Epithelial Cell Function
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
where are epithelial cells found
cover external and internal surfaces of body organs
general function of epithelial cells
•Protection: form a protective barrier (skin)
•Selective barrier; only allows selective molecules to pass through
•Gland formation: cells group together to form glands, secretes products
•Regulation: regulate the exchange of molecules
•Absorption: e.g., epithelial lining of small intestine
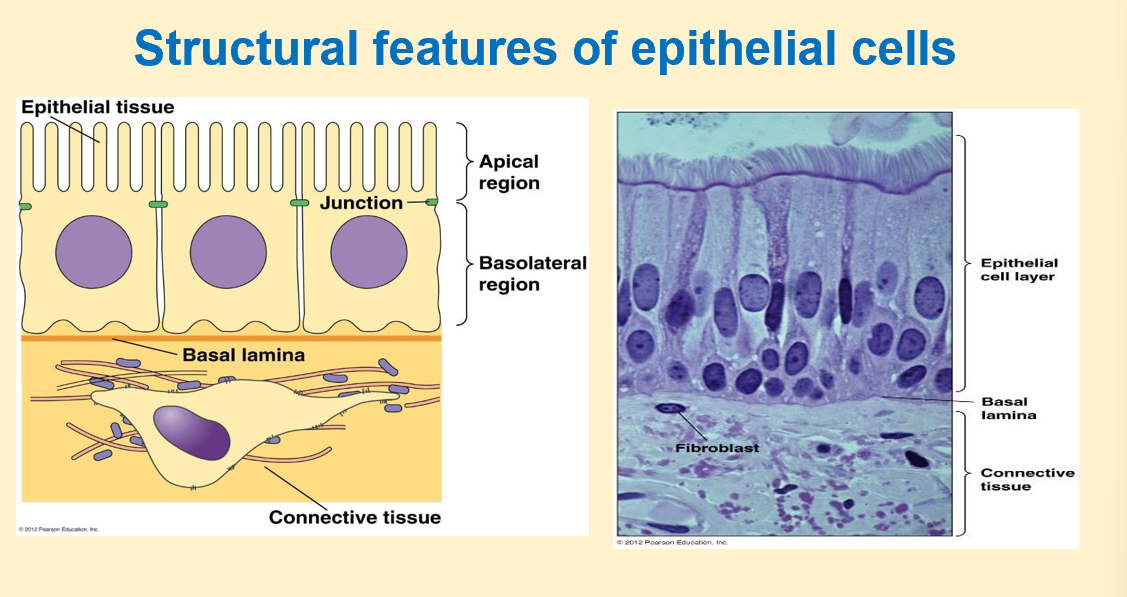
epithelial cell diagram
-basal: left to right
-lateral: up and down
-basolateral region important for cell polarity
-apical regions have specific structures which are pointed towards lumen of particular organ
-basal region: has connective tissue underneath it to provide matrix for support and is in contact with blood supply
-basal lamina: helps entire cellular lining to be embedded/ connected with connective tissue
-basal lamina and region under it is rich in lots of dif proteins and enzymes and act as reservoir for lots of dif cellular activities
-extra cellular matrix (under basal lamina): rich in connective tissue, collagen proteins, fibroblast
-lateral regions: rich in junction proteins (green): maintain tissue integrity so cells don’t start floating around in extracellular fluid, function like a tissue
epithelial cell vs endothelial cell
-both line body surface
epi:
-internal and external surfaces of body
-squamous, cuboidal and columnar
-simple(single lining of cells) or stratified(layers)
endo:
-special type of epi
-line inner surface of blood and lymph vessels
-simple squamous epithelium
endothelial cell diagram
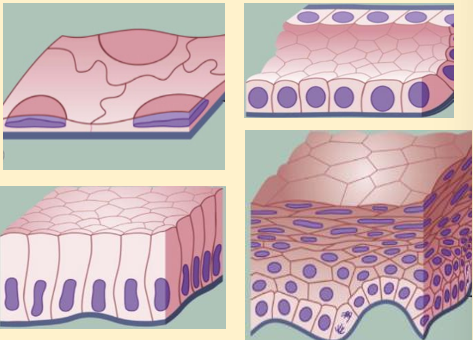
epithelial cell diagram
squamous, cuboidal, columnar and stratified
cell polarity
-epithelial cells all have polarity
-every surface has specific proteins/morphology: maintenance of cell polarity
-cells remain in their domains
what happens when cell loses its polarity
cancer
domains in cell
-apical
-lateral
-basal
what is in apical surface and what do they look like
-glycocalyx
-cilia
-microvilli
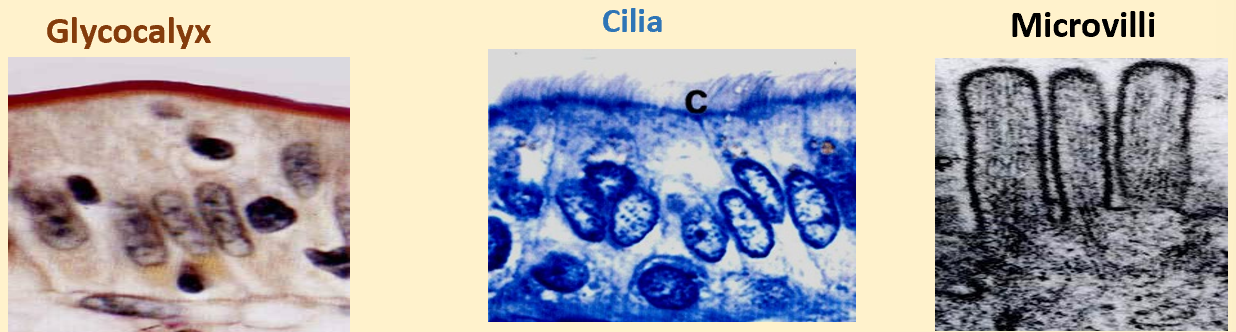
what is glycocalyx
-gel like substance present onto of cells
-carb coating (glycoproteins or glycolipids)
glycocalyx function in epithelial cells
-cell to cell recognition: helps differentiate between self and non self
-intercellular adhesion
-cell to cell communication
-embryonic development: attaches cells together and helps in movement of cells
glycocalyx function in endothelial cells
-regulates vascular(relates to rbc) permeability (exchange of molecules that happens)
-interactions between blood and endo cells
cilia sturcture
-motile cytoplasmic structure
-appear as short fine hair like structures
-length: 1-10 pm
cilia function
-capable of moving particles an fluid along epithelial surfaces
where is cilia found
-trachea
-large bronchi
-uterine walls
microvilli structure
-irregular projections of cell membrane
-1pm
-closely packed cells that have absorptive function
microvilli location found
-small intestine
-kidney
lateral domain diagram

basal domain diagram
basal region: lamina lucida & densa

function of basal domain
-helps in adhesions between epithelial cells and ecm
-acts as permeability barrier which controls entry and exit from the cell
-may control cell organisation & specialisation: resevoir for many dif proteins
what protein does the extracellular matrix have?
-collagen fibres
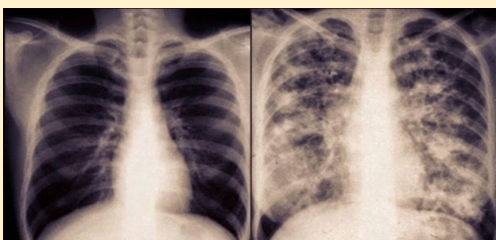
why is the lungs different
-patient has cystic fibrosis
-lots of mucus in lung
what is cystic fibrosis
-multisystem disease: lots of dif organs r affected
-not possible to treat
-genetic disorder
-autosomal recessive; both genes mutated in order for a person to have symptoms
-life shortening
-affects mostly lungs
cystic fibrosis symptoms
-thick sticky mucous blocks airways
-difficult to breath
-cough up mucus
-freq lung infection
-elevated sweat chloride levels
-dif ppl have dif deegree of symptom
why do cf pateint get freq lung infections
-mucus stays for long time
-hard for clinician to aspirate mucus out
-mucus inhabits in that region
-promotes bacterial growth
why do cf patient have elevated sweat chloride levels
-lots of NaCl accumulation on skin surface
cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (cftr)
-trans membrane protein on apical region of cell
-expressed on epithelial cell lining of lungs, gut, exocrine glands
cftr diagram
-green balls rep movement of ions across cell membrane
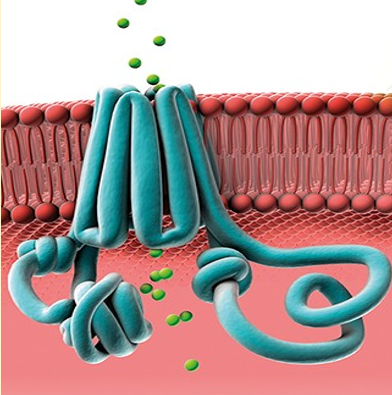
function of cftr
-allow movement of water molecules; as osmotic gradient is created
-helps maintain water salt balance on many surfaces
-transports ions across epithelial cell surfaces; pumps Cl- ions out with water mol
-allows water to flow into luminal space
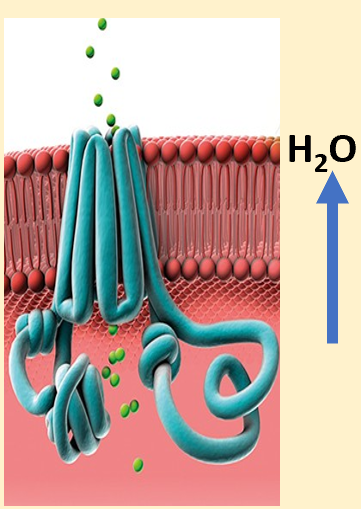
why does water flow into luminal space
-goblet cells and submucosal glands are near luminal space
-they secrete mucus; needs to be cleared
-when mixed with water is thin watery substance; easy for cilia to wipe out
-mucociliary clearance and airway defence in optimal
mutation in CTFR
-Mutations can reduce channel number/function
-Inability to establish osmotic gradient due to inhibited flow of ions
-Flow of water inhibited
-Result= Dehydration, decreased airway surface liquid, build-up of thick mucus layer on the outside of cells, static mucous
-Less airway surface liquid
-Decreased bicarbonate transport = acidic pH
cadherins diagram
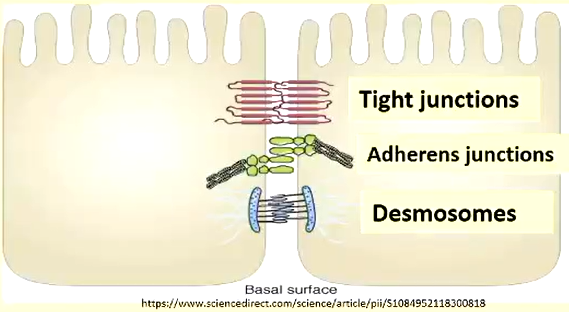
what type of cells are cadherins
-transmembrane proteins
-major constituents of adherens junctions
cadherins function
-important for cell - cell binding
-cadherins mediate intercellular adhesion
what does e-cadherin do in normal cells
-helps joining cells together
-contact inhibition: proliferation/growth ceases when cell come in contact with each other
contact inhibition diagram
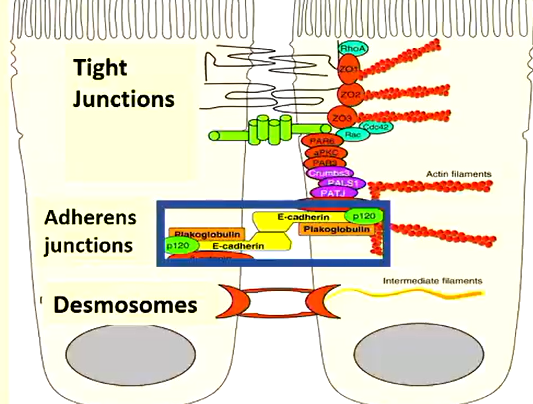
e-cadherin in cancer cells
-cells undergo malignant transformation
-loss of contact inhibition
-uncontrolled cell proliferation & tumour formation
-cells proliferate in a dysregulated fashion
-disrupted cell adhesion-multiple layers of cells formed
-some cell may detach: nothing for cells to be bound together with
what is the issue with cells detaching due to lack of e-cadherin
-float around: host into another house/organ
-causes secondary cancer
-loss of polarity
e-cadherin in cancel cells vs normal cells diagram
-yellow dashes: functional e-cadherin
-red dashes: non-functional e-cadherin
what epithelial cells provide barrier function
skin
what epithelial cells provide gas exchange
lungs/alveoli
what epithelial cells provide absorption
intestine
what epithelial cells provide reabsorption
intestine
what epithelial cells provide secretion
exocrine & endocrine glands
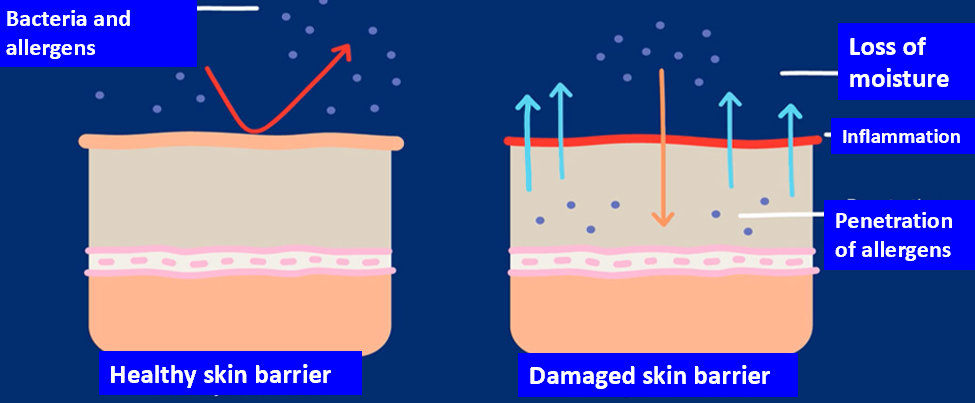
how does skin provide barrier function
-maintain physical barrier
-maintain communication between internal and external environments
barrier against:
-environmental insults
-microbial invasion
-chemicals
-toxins and allergens
healthy skin barrier vs damaged skin barrier diagram
how do lungs provide gas exchange
type I pneumocytes:
-line 95% of alveoli
-united by tight junctions
type II pneumocytes:
-prod thin layer of surfactant: covers alveolar surface
how gastrointestinal system provides absorption
-absorptive cells
-tall cells forming single layer (simple) with microvilli on their apical surface
-tight junction prevent passing material between cells
-allows only selection of material to be absorbed
-abnormal expression levels/activity of Na-K pump in diabetes, alzheimer’s disease, hypertension and tumours
how does kidney provide reabsorption
•Water/solutes transported into bloodstream
•Amino acids, glucose (100%), salts, and water (65%) reabsorbed
•Active transport- e.g. , glucose, amino acids
•Passive transport- water, chloride ions
•Concentrated urine formed
pancreas diagram
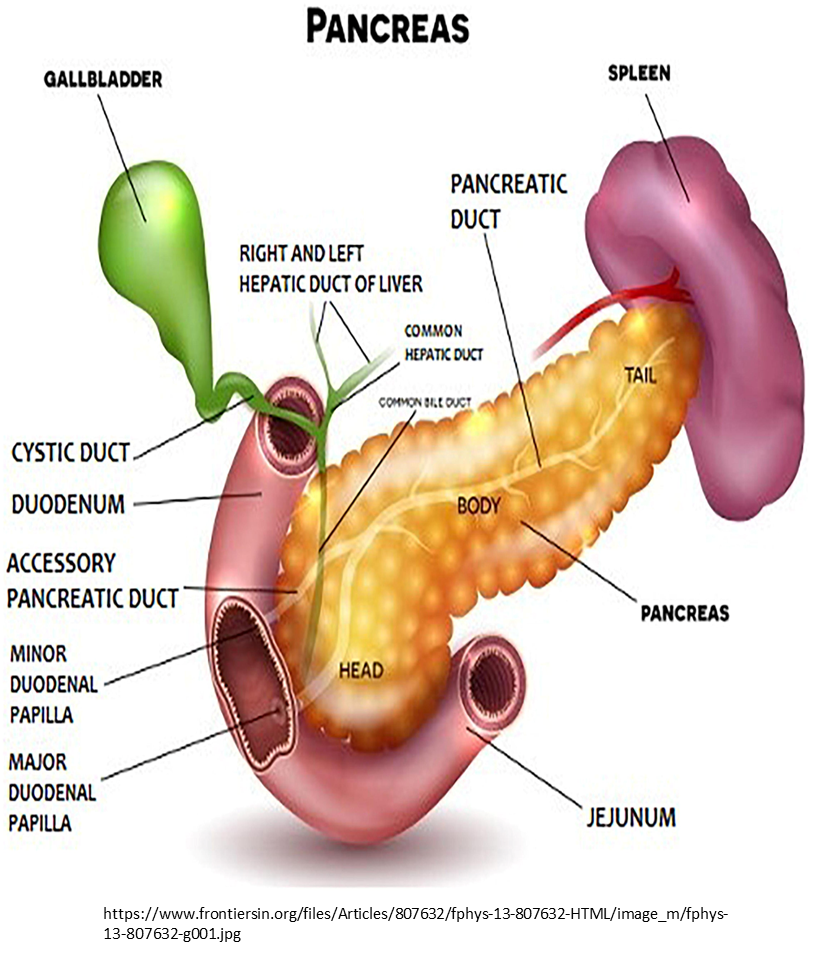
how does pancreas exocrine provide secretion
pancreatic acinar cells:
-secrete digestive enzymes, ions and water into duodenum
-high conc of NaHCO3whay
what effects acinar cells
-alcohol, high fat diet, smoking increase stress on acinar cells
what happens if acinar cell injury occurs
-loss of exocrine pancreatic function; reduced