Module 9: Neurological System
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What is the pathophysiology behind acute brain injuries?
It involves the physiological changes and long-term effects resulting from brain injuries.
What are common causes of brain injuries?
Blunt and open trauma.
What are the four varying levels of brain injury?
Focal brain injury
Contusions
Subdural and Epidural hematoma
Concussion
What does ICP stand for in neurological nursing?
Intracranial Pressure.
What factors influence ICP?
Cerebral edema, hemorrhage, excess CSF, and increased cerebral blood flow.
What is the role of the autonomic nervous system?
Regulates cardiac and smooth muscle and glands, controlling bodily functions unconsciously.
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
What is the function of the Sympathetic nervous system?
Prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses, increasing heart rate and metabolism.
What is the function of the Parasympathetic nervous system?
Promotes 'rest and digest' activities, slowing heart rate and increasing digestive functions.
What are the three main areas of the brain?
Forebrain
Cerebellum
Brainstem
What are the three parts that make up the brainstem?
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
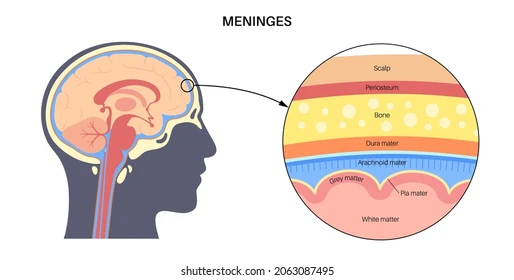
What are the 3 meninges and their role in protecting the brain?
They “PAD” the brain:
(Brain Location)
Pia mater – thin inner layer that closely covers the brain and contains blood vessels
Arachnoid mater – middle, web-like layer; subarachnoid space below it contains CSF for cushioning
Dura mater – tough outer layer under the skull; subdural space sits beneath it
(Skull Location)
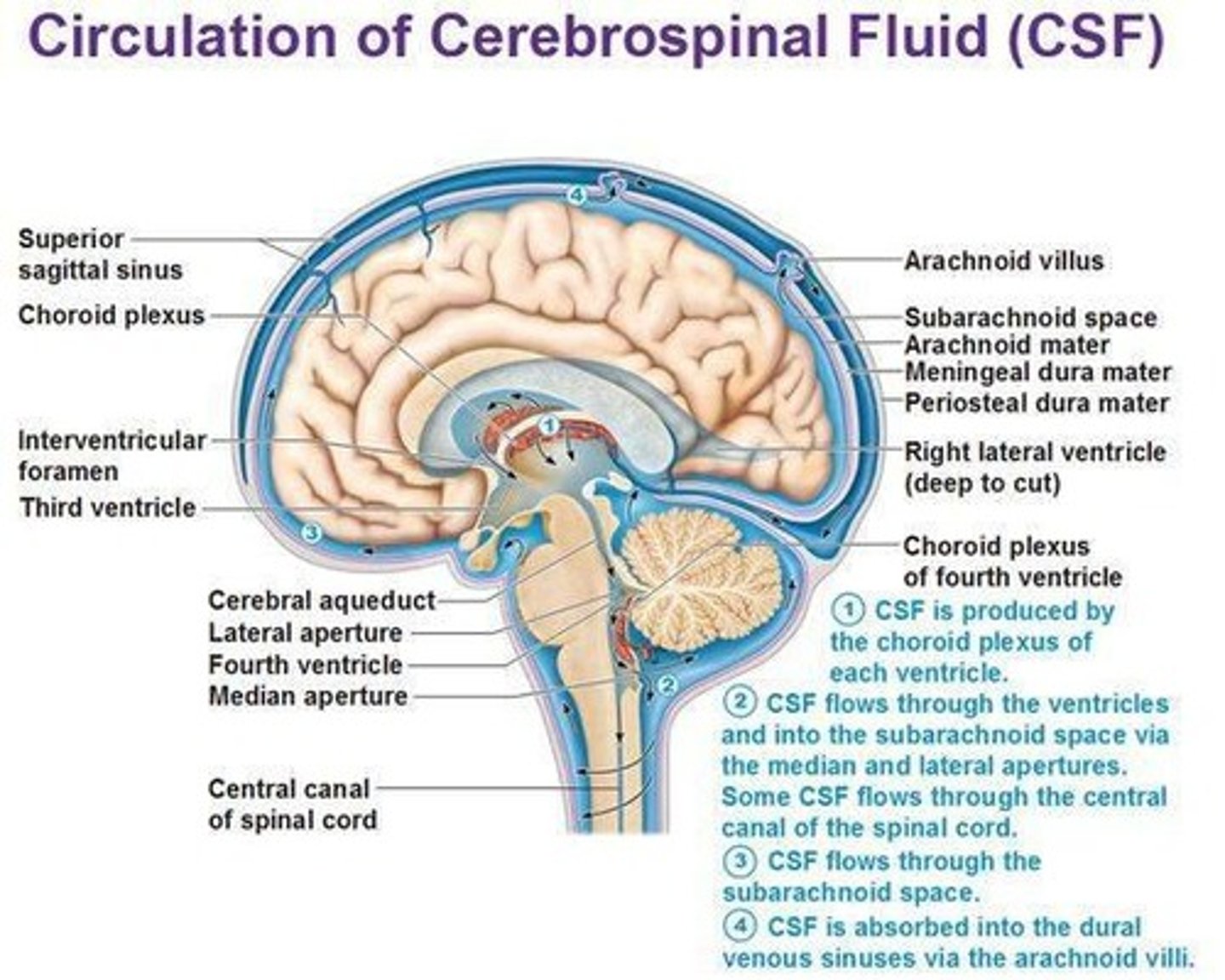
What is the function of the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)?
Cushions the brain, provides buoyancy, and removes waste.
How much CSF is present/produced?
Volume at one time: 125–150mL
Daily production: ~650mL per day
What is the content of CSF?
water, protein, glucose, and ions (Na, Cl, K)
What is the role of the choroid plexus?
It produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain ventricles.
What are the two types of neurons?
Motor Neurons (Efferent) - Carry impulses from CNS to PNS
(Exits CNS)
Sensory Neurons (Afferent) - Carry impulses from PNS towards CNS
(Arrives at CNS)
How many Cranial and Spinal nerves are there?
12 pairs of Cranial nerves with primary motor and sensory pathways in the brain, head, and neck
31 pairs of Spinal nerves carrying afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) signals
What is the function of the cranial nerves?
They are responsible for motor and sensory functions in the brain, head, and neck.
What is the Blood-Brain Barrier?
A selective barrier that protects the brain from harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients to pass.
Prevents: large molecules (Albumin)
Allows: Oxygen, Glucose, CO2, ETOH, Anesthetics, and Water
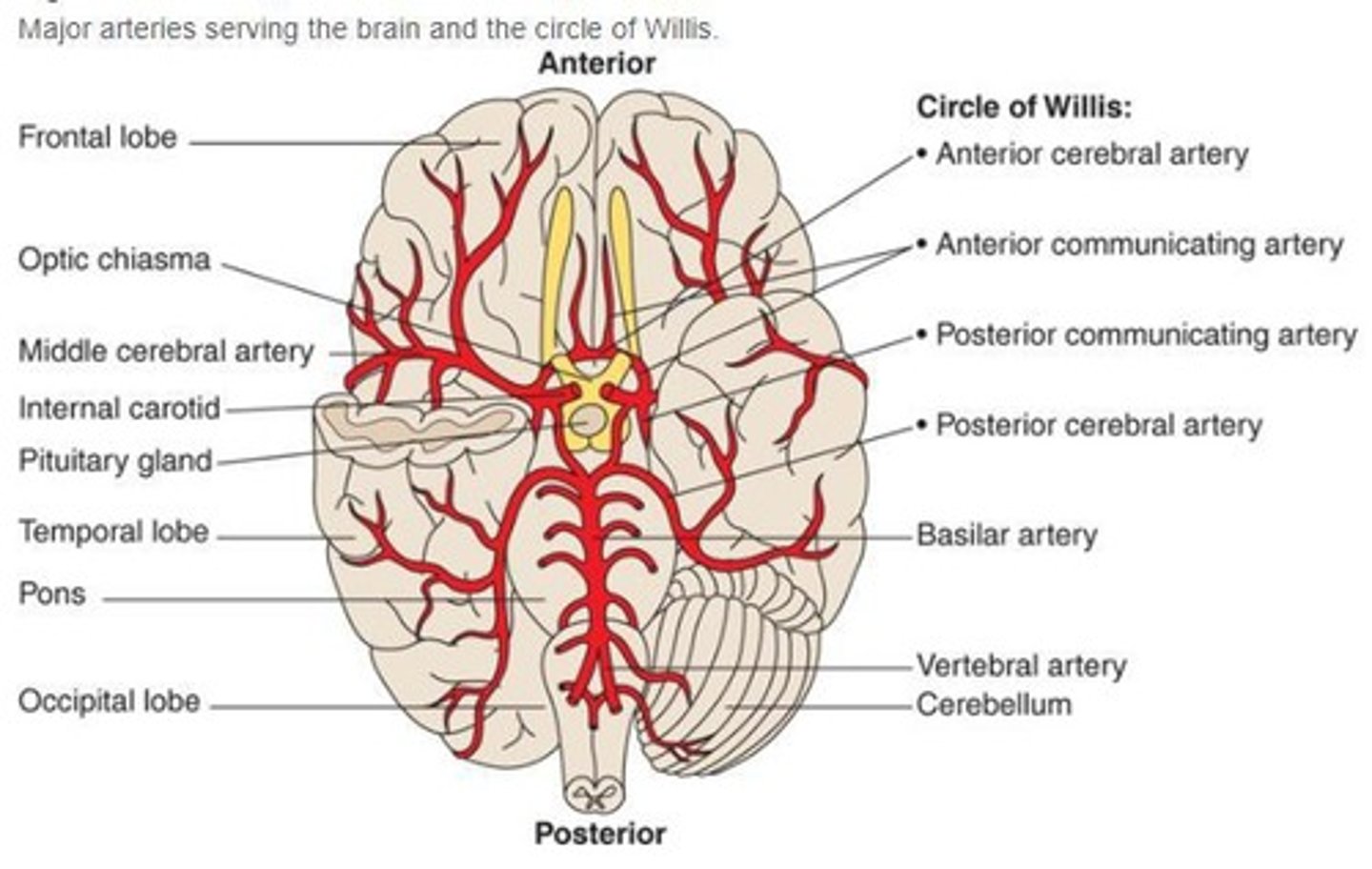
What is the Circle of Willis?
A circular network of arteries at the base of the brain that provides collateral blood flow.
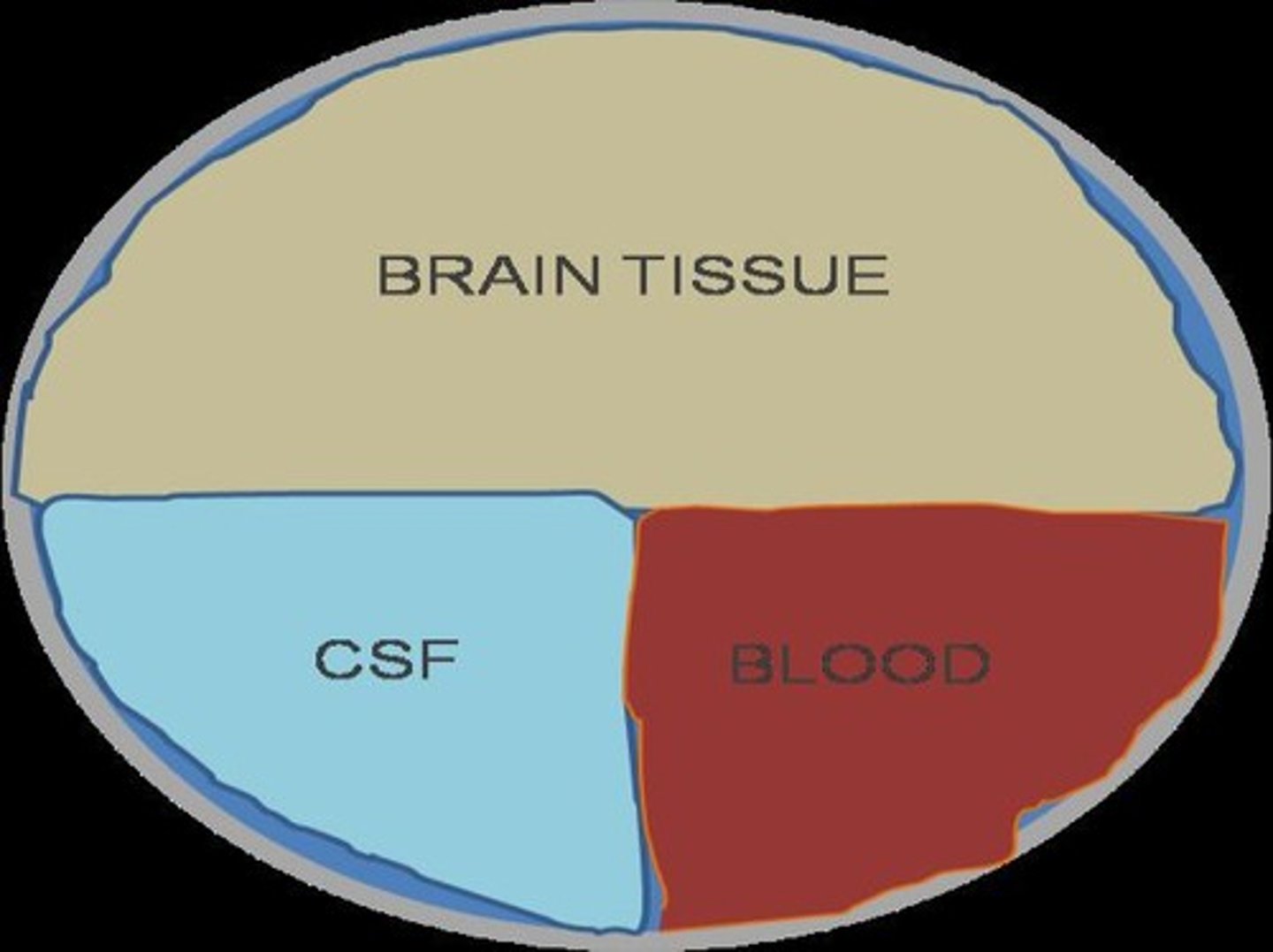
What is the Munroe-Kellie Doctrine?
States that the total volume of the cranial vault is constant; if one component increases, another must decrease to maintain ICP.
What is the normal range for ICP?
0-15mmHg.
What is the threshold for treatment of increased ICP?
Sustained ICP of 22mmHg.
What can cause increased ICP?
Cerebral edema, hemorrhage, excess CSF, and increased cerebral blood flow.
What are common signs of increased ICP?
Headache, nausea, vomiting, amnesia, behavioral changes, and decreased LOC
What is the function of the reticular system?
It controls autonomic functions and regulates alertness.
What is the significance of cerebral blood flow (CBF)?
It matches cerebral metabolic demand and is crucial for brain function.
What factors can cause vasodilation in cerebral arteries?
Hypotension, increased CO2, hypoxia, and sedation.
What factors can cause vasoconstriction in cerebral arteries?
Hypertension, decreased CO2 (alkalosis), and hyperventilation
What does CPP stand for in brain theory?
Cerebral Perfusion Pressure
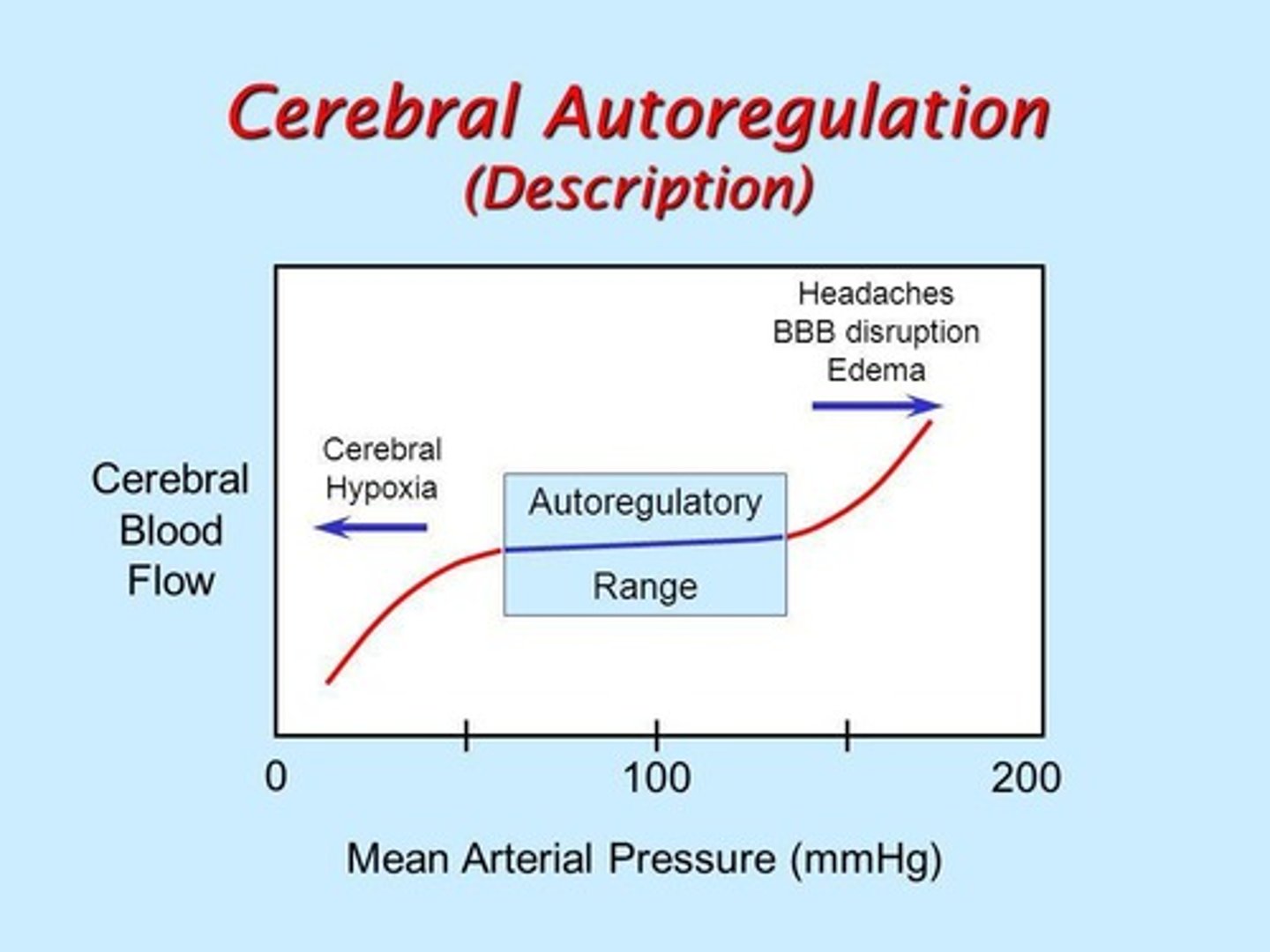
How is Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (CPP) calculated?
CPP = MAP - ICP
What is the normal range for Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (CPP)?
60-100mmHg
How do you Calculate MAP?
MAP = (SBP) + (2 x DBP)/3
What is the normal range for Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)?
60-150mmHg
Calculate the CPP:
ICP= 25mmHg
BP= 85/30mmHg
MAP = (85) + (2 × 30)/3 = 48mmHg
CCP = 145mmHg - 25 = 23mmHg
CPP= 23mmHg
Normal CCP is 60-100mmHg, a CCP of 23mmHg is critically low perfusion
What are the types of cerebral edema?
Vasogenic edema - Caused by breakdown of the blood–brain barrier
Cytotoxic edema - Caused by a head injury that leads to cells losing the ability to regulate fluids
Interstitial Cerebral edema - Caused by obstructive or non-obstructive hydrocephalus (CSF Build-up)
What is Cushing's Triad?
A clinical syndrome characterized by:
Irregular respirations
Bradycardia
Widening pulse pressure
What does a widening pulse pressure indicate?
An increased difference between systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP).
What is the #1 assessment in head injuries?
LOC Assessment
What is the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) used for?
To quantify consciousness and severity of head injury.
What is the GCS score range?
3-15
What is the significance of 'blown' pupils?
They indicate potential neurological impairment or increased ICP.
What can happen if increased ICP is untreated?
Displacement of brain tissue and potential brain herniation.
What are the two types of abnormal posturing?
Decorticate posturing
Decerebrate posturing
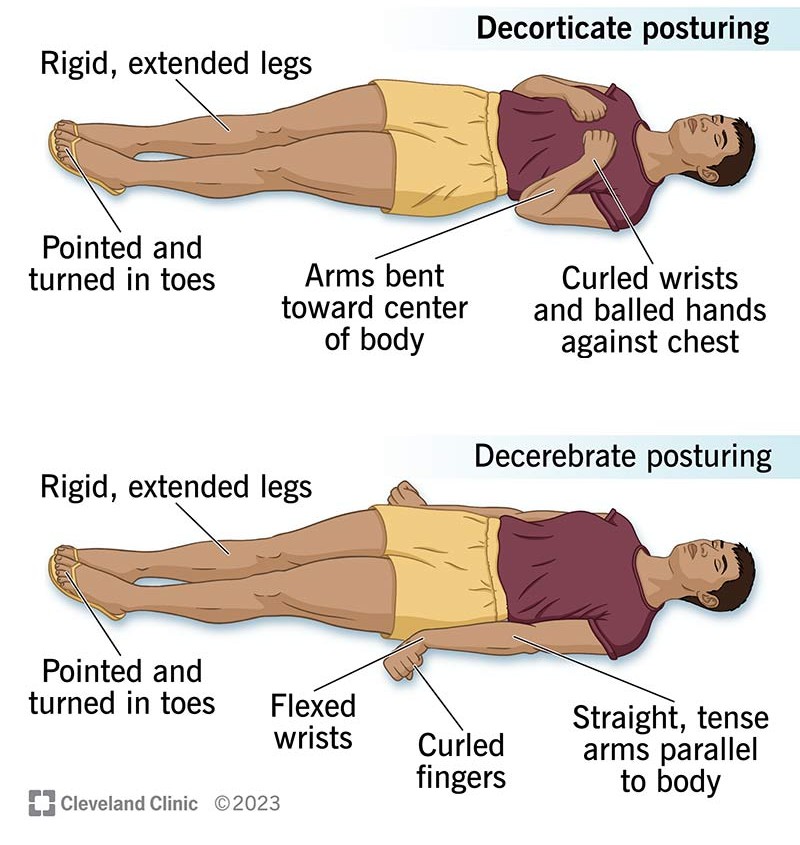
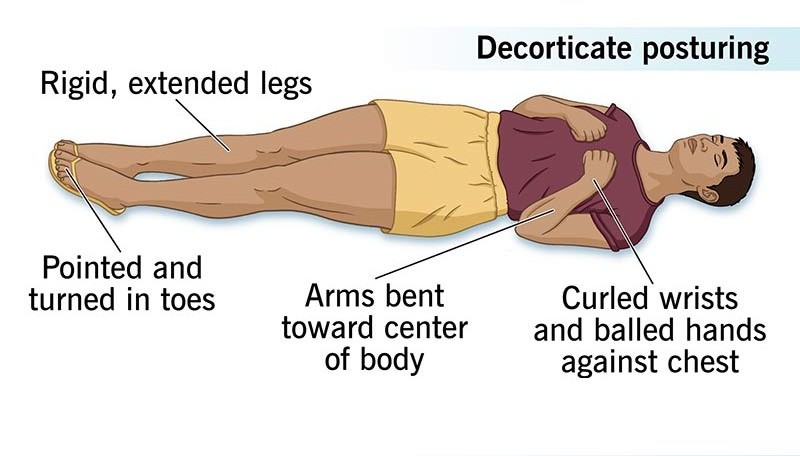
What is Decorticate posturing
Arms flexed inward toward the chest, legs extended
Indicates damage to the corticospinal tract (above the brainstem)
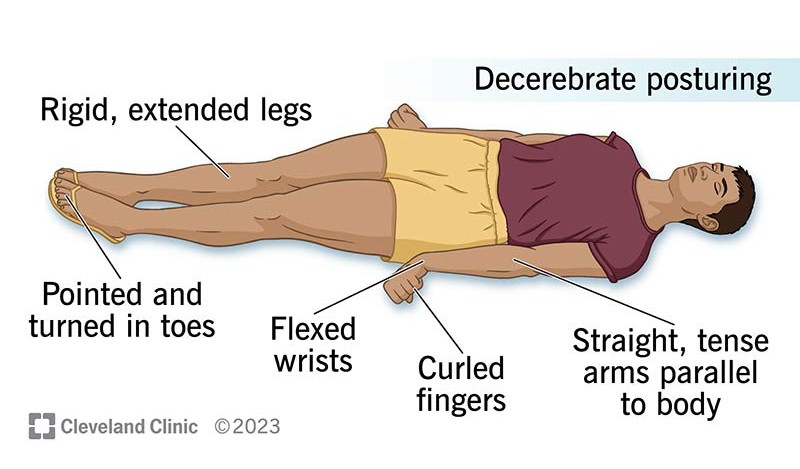
What is Decerebrate posturing
Arms and legs extended straight, flexed wrists , head arched back
Indicates damage to the brainstem
Usually a more severe sign than decorticate posturing
ABG results that increase cerebral blood flow (CBF):
Increased PaCO₂ (hypercapnia) → causes cerebral vasodilation, increasing CBF
Decreased PaO₂ (<50–60 mmHg) → triggers vasodilation, increasing CBF
What are some age-related changes affecting the brain?
Brain tissue atrophy, stretching of bridging veins, and slower cognitive processing.
What are the three common drug interventions for increased ICP?
Mannitol, hypertonic saline, and corticosteroids
What are two surgical interventions for increased ICP?
Craniotomy - A surgical procedure where a section of the skull (bone flap) is temporarily removed to access the brain
Burr Holes - Small, round holes drilled into the skull
Often done as a less invasive way to relieve pressure (e.g., from a hematoma) or to access the brain.
What are common causes of increased ICP related to patient positioning?
Supine position with head of bed flat and neck flexion/rotation.