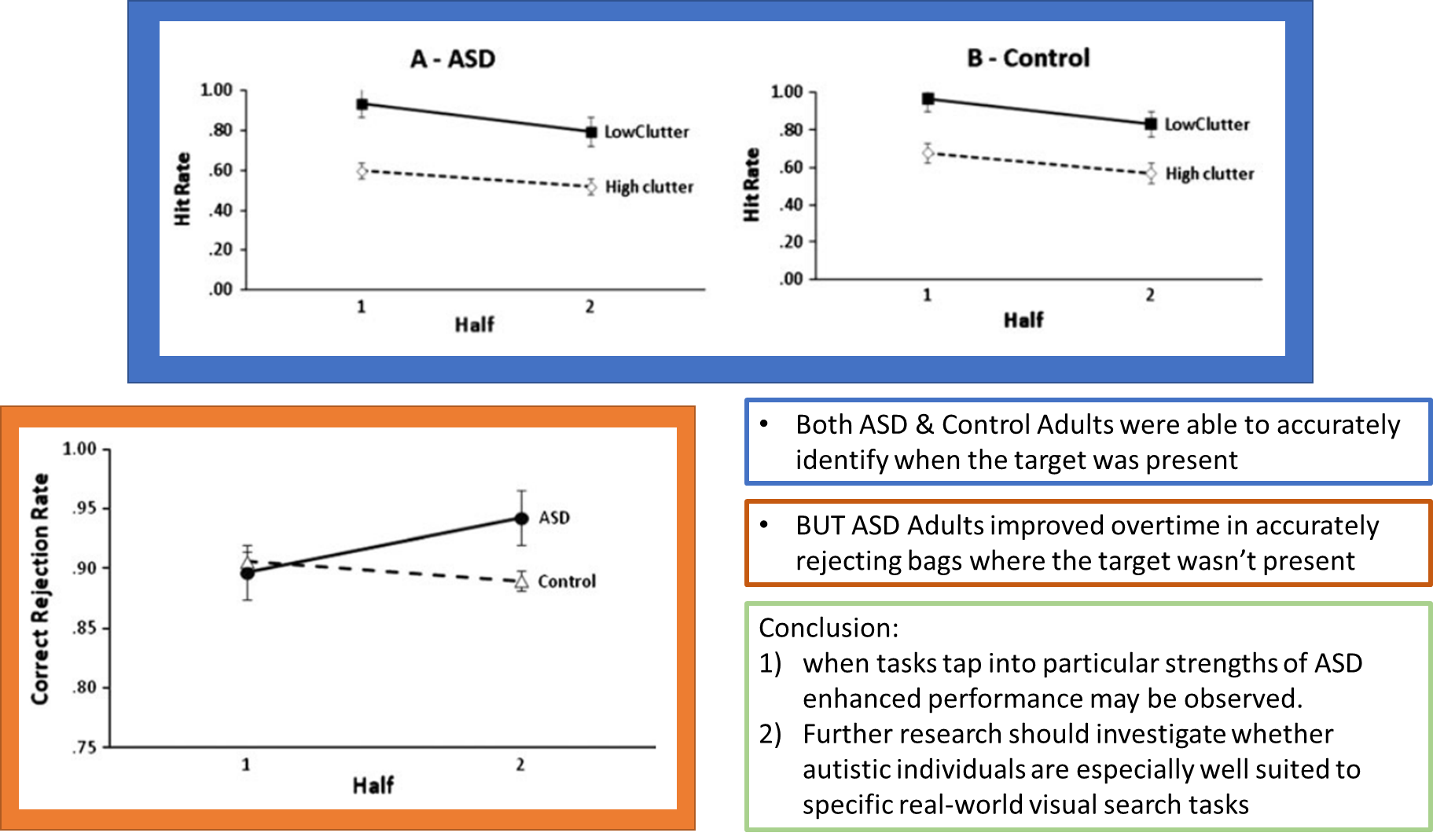
Autism - potential weaknesses
Executive function
Numerous studies suggesting that autistic individuals experience difficulties across executive functioning
inhibitory control
cognitive flexibility
working memory
Theory of mind
Difficulties in understanding the emotions, thoughts and intentions of others?
Theory of mind and autism
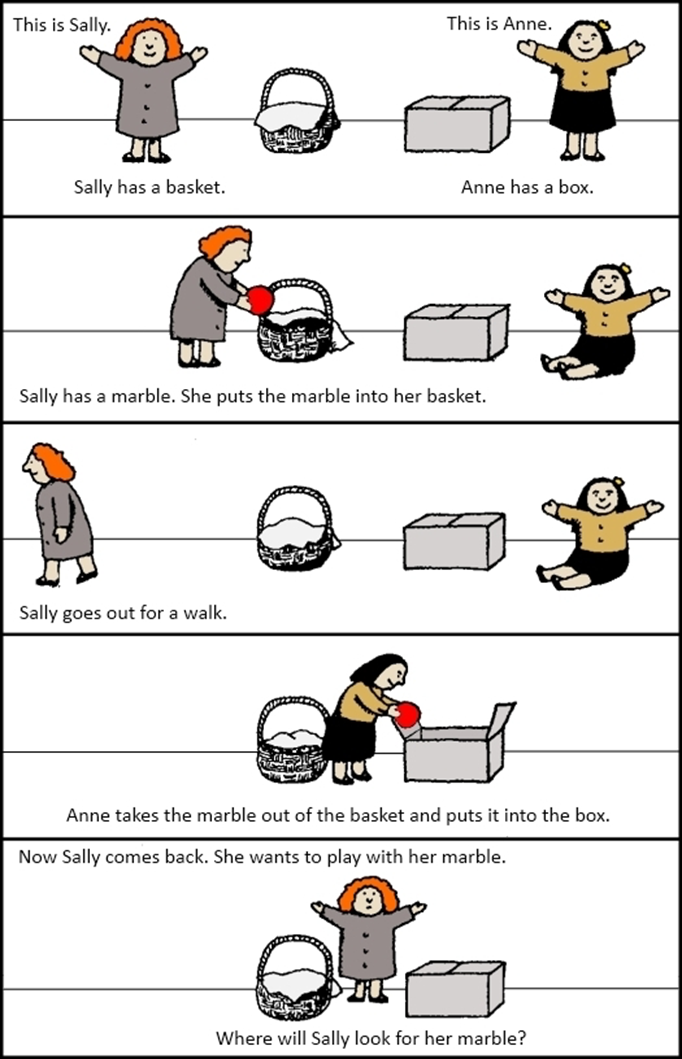
Research showed children with autism struggled with these tasks
Now research is more equivocal
Some will struggle, some won’t
Children who fail this in a few years are able to then pass it
Many different therapies and interventions
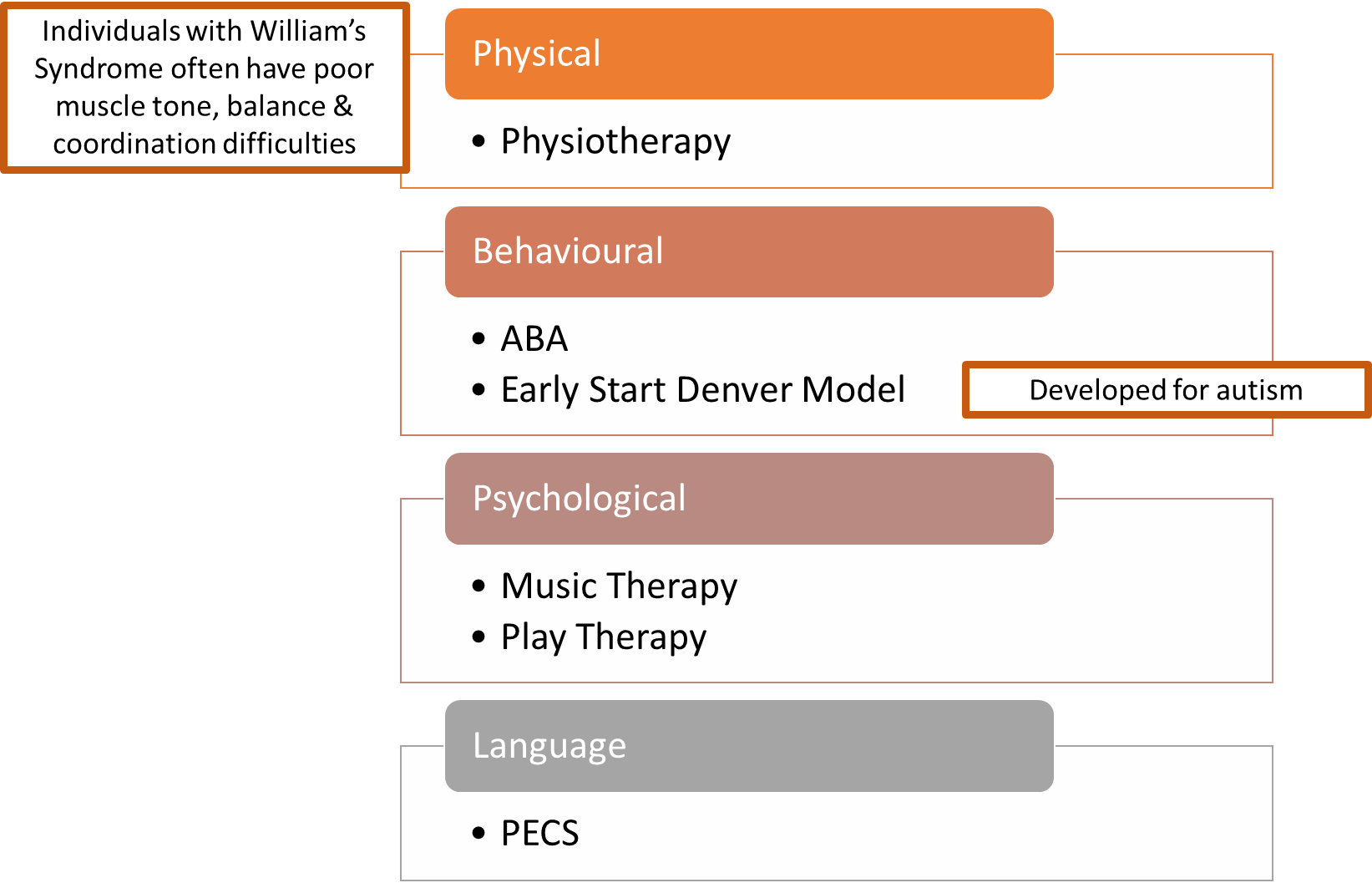
Speech & language therapy - PECS
Williams - can be delayed speech before it becomes a strength
Both Williams and Autism are associated with delays or difficulties in speech
Picture exchange communication system (PECS)
a form of alternative communication
Difficulty as a child as you know what you want but don’t know how to communicate it → lead to meltdowns and tantrums as you cannot communicate in the same way
PECS - does not rely on verbal communication
Very basic to open a window of communication
Helps build on verbal communication
Stages of PECS
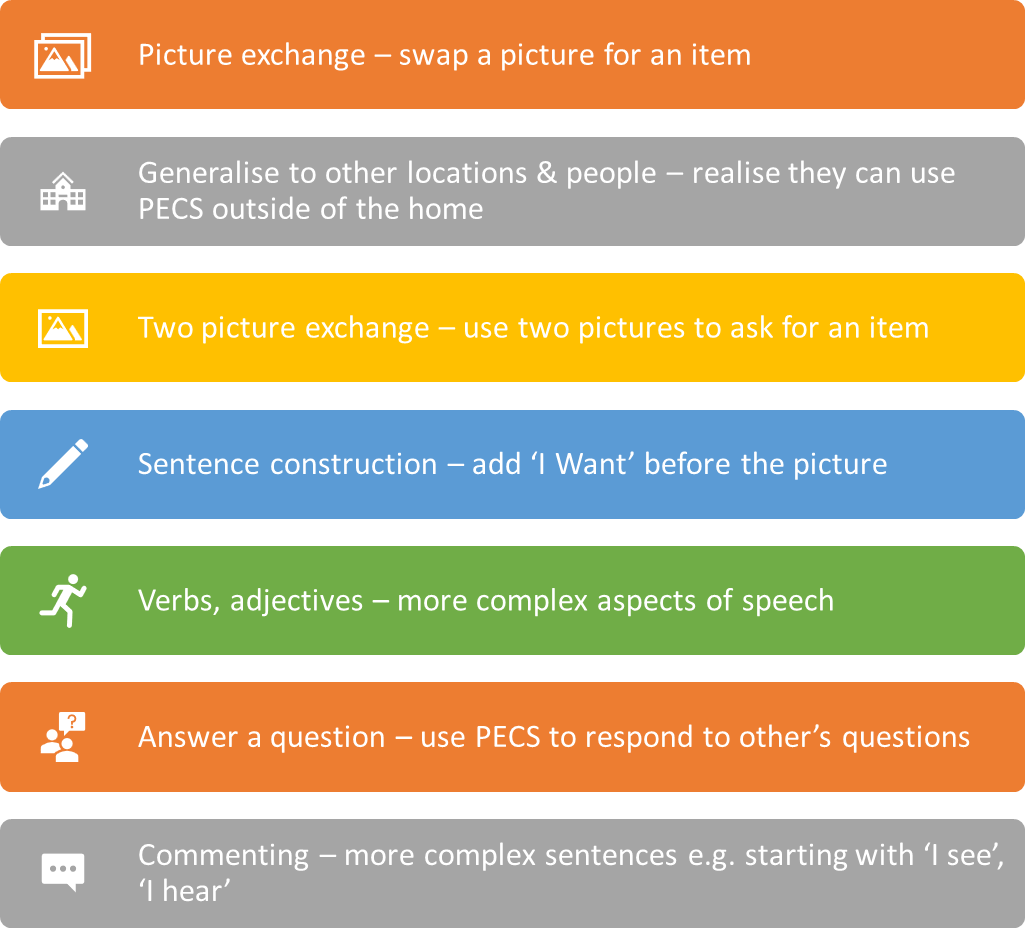
Every stage builds on previous skill to build understanding of communication
Different children may develop and stop at certain stages that are most appropriate to them so they are still able to communicate in some manner
Some may never move beyond the initial stage and some may get to the end - developmental differences
Makaton
Uses symbols (pictures) uses symbols (pictures), signs (gestures) and speech to enable people to communicate
Supports the development of essential communication skill such as attention and listening, comprehension, memory, recall and organisation of language and expression
2 vocabularies (learned suquentially)
A core vocab of essential words or concepts presented in stages of increasing complexity
A much larger, open-ended, topic based resource vocab providing an enormous banks of further signs and symbols covering broader life experiences
Makaton and BSL are entirely distinct and are used by very different communities of people
makaton is not a complete language
Makaton pahses out as speech develops naturally
for some this will be useful their whole lives
Builds on attention, listening, learning how language is organised and memory
Play therapy
If a child doesn’t express themselves in an adult world, the therapist should join the child in their world, on their level
cannot expect children to act as adults - communication gap
children learn to understand the world and their place in it through play
its where they’re free to act out their inner feelijngs and deepest emotions
toys can act as symbols and take on greater meaning - if you know what to look for
use toys and play to guide the child to understand their own behaviours and emotions
Typically 30 mins - 1 hour once a week
Therapy can take place individually or in groups
Can be directive or non-directive
Directive = therapist will take the lead by specifying the toys or games that’ll be used in the session
Non-directive - less structured - the child is able to choose toys and games and play in their own way - the therapist will observe closely and participate as appropriate
Techniques include
storytelling
role playing
toy phones
puppets
dolls and action figures
arts and crafts
blocks and construction toys and more
demonstrated to reduce behaviours associated with ADHD & social anxiety and to increase social emotional competency in autistic children
Music therapy
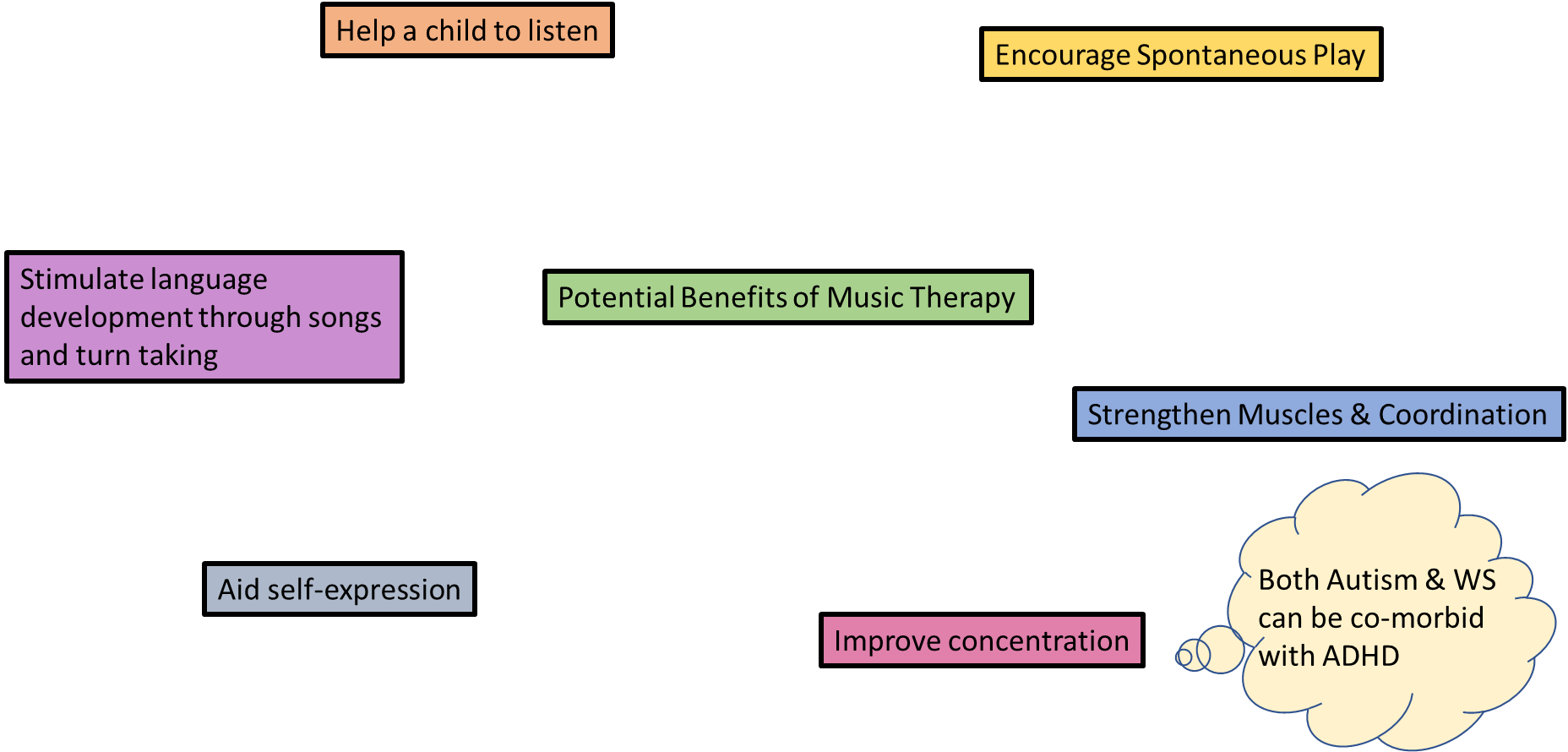
Music as an educational tool in William’s syndrome?
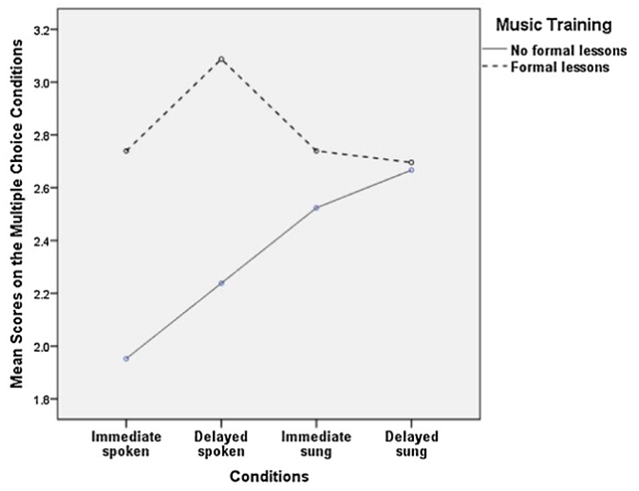
Two groups: those with music training, those without
Better verbal recall when the information was sung for those without lessons
Generally children with William's who received formal music training their recall was better
Those with training showed good recall for spoken information
Music aids verbal working memory in WS?
Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA)
ABA is a type of therapy that can improve social, communication, and learning skills through positive reinforcement
Originally developed to focus an autism, but is now used across a range of disorders / conditions
An intensive theray, it was originally recommended for 40hrs per week 1-1, although more recently this contact time has lowered
Fall upon educators and parents to conduct this in day to day life now hours have dropped
Shown effectively to remove maladaptive behaviours behaviours such as tantrums
How does ABA work?
Positive conditioning – children are rewarded for showing a desired behaviour
First a therapist will observe the child, consult with the parents and make a plan to address certain behaviours e.g.
Reducing tantrums or harmful behaviours
Increasing or improving communication
The plan will include specific strategies caregivers, teachers, and the therapist can use to achieve treatment goals.
ABA relies on parents and caregivers to help reinforce desired behaviours outside of therapy.
Something the child values when a wanted behaviour is conducted - pavlovian
Forming association
Withold the reward when they display a behaviour not desired
Do not target loads of behaviours at once
Researcher observes and plans what behaviours need to be targeted
Focus on one behaviour at a time
Doesn't now just fall on the therapist, others (families and educators) now involved in reinforcing
Understandable why it is controversial
Effectiveness of ABA
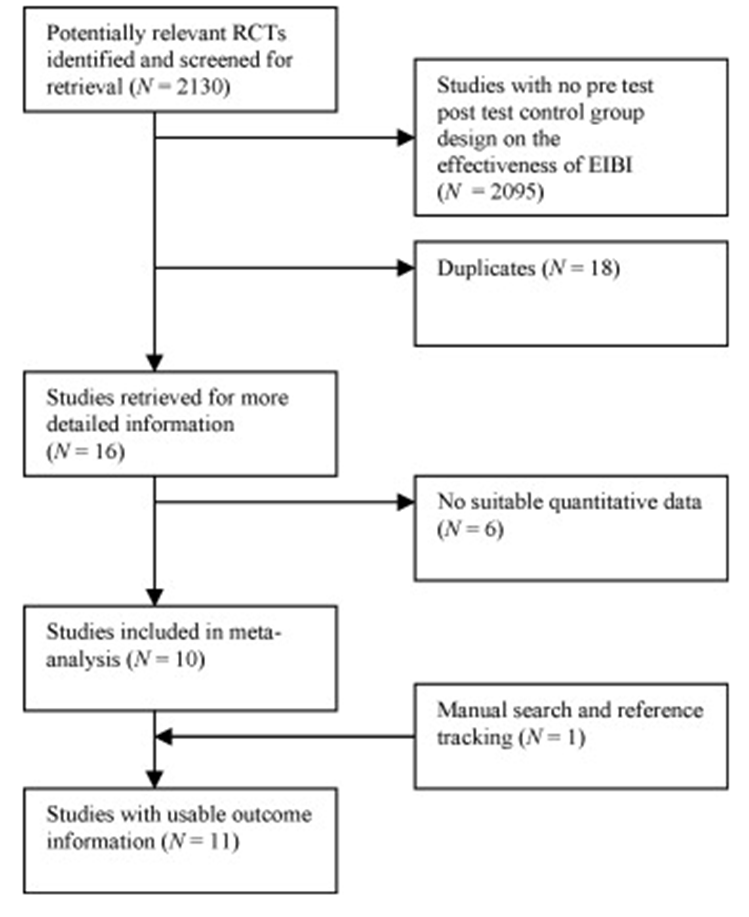
Peters-Scheffer, Didden, Korzilius & Sturmey (2011)
Meta analysis on effectiveness of Early Intensive Behavioural Intervention (a type of ABA)
11 studies with 344 children
Groups who received EIBI outperformed the control groups on IQ, non-verbal IQ, expressive and receptive language and adaptive behaviour.
ABA discussion points
ABA - received a lot of backlash even though it is highly effective Intensive and expensive
Big problem In the way it phrases autistic behaviours as being undesirable
Part of that person and you are trying to remove this
Encouraging masking
Training them to be neurotypical
Dehumanising
Training them to give a response we want them to show
Stigmatising
May suppress self-regulation behaviours such as stimming and this can cause them to dysregulate
Harmful by causing more distress
Can be useful in terms of behaviours which are damaging to them - stimming such as head banging